Punjab State Board PSEB 7th Class Social Science Book Solutions Geography Chapter 4 Ocean Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Geography Chapter 4 Ocean
SST Guide for Class 7 PSEB Ocean Textbook Questions and Answers
I. Answer the following questions in approximately 1-15 words.
Question 1.
Why does the ocean water salty?
Answer:
Many salts are mixed in seawater. That is why the seawater is salty.
Question 2.
Why there is a dense fog near Newfoundland?
Answer:
Near this place, there is a meeting of the warm gulf stream and cold labrador current. So, there is a blanket of dense fog.
Question 3.
Explain the route of Gulf-stream current.
Answer:
The gulf-stream starts from Mexico gulf and reaches the Newfoundland Islands.
Question 4.
Write down the main ocean currents of North Atlantic Oceans Cycle.
Answer:
North equatorial stream, the Kurushivo stream, North Pacific stream, the California stream.
![]()
Question 5.
What do you understand by Tsunami?
Answer:
Tsunamis are high tidal waves (30 metres high) caused by earthquakes in oceans. On 26th December, 2004; an earthquake occurred in Indian ocean. Its focus was near Indonesia. It caused Tsunamis in Indian ocean. These waves destroyed property worth millions of rupees. About 2 lakh persons died in Indonesia, Thailand, India and Sri Lanka. In India, most affected areas were Andaman Nicobar islands, Tamil Nadu coast, and eastern coast.
II. Answer the following questions in approximately 50-60 words.
Question 1.
What is the difference between Spring Tide and Neap Tide?
Answer:
The periodical vertical rise and fall of the surface of the sea water is called a tide. The rising of water is called the high tide or up tide while the falling of water is known as low tide or down tide.
Tides are caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and to some extent, the sun. Tides are useful to us as they help in navigation and fishing. At the high tide, the depth of the seas particularly gulfs, and bays increases. This enables the big ships to enter or leave the harbours easily. Due to high tides in the Hooghly river the depth of the water increases. As a result big ships enter and leave the Kolkata port which is situated on the bank of this river. Some ports such as Kandla in Gujarat and Diamond Harbour in West Bengal depend on the tides. Tides, at some places, take away the mud brought down by¬rivers and prevent silting of harbours. Thus tides make the rivers suitable for navigation.
Formation of Tides
Question 2.
Differentiate between warm water ocean current and cold water ocean current.
Answer:
- According to Ferral’s law, ocean currents move to their right in the southern hemisphere.
- Warm currents move towards cold seas and cold currents move towards the warm seas.
- In the lower latitudes, warm currents flow on the eastern shores and cold on the western shores.
- In the higher latitudes, warm currents flow on the eastern shores and cold on the western shores.
- Cold and warm currents meet along the convergence and move out along divergence.
- Cold currents move as sun-surface currents and warm currents move as surface currents.
Question 3.
Why are the ocean currents of Indian ocean not so definite and systematic?
Answer:
Unlike Atlantic and Pacific ocean, the ocean currents of Indian ocean are not so definite and systematic. It is because of the seasonal winds which flow in Indian ocean. In summer season, these winds blow in south-west direction and in winter season, these direction blow in north-eastern direction. Because of this change the ocean currents also change their direction.
![]()
Question 4.
Tide is very useful for ships. How?
Answer:
- Because of tides the mud and the soil continue to flow out of the river mouth. As a result, there is no deposits of soil on such coastal ports and ships can come in the interior.
- Big and heavy ships wait for tides in the deep sea. When there is high tide the ships along with the high tides reach the ports. Once they unload the cargo, they again wait for the tides. So, that they can go back easily to the sea. The ports of Kolkata and London are such examples.
Question 5.
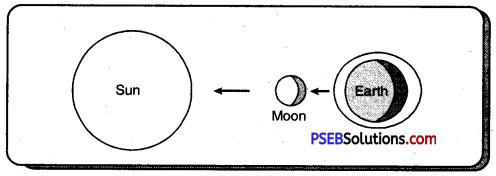
Why a spring tide occurs in full moon and no moon days?
