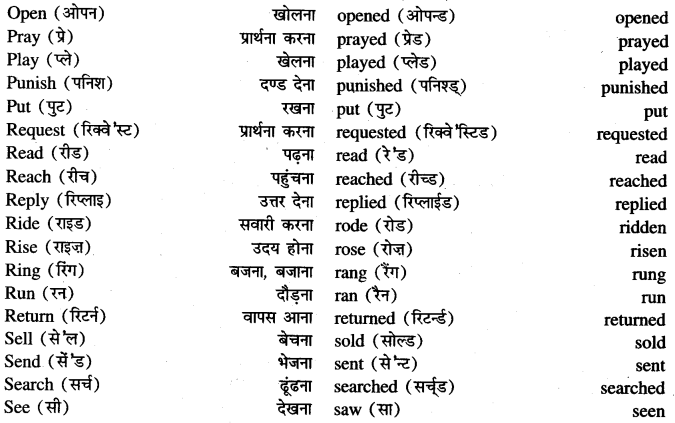
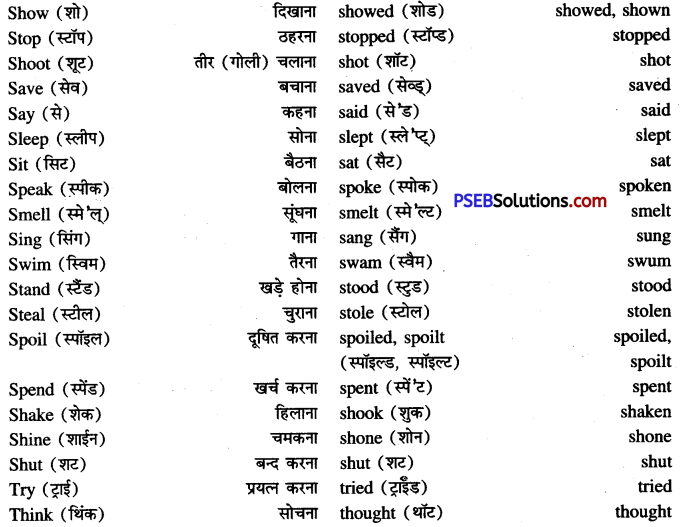
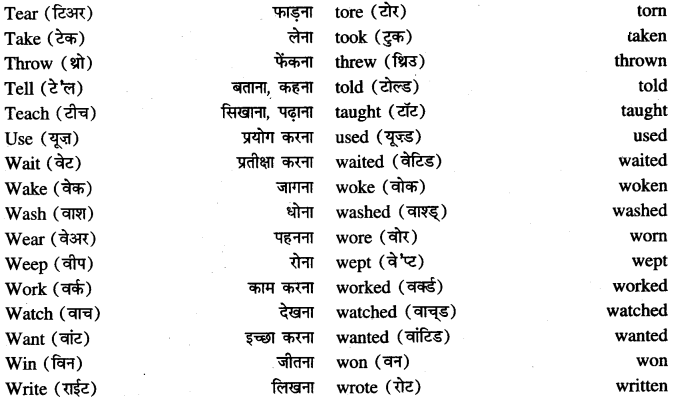
Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 5 Data Handling InText Questions and Answers.
PSEB 8th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 5 Data Handling InText Questions
Textual (Textbook Page No. 69 – 70)
1. A Pictograph : Pictorial representation of data using symbols.
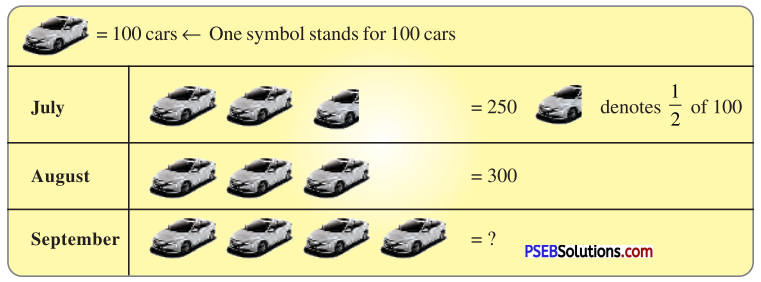
Question (i).
How many cars were produced in the month of July ?
Solution:
250 cars were produced in the month of July.
Question (ii).
In which month were maximum number of cars produced?
Solution:
Maximum number of cars were produced in the month of September.

