Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class Social Science Book Solutions History Chapter 10 The Establishment of East India Company Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Social Science History Chapter 10 The Establishment of East India Company
SST Guide for Class 8 PSEB The Establishment of East India Company Textbook Questions and Answers
I. Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Who was the first Portuguese to reach India?
Answer:
First Portuguese who reached India was Vasco-de-Gama.
Question 2.
Write down the names of the four Portuguese settlements.
Answer:
Goa, Daman, Cochin, Calicut, Dieu, etc.
Question 3.
Where the Dutch established their colonies in India?
Answer:
Dutch people established their settlements in India at Cochin, Surat, Masulipattam, Nagpattam and Pulkit.
![]()
Question 4.
When and from which Mughal emperor the British got the previliage to free trade?
Answer:
The British got the previlige to trade without paying octroi from the Mughal emperor Farrukhsiyar in 1717 A.D.
Question 5.
Among which two European companies, the First Carnatic War was fought and who got the victory?
Answer:
First war of Carnatic was fought between the Britishers and the French. The French people won this war.
Question 6.
When and among whom the battle of Plassey was fought?
Answer:
Battle of Plassey was fought on 23rd June, 1757 A.D. between the British and Nawab of Bengal Siraj-ud-daula.
Question 7.
When and among whom the battle of Buxar was fought?
Answer:
The battle of Buxar was fought between the British and Mir Qasim, Siraj-ud- Daulah and Shah Alam II.
Question 8.
Write down a note on third Carnatic War.
Answer:
The third Carnatic war was fought between 1756 A.D. to 1763 A.D. In this war the British emerged victorious and the French were defeated.
Causes. In 1756 A.D., once again, England and France were engulfed in a war in Europe (Seven Years War). Consequently, in India too, war broke out between the English and the French.
Question 9.
Explain in brief the victory of Bengal by the British.
Or
How did the English became the Masters of Bengal?
Answer:
The English fought two battles with the Nawab of Bengal to gain control over Bengal
- Battle of Plassey and
- Battle of Buxar.
The Battle of Plassey took place in 1757 A.D. Siraj-ud-daulah was the Nawab of Bengal at that time. The English, through a conspiracy, won over the confidence of Mir Jafar, the army commander of the Nawab. He remained aloof in the battlefield and thus Siraj-ud-daulah was defeated. After this, Mir Jafar was appointed as the Nawab of Bengal. After some time, Mir Jafar was removed and Mir Qasim was made the Nawab, but after some time, the English tinned against him as well. A battle between the English and Mir Qasim took place at Buxar. Mir Qasim was defeated and Bengal came under the control of the British.
![]()
Question 10.
Write down a note on the Battle of Plassey.
Answer:
The Battle of Plassey was fought between the British East India Company and the Nawab of Bengal, Siraj-ud-daulah. The Nawab was annoyed with the British due to various reasons. He caused a great loss to the British by invading Qasim Bazar. To take revenge, Clive hatched a conspiracy against him and won the confidence of Mir Jafar, the army commander of the Nawab of Bengal. When the battle started, Mir Jafar stood aside. Siraj-ud-daulah was discouraged as a result of this treachery of Mir Jafar and ran away from the battlefield.

Siraj-Ud-Daulah
Meerah, son of Mir Jafar, killed him. This battle proved to be very important for the English from historical point of view. The English became the real masters of Bengal and it became easy for them to expand their power in India.
Siraj-Ud-Daulah
Question 11.
Write down a note on Dual system in Bengal.
Answer:
Robert Clive started a new administrative system in Bengal which is known as the Dual administrative system. According to it, the administration of Bengal was divided in two parts. The work of tax collection remained with the British, while the Nawab was given the responsibility to run the administration. A fixed amount of money was paid to him for running the administration. As there were two types of administration in Bengal, so this system came to be known as dual administrative system. Real power of the administration in Bengal came in the hands of the British company as a result of this system and the Nawab remained a puppet in the hands of the British.
Question 12.
What do you mean by subsidiary alliance?
Answer:
The subsidiary alliance system was started by Lord Wellesley in 1798 A.D. He wanted to expand the British Empire in India and to make the company very powerful. It was possible only if all the native rulers and Nawabs were made powerless. He took advantage of the subsidiary alliance system and brought many native rulers under the British control.
Terms of the Subsidiary Alliance. Subsidiary Alliances were made between the company and the native rulers. The company promised to give military help to the rulers who entered into subsidiary alliances with it in case of any internal or external trouble.
In lieu of it, the local rulers had to accept the following terms :
- He had to accept the supremacy of the company. He was not allowed to make war or any treaty with any other ruler without the permission of the company.
- He had to keep a battalion of the English army in his state for his safety and he had to pay its expenses to the British.
- He had to keep an English Resident at his court.
![]()
Question 13.
Write a note on “Policy of Lapse.”
Answer:
The Policy of Lapse was adopted by Lord Dalhousie. According to this doctrine, succession to protected state depended upon the will of the British. Lord Dalhousie decided that if the ruler of a dependent state had no male child, he could not adopt a son. It meant that if a native ruler died without leaving a son behind, the dependent state would pass onto the hands of the British. On the grounds of Doctrine of Lapse, Dalhousie annexed seven dependept kingdoms into the British Empire which included Nagpur, Jhansi, Jaitpur and Satara.
II. Fill in the Blanks :
Question 1.
After the battle of ________a treaty of Allahabad was signed among the British, Siraj-ud-Daulah and Shah Alam in 1765 A.D.
Answer:
Buxar
Question 2.
In 1772 A.D. the ________ was abolished in Bengal.
Answer:
Dual administration
Question 3.
Lord Welleselly introduced the ________ system for expansion of the British Empire.
Answer:
Subsidiary alliance.
