Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class Science Book Solutions Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions
PSEB 8th Class Science Guide Cell Structure and Functions Textbook Questions and Answers
Answer These
Question 1.
Indicate whether the following statements are True [T] or False [F].
(a) Unicellular organisms have one-celled bodies.
Answer:
True
(b) Muscle cells are branched.
Answer:
False
(c) The basic living unit of an organism is an organ.
Answer:
False
(d) Amoeba has irregular shape.
Answer:
True
![]()
Question 2.
Make a sketch of the human nerve cell. What function do nerve cells perform ?
Answer:

Functions of Nerve Cell:
- It receives and transfers messages.
- It control and co-ordinate the functioning of different parts of the body.
Question 3.
Write short notes on the following :
(a) Cytoplasm
(b) Nucleus of a cell.
Answer:
(a) Cytoplasm.
It is a jelly-like fluid present inside the cell membrane. Various cell organelles are present in it. It contains water, sugar, minerals, lipids proteins etc.
(b) Nucleus.
As true nucleus is present in all the eukaryotic cells except mammalian RBCs, sieve tube cells, tracheids and vessels. It is formed of four components:
(i) Nuclear Membrane.
It is a two-layered envelope around the nuclear sap. It is porous (with nuclear pores) and semi-permeable membrane. Outer membrane is studded with ribosomes. It regulates exchange of materials between nucleoplasm and cytoplasm.
(ii) Nucleoplasm.
It is a semifluid colloidal substance in which nucleoli and chromatin fibres are present. It acts as nuclear skeleton and forms spindle for the cell division.
(iii) Nucleolus.
It is dense, spherical, naked and darkly stained structure and it is site of formation and store house of RNA.
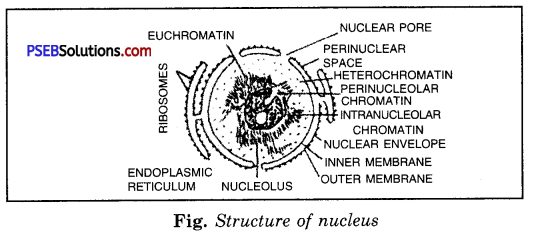
(iv) Chromatin Fibres.
These are long, fine and darkly stained threads which collectively form nuclear reticulum. During prophase of mitosis and meiosis, these condense to form a specific number of rods, called chromosomes. These are embedded with genes which are chemically formed of DNA and act as units of heredity and variation. They also help in the synthesis of structural and enzymatic protein.
Question 4.
Which part of the cell contains organelles ?
Answer:
Cytoplasm contains organelles.
Question 5.
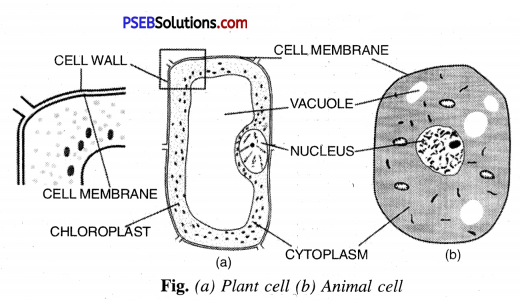
Make sketches of animal and plant cells. State three differences between them.
Or
State four differences between animal and plant cells.
Answer:
Animal cells differ from plant cells in the following definite ways :
| Plant cells | Animal cells |
| 1. Plant cells have cell wall made up of cellulose. | 1. Animal cells have no such walls and no cellulose. |
| 2. Plant cells have chloroplasts. | 2. Animal cells do not possess the chloroplasts. |
| 3. Plants cells have thin cytoplasm and large vacuole. | 3. Animal cells have thick cytoplasm with no vacuole. |
| 4. Centrosome absent. | 4. Centrosome present. |
| 5. Reserve food is in the form of starch. | 5. Reserve food is in the form of glycogen and param sylum. |
Question 6.
State the difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
Answer:
Eukaryotes.
These are the organisms whose cells contain well defined nucleus with a clear nuclear membrane. Examples are onion cells, cheek cells.
Prokaryotes.
These are the organisms whose cells have no definite nucleus i.e. without nuclear membrane. Examples are bacteria, blue green algae.
![]()
Question 7.
Where are chromosomes found in a cell ? State their function.
Answer:
Chromosomes are found in nucleus of a cell. Chromosomes carry genes and help in inheritance or transfer of characters from the parents to the offspring.
Question 8.
‘Cells are the basic structural units of living organisms’. Explain.
Answer:
As a building cannot be constructed without bricks. Similarly, a body of living organism has basic structural unit such as cell. Cells are of different size, shapes and group together to form organs, organ systems etc.
Question 9.
Explain why chloroplasts are found only in plant cells ?
Answer:
Chloroplast are green coloured plastids. They impart green colour to plants and only plants make use of green colour to synthesis food.
Question 10.
