This PSEB 9th Class Science Notes Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure will help you in revision during exams.
PSEB 9th Class Science Notes Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure
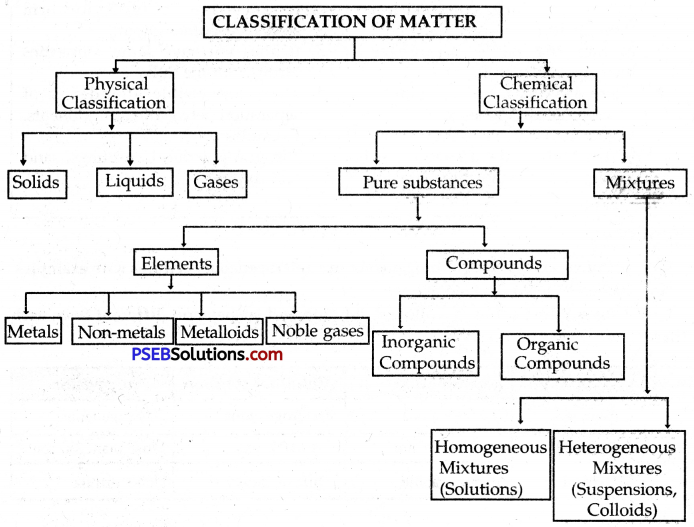
→ A pure substance consists of only one type of particle.
→ Mixtures are constituted by more than one kind of pure form of matter known as a substance.
→ The mixture is obtained by mixing one or more pure elements and/or compounds.
→ A substance cannot be separated into other kinds of matter by any known physical process.
→ Whatever the source of the substance may be, it will always have the same characteristic properties.
![]()
→ Homogeneous mixtures may have different separate components.
→ Heterogeneous mixtures can be separated into their respective constituents by simple physical methods.
→ A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances.
→ Alloy is a solid solution and the air is a gaseous solution.
→ The component of a solution which is generally in small amounts and is dissolved into another component is called the solute.
→ The component of a solution that dissolves the other component is called the solvent.
→ This component is generally present in large amounts.
→ Air is a mixture of gas. A solution of sugar in water is solid in a liquid solution. A solution of iodine in alcohol is known as ‘tincture of iodine.
→ Aerated drinks are gas in liquid solutions.
→ A solution is a homogeneous mixture.
→ The particles of the solution are smaller than 1 nm (10-9 m) in diameter.
→ Depending upon the amount of solute present in the solution, it can be called a dilute, concentrated or saturated solution.
![]()
→ The different substances have different solubilities in the given solvent at the same temperature.
→ Suspension is a heterogeneous mixture and the particles of a suspension can be seen with a naked eye.
→ In the suspension, the solute particles do not dissolve but remain suspended throughout the bulk of the medium.
→ The suspended particles have sizes of more than 100 nm.
→ The particles of a colloid are uniformly spread throughout the solution.
→ The scattering of a beam of light is called the Tyndall effect.
→ The size of colloidal particles lies between 1 to 100 nm and they can’t be seen with the naked eye.
→ The colloidal particles cannot be separated from the mixture by the process of filtration but can be separated by ultracentrifugation.
→ The volatile component of a solution (solvent) can be separated from the non-volatile component (solute) by the method of evaporation.
→ The cream is separated from milk by a centrifugal machine.
→ Ammonium chloride, camphor, naphthalene, and anthracene can be separated by sublimation.
→ The process of separation of coloured components of a mixture is known as chromatography.
→ The crystallization method is used to purify solids.
→ Crystallization technique is better than simple evaporation technique.
→ Colour, hardness, rigidity, fluidity, density, melting point, boiling point, etc. are the physical properties.
![]()
→ Chemical change brings a change in the chemical properties of a matter and we get new substances.
→ A chemical change is also called a chemical reaction.
→ Robert Boyle was the first scientist to use the term element in 1661.
→ An element is a basic form of matter that cannot be broken down into simple substances by chemical reactions.
→ Elements can be normally classified into metals, non-metals, and metalloids.
→ Mercury is the only metal that is liquid at room temperature.
→ Metalloids show the properties of metals as well as non-metals.
→ Pure substances can be elements.
→ The process of separation of components of a mixture containing two miscible liquids that boil without decomposition and have sufficient difference in their boiling points.
→ The different gases in the air and different components of petroleum can be separated by fractional distillation.
→ Mixtures are of two types:
- Homogeneous mixtures
- Heterogeneous mixtures
→ Pure Substance: It is a material containing particles of only one kind having a definite set of properties. Pure substances include elements and compounds.
→ An Element is a pure substance that is made up of only one kind of particle called atoms.
→ It can neither be built up nor broken down into two or simpler substances by any known physical or chemical methods, e.g., copper, silver, etc.
![]()
→ A compound is a pure substance that is obtained by the chemical combination of two or more elements in a fixed ratio by mass, e.g., water, ammonia, etc.
→ Mixture: It is a material obtained by mixing two or more substances in any proportion without any chemical change taking place.
→ The solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances whose composition can be changed within certain fixed limits.
→ A binary solution is a solution having two components.
→ The solute is the minor component of a solution whereas solvent is the major component of a solution.
→ The concentration of a solution is the amount of solute present per unit volume or per unit mean of solvent or solution.
→ A saturated solution is one that does not dissolve any more of the solute at a given temperature and pressure.
→ Colloids are heterogeneous mixtures in which the particles have a size of more than 100 nm.
→ These particles are called colloidal particles and constitute the dispersed phase whereas the medium in which colloidal particles are dispersed constitutes the dispersion medium.
→ Suspensions: Materials that are insoluble in a solvent and have particles that are visible to naked eyes form suspensions.
→ Physical Change: It is a temporary change in which only the physical properties of substances change and can be reversed.
→ Chemical Change: It is a permanent change in which the chemical properties of substances change and there is a change in composition and cannot be reversed.
→ Filtration: The process of separation of an insoluble solid component of a mixture from a liquid component is called filtration.
→ Evaporation: It is the slow process of conversion of liquid into a gaseous state (vapour) at a temperature below its boiling point.
![]()
→ Distillation: It is the process of conversion of liquid into a gaseous state by heating it to the boiling point and condensing the vapour to get pure liquid.
→ Fractional distillation: It is the process of separating two miscible liquids having different boiling points by distillation using a fractionating column.
→ Chromatography: It is the process of separation of dissolved components of a mixture by adsorbing on a suitable substance (called adsorbent).