III. Write ‘True’ or ‘False’ in the brackets given after each statement:
Question 1.
First of all Vasco-De-Gama a Portuguese captain, reached Calicut in India on 27th May, 1498 A.D.
Answer:
True
![]()
Question 2.
Two Carnatic wars were fought between the Britishers and French.
Answer:
False
Question 3.
During the battle of Plassey with the Britishers, Mir Jaffer was the Nawab of Bengal.
Answer:
False.
IV. Something To Do:
Question 1.
Suppose you are nephew of Nawab. The Nawab have no son. From the beginning you are said that after the death of Nawab you will become a king. But under the policy of Doctrine of Lapse the British does not become a king to you. What will you do for become a king?
Answer:
Do it yourself with the help of your teacher.
Question 2.
Make a list on a chart of methods adopted by the Lord Dalhousie for the expansion of British Empire and which states were annexed in this empire by the Lord Dalhousie?
Answer:
Do it yourself with the help of your teacher.
PSEB 8th Class Social Science Guide The Establishment of East India Company Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
When was Bahadur Shah Zafar arrested?
(a) 1857 A.D.
(b) 1859 A.D.
(c) 1858 A.D.
(d) 1860 A.D.
Answer:
(c) 1858 A.D.
![]()
Question 2.
When did Vasco de Gama discover sea route to India?
(a) 1456 A.D.
(b) 1498 A.D.
(c) 1490 A.D.
(d) 1496 A.D.
Answer:
(b) 1498 A.D.
Question 3.
What was a Farman?
(а) A royal order issued by Aurangzeb
(б) A royal edict issued by British
(c) A verdict 6f rule over Bengal
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) A royal order issued by Aurangzeb.
Question 4.
Which Nawab of Bengal died in 1756 A.D.?
(a) Sirajuddaulah
(b) Mir Qasim
(c) Mir Jafar
(d) Alivardi Khan.
Answer:
(d) Alivardi Khan.
Question 5.
Which Governor-General defeated Sirajuddaulah at the battle of Plassey?
(a) Robert Clive
(b) William Bentinck
(c) Warren Hastings
(d) Lord Wellesley.
Answer:
(a) Robert Clive.
Question 6.
Which Nawab of Bengal was defeated in the battle of Buxar?
(a) Mir Jafar
(b) Sirajuddaulah
(c) Mir Qasim
(d) Murshid Quli Khan.
Answer:
(c) Mir Qasim.
![]()
Question 7.
After which battle the company appointed residents in the Indian states?
(a) Battle of Plassey
(b) Battle of Buxar
(c) Battle of Awadh
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Battle of Buxar.
Question 8.
Who granted Diwani rights of Bengal to the British?
(a) Mir Qasim
(b) Murshid Quli Khan
(c) Mir Jafar
(d) Mughal Emperor Shah Alam.
Answer:
(d) Mughal Emperor Shah Alam.
Question 9.
Who was the son of Haider Ali?
(a) Tipu Sultan
(b) Mir Jafar
(c) Alivardi Khan
(d) Mir Qasim.
Answer:
(a) Tipu Sultan.
Question 10.
Which ruler of Mysore stopped the export of many things through the ports of his kingdom?
(a) Haider Ali
(b) Alivardi Khan
(c) Tipu Sultan
(d) Mir Jafar.
Answer:
(c) Tipu Sultan.
Question 11.
How many Mysore wars were fought?
(a) Two
(b) Four
(c) Three
(d) Five.
Answer:
(b) Four.
Question 12.
In which battle Tipu Sultan was defeated?
(a) Battle of Buxar
(b) Battle of Awadh
(c) Battle of Plassey
(d) Battle of Seringapatam.
Answer:
(d) Battle qf Seringapatam.
![]()
Question 13.
Identify the shaded state where the three Anglo French wars were fought:
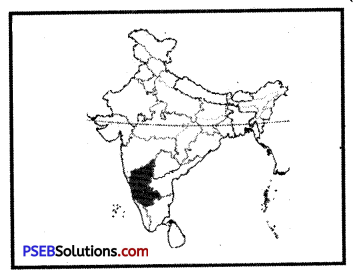
(a) Tamil Nadu
(b) Kerala
(c) Karnataka
(d) Andhra Pradesh.
Answer:
(c) Karnataka.
Question 14.
Why did Vasco-de-Gama come to India through sea route?
(a) To rule India
(b) To discover a new route to reach India
(c) To attack India
(d) On a vacation journey.
Answer:
(b) To discover a new route to reach India.
Question 15.
The person given in picture was the king of a famous kingdom in South India during late 18th century who fought four wars with the British. Name the king.

(a) Tipu Sultan
(b) Hyder Ali
(c) Mir Jafar
(d) Mir Qasim.
Answer:
(a) Tipu Sultan.
![]()
Question 16.
The person given in the picture defeated Nawab of Bengal Siraj-ud-daulah in the battle of Plassey. Name the person.

(a) Warren Hastings
(b) Robert Clive
(c) William Bentick
(d) Lord Canning.
Answer:
(b) Robert Clive.
Question 17.
Vasco-de-Gama was the first explorer who reached India by Sea. Which country did he belong to?
(a) England
(b) Portugal
(c) France
(d) Russia.
Answer:
(b) Portugal.
Fill in the Blanks :
Question 1.
The battle of ________ was fought between the British and Shuja-ud-daulah, Shah Alam and Mir Qasim in 1764.
Answer:
Buxer
![]()
Question 2.
________ system was ended in Bengal in 1772 A.D.
Answer:
Dual,
Question 3.
Lord Wellesley adopted system of ________
Answer:
Subsidiary Alliance.
Tick the Right (✓) or Wrong (✗) Answer :
Question 1.
Vasco-de-Gama reached Calicut on 27th May, 1498.
Answer:
(✓)
Question 2.
