Punjab State Board PSEB 11th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 22 Chemical Coordination and Integration Important Questions and Answers.
PSEB 11th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 22 Chemical Coordination and Integration
very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
There are many endocrine glands in human body. Name the gland, which is absent in male and the one absent in female. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
The glands, which are absent in male are ovaries and which are absent in female are testes.
Question 2.
Which of the two adrenocortical layers, zona glomerulosa and zona reticularis lies outside enveloping the other?
[NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Zona glonierulosa (outer layer) envelopes zona reticularis (inner layer) from the outside.
Question 3.
Name the only hormone secreted by pars intermedia of pituitary gland. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone (MSH).
Question 4.
Mention the name of the largest and the smallest endocrine gland found in man.
Answer:
Thyroid gland is the largest endocrine gland and pituitary gland is the smallest endocrine gland.
Question 5.
A patient complains of constant thirst, excessive passing of urine and low the level blood pressure. When the doctor checked the patient’s blood glucose and blood insulin level, the level were normal or slightly low. The doctor diagnosed the condition as diabetes insipidus. But he decide to measure one more hormone in patient’s blood. Which hormone does the doctor intend to measure? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Glucagon.
![]()
Question 6.
The outermost layer of adrenal cortex is responsible for secretion of which hormone. Identify?
Answer:
Mineralocorticoids.
Question 7.
Identify the neurohormone that has its functioning in inhibiting the secretion of growth hormone from anterior lobe of pituitary.
Answer:
Somatostatin inhibits the secretion of growth hormone from anterior lobe of pituitary gland.
Question 8.
State the reason for the occurrence of diabetes insipidus in a individual.
Answer:
Deficiency in the secretion of vasopressin (ADH) leads to the disorder known as diabetes insipidus.
Question 9.
Define the term erythropoiesis. Also name the hormone that stimulates it. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Erythropoiesis is the process of formation of RBCs. The juxtaglomerular cells of kidney produce a peptide hormone called erythropoietin which stimulates it.
Question 10.
What do you understand by the term ANF?
Answer:
Atrial wall of human heart secretes a peptide hormone called atrial natriuretic factor which decreases blood pressure by dilation of the blood vessels.
Question 11.
Mention the name given to the hormones produced by some non-endocrine tissues.
Answer:
Hormones produced by some non-endocrine tissues are called growth factors.
Question 12.
Which two hormones are steroids chemically?
Answer:
Cortisol and testosterone are chemically steroid in nature.
![]()
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the function of melanin.
Answer:
Melanin controls the circadian variations of the body. During 24 hours different organ system of our body works at different pace. During sleep certain body functions slow down. All of this is known as circadian rhythm. Additionally, melanin influences metabolism, pigmentation, menstruation and defence capability.
Question 2.
How does parathyroid hormone influences calcium uptake in the body?
Answer:
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) increases the Ca2+ levels in the blood. PTH acts on bones and stimulates the process of bone reabsorption (dissolution/demineralization). PTH also stimulates reabsorption of Ca2+ by the renal tubules and increases Ca2+ absorption from the digested food. It is, thus, clear that PTH is a hypercalcemic hormone, i.e., it increases the blood Ca2+ levels. Along with TCT, it plays a significant role in calcium balance in the body.
Question 3.
How do fight or flight hormones prepare our body to fight emergency?
Answer:
Adrenaline and noradrenaline are rapidly secreted in response to stress of any kind and during emergency situations and are called emergency hormones or hormones of fight or flight. These hormones increase alertness, pupillary dilation, piloerection (raising of hairs), sweating etc. Both the hormones increase the heartbeat, the strength of heart contraction, and the rate of respiration. Finally, the body is ready to counter the emergency situations.
Question 4.
What are secondary sexual characters?
Answer:
Characters which do not play direct role in sexual reproduction but are basically means of sexual differentiation are called secondary sexual characters. For example, facial hair and deep voice in males and thin voice in females are secondary sexual characters.
Question 5.
What is acromegaly?
Answer:
Excess secretion of growth hormone in adults, especially in middle age can result in severe disfigurement (especially of the face). This is called acromegaly. This can lead to serious complications and even death; if unchecked. The disease is hard to diagnose in the early stages and is frequently missed for many years, until changes in external features become noticeable.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Hypothalamus is a super master endocrine gland. Elaborate. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Hypothalamus regulates a wide spectrum of body functions. It contains several groups of neurosecretory cells called nuclei, which produce hormones. These hormones regulate the synthesis and secretion of pituitary hormones. However, the hormones produced by hypothalamus are of two types, the releasing hormones (which stimulate secretion of pituitary hormones) and the inhibiting hormones (which inhibit secretions of pituitary hormones).
The hormones reach the pituitary gland through a portal circulatory system and regulate the functions of the anterior pituitary. The posterior pituitary is under the direct regulation of hypothalamus. The oxytocin and vasopressin are the two hormones synthesized by hypothalamus that are transported to posterior pituitary.
Question 2.
A sample of urine was diagnosed to contain high content of glucose and ketone bodies. Based on this observation, answer the following: (NCERT Exemplar)
(i) Which endocrine gland and hormone is related to this condition? %
(ii) Name the cells on which this hormone acts.
(iii) What is the condition called and how can it be rectified?
Answer:
(i) Pancreas gland and insulin hormone is related to this condition.
(ii) The (3-cells of islets of Langerhans of pancreas.
(iii) Prolonged hyperglycemia leads to a complex disorder, called diabetes mellitus, which is associated with loss of glucose through urine and formation of harmful compounds known as ketone bodies. Diabetic patients are successfully treated with insulin therapy.
![]()
Question 3.
(i) Give a diagrammatic representation of the mechanism of protein hormone (e. g., FSH) action.
(ii) Illustrate the differences between the mechanism of action of, a protein and a steroid hormone. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
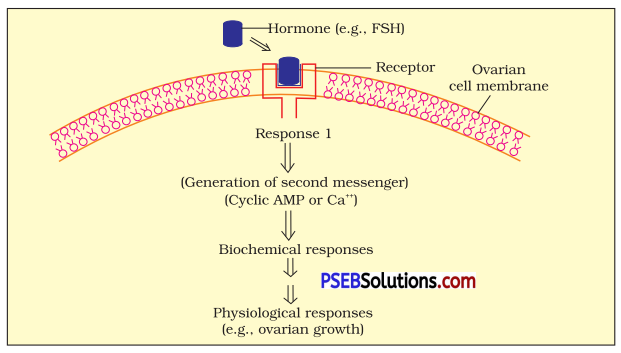
(ii) Differences between mechanism of action of a protein and a steroid hormone
| Protein Hormone | Steroid Hormone |
| Protein hormones interact with membrane-bound receptors. | They interact with intracellular receptors. |
| They generate second messengers (cyclic AMP, IP3, Ca2+, etc.) | They regulate gene expression or chromosome function by the interaction of the hormone-receptor complex with the genome. |
| The second messengers regulate. cellular metabolism. | Cumulative biochemical action of hormone-receptor complex results in physiological and developmental effects. |
