Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 15 Polymers Important Questions and Answers.
PSEB 12th Class Physics Important Questions Chapter 15 Polymers
Very short answer type questions
Question 1.
Which of the following is a natural polymer? Buna-S, Proteins, PVC
Answer:
Proteins.
Question 2.
Can enzyme be called a polymer? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Enzymes are biocatalysts which are proteins and are thus polymers.
Question 3.

Answer:
Homopolymer.
Question 4.
Identify the type of polymer -A-B-B-A-A-A-B-A- [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Copolymer.
Question 5.
Out of chain growth polymerisation and step-growth polymerisation, in which type will you place the following: [NCERT Exemplar]
![]()
Answer:
Chain growth polymerisation, as there is no loss of small molecules like water; methanol, etc.
![]()
Question 6.
What is the role off-butyl peroxide in the polymerisation of ethene?
Answer:
It acts as a free radical generating initiator in the chain initiation step of polymerisation of ethene.
![]()
Question 7.
Can nucleic acids, proteins and starch be considered as step growth polymers? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Yes, step-growth polymers are condensation polymers and they are formed by the loss of simple molecules like water leading to the formation of high molecular mass polymers.
Question 8.
Write the structure of the monomer used for getting the melamine-formaldehyde polymer.
Answer:
Melamine and formaldehyde
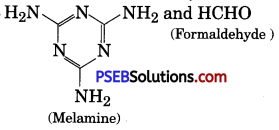
Question 9.
How is the following resin intermediate prepared and which polymer is formed by this monomer unit?
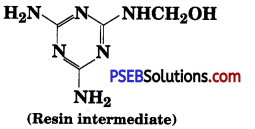
Answer:
Melamine and formaldehyde are starting materials for this intermediate. Its polymerisation gives melamine polymer.
Question 10.
Why does cis-polyisoprene possess elastic property? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
cis-polyisoprene is also known’ as natural rubber. Its elastic property is due to the existence of weak van der Waals’ interactions between their various polymer chains.
Short answer type questions
Question 1.
Which of the following polymers soften on heating and harden on cooling? What are the polymers with this property collectively called? What are the structural similarities between such polymers? Bakelite, urea-formaldehyde resin, polythene, polyvinyls, polystyrene. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Polythene, polyvinyls and polystyrene soften on heating and harden on cooling. Such polymers are called thermoplastic polymers. These polymers are linear or slightly branched long-chain molecules. These possess intermolecular forces whose strength lies between strength of intermolecular forces of elastomers and fibres.
Question 2.
What is the role of benzoyl peroxide in addition polymerisation of alkenes? Explain its mode of action with the help of an example. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Role of benzoyl peroxide is to initiate the free radical polymerisation reaction which can be easily understood by taking an example of polymerisation of ethene of polythene.
(i) Chain initiation
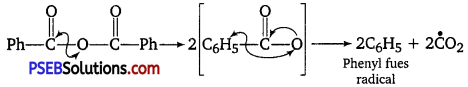
(ii) Chain propagation
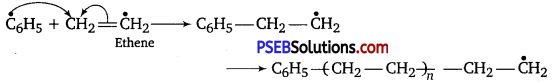
(iii) Chain terminator step
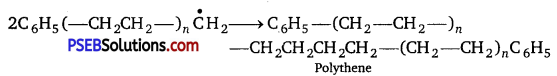
Question 3.
Low-density polythene and high-density polythene, both are polymers of ethene but there is marked difference in their properties. Explain. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Low density and high-density polythenes are obtained under different conditions. These differ in their structural features. Low-density polythenes are highly branched structures while high-density polythene consists of closely packed linear molecules. Close packing increases the density.
![]()
Question 4.
Differentiate between rubbers and plastics on the basis of intermolecular forces. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Rubber is a natural polymer which possess elastic properties. Natural polymer is a linear polymer of isoprene (2-methyl-1, 3-butadiene).
In natural rubber cis-polyisoprene molecules consists of various chains held together by weak van der Waals’ interaction and has coiling structure. So, it can be stretched like a spring.