Two carnatic wars were fought between the British and French.
Answer:
(✗)
![]()
Question 3.
Mir Jafar was the Nawab of Bengal in the battle of Plassey.
Answer:
(✗)
Match the Following :
Question 1.
| A | B |
| 1. Battle of Plassey | (i) Lord Hastings |
| 2. Battle of Buxor | (ii) Siraj-ud-daulah |
| 3. Attack on Arcott | (iii) Mir Qasim |
| 4. British Gorkha War | (iv) Robert Clive |
Answer:
| A | B |
| 1. Battle of Plassey | (ii) Siraj-ud-daulah |
| 2. Battle of Buxor | (iii) Mir Qasim |
| 3. Attack on Arcott | (iv) Robert Clive |
| 4. British Gorkha War | (i) Lord Hastings |
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Who discovered new sea route to reach India from Europe?
Answer:
Portuguese sailor (captain) Vasco-de-Gama discovered new sea route to reach India from Europe.
Question 2.
When and on which port did Vasco-de-Gama reached India?
Answer:
27 May, 1498 on the port of Calicut.
![]()
Question 3.
When the English East India Company was.established?
Answer:
On 31 Dec. 1600 A.D.
Question 4.
When the French East India Company was established?
Answer:
In 1664 A.D.
Question 5.
Name the two French Governors in India under whom French power was spread in India.
Answer:
Dooma and Dupleix.
Question 6.
Name the British representatives who were sent to the Mughal Durbar to get trade concessions?
Answer:
William Hawkins and Sir Thomas Roe.
Question 7.
Name the French settlements near Chennai (Madras) and Kolkata (Calcutta).
Answer:
Pondicherry near Chennai and Chandernagar near Kolkata were the French settlements.
![]()
Question 8.
Between which European companies the third carnatic war was fought?
Answer:
This war was fought between French East India Company and English East India Company.
Question 9.
Give any one cause of the First Carnatic War (1746-48).
Answer:
War broke out in Europe between England and France. As a result, war also started in India between the two powers.
Question 10.
When the first Carnatic War ended? Mention one result of this War.
Answer:
The First War of Carnatic come to an end in 1748 A.D. The English got back the region of Madras (now Chennai) as a result of the peace treaty.
Question 11.
Give any one cause of the Second Carnatic War.
Answer:
The French supported Nasir Jang the ruler of Hyderabad and Chanda Sahib, the ruler of the Carnatic. The English could not tolerate this so they gave recognition to their opponents and waged a war against the French in 1751 A.D.
Question 12.
What was the result of Second War of Carnatic?
Answer:
French were defeated in the Second Carnatic War. It increased the power and prestige of the British Company in India.
Question 13.
Which Indian powers got involved in the Second War of Carnatic?
Answer:
The following Indian powers got themselves involved in the Second Carnatic War :
- Claimants to the throne of Carnatic.
- Claimants to the state of Hyderabad.
Question 14.
Mention any one cause of the third Carnatic War. (1756-1763).
Answer:
The Seven Years War began in Europe between England and France in 1756 A.D. Subsequently, a war between England and France also started in India. This was the Third War of Carnatic.
![]()
Question 15.
When did the third War of Carnatic take place. Which two European companies fought the third Battle of Carnatic? Who was defeated in this War?
Answer:
The Third War of Carnatic took place in 1J56 A.D. It was fought between the English East India Company and The French East India Company. The French were defeated in it.
Question 16.
What was the result of the third War of Carnatic?
Answer:
France lost her power in India as a result of the third War of Carnatic and the British emerged as a great power in India.
Question 17.
Who was Dupleix? What was his plan?
Answer:
Dupleix was the Governor of French possessions in India. He had prepared a plan for enhancing the French influences in Southern India.
Question 18.
Why was Dupleix called back?
Answer:
Dupleix was called back to France on account of the French defeat in the second Carnatic war.
Question 19.
Who was Robert Clive? What part did he play in the second War of Carnatic?
Answer:
Robert Clive was a very able English army Commander. He occupied Arcot, the capital town of Chanda Sahib in the Second War of Carnatic and compelled Chanda Sahib to leave Trichnapalli, As a result, the British won the war.
Question 20.
When and between whom the Treaty of Paris was signed? What were the effects of this treaty on India?
Answer:
The Treaty of Paris was signed in 1763 A.D. between France and England. The Third War of Carnatic in India also came to an end by this treaty.
Question 21.
State any one reason for the success of the British against the French in the Carnatic Wars.
Answer:
The English had a powerful navy. They were in a position to send their army with the help of navy from one place to another.
Question 22.
Between which powers did the Battle of Plassey take place?
Answer:
Between the British East India Company and Nawab Siraj-ud-daulah of Bengal.
Question 23.
State any one cause of the Battle of Plassey.
Answer:
The British started fortifying Calcutta (now Kolkata) in order to strengthen their position in Bengal. Calcutta (Kolkata) was a part of the kingdom of the Nawab. It strained the relations between the British and the Nawab.
![]()
Question 24.
Write any one result of the battle of Plassey.
Answer:
Nawab Siraj-ud-daulah was defeated in this battle and Mir Jafar became the new Nawab of Bengal. Mir Jafar gave huge amount of money and the district of 24 Parganas to the British.
Question 25.
What was the importance of the Battle of Plassey for the British?
Answer:
This battle greatly enhanced the power and prestige of the British which was the largest and most prosperous state in India. As a result, the key to the conquest of India fell into the hands of the English.
Question 26.
Write any one cause of the battle of Buxar.
Answer:
The British Company had got permission to trade freely in Bengal, but the officials of the Company had been trading privately. It caused financial loss to the Nawab of Bengal.
Question 27.
Clive is considered to be “the founder of the British Empire in India.” Give one reason in support of this view.