Answer:
At the time of high tide the sea water is on the rise. It happens only on full moon night and without moon night. Because on these two days the sun, moon and earth are in a straight line. On this day, the sun and moon together attract the sea water upwards. Because of this double attraction the tides rise high and it is known as high tide condition.
Question 6.
How does the Gulf-stream affect the climate of Europe?
Answer:
The Gulf-stream is the most important warm current of the world. Its width is 400 km approximately. The speed of its water is 5 km/hr. Near Newfoundland it meets labradors cold streams. As a result, there is dense fog conditioh. Here, the fish are also found in excess quantities. After this, it moves towards Europe. Because of its impact the winter in North-West Europe is not so cold.
Question 7.
What is the difference between ocean waves and the ocean currents?
Answer:
The sea water continues its up and down movement. According to climatic positions, the speed sometimes increases and sometimes slows down and it produces waves. The water particles run up and down and it looks as if there are wrinkles on the surface of the sea.
Sometimes the ocean water takes a fix direction, then it is called oceanic current. In the ocean water leaves one place and moves towards the other place regularly. The speed of the current can be 2 km/hr to 10 km/hr.
![]()
Question 8.
Write down a case study of a place that is affected by Tsunami.
Answer:
On 26th Dec, 2004 there were most dangerous Tsunami tides in Indian Ocean. These were created by an earthquake which came on the sea surface measuring 9 points on Richter scale. The epicentre of this earthquake was the western course of Indonesia. In a matter of a few hours these waves brought heavy destruction in 11 countries bordering Indian Ocean. There was a great loss of life and property and the effect was experienced from Africa to Thailand.
According to an estimated figure, there was a loss Of life and property worth Rs. 5322 crore in India. The worst affected were Tamil Nadu, Kerela, Andhra Pradesh and Pondicherry. More than 2 lakh people were killed and many more were injured.
PSEB 7th Class Social Science Guide Ocean Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions :
Question 1.
Which is not a warm ocean current?
(a) Labrador current
(b) Gulf stream
(c) Venezuela
(d) Kuroshio.
Answer:
(a) Labrador current.
Question 2.
Which is a tidal port in India?
(a) Mumbai
(b) Chennai
(c) Kandla
(d) Cochi.
Answer:
(c) Kandla.
![]()
Question 3.
The rythmic rise and fall of ocean water twice in a day is called :
(o) Tide
(b) Ocean current
(c) Wave
(d) Current.
Answer:
(a) Tide.
Question 4.
How much of total water is fresh water?
(a) 0.5%
(b) 1.0%
(c) 2.5%
(d) 3.0%. .
Answer:
(c) 2.5%
Question 5.
Peru’s current is :
(a) Cold stream
(b) Hot stream
(c) Dry stream
(d) Wet stream.
Answer:
(a) Cold stream.
Fill in the Blanks :
Question 1.
The currents can be divided into _________________ ocean and two main parts.
Answer:
Northern ocean and southern ocean
![]()
Question 2.
Area of pacific ocean is _________
Answer:
16.6 crore sq. km
Question 3.
_________ ocean is longest and deepest ocean on earth.
Answer:
Pacific
Question 4.
The Falkland current is the main current of __________ ocean.
Answer:
South Atlantic
Question 5.
The gulf stream starts from ___________ gulf.
Answer:
Maxico.
True / False :
Question 1.
Tsunamis are high tidal waves caused by earthquake.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Generally warm ocean currents originate near poles.
Answer:
False
Question 3.
Ocean currents are strong seismic waves.
Answer:
False
![]()
Question 4.
Venezuela current is the main current of South Atlantic ocean cycle.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
Tides happens twice in 24 hrs.
Answer:
True.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by Ocean? Write its one feature.
Answer:
On the surface of earth, there are big storehouses of water which are known as oceans. The water of these oceans is salty.
Question 2.
What do you mean by tides?
Answer:
The ocean water twice rises to the coast and twice goes down towards the sea. This up and down movement of water is known as tide.
Question 3.
Why does high tide take place on a full moon night and without moon night?
