Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Important Questions and Answers.
PSEB 12th Class Physics Important Questions Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Very short answer type questions
Question 1.
Write the product in the following reaction:
![]()
Answer:
CH3– CH = CH-CH2– CHO Pent-3-en-1-al
Question 2.
Complete the following reaction sequence: (NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Question 3.
Illustrate the following name reaction: Clemmensen reduction.
Answer:
Clemmensen reduction: The carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones is reduced to CH2 group on treatment with zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid.
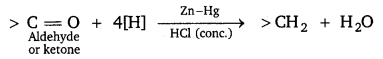
Question 4.
Name the electrophile produced in the reaction of benzene with benzoyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3.
Name the reaction also. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:

![]()
Question 5.
Which acid of each pair shown here would you expect to be stronger?
(i) F-CH2 -COOH or Cl-CH2 -COOH
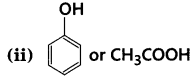
Answer:
(i) F-CH2-COOH > Cl-CH2-COOH, because of stronger -ve-I effect of F than Cl.

Question 6.
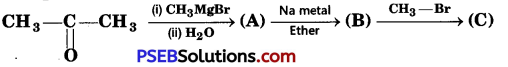
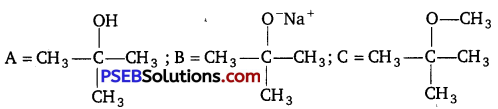
Identify the compounds A, B, and C in the following reaction. [NCERT Exemplar]
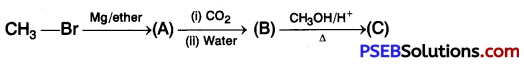
Answer:
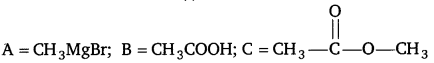
Question 7.
Write the product(s) in the following reaction:
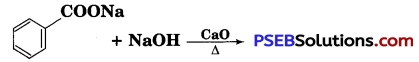
Answer:
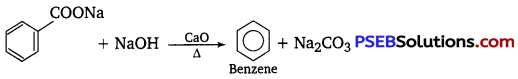
Question 8.
Name the aldehyde which does not give Fehling’s solution test.
Answer:
Benzaldehyde.
Question 9.
Give the name of the reagent that brings the following transformation: But-2-ene to ethanal.
Answer:
O3/H2O-Zn dust
Question 10.
Write TUPAC names of the following structures: (NCERT Exemplar)
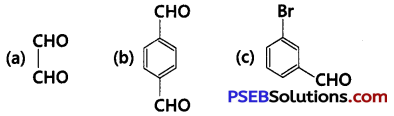
Answer:
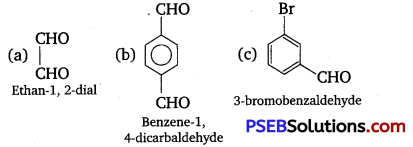
Question 11.
(CH3) 3C-CHO does not undergo aldol condensation comment.
Answer:
Because no α-H is present.
![]()
Short answer type questions
Question 1.
Write the reactions involved in the following:
(i) Etard reaction
(ii) Stephen’s reduction
Answer:
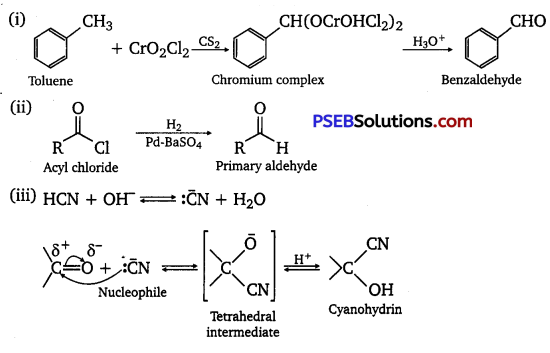
(i) Etard reaction: Chromyl chloride oxidizes toluene to chromium complex which on hydrolysis gives benzaldehyde.
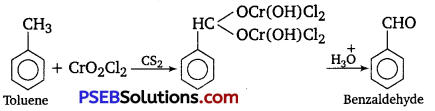
(ii) Stephen reductIon: Nitriles are reduced to corresponding imines with SnCl2 in the presence of HCl, which on hydrolysis give the corresponding aldehyde.