Answer:
Clive won the Second War of the Carnatic and also the Battle of Plassey for the British. Both these victories proved to be the foundation stone of the British Empire in India.
Question 28.
Who was Mir Jafar? For how long he remained the Nawab of Bengal?
Answer:
Mir Jafar was an army commander who betrayed Siraj-ud-daulah, the Nawab of Bengal. He remained the Nawab of Bengal from 1757 A.D. to 1760 A.D.
Question 29.
When and between whom was the Treaty of Allahabad signed?
Answer:
The Treaty of Allahabad was signed on May 3rd, 1765 between the British, Nawab of Awadh and the Mughal Emperor Shah Alam.
Question 30.
Write any one term of the treaty of Allahabad.
Answer:
The British Company got the right of Diwani of Bengal, Bihar and Orissa from the Mughal Emperor Shah Alam. As such, the English became the real rulers of Bengal.
![]()
Question 31.
“Buxar completed the work of Plassey.” Justify this statement.
Answer:
The battle of Plassey had paved the way for the increase of power and influence of the British in Bengal but they became the real rulers of Bengal after the battle of Buxar.- Shuja-ud-Daulah, the Nawab of Avadh and Shah Alam, the Mughal Emperor came completely under the control of the British Company. It is, therefore, said that Buxar completed the work of Plassey.
Question 32.
Which treaty was imposed by Lord Wellesley to expand the British Empire?
Answer:
Lord Wellesley followed the policy of expansion by making Subsidiary Alliances with the Indian states.
Question 33.
Name the two states affected by the Doctrine of Lapse.
Answer:
States of Jhansi and Nagpur were affected by Doctrine of Lapse. They both were annexed into the British empire.
Question 34.
When was Avadh annexed by the British?
Answer:
The British annexed Avadh in 1856 A.D.
Question 35.
Write any one term of Subsidiary Alliance.
Answer:
According to Subsidiary Alliance system, Indian rulers were not allowed to maintain any political relations with any internal or external power.
Question 36.
What promises the British Company made with any Indian ruler entering Subsidiary Alliance?
Answer:
The British East India Company promised security of the native ruler under this system in case of internal revolt or external aggression. The British company promised to protect the Indian rulers.
Question 37.
How was the British East India Company benefited by the Subsidiary Alliances? Mention any one benefit.
Answer:
Political position of the English East India-Company became very strong as a result of the Subsidiary Alliances.
Question 38.
How were the Indian rulers affected by the Subsidiary Alliances? Mention one effect.
Answer:
Local rulers who entered into Subsidiary Alliances with the company, were free from internal and external dangers. They started leading a luxurious life and became careless about the welfare of their subjects.
Question 39.
When did the Dual administrative system come to an end in Bengal?
Answer:
In 1772 A.D.
Question 40.
Name the three governors-general under whom the British empire expanded to a great deal.
Answer:
Lord Wellesley, Lord Hastings and Lord Dalhousie.
![]()
Question 41.
When and by whom independent Mysore state was established?
Answer:
Hyder Ali established independent Mysore state in 1761 A.D.
Question 42.
When first Mysore war took place? Who emerged victorious?
Answer:
First Mysore war took place in 1767-1769 A.D. Hyder Ali emerged victorious out of this war.
Question 43.
When was Hyder Ali died? Who became Sultan of Mysore after him?
Answer:
Hyder Ali was died in 1782 A.D. After him, his son Tipu Sultan became Sultan of Mysore.
Question 44.
When and how did Tipu Sultan die?
Answer:
Tipu Sultan died in 1799 A.D. while fighting fourth war of Mysore against the British.

Tipu Sultan
Question 45.
When treaties of Basin and Dewgao took place?
Answer:
In 1802 A.D. and 1803 A.D. respectively.
Question 46.
Between whom the treaty of Dewgao took place? Which two states were given to the British after this treaty?
Answer:
Treaty of Dewgao took place between Maratha Sardar Bhonsle and the British. The British got the states of Cuttock and Balasor through this treaty.
Question 47.
How many states of Rajasthan came under subordination of the British under Lord Hastings? Name four main states out of them.
Answer:
19 States of Rajasthan came under the subordination of the British during the tenure of Lord Hastings. Jaipur, Jodhpur, Udaypur and Bikaner were four main states out of those 19 states.
![]()
Question 48.
Name Dutch settlements in India.
Answer:
Dutch had their settlements in India at Surat, Cochin, Pulikat, Nagapattam, Chinsura etc.
Question 49.
By whom and for how many years the East India Company was granted the trade privileges to trade with India?
Answer:
The British Queen Elizabeth-I granted the East India Company the trade privileges of 15 years to trade with India.
Question 50.
Who was Assif Shah and when did he die?
Answer:
Assif Shah was the Nizam of Hyderabad. He died in 1748 A.D.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why did the European Trading Companies clash with one another and what were the results of the clash?
Answer:
Causes of the Clash. Many European companies came to India for trade. The traders of these companies were very greedy, selfish and ambitious. All the companies wanted to establish their complete control over the trade in India. So, this clash of interests was the main cause of conflict among the trading companies.
Results of the Conflicts. First of all, the Dutch defeated the Portuguese and took over the control of whole trade in their hands. In between, the English increased their activities. They defeated the Dutch and drove them away from India. So only the English and the French were left in India. A long struggle for supremacy in India began between these two powers. The English were the winners in this conflict and they established full control over trade in India. Gradually, they also established their political power in India.
![]()
Question 2.
Describe the First Carnatic War.
Answer:
War for the throne of Austria went on in Europe between 1740-48 A.D. England and France fought against each other in this war. As a result, the war between these two nations also started in India. The French looted the English trade centre of Fort Saint George (Madras). When the Nawab of Carnatic sent his army against them, it was also defeated by the French. Dupleix was the Governor of the French possessions in India during those days. The prestige of the French was greatly enhanced in India. In 1748 A.D., the war between the English and the French in Europe came to an end. In this year, a treaty was signed between the English and the French in India as well. The French returned Madras (now Chennai) to the English.