Answer:
This happens because on these two nights the attraction of sun doubles up with the attraction of moon. Because of its double attraction the high tide takes place.
Question 4.
What are the three different speeds of ocean water?
Answer:
The ocean water has three speeds waves, currents and tides.
![]()
Question 5.
Write any one difference between wave and current.
Answer:
In wave, the water goes up and down continuously but it does not take speed. On the contrary in the current, water moves from one place to another.
Question 6.
How many oceans are there on earth?
Answer:
There are five oceans on earth. Their names are :
- Pacific ocean, Atlantic oceans, Indian ocean, Arctic ocean, Antarctic ocean.
- All these oceans are” combined with each other. The water of one ocean mixes with the other.
Question 7.
Write the areas of oceans.
Answer:
table-2
Question 8.
What is the difference between fresh water and saline water?
Answer:
Fresh Water. Rainfall, melting snow, rivers, canal, water pumps, etc. give us fresh water.
Saline Water. Mostly found in oceans. The most salt is in Dead sea. It is surrounded by earth from all the sides.
Question 9.
What is the most important hot water stream in the world?
Answer:
The most important hot water stream in the world is Gulf Stream. It starts from Mexico Gulf and reaches Newfoundland Islands.
Question 10.
Why do the fishermen of Norway go deep into sea for fishing?
Answer:
There is the hot current of water which is called North Oceanic hot water current. It flows near the Norway Coast. So, the fishermen go deep into the sea for fishing.
![]()
Question 11.
Why do the western ports of West European countries remain open during winters also.
Answer:
Because of the effect of North Oceanic warm current these ports do not freeze and remain open even during the winter season.
Question 12.
Why are there deserts in the places where the cold currents pass?
Answer:
Whenever some winds pass over the cold currents, then these become cold and dry. So, the closer regions become deserts.
Question 13.
What is the effect of oceanic currents on ship movement?
Answer:
The ships generally move in the direction of currents. It increases there speed and consumes less fuel.
Question 14.
Write down the main currents of South Atlantic ocean cycle.
Answer:
South Atlantic ocean has two main currents :
- The Falkland current and
- Venezuela current.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the effect of oceanic currents on the climate of some countries?
Answer:
- The warm currents increased the temperature of their neighbouring areas and cold currents decrease the temperature of their neighbouring areas.
- The winds passing over warm currents absorb the humidity and bring rainfall on coastal areas. Whereas the winds passing over cold currents become cold and dry.
![]()
Question 2.
What do you mean by wave? How is it created?
Answer:
The ocean water always remains up and down. The water particles keep on jumping and this makes the ripples on the surface of sea. These are called waves. The waves are created because of the speed of the winds. When winds passes over the sea they shake the surface of water. This shaking and shivering of water surface is called waves.
Question 3.
Why do the North Indian Oceanic currents flow in reverse directions during Summer and winter?
Answer:
The local winds have the greatest effect on the direction of the currents. The direction in which the winds blow for a longer period, the ocean water also takes the same direction. In the north-Indian ocean the winds move in reverse direction in summer and winter. So, the water current also has reverse direction during summer and winter.
Question 4.
Why does low tide come on the sevenfh and twenty-first of full moon night?
Answer:
On these two dates the Moon and the Sun make 90° turn with the Earth. As a result, both attract the sea water in reverse directions. Because moon is closer to-the sea, the water jumps more towards the moon. But because of counter attractions of sun the effect of moon’s attractions becomes very less and as a result the jump of water becames too low and it is called low tide.
Question 5.
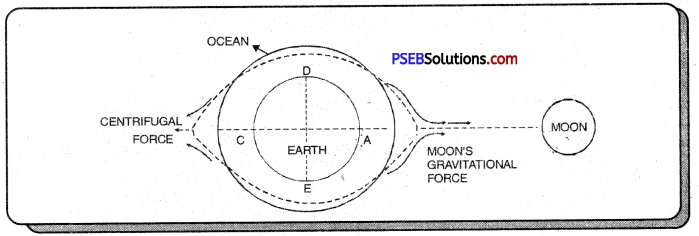
What are tides and how are they caused?