2. A Bar Graph : A display of information using bars of uniform width, their heights being proportional to the respective values.
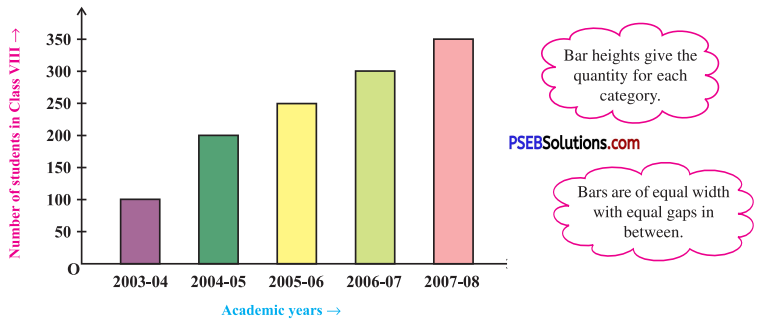
Question (i).
What is the information given by the bar graph ?
Solution:
Here, the bar graph gives information about number of students of class VIII in different academic years.
Question (ii).
In which year is the increase in the number of students maximum ?
Solution:
In year 2004-05, the increase in the number of students is maximum.
Question (iii).
In which year is the number of students maximum ?
Solution:
In year 2007 – 08, the number of students is maximum.
Question (iv).
State whether true or false:
‘The number of students during 2005 – 06 is twice that of 2003 – 04.’
Solution :
False, the number of students during 2005 – 06 is not twice that of 2003 – 04 but more than twice.

3. Double Bar Graph : A bar graph showing two sets of data simultaneously. It is useful for the comparison of the data.
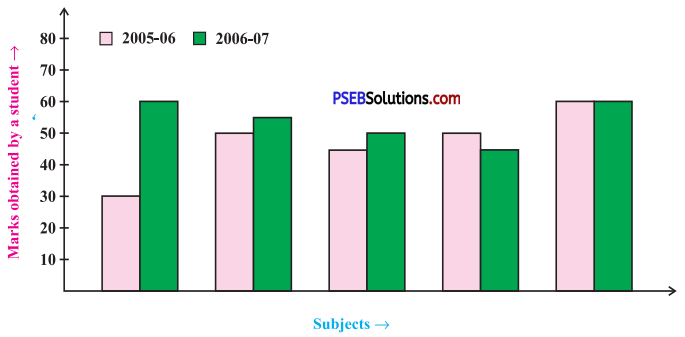
Question (i).
What is the information given by the double bar graph?
Solution :
Here, the double bar graph provides information about marks obtained by a student in different subjects and comparison of his marks in year 2005 – 06 and 2006 – 07.
Question (ii).
In which subject has the performance improved the most?
Solution :
In the subject Maths, the performance has improved the most.
Question (iii).
In which subject has the performance deteriorated?
Solution :
In the subject English, the performance has deteriorated.
Question (iv).
In which subject is the performance at par?
Solution:
In the subject Hindi, the performance is at par.
Think, Discuss and Write (Textbook Page No. 71)
Question 1.
If we change the position of any of the bars of a bar graph, would it change the information being conveyed? Why?
Solution:
If the height of a bar remains unchanged, then changing of its position does not change the information being conveyed.