Question 3.
What were the results of the Second Carnatic War?
Answer:
- Chanda Sahib was killed and Arcot was occupied by the English.
- The English declared Muhammad Ali as the ruler of Carnatic.
- The French influenced continued in Hyderabad. They got the right of collecting revenue. They also stationed a battalion of their army there.
- The English Commander Clive became famous as a result of this war.
Question 4.
What were the results of the Third Carnatic War?
Answer:
The Third War of Carnatic started in 1756 A.D. and ended in 1763 A.D. Given below are the results of the war :
- The French lost their hold on the state of Hyderabad and the English influences was established there.
- The English got the territory of Northern Sarkars.
- The French power in India completely broke down and it became easy for the English to expand their power in India.
Question 5.
What were the causes of animosity between the English and the French in the 18th century?
Answer:
The following were the three main causes of animosity between the two powers :
- England and France had been the enemies of each other for a long time.
- There was a trade competition between the two countries in India.
- Both the countries wanted to establish their political power in India.
Actually, whenever there was a war between England and France in Europe, a conflict between the two powers also started in India.
Question 6.
Describe the main provisions of the Treaty of Allahabad.
Answer:
The following were the main terms of the Treaty of Allahabad (1765) :
- The English and the Nawab of Awadh promised to help each other in case of any war.
- The Nawab promised to pay fifty lakh rupees to the English as compensation of war.
- The Mughal Emperor Shah Alam granted Diwani of Bengal, Bihar and Orissa to the British Company. The English, in return, agreed to pay a pension of? 26 Lakhs per annum to Shah Alam.
- The Nawab of Awadh promised not to give shelter to Mir Kasim in his state.
![]()
Question 7.
Which of the three Wars of Carnatic was the most important and why?
Answer:
The Second War of Carnatic was the most important war out of the three wars of Carnatic. This war was a symbol of the diplomatic victory of the English. Before this, the English were badly defeated by the French in the First War of Carnatic. As a result, the French power in India became very strong. In the Second War of Carnatic too, the English were on the verge of defeat.
But Robert Clive cleverly changed the situation. He turned the war plan of the French into a failure. After this war, the power of the French rapidly declined. Consequently, the English easily defeated the French in the Third War of Carnatic. Had the English been defeated in the Second War of Carnatic, they would have not only lost trade in India, but would have to leave India like the Portuguese and the Dutch.
Question 8.
Why was Siraj-ud-daulah defeated in the battle of Plassey?
Answer:
Given below were the causes of defeat Siraj-ud-daulah in the Battle of Plassey :
1. Conspiracy of Clive. Clive gave a hitting blow to Siraj-ud-daulah by hatching a conspiracy against him. He won over the support of Mir Jafar, the army commander of Siraj-ud-daulah, and easily defeated Siraj-ud-daulah.
2. Lack of farsightedness of Siraj-ud-daulah. Siraj -ud-daulah was not a farsighted ruler. Had he been a wise ruler, he would have kept an eye on the activities of the English and his other opponents. He would have noticed the conspiracy beforehand which was being hatched by Clive. So, lack of his farsightedness became a cause of his defeat.
3. Lack of Military resources. The military set up of Siraj-ud-daulah was faulty. His soldiers were neither trained like the English soldiers nor they had modern weapons of war. Soldiers of the Nawab fought like a crowd in the battle. They lacked discipline.
Question 9.
What were the causes of the success of the British in the conflict between the French and the British?
Answer:
The following causes were responsible for the success of’the British against the French:
1. Powerful Navy of Britain. The English navy was more powerful than that of the French. The British had large ships to bring soldiers and war material from England to India.
2. Sound Financial Condition of the British. Economic condition of the British was very sound. Their trade activities continued even during the war days. But as the French usually kept themselves involved in politics, they therefore, lacked financial resources.
3. British Victory over Bengal. Bengal, a rich state of India, came under the control of the British after the battle of Plassey. Need of money for winning a war is very great. The British trade in Bengal continued even during the war days. The money they earned from this trade was utilised by them for their wars in the south.
4. Efficient infantry and able army commanders. The infantry wing of the British army was better trained and organised than that of the French army. English commanders like Robert Clive, Sir Ayercoote and Major Lawrence were very capable persons. On the other hand, the French army commanders like Dupleix, Lally and Bussey were not so capable and efficient persons. This factor also contributed to the success of the British.
![]()
Question 10.
What were the causes of conflict between Siraj-ud-daulah and the British? (P.S.E.B. 2005, 2003)
Answer:
The following causes were responsible for the conflict between Siraj-ud-daulah and the British :
- The British gave no gifts to Siraj-ud-daulah on his appointment as the Nawab of Bengal. Siraj-ud-daulah was therefore, angry with the British.
- The British gave shelter to a deserter of Siraj-ud-daulah’s service. The Nawab demanded the return of the traitor, but the British turned a deaf ear to his demand.
- The English started deploying forces in Calcutta (Kolkata) and in spite of refusal of the Nawab to allow them to keep their forces there, the British did not withdraw them.
- There was misappropriation of funds in the Dacca treasury of Nawab and the Nawab held that the misappropriated amount was in the possession of the English. He asked them to return the amount but the English refused.
Question 11.
What was the significance of the Battle of Buxar in Indian history?
Answer:
The Battle of Buxar is more important than the Battle of Plassey in the history of India. As a result of this battle, the British became a great political force in India. It paved for them the way for the conquest of more territories in India. The English consolidated their position in Bengal, Bihar and Orissa. The Nawab of Avadh Shuja-ud- daulah and the Mughal Emperor Shah Alam came completely under the British control.