Answer:
Along coasts, the water slowly rises up over the shore and slowly falls back again. When the water has risen to its highest level, covering much of the shore, it is at high tide. When the water falls to its lowest level, it is low tide.
Tides
Tides are caused by gravitational pull of the moon, and to some extent the pull of the sun on the earth’s surface.
The moon exerts gravitational pull on the earth as it orbits around it. This has little effect on land which is solid and inflexible but it has a great effect on the ocean waters because water is liquid can freely move about.
![]()
Question 6.
What are ocean currents?
Answer:
These are streams of water move along the surface of ocean in definite paths. Such more or less permanent streams of water which flow in a definite direction are known as ocean currents. These are like rivers in the ocean, thousands of kilometres in length and sometimes about 200 km wide. Ocean currents can be cold and warm.
Question 7.
Ocean water is salty. Why?
Answer:
Sea water is salty or saline. This is because the sea contains a great variety of salts and minerals in solution. These minerals are brought down by the rivers in the silt they carry. It is estimated that the ocean contains enough salt to cover the continents with a layer 100 metres thick.
Question 8.
The quality of water is deteriorating. Why?
Answer:
The quality of water is deteriorating due to water pollution. The following factors affect water pollution—Domestic sewage, industrial wastes, agricultural activities, thermal pollution and marine pollution.
Question 9.
Why is the earth called a watery planet? Describe the distribution of water on the earth.
Answer:
The earth is the only planet of the solar system which contains water in abundance. Hence it is called a ‘watery planet’. Three fourth of the earth’s total surface is covered with water.
Distribution: Oceans contain about 97 percent of the total water available on the earth’s surface. The remaining three percent is the fresh water found in the form of snow and ice on the ground and in lakes and rivers. ”
![]()
Question 10.
How are oceans useful to us?
Answer:
Oceans are useful to us in the following ways :
- They modify land temperature.
- Oceans are the source of water vapour which forms clouds. These clouds cause rainfall on the earth.
- Oceans are a major source of food for the mankind.
- They are an .excellent means of transport for bulk cargo.
Question 11.
Give reasons, why the western harbours of Britain remain open even in winter season whereas the eastern harbours of North America situated at the same latitude remain frozen?
Answer:
The currents affect the climate of the country deeply. In winters, there are cold conditions in north west of Britain. But, the north atlantic sea current takes easternly direction under the impact of western winds. This warm current reaches Norway and Sweeden cold countries through the north-west of Britain. Because of the impact of warm currents the western ports of Britain remain open. But, in the absence of such a climate the eastern ports of North America remain frozen and closed.
Question 12.
What is ‘Sargasso Sea’ and how does it form?
Answer:
The currents of north Altantic sea start from the equator and go towards the north. These move forward along with American Coast and when these came back along the European Coast these mix with equotorial current and complete there clockwise circle. The part of north Atlantic sea which comes inside the circle is called Sargaso sea.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
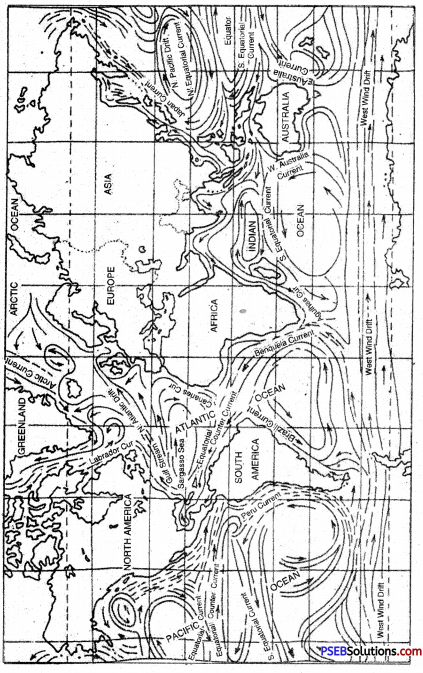
Describe in detail the currents of Indian ocean. Show these on the map also.
Answer:
The circle of Indian ocean currents is not fixed or regular. The main reason is seasonal winds of this ocean. These winds change their directions with the change in season. With this, the direction of Indian ocean currents also change.