SnCl2 + 2HCl → SnCl4 + 2[H]
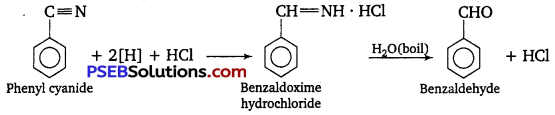
Question 2.
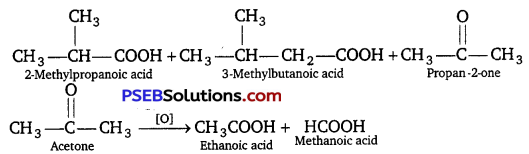
Oxidation of ketones involves carbon-carbon bond cleavage. Name the products formed on oxidation of 2,5-dimethyl hexane-3-one. [NCERT Exemplar]
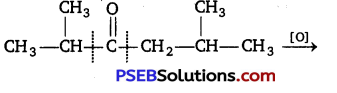
Answer:
Question 3.
Carboxylic acids contain carbonyl group but do not show the nucleophilic addition reaction like aldehydes or ketones. Why? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Carboxylic acids contain, carbonyl group but do not show nucleophilic addition reaction like aldehyde and ketone. Due to resonance as shown below the partial positive charge on the carbonyl carbon atom is reduced.
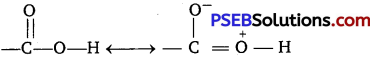
Question 4.
Give reasons:
(i) The α-hydrogen atoms of aldehydes and ketones are acidic in nature.
(ii) Propanone is less reactive than ethanal toward addition of HCN
(iii) Benzoic acid does not give Friedel Crafts reaction.
Answer:
(i) The acidity of a-hydrogen atom of carbonyl carbon is due to the strong withdrawing effect of the carbonyl group and resonance stabilization of the conjugate base.
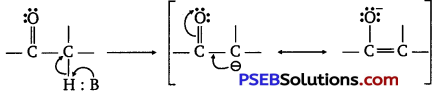
(ii) This is due to steric and electronic reasons. Sterically, the presence of two methyl groups in propanone hinders more the approach of nucleophile to carbonyl carbon than in ethanal having one methyl group. Electronically two methyl groups reduce the positivity of the carbonyl carbon more effectively in propanone than in ethanal.
(iii) Benzoic acid does not give Friedel Craft reaction because:
- the carboxyl group is strongly deactivating.
- the catalyst AlCl3 which is a lewis acid gets bonded to the carboxyl group strongly.
![]()
Question 5.
An organic compound T having molecular formula C4H8O gives orange-red ppt. with a 2,4-DNP reagent.
It does not reduce Tollen’s reagent but gives yellow ppt. of iodoform on heating with NaOI.
Compound X on reduction with LiAlH4 gives compound T’ which undergoes dehydration reaction on heating with -cone. H2SO4 to form but-2-ene. Identify the compounds X and Y.
Answer:
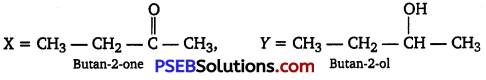
Reaction involved:
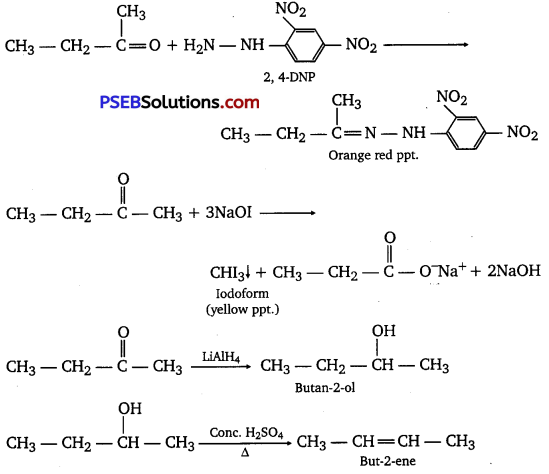
Long answer type questions
Question 1.