Question 12.
What were the causes of the Battle of Plassey (1757 A.D.)?
Answer:
The following were the causes of the battle of Plassey :
Causes:
- The English gave no gifts to Siraj-ud-daulah on his appointment as the Nawab of Bengal. He was, therefore, angry with the British.
- The British stationed their armed troops at Calcutta (Kolkata) and continued reinforcing them in spite of the Nawab’s protests.
- The English hatched a conspiracy against the Nawab with the co-operation of Seth Amin Chand and army commander Mir Jafar of Bengal.
Question 13.
What were the causes of the Battle of Buxar?
Answer:
The following are the causes of the Battle of Buxar :
- The officials of the English Company were misusing the trade concessions allowed to them by the Nawab. It resulted in the decline in the income of the Nawab of Bengal.
- Mir Qasim strengthened his army. He established an arms and ammunition factory and shifted his treasury from Calcutta (Kolkata) to Mungher. The English did not like the activities of Mir Qasim.
- Mir Qasim also allowed Indian traders to trade without paying any tax like the English. It increased the animosity between the English and the Nawab.
![]()
Question 14.
Who was Tipu Sultan? Explain his conflict with the British.
Answer:
Tipu Sultan was the son of ruler of Mysore, Hyder Ali. He became ruler of Mysore in 1782 A.D. after the death of his father, Hyder Ali. At that time, second Mysore xwar was going on. Tipu carried on the war. In the beginning, he got some success but he was defeated in 3rd battle of Mysore (1790-92). He was forced to surrender some part of his kingdom to the British. He wanted to take revenge of his defeat and that’s why he again declared war against the British. Tipu Sultan died in this war (1799) and most of the part of his kingdom was annexed into the British empire. Remaining part of the Mysore was given to Prince Krishna Rao.
Question 15.
Write a note on the British-Gorkha War (1814-1816 A.D.).
Answer:
Gorkhas of Nepal captured some of the border areas of the British. That’s why Lord Hastings send a huge army to suppress the power of Gorkhas. It was send under Aukhterloani. Gorkha’s were defeated in this war. That’s why they were forced to give many areas to the British. Except this, they also agreed to keep a British resident in Kathmandu, the capital of Nepal.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Discuss the expansion of the British empire in India from 1823 till 1848 A.D.
Answer:
From 1823 till 1848 A.D., the British empire in India was expanded by Lord Emerhest, Lord William Bentick, Lord Auckland, Lord Allenbrough and Lord Harding.
It’s description is given below :
- Lord Emerhest won the First Anglo Burmese war (1824-26 A.D.) and annexed the states of Arakan and Assam into the British empire.
- After this, Lord William Bentick captured Kutch, Mysore and Kurg. He made a Trade treaty with amirs of Sindh in 1832. It led to stoppage of expansion of Maharaja Ranjit Singh in this direction.
- Lord Auckland made a subsidiary alliance with amirs of Sindh in 1839 A.D. and expanded the British empire.
- Charles Napier captured Sindh in 1843 A.D. during the tenure of Lord Allenbrough and annexed it into British empire.
- Lord Harding defeated the Sikhs in first Anglo-Sikh War. As a result, Jalandhar, Kangra and Kashmir were captured by the British.
![]()
Question 2.
How different Maratha kingdoms won over by the British?
Answer:
Till 1772 A.D., Chief of Marathas, Peshwa, remained very powerful. After this, Maratha Chief Nana Fadnavis kept Maratha power in one way or the other. During this age, most important Maratha chiefs were Scindhia, Bhonsle, Holkar and Gaikwad. But Peshwas and different chiefs were defeated one by one by the British.
1. Decline of Peshwa. After the death of fourth Peshwa, Madhav Rao, in 1771 A.D. his son Narayan Rao became next Peshwa. But he was killed by his uncle Raghoba. At this moment of problem, Nana Fadnavis took charge of Marathas. He declared son of Narayan Rao as next Peshwa and declared himself as his guardian. He fought a long battle with the British but did not accepted the Subsidiary Alliance. But Maratha chiefs were divided after his death. Peshwa was afraid by Maratha chief Holkar. That’s why he came under the protection of the British in 1802 A.D. and accepted Subsidiary Alliance under the treaty of Bassein.
2. End of Power of Scindhia and Bhonsle. Scindhia and Bhonsle didn’t like the acceptance of subsidiary alliance by the Peshwa. They considered it as a disrespect of the whole Maratha community. They declared war against the British to take revenge of this disrespect. Gaikwad gave his support to the British. Lord Lake defeated Scindhia and captured Delhi, Agra and Aligarh. Areas of Cuttock and Balasor also came under occupation of the British. In the end, Scindhia and Bhonsle both accepted the Subsidiary Alliance.
3. End of Power of other Maratha Chiefs. The Peshwa, once again tried to create unity among Marathas. In 1817 A.D., Lord Hestings defeated the forces of Peshwa, Bhonsle and Holker. Peshwa was given pension and his title was abolished. Whole of his kingdom was annexed into the British empire. After this, other Maratha chiefs also accepted the subordination of the British. In this way, all the Maratha kingdoms were annexed into the British empire.
Question 3.
Explain briefly the Anglo-Mysore wars.
Answer:
The Kingdom of Mysore was very powerful. This kingdom became very prosperous under Hyder Ali and military power of the state was also increased to a great extent. The British made an alliance with the enemies of Hyder Ali—Marathas and the Nizam of Hyderabad, to suppress the increasing power of Mysore. This was unbearable for Hyder Ali.
That’s why he declared war against the Britishers.
1. First war of Mysore. This war started between Hyder Ali and the British in 1767 and fought till 1769 A.D. Hyder Ali reached till Madras in this war. Then in 1769 A.D. one defensive treaty took place between both the parties. Conquered areas of both the parties were given back to each other.