Try These (Textbook Page No. 71)
Question 1.
Draw an appropriate graph to represent the given information:

Solution:
To represent the given data by a bar graph, draw two axes perpendicular to each other. Let us represent ‘Months’ on \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OX}}\) and ‘Number of watches sold’ \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OY}}\) on OY. Let us make rectangles of same width. The heights of the rectangles are proportional to the number of watches, using a suitable scale :
Here, scale is 1 cm = 500 watches
Since, 500 watches = 1 cm
1000 watches = 2 cm
1500 watches = 3 cm
2000 watches = 4 cm
2500 watches = 5 cm
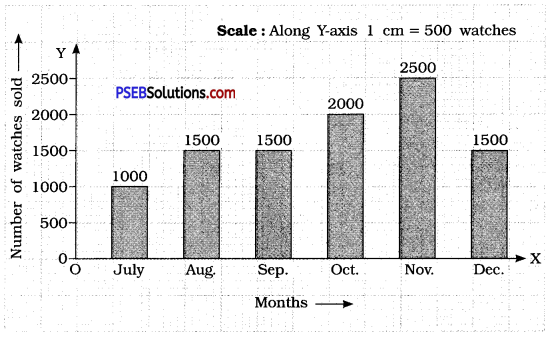
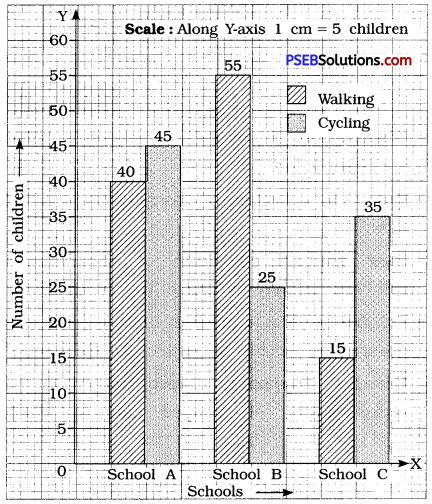
Question 2.
| Children who prefer |
School A |
School B |
School C |
| Walking |
40 |
55 |
15 |
| Cycling |
45 |
25 |
35 |
Solution:
Since, a comparison of two activities is to be represented, therefore a double graph is drawn by taking the ‘Schools’ along X-axis and ‘Number of children’ along Y-axis, using a scale of 1 cm = 5 children.

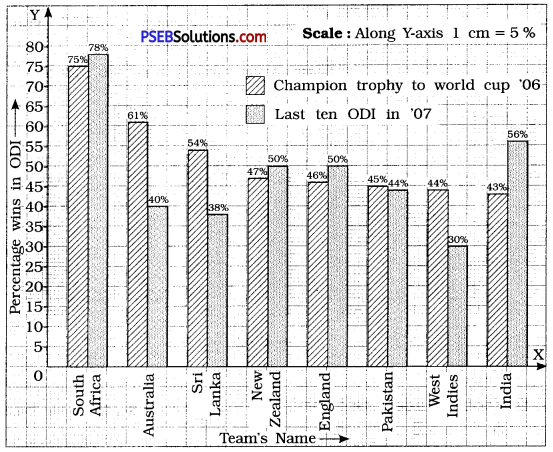
Question 3.
Percentage wins in ODI by 8 top cricket teams.
| Teams |
From Champions Trophy to World Cup ’06 |
Last 10 ODI in ’07 |
| South Africa |
75% |
78% |
| Australia |
61 % |
40% |
| Sri Lanka |
54% |
38% |
| New Zealand |
47% |
50% |
| England |
46% |
50% |
| Pakistan |
45% |
44% |
| West Indies |
44% |
30% |
| India |
43% |
56% |
Solution:
To compare the percentage win in ODI achieved by various teams, we represent the data by a double bar graph. We represent the ‘Team’s Names’ along the X-axis and their ‘percentage win’ along Y-axis, using the scale 1 cm – 5%.
Try These (Textbook Page No. 72)
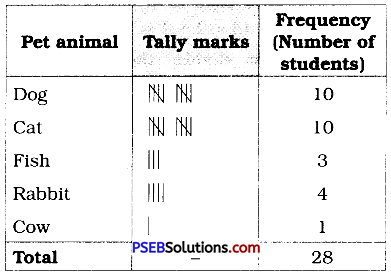
1. A group of students were asked to say which animal they would like most to have as a pet. The results are given below:
dog, cat, cat, fish, cat, rabbit, dog, cat, rabbit, dog, cat, dog, dog, dog, cat, cow, fish, rabbit, dog, cat, dog, cat, cat, dog, rabbit, cat, fish, dog.
Make a frequency distribution table for the same.
Solution:
Using tally-marks, we have