(a) Account for the following:
(i) Cl – CH2COOH is a stronger acid than CH3COOH.
(ii) Carboxylic acids do not give reactions of carbonyl group.
(b) Out of CH3CH2 – CO – CH2 – CH3 and CH3CH2 – CH2 –
CO – CH3, which gives iodoform test?
Answer:
(a) (i) Because of -I effect of Cl atom in ClCH2COOH and +I effect of CH3 group in CH3COOH the electron density in the O-H bond in ClCH2COOH is much lower than CH3COOH.
As a result O-H bond in ClCH2COOH is much weaker than in CH3COOH therefore loses a proton more easily than CH3COOH.
Hence ClCH2COOH acid is stronger acid than CH3COOH.
(ii) Carboxylic acids are resonance hybrid of the following structures:
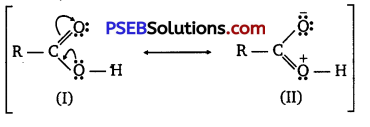
Similarly, a carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones may regarded as resonance hybrid of following structures :
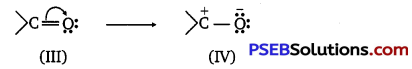
Because of contribution of structure (IV), the carbonyl carbon in aldehydes and ketones is electrophilic. On the other hand, electrophilic character of carboxyl carbon is reduced due to contribution of structure (II). As carbonyl carbon of carboxyl group is less electropositive than carbonyl carbon in aldehydes and ketones, therefore, carboxylic acids do not give nucleophilic addition reactions of aldehydes and ketones.
(b) CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – COCH3.
Question 2.
Write the products formed when ethanal reacts with the following reagents:
(i) CH3MgBr and then H3O+
(ii) Zn-Hgyconc.HCl
(iii) C6H5CHO in the presence of dilute NaOH
Answer:
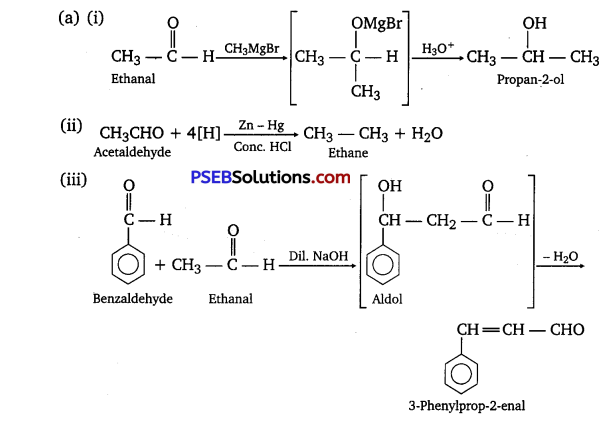
Question 3.
(a) Write the products of the following reactions :
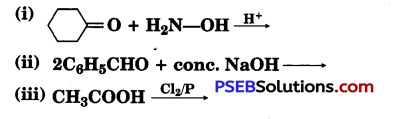
(b) Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(i) Benzaldehyde and Benzoic acid
(ii) Propanal and Propanone
Answer:
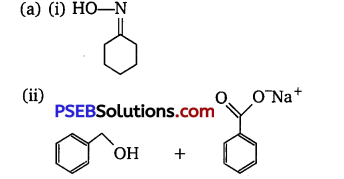
(iii) Cl-CH2-COOH
(b)
(i) NaHCO3 test
(ii) Iodoform test or Fehling test or Tollen’s test.
![]()
Question 4.
(a) Account for the following:
(i) CH3CHO is more reactive than CH3COCH3 towards reaction with HCN.
(ii) 2-Fluorobutanoic acid is a stronger acid than 3-Fluorobutanoic acid.
(b) Write the chemical equations to illustrate the following name reactions:
(i) Etard reaction.
(ii) Rosenmund’s reaction.
(c) Give the mechanism of cyanohydrin formation when carbonyl compounds react with HCN in the presence of alkali.
Answer:
(a)
- CH3CHO is more reactive than CH3COCH3 towards reaction with HCN due to steric and electronic factors.
- Because the inductive effect decreases with distance and hence the conjugate base of 2-Fluorobutanoic acid is more stable.
(b)