2. Second War of Mysore. Hyder Ali also showed a great courage in the second war of Mysore (1780—84). But he was defeated at Portonona because he was unable to get expected help from the French. Hyder Ali died in 1782 A.D. and Tipu Sultan carried on the war. Later on, according to the treaty of Mangalore in 1784 A.D., conquered areas of both the parties were given back to each other.

Tipu Sultan
3. Third War of Mysore. In third war of Mysore (1790-92 A.D.), Tipu Sultan attacked on the British forces. But in the end he was defeated by Lord Cornwallis. According to the treaty of Srirangapattnam, half of the kingdom of Tipu Sultan was taken away by the British and Tipu Sultan was also forced to give? 3 crore as a compensation of war to the British
4. Fourth War of Mysore. Tipu Sultan died (1799 A.D.) in fourth war of Mysore while saving his capital. After his death, some area of his kingdom was given to old Mysore dynasty, some area was given to Nizam and some area was taken away by the British.
In this way, the power of Hyder Ali and Tipu Sultan was completely destroyed by the British.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain in brief merchantilism and Trade Wars.
Answer:
There were trade relations between India and Europe right from ancient times. Three main routes were there of this trade :
- First route was northern route. This route was going on through Afganisthan, Caspean Sea and Black Sea.
- Second route was middle route which was going on through Iran, Iraq and Seria.
- Third route was southern route. This route was going on through Indian Ocean, Arabian Sea, Red Sea and Egypt.
States of Western Asia and Southern-Eastern Europe were occupied by Turkey in 15th century. It led to closure of ancient trade routes between India and Europe. That’s why European countries tried to find new sea routes to reach India. First of all the Portuguese sailor Vasco-de-Gama reached port of Calicut of India on 27th May 1498. So, Portuguese started to do trade with India. This process is known as Merchantilism whose objective was to earn money.
Trade Wars. Other European powers also established trade relations with India When they found Portuguese earning money through trade with India. These European powers were Dutch, the British and the French. Wars started between them to establish their supremacy on Indian trade. These wars are known as Trade Wars.
Gradually they established their factories and establishments in India.
- Main Portuguese establishments in India were at Goa,’ Daman, Basin, Bombay, Saint Tom, Hugli and Salset.
- Main Dutch establishments in India were at Cochin,* N&gapatnam, Pulkit and Chinsura.
- Main British establishments in India were at Surat, Ahmedabad, Baloch, Agra, Bombay and Calcutta.
- Main French establishments were at Pondicherry, Chandranagar and Karikal.
With the passage of time, all these four European powers came in direct conflict with each other to win over each other’s establishments. Impact of Portuguese and Dutch reduced to a great extdht till 17th century due to this conflict. Till this time, only French and the British remained in Indian scenario. They both were also engaged in conflict with each other to keep monopoly over Indian trade. Later on the British emerged victorious out of this conflict.
Question 5.
Explain the establishment of the British the East India Company.
Answer:
Establishment of the Company. Like the Pbrtuguese and the Dutch the British too decided to trade with India. Britain had strengthened her navy after defeating Spain in 1588 A.D.. In 1600 A.D., traders of England sought the permission of Queen Elizabeth for trade with India and established the British East India Company. They wanted to establish trade relations with eastern islands. But eastern islands were under the control of the Dutch. The Dutch harassed the British traders and compelled them to withdraw from the East Indies.
Concessions from the Mughal Emperor. Now the British” East India Company increased its trade activities in India. In 1608 A.D., Capt. Hawkins obtained permission of the Mughal Emperor Jahangir to trade with India. In 1615 A.D., Sir Thomas Roe came to the Court of Jahangir as an ambassador of James I, the king of England. He sought permission of Jahangir to establish a factory at Surat and also obtained several other concessions. As such, Surat became a trade centre of the English.
Growth of power of the British East India Company. In 16li A.D., the English established a factory at Masulipattam in South India. After this, they purchased some land and laid the foundation of the city of Madras (Chennai) and established -a factory there. In 1651 A.D., the British Emperor Charles’ II got Bombay (Mumbai) from the Portuguese as dowry and the British Company established a cotton, cloth factory there.
Permission for free trade. The British East India: Company established its first factory in 1633 in the East India, in Orissa. Soon they set up their “factories at Hugli, Patna, Balasor and Dacca. Surat continued to be th^headquartes of the British Company till 1686 A.D. A mint was set up in Bombay (Mumbai). Coins made in this mint were in circulation in the Mughal Empire. In 1717 A.D., the British Company got the permission to trade freely (free from Octroi tax) in lieu of payment of Rs. three thousand per annum to the Mughal Emperor Farrukhsiyar.
In this way, trade of the British East India Company flourished a lot. With the expansion of trade, cities like Madras (Chennai), Bombay (Mumbai) and Calcutta (Kolkata) became very prosperous.
![]()
Question 6.
Explain Anglo-French struggle.
Or
Write the phases of struggle between the British and the French.
Answer:
The wars which took place between the British and the French in South India are known as the wars of Carnatic. Following is the chronological order of this conflict :
1. First Carnatic War: The First Carnatic War was fought during 1746-1748 A.D.
Causes:
- The English and the French wanted to establish their supremacy in trade in the whole of India. This was the main cause of animosity between them.
- At that time, war broke out between England and France in Europe. As a result, war between the English and the French also started in India.
Events. In 1746 A.D., the French attacked the British territory and occupied Madras (now Chennai). As Madras was a part of Carnatic state, the British requested the Nawab of Carnatic to come to their help. The Nawab sent ten thousand soldiers to stop the war between the British and the French. The Nawab’s army was defeated by the French army. In 1748 A.D., the war ended in Europe:
Consequently, the War between the English and the French also came to an end in India.