The currents can be divided into two main parts :
- Northern Ocean
- Southern Ocean.
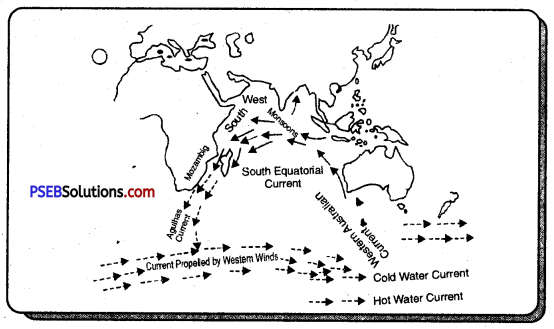
1. Northern Ocean:
- South-West Monsoon Current. Under the impact of south-west monsoons, the Indian oceanic current starts from west and flows towards east, this is called South-West Monsoon Current.
- North Equatorial Current. On the north of equator, the south-west equatorial current has east to west direction. It is a hot water stream.
- North Eastern Monsoon Current. On the north of equator, the North Equatorial Current flows from east to west. It is a hot water stream.
2. Southern Ocean: In the South hemisphere, mostly the currents have a fixed route which is as follows :
- Southern Current of Equator: It is a hot water stream which flows from east to west in the south of equator.
- Mozambiq Current: It is a part of the southern current of equator. When it hits the eastern coast of Africa then it takes southward direction. It is a hot water current.
- Agulhas Current: Before Malagasi islands, one branch goes towards south, it is called Agulhas Current.
- Western Australian Current: The south Indian oceanic current hits the south-west coast of Australia and one part moves towards north. This is called Western Australian Current. This cold current, at last meets North equatorial current and completes the circle.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain with diagram the formation of Tides.
Answer:
Tides are caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and to some extent the pull of the sun on the earth’s surface.
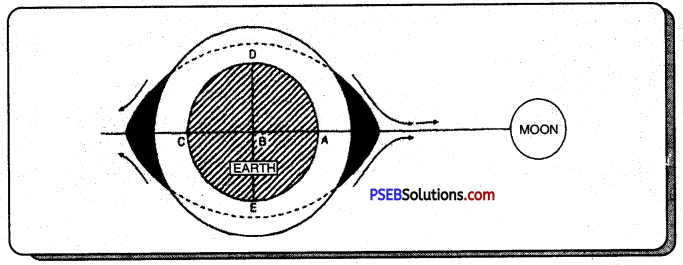
- The moon exerts a gravitational pull on the earth as it orbits around it. This has little effect on land which is solid and inflexible but it has a great effect on the ocean waters because water is liquid and can freely move about.
- The moon’s attraction causes the water of the earth from one region to pile up in on the side nearest the moon, i.e. at A. This being of water at A is an ordinary high tide. ‘
- At the same time, a counter-bulge occurs on the opposite side of the earth, resulting in a high tide at B. The cause for this high tide is to be found in the ‘centrifugal force’ that is set up by the rotation.
- Between these areas of high tides are areas o£ lower water at C and D since the moon’s pull draws water from these parts. These are areas of low tides.
Question 3.
Why do the ocean currents flow? How do they affect the climate of any country?
Answer:
Influence of Oceanic Currents :
1. Influence on Temperature. Warm currents raise and cold currents lower the temperature of the coastal regions along which they flow. Labrador coast remains ice-bound for about nine months in a year due to the cold Labrador current.
On the other hand, the temperature of the British Isles remains comparatively high due to the warm Gulf Stream (a warm current in the North Atlantic Ocean),
2. Influence on Rainfall. Winds blowing over warm currents pick up moisture which when condenses causes heavy rains. On the other hand, winds blowing over cold currents get cold and thus do not pick up moisture. Therefore, they do not cause rains. Western Europe receives heavy rainfall due to the warm Gulf Stream. On the other hand, the western coasts of South America, Africa and Australia are washed by the cold currents and therefore, do not get any rain. As a result, big deserts such as Atacama (South America), Sahara, Kalahari and Namib (Africa) and West Australia have 1, formed.
