Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance Important Questions and Answers.
PSEB 12th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance
Question 1.
Name the specific components and the linkage between them that form deoxyadenosine.
Answer:
Nitrogenous base (Adenine) and pentose sugar and N-glycosidic linkage.
Question 2.
Why is RNA more reactive in comparison to DNA?
Answer:
RNA is more reactive because:
- It is single stranded.
- Every nucleotide has an additional OH– group present at position 2 in the ribose.
- Mutates faster as compared to DNA.
Question 3.
In an experiment, DNA is treated with a compound which tends to place itself amongst the stacks of nitrogenous base pairs. As a result of this, the distance between two consecutive base increases from 0.34 nm to 0.44 nm. Calculate the length of DNA double helix, which has 2 × 109 bp in saturating the presence of this compound. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
The new length of DNA helix would be
= 2 × 10-9 × 0.44 × 10-9bp.
![]()
Question 4.
In a nucleus, the number of RNA nucleoside triphosphates is 10 times more than the number of DNA nucleoside triphosphates,
still only DNA nucleotides are added during the DNA replication, and not the RNA nucleotides. Why?
[NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
DNA polymerase is highly specific to recognise only deoxyribonucleoside r triphosphates. Therefore, it cannot hold RNA nucleotides.
Question 5.
Name the enzyme involved in the continuous replication of DNA strand. Mention the polarity of the template strand.
Answer:
DNA polymerase is involved in continuous replication of DNA strand. The polarity of template strand is 3′ → 5′.
Question 6.
What is a cistron?
Answer:
Cistron is a segment of DNA coding for a polypeptide chain.
Question 7.
Name the transcriptionally active region of chromatin in a nucleus.
Answer:
Euchromatin or Exon.
Question 8.
Write the function of RNA polymerase n.
Answer:
RNA polymerase II transcribes precursor of mRNA or hnRNA.
![]()
Question 9.
Mention the two additional processings which /mRNA needs to
undergo after splicing so as to become functional.
Answer:
Capping and tailing.
Question 10.
Give an example of a codon having dual function.
Answer:
AUG has dual function. It acts as initiation codon and also codes for methionine.
Question 11.
Sometimes cattle or even human beings give birth to their young ones that have extremely different sets of organs like limbs/position of eye(s), etc. Why? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
This is due to a disturbance in coordinated regulation of expression of sets of genes associated with organ development or due to mutations.
Question 12.
How does a degenerate code differ from an unambiguous one?
Answer:
Degenerate code means that one amino acid can be coded by more than one codon. Unambiguous code means that one codon codes for only one amino acid.
Question 13.
What is aminoacylation? State its significance.
Answer:
Aminoacylation of t-RNA involves activation of amino acids by ATP which gets linked to OH’ present at the 3′ end of specific t-RNA. The process is also called charging of t-RNA.
![]()
Question 14.
Mention how c|oes DNA polymorphism arise in a population?
Answer:
DNA polymorphism in a population arise due to presence of inheritable mutations at high frequency.
Question 15.
How is repetitive/satellite DNA separated from bulk genomic DNA for various genetic experiments?
Answer:
By using density gradient centrifugation, where satellite DNA forms small peaks.
Short answer type questions
Question 1.
Recall the experiments done by Frederick Griffith, Avery, MacLeod and McCarty, where DNA was speculated to be the genetic material. If RNA, instead of DNA was the genetic material, would the heat killed strain of Pneumococcus have transformed the 12-strain into virulent strain? Explain.
[NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
RNA is more labile and prone to degradation, owing to the presence of 2’OH group in its ribose. Hence, heat-killed S-strain may not have retained its ability to transform the R-strain into virulent form if RNA was its genetic material.
Question 2.
Name a few enzymes involved in DNA replication other than DNA polymerase and ligase. Name the key functions for each of them. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
The enzymes involved in DNA replication other than DNA polymerase and ligase are listed below with their functions:\
- Helicase – Opens the helix
- Topoisomerases – Removes the tension caused due to unwinding
- DNA ligase – Joins the cut DNA strands
![]()
Question 3.
Following are the features of genetic codes. What does each one indicate?
Stop codon; Unambiguous codon; Degenerate codon; Universal codon.
Answer:
- Stop codon is a codon, which does not code for any amino acid and here the polypeptide chain is released e.g., 3 codons – UAA, UAG, UGA.
- Unambiguous codon : One codon codes for only one specific amino acid.
- Degenerate codon : Here, one amino acid is coded by more than one codon e.g., amino acid glycine is coded by four codons (GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG).
- Universal codon means a codon specifies the same amino acid in all
the organisms even in a virus. ,
Question 4.
A single base mutation in a gene may not ‘always’ result in loss or gain of function. Do you think the statement is correct? Defend your answer. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
The statement is correct because of degeneracy of codons, mutations at third base of codon, usually does not result into any change in phenotype. This is called silent mutations but at other times it can lead to loss or formation of malformed protein changing the phenotype.
Question 5.
(a) Name the scientist who called tRNA an adapter molecule.
(b) Draw a clover leaf structure of fRNA showing the following:
(i) Tyrosine attached to its amino acid site.
(ii) Anticodon for this amino acid in its correct site (codon for tyrosine is UCA).