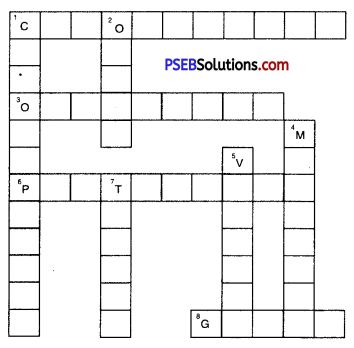
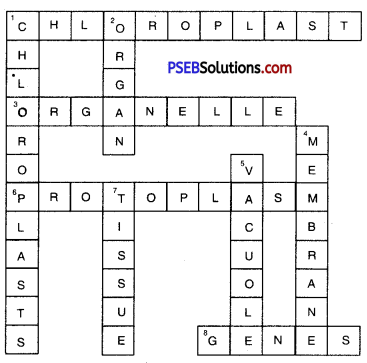
Complete the crossword with the help of clues given below.
Across
1. This is necessary for photosynthesis.
3. Term for component present in the cytoplasm.
6. The living substance in the cell.
8. Units of inheritance present on the chromosomes.
Down
1. Green plastids.
2. Formed by collection of tissues.
4. It separates the contents of the cell from the surrounding medium.
5. Empty structure in the cytoplasm.
7. A group of cells.
Answer:
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Cell Structure and Functions Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
A slide is given in the figure below. What does this show ?
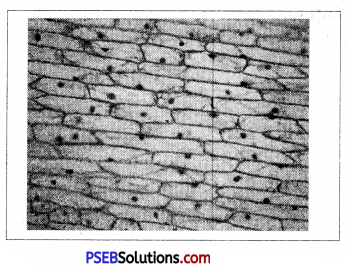
(a) Cork cells
(b) Onion membrane
(c) Unicellular organism
(d) Multicellular Organism.
Answer:
(b) Onion membrane.
![]()
Question 2.
What is the name of basic structural unit in living organism ?
(a) Tissue
(b) Organ of body
(c) Cell
(d) Molecule.
Answer:
(c) Cell.
Question 3.
Which out of the following cell-organ is found in plants only ?
(a) Mitochondria
(b) Chloroplast
(c) Cell membrane
(d) Nucleus
Answer:
(b) Chloroplast.
Question 4.
Which organism is not unicellular ?
(a) Bacteria
(b) Amoeba
(c) Paramecium
(d) Algae or mould
Answer:
(d) Algae or mould.
Question 5.
Which of the cell organelle synthesise protein ?
(a) Lysosome
(b) Chromosome
(c) Ribosome
(d) Centrosome
Answer:
(c) Ribosome.
Question 6.
Who discovered cell ?
(a) Robert Hook
(6) M.J. Schleiden
(c) Schwann
(d) Robert Brown
Answer:
(a) Robert Hook
Question 7.
Which cell organelle is called suicidal bag ?
(a) Ribosome
(b) Lysosome
(c) Chromosome
(d) Centrosome
Answer:
(b) Lysosome
![]()
Question 8.
Which out of the following is unicellular organism?
(a) Amoeba
(b) Paramecium
(c) Bacteria
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(d) All of these.
Question 9.
Which is the power-house of cell?
(a) Centrosome
(b) Chloroplast
(c) Mitochondria
(d) Ribosome.
Answer:
(c) Mitochondria.
Question 10.
Name a human cell which can change its shape.
(a) White blood cells
(b) Red blood cells
(c) Platelets
(d) Plasma
Answer:
(b) Red blood cells.
Question 11.
Which organ of the cell is found in plant cell only?
(a) Cell wall
(b) Chromosome
(e) Nucleus
(d) Cytoplasm
Answer:
(a) Cell wall.
Question 12.
Which is the longest cell of human body?
(a) Nerve cell
(b) Muscular cell
(c) Red blood cells ,
(d) White blood cells
Answer:
(a) Nerve cell.
Question 13.
Of what the cell wall is made?
(a) Fat
(b) Cellulose
(c) Protein.
(d) Mineral Salt.
Answer:
(b) Cellulose.
![]()
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks.
1. The cell is the …………………. and functional unit of organism.
2. Cell wall is found in ……………….. cells.
3. Power house of the cell is ………………….
4. Amoeba and Paramecium consists of a single …………………
5. Plastids are present only in ……………….. cells.
Answer
1. structural
2. plant
3. mitochondrion
4. cell
5. plant.
Question 2.
Choose the correct answer.
1. Suicidal bags of cells are ?
(a) Lysosomes
(b) Chloroplast
(c) Mitochondria
(d) Ribosomes.
Answer:
(a) Lysosomes
2. Plant cells do not have:
(a) Cell wall
(b) Centrosomes
(c) Plastids
(d) Mitochondria.
Answer:
(b) Centrosomes.
Question 3.
What is structural and functional unit of life ?
Answer:
Cell.