3. Influence on Marine Life. Where a warm and cold current meet together, thick fog is formed. Near Newfoundland the warm Gulf Stream and the cold Labrador current meet together and this results in the formation of very thick fog. As a result, fish gather here in large number and these areas have become the fishing grounds of the world.
4. Influence of Navigation. In pre-steamship days the influence of currents was very important. The ships used to drift with the help of currents. Ships from India used to sail towards Iran and Arabia with the north-east monsoon drift in winter and would return to India with the south-west monsoon drift in summer. In the modern times also, ships prefer to sail with the ocean current as it adds to their speed.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain with illustration the Atlantic Ocean Currents.
Answer:
There are two fixed circles of Atlantic ocean currents :
- North Circle,
- South Circle.
1. North Circle:
- North equatorial current: Because of trading winds, the water of the ocean starts flowing from east to west. It happens in the north of equator. It is a hot water current.
- Gulf Stream: North equatorial current flows from Africa to America. When this current goes to north-west along the eastern coast of America then it becomes Gulf stream. It starts from Maxico and reaches Newfoundland Islands.
- The Labrador Current: It is a cold current. It comes from north side and meets the Gulf stream near the Newfoundland Islands.
- North Oceanic Current: After Newfoundland the Gulf stream takes easterly direction under the effect of western winds.
- Canery Current: The north oceanic current hits the western coast of Europe and is divided into two parts. Its one part goes to south which is known as Canery current. It is a cold current. In the end this current meets north equatorial current and completes the north circle.
2. South Circle: This circle moves in anti-clockwise direction.
- South Equatorial Current.: It is a hot water current. Because of the effect of trading winds, the sea current starts flowing from East to West on the south of equator.
- Brazilian Current: The South Equatorial current hits the Brazilian coast where it is divided into two parts—The part which flows towards south along side Brazilian coast is known as Brazilian Current.
- Falkland Current: A cold stream from South side meets the Brazilian current and is called Falkland Current. Then this current goes eastways under the effect of western winds.
- Venezuela Current: Its a cold water stream. It is generated from Faulkland current. It flows towards north alongside the western coast of South Africa.
Question 5.
Explain with illustration the Pacific Ocean Currents.
Answer:
The Pacific Ocean is the biggest and the deepest ocean. Its currents can be divided into two parts :
1. North Circle:
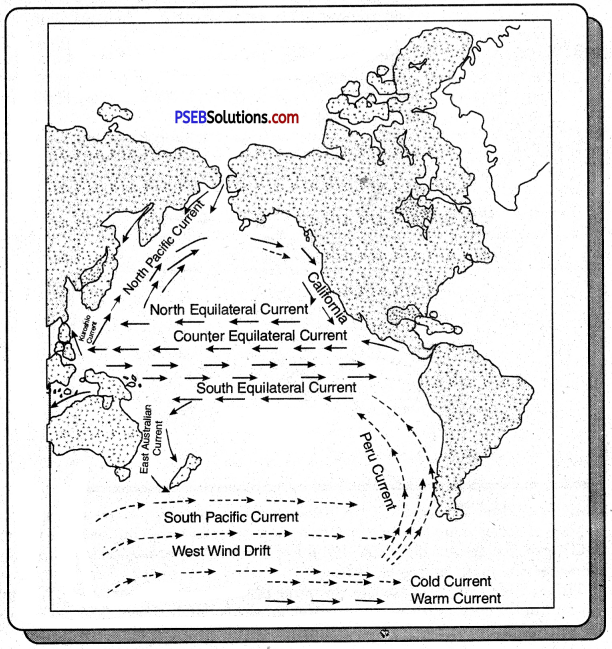
- North Equatorial Current: In the northern part of Pacific ocean, there are trading winds which make the currents flow from east to west. This current is known as north equatorial current. It is a hot water current.
- Kuroshivo Current: The north equatorial current flows towards north when it comes in eastern islands. Here it is called Kuroshivo current.
