Punjab State Board PSEB 11th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 11 Transport in Plants Important Questions and Answers.
PSEB 11th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 11 Transport in Plants
Very short answer type questions
Question 1.
Define translocation.
Answer:
Transport over longer distances proceeds through the vascular system (the xylem and the phloem) and known as translocation.
Question 2.
Osmosis is a special kind of diffusion, in which water diffuses across the cell membrane. The rate and direction of osmosis depends upon both. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Pressure and concentration gradient.
![]()
Question 3.
The plant cell cytoplasm is surrounded by both cell wall and cell membrane. The specificity of transport of substances are mostly across the cell membrane, because. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
The cell wall is freely permeable to water and other substances in the solution but the plasma membrane is selectively permeable.
Question 4.
Why does rate of transport reach maximum or becomes saturated in facilitated diffusion?
Answer:
The transport rate reach a maximum because all the transport proteins are occupied/saturated.
Question 5.
Imbibition is considered a method of diffusion. Comment.
Answer:
Imbibition is considered as a method of diffusion because the movement of water occurs along the concentration gradient during this process.
Question 6.
Give one basic difference between antiport and uniport.
Answer:
In antiport both the molecules cross the membrane in opposite directions whereas, in uniport molecules moves across a membrane independent of any other passing molecule.
Question 7.
Mention two .factors on which net direction of molecules and rate of osmosis depends.
Answer:
The two factors responsible are:
- Pressure gradient
- Concentration gradient.
![]()
Question 8.
A flowering plant is planted in an earthen pot and irrigated. Urea is added to make the plant grow faster, but after sometime the plant dies. This may be due to which factor? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
As urea content make the soil hypertonic in nature, therefore, the plant dies due to exosmosis.
Question 9.
The endodermis is impervious to water. Comment.
Answer:
The inner boundary of the cortex, i.e., endodermis is impervious to water because of a band of suberised matrix called the casparian strip.
Question 10.
Identify the vascular tissue responsible for translocation of organic and inorganic substances from leaves to other parts of the plant.
Answer:
Phloem is responsible for this type of translocation.
Question 11.
How do root hairs increase the absorption of water by plants?
Answer:
Root hairs increase the surface area of roots. This helps in making contact with larger volume of water. Thus, the presence of root hairs helps in absorption by plants.
![]()
Question 12.
It is seen that the number of stomata are greater on the lower surface of the leaf than the upper surface. Why is it so ?
Answer:
Stomata are present in greater number on the lower surface because if more number of stomata will be present on the upper surface, it would lead to great amount of water loss through transpiration. Thus, to avoid the excessive transpiration, stomata are present in greater number on lower surface of the leaf.
Question 13.
Elucidate the channels of food transport in plants.
Answer:
The channels of food transport are sieve tubes and sieve cells of phloem.
Question 14.
How are companion cells helpful to sieve tubes?
Answer:
The companion cells are connected to the sieve tubes by plasmodesmata and provide them with proteins, ATP and other nutrients.
Short answer type questions
Question 1.
Define facilitated diffusion.
Answer:
Membrane proteins provide sites at which movement of certain molecules takes place. These molecules have hydrophilic moiety and hence it is difficult for them to cross a membrane. They- need assistance of membrane proteins to cross the membrane. This is called facilitated diffusion.
![]()
Question 2.
Give a comparison table of different transport mechanisms.
Answer:
Comparison of Different Transport Mechanisms
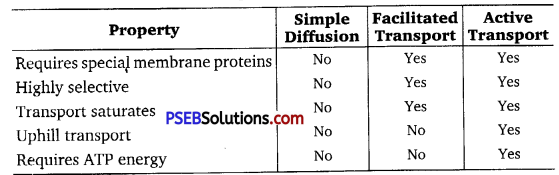
Question 3.
Photosynthesis needs constant supply of water. But transpiration can hamper this supply. How do plants of desert area manage to get sufficient water in spite of faster transpiration?
Answer:
Desert plants have a different mechanism of photosynthesis and it is called C4 pathways. The evolution of the C4 photosynthetic system is probably one of the strategies for maximising the availability of CO2 while minimising water loss. C4 plants are twice as efficient as C3 plants in terms of fixing carbon (making sugar). However, a C 4 plant loses only half as much water as a C3 plant for the same amount of CO2 fixed.
Question 4.
What is the significance of transpiration?
Ans. Significance of Transpiration
- Transpiration pull facilitates movement of water from roots.
- Transpiration supplies water for photosynthesis.
- It pulls minerals from soil.
- Helps in cooling of plants.
- Maintains shape of plant cells.
Question 5.
Describe the movement of water in leaves.
Answer:
Evaporation from the leaf sets up a pressure gradient between the outside air and the air spaces of the leaf. The gradient is transmitted into the photosynthetic cells and on the water-filled xylem in the leaf vein. This facilitates movement of water from xylem to the guard cells of stomata.
Long answer type questions
Question 1.
Observe the given figure and answer the following questions:
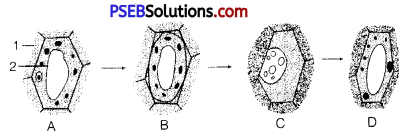
(i) State the nature of solution marked (1).
(ii) What process has been depicted in figures C to D?
(iii) In which figures turgor pressure will be zero?
(iv) In which figures wall pressure will he positive?
Answer:
(i) The solution marked as (1) will he hypertonic (more concentrated) due to which cell shrinks.
(ii) From C to D, figure is showing the process of deplasmolysis as shrinked cell has again regained its original shape.
(iii) Turgor pressure will be zero in figure B and C because cell is in a flaccid condition.
(iv) Wall pressure will be positive in figure A and D because in these figure cell wall is exerting ‘equal and opposite pressure against the expanding protoplasm.
![]()
Question 2.
Minerals are present in the soil in sufficient amount. [NCERT Exemplar]
(i) Do plants need to adjust the types of solute that reach xylem.
(ii) Which molecules help to adjust this?
Answer:
(i) An analysis of the xylem exudates shows that though some of the nitrogen travels as inorganic ions, much of it is carried in the organic form as amino acids and related compounds. Similarly, small amount of P and | S are carried as organic compounds. In addition, small amount of exchange of materials does take place between xylem and phloem.
(ii) Mineral ions are frequently remobilised, particularly from older, sensecing parts. Older dying leaves export much of their mineral content to younger leaves. Similarly, before leaf fall in deciduous plants, minerals are removed to other parts. Elements most readily mobilised are phosphorus, sulphur, nitrogen and potassium. Some elements that are structural components like calcium are not remobilised.