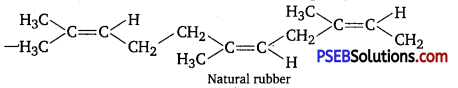
Plastics are generally polymers of ethene known as polythene. Polythene is thermoplastic polymer which may be linear (HDP) or branched (LDP) these type of polymers. Possesses intermediate intermolecular forces of attraction. It has linear, structure that can be moulded but can’t be regained on its original shape after stretching.
Question 5.
A natural linear polymer of 2-methyl-l, 3-butadiene becomes hard on treatment with sulphur between 373 to 415 K and -S-S- bonds are formed between chains. Write the structure of the product of this treatment? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
The product is called vulcanised rubber. Its structure is as follows :
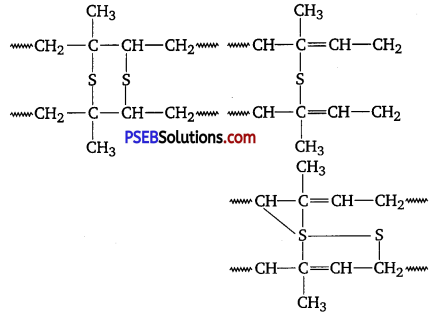
Question 6.
Name the type of reaction involved in the formation of the following polymers from their respective monomers
(i) PVC.
(ii) Nylon6.
(iii) PHBV.
Answer:
(i) Addition
(ii) Condensation/Hydrolysis
(iii) Condensation.
Long answer type questions
Question 1.
Explain the following terms giving a suitable example for each:
(i) Elastomers
(ii) Condensation polymers
(iii) Addition polymers
Answer:
(i) Elastomers: These are the polymers having the weakest intermolecular forces of attraction between the polymer chains. The weak forces permit the polymer to be stretched. A few ‘cross links’ are introduced between the chains, which help the polymer to retract to its original position after the force is released as in vulcanised rubber. Elastomers thus possess an elastic character. For example, buna-S, buna-N, neoprene, etc.
(ii) Condensation polymers: The condensation polymers are formed by the repeated condensation reaction between different bi-functional or tri-functional monomer units usually with elimination of small molecules such as water, alcohol, hydrogen chloride, etc. For example, Nylon-6,6, nylon 6, terylene, etc.
(iii) Addition polymers: Addition polymers are formed by repeated addition of same or different monomer molecules. The monomers used are unsaturated compounds. For example, alkenes alkadienes and their derivatives. Polythene is an example of addition polymer.
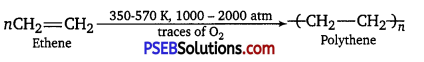
![]()
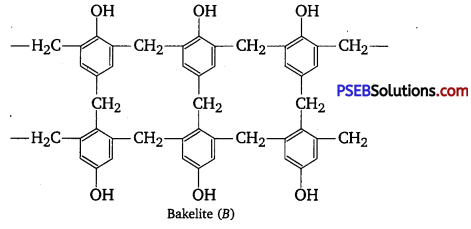
Question 2.
Phenol and formaldehyde undergo condensation to give a polymer (A) which on heating with formaldehyde gives a thermosetting polymer (B). Name the polymers. Write the reactions involved in the formation of (A). What is the structural difference between two polymers? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Phenol and formaldehyde undergo condensation to give a polymer novolac (A) which on heating with formaldehyde gives bakelite (B) as a thermosetting polymer.
A sequence of the reaction can be written as follows :
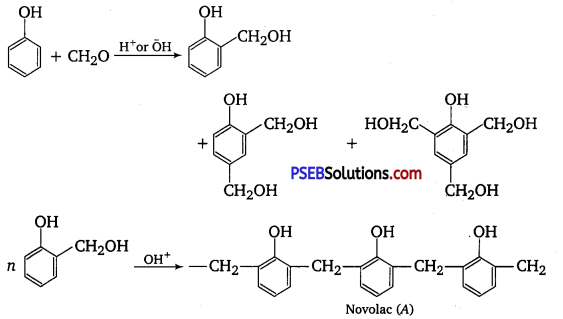
Structural difference in between these two is that novolac is a linear polymer while bakelite is a cross-linked polymer.