- North Atlantic Ocean Current: When Kuroshivo current hits the eastern coast of India then it start flowing towards north east. It is called north Atlantic ocean current.
- The California Current: The north Atlantic ocean current hits the western coast of North America. Here, it is divided into two parts: One part is called Alaska current and the other is known as California current. Because the California current comes from polar region. So, it is a cold current.
2. South Circle:
- South Equatorial Current: In the South of equator the sea water starts flowing east to west under the impact of trading winds. It is a hot water current,
- Eastern Australian Current: It is also a hot water current. When the south equatorial current reaches the eastern island, it takes southward direction and starts moving near the eastern coast of Australia. So it is called eastern Australian current.
- Pacific Ocean Southern Current: It is again a hot water current. Eastern Australian current takes eastward direction because of the effect of western winds. Because it is in south hemisphere, it bends towards west and is known as pacific ocean southern current.
- Peru’s Current: It is a cold stream. The Pacific ocean’s southern current hits the western coast of South America and starts flowing from south to north. It is Peru’s current, it meets the equatorial current and completes the circle of Pacific ocean currents.
![]()
Question 6.
How does the Tide occur? Justify with diagram.
Answer:
The oceanic water twice rises towards the coast and twice comes down towards the sea. This up and down movement is called the tide.
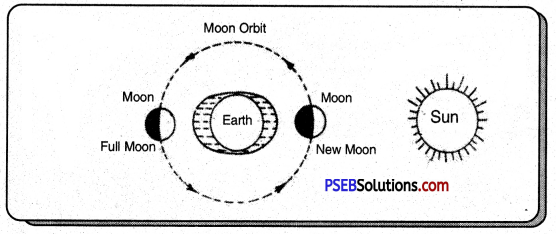
Reasons For Tide: Tides take place because of the attraction of the sun and moon. The attraction of the sun is many times more than the moon attraction but because the moon is nearer to earth so it creates more effect on the oceanic water i.e. why the moon attraction is considered as the main source of tides.
High Tides: High tide means when the wave in the ocean rises very high, it happens when the sun and moon both pull the ocean water upwards. High tides take place only on high moon days or no moon days. Because on both these days sun, moon and earth are in a straight line, and the waves in the ocean are more than what they normally are.
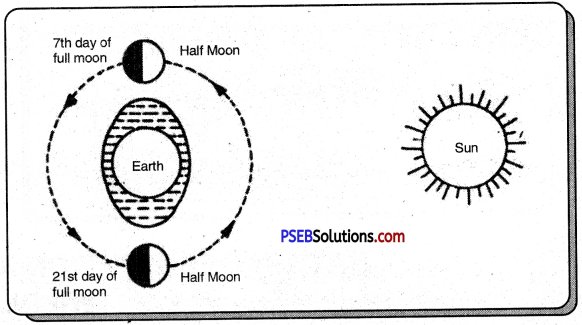
Low Tides. On the 7th and 21st day of full moon night both moon and sun make 90° angle with the earth. So both these pull the ocean water towards each other. Because the moon is closer to the earth, the water rises towards the moon, but the opposite power of the sun almost cancels the effect of moon power. So the rise of the sea waves is reduced to a low level. It is called low tides.
Question 7.
What are ocean currents? What are the causes of their origin?
Answer:
That part of seawater that systematically moves from one place to another place in a fixed direction, is known as current. In fact, these are the reverse of hot and cold water flowing inside the sea.
The reasons for currents are as follows:
- The Winds. Routine winds always flow in the same direction. They make the seawater also flow alongside. Thus the currents take place.
- The difference in Temperature. The temperature is more in equatorial regions. Because the seawater expands and moves towards the polar region. On the other side, the polar regions have low temperatures and the water there starts moving towards the equator inside the sea. Thus currents are created.
- The difference in Salinity. There are so many salts mixed in seawater. The water which has more salts it becomes heavy and starts going down the sea. To take its place the water with less salt, which is lighter, starts flowing towards the heavy salt side, so the currents take place.
- Formation of Continental Coasts. The currents flow along the Continental Coasts. So the formation of continental coasts gives new direction to the currents. With every change of direction, a new current is born.