Results:
- The French supremacy was established in South India as a result of their victory in this war.
- The control of Chennai (Madras) was given back to the British as a result of the peace treaty.
2. Second Carnatic War (P.S.E.B. 2002 B):
The Second Carnatic War was fought between 1751 A.D. and 1754 A.D.
Causes: The Second Carnatic War was started due to the dispute about succession to the thrones in two states namely, Hyderabad and Carnatic. In each state, there were two claimants to the throne. Nasir Jang and Muzafar Jang were claimants to the throne of Hyderabad and Anwar-ud-Din and Chanda Sahib to that of Carnatic. The French army Commander Dupleix supported Muzafar Jang and Chanda Sahib and made them the rulers of Hyderabad and Carnatic respectively.
The English did not remain silent spectators. They supported Nasir Jang in Hyderabad and Muhammad Ali, son of Anwar-ud-Din in Carnatic.

Events: In the beginning, the French won some victories. Chanda Sahib, with the help of the French, defeated his enemies at Trichnapali. But the English army commander Robert Clive changed the whole position. He laid siege to Arcot, the capital of the state ruled by Chanda Sahib. Chanda Sahib ran away from Trichnapali for the protection of his capital, but he could neither protect his capital nor himself. In this way, Carnatic came under the rule of the British.
Results:
- A treaty was signed in 1755 A.D. between the English and the French. Both the parties decided to remain aloof from the conflicts between Indian rulers.
- The prestige of the English was enhanced as a result of this war.
3. Third Carnatic War. The Third Carnatic War was fought between 1756 A.D. to 1763 A.D. In this war too, the English came out victorious and the French were defeated.
Causes: In 1756 A.D., once again, England and France were engulfed in a war in Europe, (Seven Years War). Consequently, in India too, war broke out between the English and the French.
Events: First of all, the French occupied the English fort named Saint David. After this, they attacked Madras (now Chennai). But in 1760 A.D., an English Army Commander Eyer Coot badly defeated the French in the battle of Vandivash. In 1763 A.D., the war in Europe (Seven Years War), came to an end by the treaty of Paris. Consequently, the war between the English and the French in India also came to an end.
Results:
- The power of the French in India was almost finished. The French were left with only Pondicherry, Mahe and Chandernagar.
- The British became the most powerful political power in India.
![]()
Question 7.
Explain the expansion of the British Empire during the time of Lord Wellesley.
Answer:
Lord Welleslly came to India as Governor-General in 1798 A.D. He wanted to spread the British empire in India. He adopted a number of methods of fulfil this objective and captured many Indian states.
In short, he used following methods to spread the British empire in India:
1. Through Wars. Lord Welleslly defeated Tipu Sultan in fourth Mysore war in 1799 A.D. and captured lot of his territory. He also defeated Marathas in 1802 A.D. and captured Delhi, Agra, Cuttock, Balasor, Bharoch, Buftdelkhand to spread British empire. Wellesley also captured Indore, which was the capital to Maratha king Jaswant Rao Holker.
2. Through Subsidiary Alliance. Welleslly also adopted the policy of Subsidiary Alliance to spread the British Empire. It was made between the company and native rulers. The company promised to give military help to the rulers who entered into subsidiary alliances with it in case of any internal or external trouble. But in that case local ruler was not allowed to make war or any treaty with any ruler without the permission of the company.
First of all, this alliance was accepted by Nizam of Hyderabad in 1798 A.D. Even he gave some of his areas to the British. After Nizam, this alliance was also accepted by Nawab of Awadh. Even he gave area of Ruhelkhand and Doab of Ganga-Yamuna to the British for the expanses of military which was kept in its state.
3. Through Pensions. Wellesley gave pension to King of Surat- in 1800 A.D. and included Surat in the British empire. Nawab of Karnataka died in 1801 A.D. He fixed pension for his son and included his state in the British empire.
In this way Lord Welleslly expanded the British empire, to a great deal, in India.
Question 8.
Explain the expansion of the British empire during the time of Lord Dalhousie.
Answer:
Lord Dalhousie spread the British empire in India through four following methods:
- Through Conquests
- Though Doctrine of Lapse
- On the basis of Mal-administration
- By discontinuing titles and pensions.
1. Through Conquests:
- Lord Dalhousie took advantage of the opposition of Moolraj and Chatar Singh and declared war against the Lahore Darbar. It is also known as Second Anglo-Sikh War (1848-1849 A.D.). The British emerged victorious from this war. As a result, Punjab was annexed on 29th March 1849 and it become part of the British empire.
- Lord Dalhousie attacked Sikkim in 1850 A.D. and defeated its ruler. In this way, Sikkim was also annexed into the British empire.
- The next turn was of Burma. The British emerged victorious from the second Anglo-Burmese war in 1852 A’.D. So, the Prom and Pegu states of Burma were annexed into the British empire.
2. Doctrine of Lapse. Lord Dalhousie adopted the policy of Lapse to annex Indian states into the British empire. According to this policy if the ruler of a dependent state had no male issue he could not adopt a son. It meant that if a native ruler died without leaving a son behind, the dependent state would pass into the hands of the British. On the grounds of this doctrine, Dalhousie annexed seven dependent kingdoms into the British empire which included Nagpur, Jhansi, Jaitpur, and Satara.
3. On the basis of Mal-Administration. In 1856-A.D., Lord Dalhousie accused Nawab of Awadh that the administration of Awadh is mismanaged. That’s why Avadh was annexed into the British empire. This action of Dalhousie .was totally against ethics.
4. By discontinuing titles and pensions. Lord Dalhousie took away the titles of rulers of Karnataka, Poona, Thanjavur, and Surun and discontinued their pension. Later on, these states were annexed into the British empire.