(c) What does the actual structure of JRNA look like?
Answer:
(a) Francis Crick
(b) 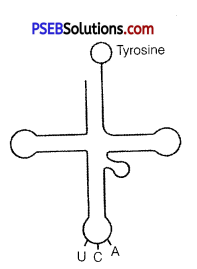
(c) The actual structure of t-RNA looks like inverted L.
Question 6.
A low level of expression of lac operon occurs at all the time. Can you explain the logic behind this phenomena. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
In the complete absence of expression of lac operon, permease will not be synthesised which is essential for transport of lactose from medium into the cells. And if lactose cannot be transported into the cell, then it cannot act as inducer. Hence, cannot relieve the lac operon from its repressed state. Therefore, lac operon is always expressed.
![]()
Question 7.
Would it be appropriate to use DNA probes such as VNTR in DNA fingerprinting of a bacteriophage? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Bacteriophage does not have repetitive sequences such as VNTRs in its genome, as its genome is very small (i.e., 5386bp) and have all the coding sequence. Therefore, DNA fingerprinting is not done for phages.
Long answer type questions
Question 1.
Describe Meselson and Stahl’s experiment that was carried in 1958 on E.coil. Write the conclusion they arrived at after the experiment.
Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl (1958) grew E. coli in a medium containing 15NH4Cl (15N is the heavy isotope of nitrogen) as
the only nitrogen source for many generations. The result was that 15N was incorporated into newly synthesised DNA (as well as other nitrogen containing compounds). This heavy DNA molecule could be distinguished from the normal DNA by centrifugation in a cesium chloride (CsCl) density gradient.
They transferred the cells into a medium with normal 14NH4Cl and took samples at various definite time intervals as the cells multiplied, and extracted the DNA that remained as double-stranded helices. The various samples were separated independently as CsCl gradients to measure the densities of DNA.
Thus, the DNA that was extracted from the culture one generation after the transfer from 15N to 14N medium (that is after 20 minutes; E.coli divides in 20 minutes) had a hybrid or intermediate density. DNA extracted from the culture after another generation (that is after 40 minutes, II generation) was composed of equal amounts of hybrid DNA and of light DNA.
Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl’s experiment demonstrated that DNA replication is semi-conservative.
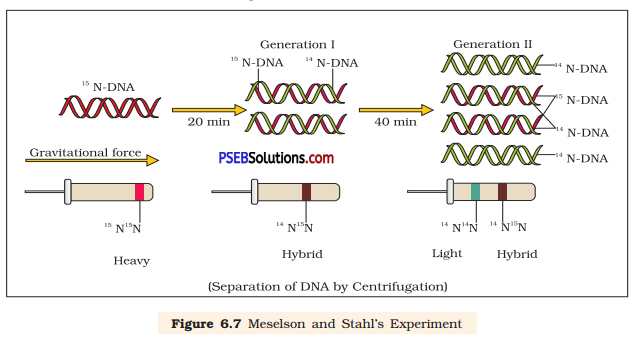
Generation I Generation II
![]()
Question 2.
(a) Describe the series of experiments of F. Griffith. Comment on the significance of the results obtained.
(b) State the contribution of MacLeod, McCarty and Avery.
Answer:
(a) Frederick Griffith (1928), a British doctor, was studying the pathogenicity of different strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae. It has two strains- (i) virulent cause pneumonia, has S-type of bacteria, covered by sheath of mucilage, (ii) non-virulent do not produce the disease, has R-type of bacteria, devoid of sheath of mucilage.
Griffith found that on injecting live R-type bacteria did not produce the disease while live S-type caused pneumonia and the death in mice. However, when heat-killed S-type injected, they did not produce the disease. Finally, Griffith injected a combination of live-R-type and heat-killed S-type bacteria into mice. Some mice survived while others developed the disease of pneumonia and died. Autopsy of dead mice showed that they possessed both the type of bacteria (virulent-S-type and non-virulent-R-type) in living form through the mice that had been injected with dead virulent (S-type) and living non-virulent (R-type) bacteria.
From the above experiment, Frederick Griffith concluded that the occurrence of living S-type virulent bacteria is possible only by their formation from R-type non-virulent bacteria which pick-up the trait of virulence from dead bacteria. This phenomenon is called Griffith effect or transformation. Griffith proposed that the transforming principle is a chemical substance released by heat-killed S-type, which changed the S-type into S-bacteria. It was a permanent change as the new S-type formed only S-type progeny.
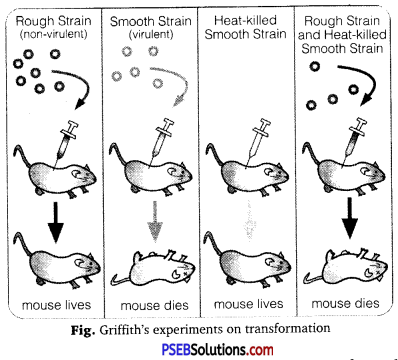
(b) Avery, MacLeod, McCarty discovered that DNA from the heat-killed S-strain caused the living R-strain bacteria to become transformed into living S-type. They found proteases and RNAases did not affect transformation while DNAases inhibit transformation. They concluded that DNA is the hereditary material.
