Punjab State Board PSEB 7th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 10 Practical Geometry Ex 10.5 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 10 Practical Geometry Ex 10.5
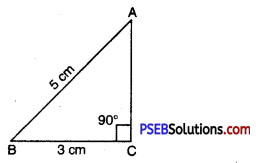
1. Construct a right angled triangle ABC with ∠C = 90°, AB = 5 cm and BC = 3 cm.
Solution:
Given : Two sides of ΔABC as
AB = 5 cm,
BC = 3 cm
and ∠C = 90°.
To construct : A triangle with these two sides and one right angle.
Steps of Construction :
Step 1. We first draw a rough sketch of the triangle ABC and indicate the measure of these two sides and mark the right angle.
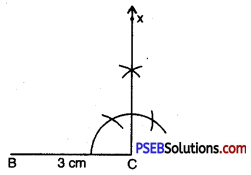
Step 2. Draw BC of length 3 cm.
![]()
Step 3. At C, draw CX ⊥ BC. (A should be somewhere on this perpendicular).
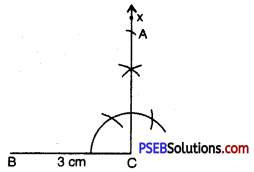
Step 4. With B as centre, draw an arc of radius 5 cm. (A must be on this arc since it is at a distance of 5 cm from B).
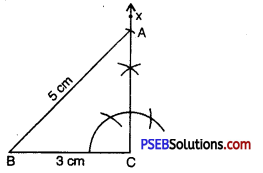
Step 5. A has to be on the perpendicular line CX as well as on the arc drawn with centre C.
∴ A is the meeting point of these two.
ΔABC is now obtained.
![]()
2. Construct an isosceles right angled triangle DEF where ∠E = 90° and EF = 6 cm.
Solution:
Given : An isoscele right angled ΔDEF where ∠E = 90° and EF = 6 cm.
To Construct: A right angled triangle with one side.
Steps of Construction:
Steps 1. Draw a rough sketch of given measures.
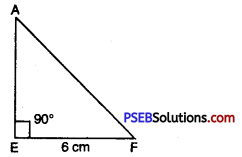
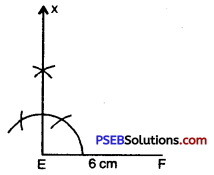
Step 2. Draw a line segment EF = 6 cm.
![]()
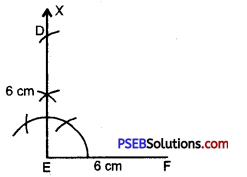
Step 3. With the help of compass taking E as centre, draw a ray EX making an angle of 90° with EF.
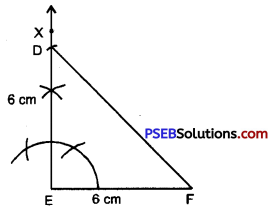
Step 4. With E as centre and radius 6 cm (= DE) draw an arc intersecting EX at D.
Step 5. Join D and F. Therefore ΔDEF is required isosceles right triangle.
![]()
3. Construct a right-angled triangle PQR in which :
∠Q= 90°, PQ = 3.6 cm and PR = 8.5 cm
Solution:
Given : Right triangle be PQR; right-angled at Q
i. e. ∠Q = 90°
and PQ = 3.6 cm,
PR = 8.5 cm
To construct : A triangle with these two sides and one right angle.
Steps of Construction :
Step 1. We first draw a rough sketch of the triangle PQR and indicate the measure of these two sides and mark the right angle.
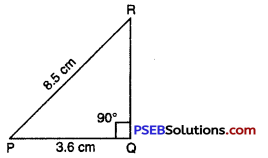
Step 2. Draw PQ of length 3.6 cm.
![]()
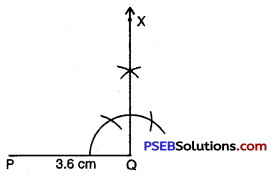
Step 3. At Q, draw QX ⊥ PQ.
(R should be somewhere on this perpendicular).
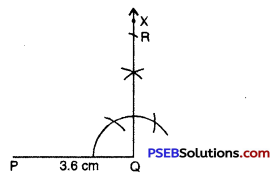
Step 4. With P as centre, draw arc of radius
(R must be on this arc, since it is at a distance of 8.5 cm from P).
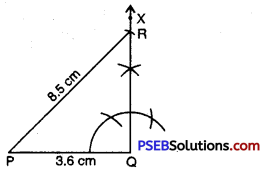
Step 5. R has to be on the perpendicular line QX as well as on the arc drawn with centre P.
∴ R is the meeting point of these two.
ΔPQR is now obtained.
![]()
4. Question (i).
Which of the following is a pythagorian triplet ?
(a) 1, 2, 3
(b) 2, 3, 4
(c) 4, 5, 6
(d) 12, 13, 5
Answer:
(d) 12, 13, 5
Question (ii).
Construction of unique triangle is not possible when :
(a) Three sides are given.
(b) Two sides and an included angle are given.
(c) Three angles are given.
(d) Two angles & included side are given.
Answer:
(c) Three angles are given.