Try These (Textbook Page No. 73-74)
1. Study the following frequency distribution table and answer the questions given below.
Frequency Distribution of Daily Income of 550 Workers of a factory:
| Class Interval (Daily Income in ₹) |
Frequency (Number of workers) |
| 100 – 125 |
45 |
| 125 – 150 |
25 |
| 150 – 175 |
55 |
| 175 – 200 |
125 |
| 200 – 225 |
140 |
| 225 – 250 |
55 |
| 250 – 275 |
35 |
| 275 – 300 |
50 |
| 300 – 325 |
20 |
| Total |
550 |
Question (i).
What is the size of the class intervals ?
Solution:
Class size = [Upper class limit] – [Lower class limit]
= 125 – 100
= 25
Question (ii).
Which class has the highest frequency ?
Solution:
The class 200 – 225 is having the highest frequency (140).
Question (iii).
Which class has the lowest frequency ?
Solution :
The class 300 – 325 has the lowest frequency (20).
Question (iv).
What is the upper limit of the class interval 250 – 275?
Solution:
The upper limit of the class interval 250 – 275 is 275.
Question (v).
Which two classes have the same frequency ?
Solution :
The classes 150 – 175 and 225 – 250 are having the same frequency (55).

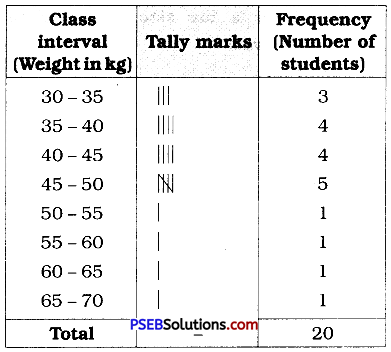
2. Construct a frequency distribution table for the data on weights (in kg) of 20 students of a class using intervals 30 – 35, 35 – 40 and so on.
40, 38, 33, 48, 60, 53, 31, 46, 34, 36, 49, 41, 55, 49, 65, 42, 44, 47, 38, 39
Solution:
Lowest observation = 31
Highest observation = 65
Class intervals :
30-35, 35-40, 40-45, ……..
The frequency distribution table for above data can be prepared as follows :
Try These (Textbook Page No. 75 – 76)
1. Observe the histogram and answer questions given below:
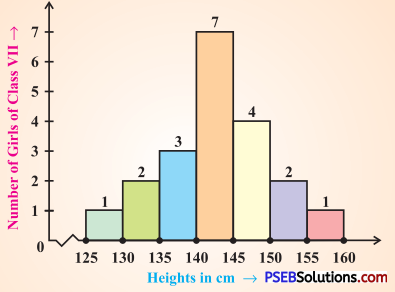
Question (i).
What information is being given by the histogram ?
Solution:
This histogram represents the heights (in cms) of girls of class VII.
Question (ii).
Which group contains maximum girls ?
Solution:
The group 140- 145 contains maximum number of girls (7).
Question (iii).
How many girls have a height of 145 cms and more?
Solution:
7 girls have a height of 145 cm and more (4 + 2 + 1 = 7).
Question (iv).
If we divide the girls into the following three categories, how many would there be in each?
150 cm and more-Group A
140 cm to less
than 150 cm – Group B
Less than 140 cm – Group C
Solution:
Number of girls in
Group A : 150 cm and more = 2 + 1 = 3
Group B : 140 cm and less than 150 cm = 7 + 4 = 11
Group C : Less them 140 cm = 3 + 2 + 1 = 6

Try These (Textbook Page No. 78)
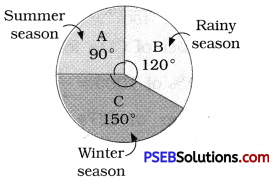
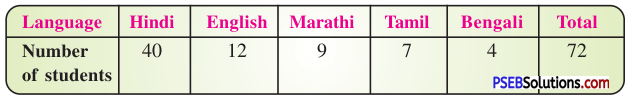
1. Each of the following pie charts gives you a different piece of information !; about your class. Find the fraction of the circle representing each of these information:
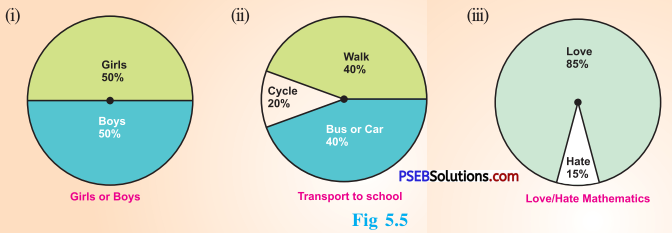
Solution:
(i) Fraction of the circle representing the ‘girls’ 50 % = \(\frac {50}{100}\) = \(\frac {1}{2}\)
Fraction of the circle representing the ‘boys’ 50% = \(\frac {50}{100}\) = \(\frac {1}{2}\)
(ii) Fraction of the circle representing ‘walk’ 40 % = \(\frac {40}{100}\) = \(\frac {2}{5}\)
Fraction of the circle representing ‘bus or car’ 40 % = \(\frac {40}{100}\) = \(\frac {2}{5}\)
Fraction of the circle representing ‘cycle’ 20 % = \(\frac {20}{100}\) = \(\frac {1}{5}\)
(iii) Fraction of the circle representing those who love mathematics = (100 – 15)%
= 85 %
= \(\frac {85}{100}\) = \(\frac {17}{20}\)
Fraction of the circle representing those who hate mathematics = 15%
= \(\frac {15}{100}\) = \(\frac {3}{20}\)
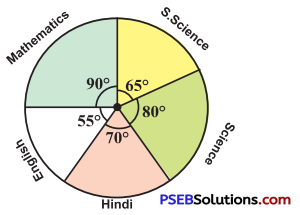
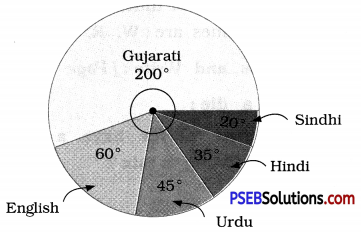
2. Answer the following questions based on the pie chart given:
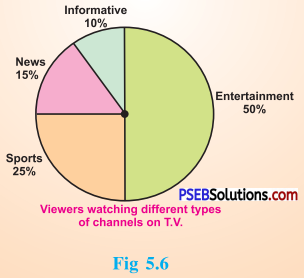
(i) Which type of programmes are viewed the most?
(ii) Which two types of programmes have number of viewers equal to those watching sports channels ?
Solution:
From the given pie chart,
| Type of viewers |
Percentage |
| Sports viewers |
25 % |
| News viewers |
15 % |
| Information viewers |
10 % |
| Entertainment viewers |
50% |
(i) The entertainment programmes are viewed the most (50 %).
(ii) The news and informative programmes have the number of viewers equal to those watching sports channels (15 % + 10 % = 25 %).

Try These (Textbook Page No. 81)
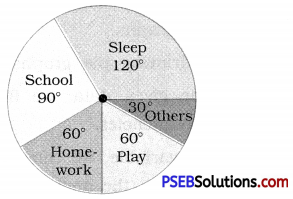
1. Draw a pie chart of the data given below : The time spent by a child during a day.
Sleep – 8 hours
School – 6 hours
Homework – 4 hours
Play – 4 hours
Others – 2 hours
Solution:
First we find the central angle corresponding to each of the given activities.
| Activity |
Duration of the activity in a day out of 24 hours |
Central angle corresponding to the activity |
| Sleep |
8 hours |
\(\frac {8}{24}\) × 360° = 120° |
| School |
6 hours |
\(\frac {6}{24}\) × 360° = 90° |
| Home work |
4 hours |
\(\frac {4}{24}\) × 360° = 60° |
| Play |
4 hours |
\(\frac {4}{24}\) × 360° = 60° |
| Others |
2 hours |
\(\frac {2}{24}\) × 360° = 30° |
The required pie chart is given below.
[Note: Dividing a circle into sectors with corresponding angle (with protractor) you get the required pie chart.]
Think, Discuss and Write (Textbook Page No. 81)
Which form of graph would be appropriate to display the following data.
Question 1.
Production of food grains of a state.
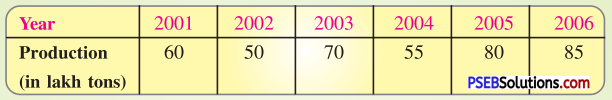
Solution :
A bar graph will be an appropriate representation to display given data.

Question 2.
| Favourite food |
Number of people |
| North Indian |
30 |
| South Indian |
40 |
| Gujarati |
25 |
| Others |
25 |
| Total |
120 |
Solution :
A pie chart (circle graph) will be an appropriate representation to display given data.
Question 3.
The daily income of a group of a factory workers:
| Daily income (in Rupees) |
Number of workers (in a factory) |
| 75 – 100 |
45 |
| 100 – 125 |
35 |
| 125 – 150 |
55 |
| 150 – 175 |
30 |
Solution :
A histogram will be an appropriate representation to display given data.
Try These (Textbook Page No. 83 – 84)
Question 1.
If you try to start a scooter, what are the possible outcomes ?
Solution:
It may start.
It may not start.
Question 2.
When a die is thrown, what are the six possible outcomes?
Solution:
When a die is thrown, the possible outcomes are: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6 on the upper face of the die.
Question 3.
When you spin the wheel shown, what are the possible outcomes ? (Fig 5.9)
List them.
(Outcome here means the sector at which the pointer stops.)
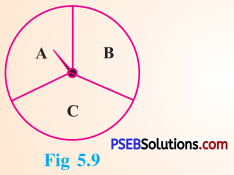
Solution:
When we spin the wheel shown, the possible outcomes are A, B or C.
[Note: The sector at which the pointer stops is outcome.]
Question 4.
You have a pot with five identical balls of different colours and you are to pull out (draw) a ball without looking at it; list the outcomes you would get (Fig 5.10).
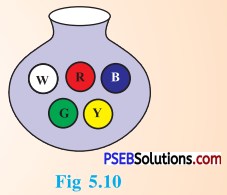
Solution:
When we draw a ball from a bag with five identical balls of different colours, the possible outcomes are : W, R, B, G or Y.

Think, Discuss and Write (Textbook Page No. 84)
In throwing a die:
1. Does the first player have a greater chance of getting a six?
Solution:
No.
2. Would the player who played after him have a lesser chance of getting a six?
Solution:
No.
3. Suppose the second player got a six. Does it mean that the third player would not have a chance of getting a six ?
Solution:
No.
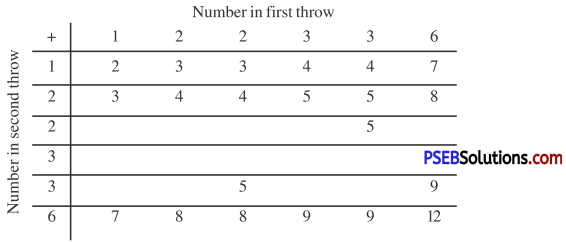
Try These (Textbook Page No. 86)
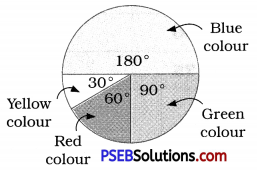
Suppose you spin the wheel:
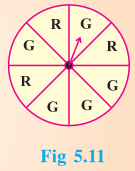
1. ( i ) List the number of outcomes of getting a green sector and not getting a green sector on this wheel.
Solution:
Number of outcomes of getting a green sector = 5
Number of outcomes of not getting a green sector = 3
(ii) Find the probability of getting a green sector.
Solution :
∴ The total number of outcomes = 8
Number of outcomes of getting a green sector = 5
∴ Probability of getting a green sector = \(\frac {5}{8}\)
(iii) Find the probability of not getting a green sector.
Solution:
∴ The total number of outcomes = 8
Number of outcomes of not getting a green sector = 3
∴ Probability of not getting a green sector = \(\frac {3}{8}\)

![]()



![]()

![]()
![]()