Question 4.
What is the contribution of Robert Brown in cell biology ?
Answer:
He discovered nucleus in the cells of orchid.
Question 5.
Who proposed the cell theory ?
Answer:
M.J. Schleiden and Theodore Schwann.
Question 6.
Name the smallest and largest cell.
Answer:
Smallest cell – Mycoplasma.
Largest cell – Ostrich egg.
Question 7.
Name the smallest and largest cell of human body.
Answer:
- Smallest cell – nephron.
- Largest cell – neuron.
Question 8.
Who called the protoplasm as the physical basis of life ?
Answer:
Huxley.
![]()
Question 9.
Give the contribution of Rudolf Virchow in the field of biology.
Answer:
He stated “omnis cellula e cellula” which means new cells are formed by the growth and division of pre-existing cells.
Question 10.
What are two types of cells on the basis of nature of nucleus ?
Answer:
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells.
Question 11.
What is nucleoid ?
Answer:
Nucleoid. It is incipient nucleus of prokaryotes like bacteria and blue-green algal cells and is without nuclear membrane.
Question 12.
What is contribution of Robert Hooke in the field of cell biology ?
Answer:
Robert Hooke discovered the cell.
Question 13.
What are the three functional regions of a cell ?
Answer:
Plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus.
Question 14.
Give the primary function of plasma membrane.
Answer:
It regulates exchange of material between cytoplasm and extra-celluar fluid.
Question 15.
Name the smallest sized cell organelle.
Answer:
Ribosome.
Question 16.
Which cell organelle is called suicidal bag ?
Answer:
Lysosome.
![]()
Question 17.
Name the largest sized cell organelle.
Answer:
Plastids.
Question 18.
Which cell organelle is called cell centre ?
Answer:
Centrosome.
Question 19.
What are organs ?
Answer:
Organs. Various body parts of animals and plants are called organs.
Question 20.
Who coined the word ‘Cell’ ?
Answer:
Robert Hooke.
Question 21.
Why Robert Hooke coined the word cell ?
Answer:
Robert Hooke was excited when he observed spaces in a cork slice those appeared like honeycomb. He called these compartments as cells.
Question 22.
Name some organs of plants.
Answer:
Roots, stem, leaves, flower, fruit.
Question 23.
Write examples of unicellular organisms.
Answer:
Amoeba, Paramecium, Bacteria, etc.
![]()
Question 24.
What is size of the smallest cell ?
Answer:
0.1 micron (μm) i.e. ten thousandth part of a millimetre.
Question 25.
What is yellow yolk in the egg of a hen ?
Answer:
It represents single cell.
Question 26.
Write the size of largest cell observable with naked eyes.
Answer:
170 mm.
Question 27.
What are cell organelles ?
Answer:
The parts of a cell are called cell organelles.
Question 28.
What role does cell membrane play in a cell ?
Answer:
Cell membrane encloses a liquid substance known as protoplasm. It regulates the flow of substances both into the cell and out of it.
Question 29.
Name four major elements responsible for protoplasm.
Answer:
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen.
![]()
Question 30.
What is nucleoplasm ?
Answer:
Nucleoplasm. It is the liquid protoplasm in the nucleus.
Question 31.
Who controls the activities of a cell ?
Answer:
Nucleus.
Question 32.
What do chromosomes do ?
Answer:
Chromosomes help in inheritance or transfer of characters from the parents to next generation.
Question 33.
What are chloroplasts ?
Answer:
The green plastids in the plants are called chloroplasts.
Question 34.
What is the shape of mitochondria ?
Answer:
Rod-shaped or spherical.
Question 35.
Name the power house of a cell.
Answer:
Mitochondria.
![]()
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is a cell ?
Answer:
Cell.
Just as the bricks are the units of all types of houses, the cells are the units or building blocks of living organisms. Animals and plants like ant, housefly, dog, elephant, sunflower, neem etc. consist of cells.
Question 2.
Write the names of cell organelles.
Answer:
Cell Organelles.
Cell organelles are living strictures of cytoplasm. These include : Endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, ribosomes, lysosomes, peroxisomes, plastids, sphaerosomes, glyoxysomes, centrosome. microtubules, microfilaments, cilia and flagella.
Question 3.
What is the difference between the plasma membrane and cell wall ? Give the functions of each one.
Answer:
| Characters | Plasmsa membrane | Cell Wall |
| 1. Occurrence | Around the protoplasm of all the cells. | Outside the plasma membrane in plant cells, bacteria, blue-green algae, fungi etc. |
| 2. Nature | Thin and selective permeable. | Thick and freely permeable. |
| 3. Chemistry | Lipoproteinous and trilaminar. | Formed of cellulose hemicellulose, pectin, water, etc. |
| 4. Function | Regulates the exchange of materials between cytoplasm and extracellular fluid. | It is protective and supportive in function. It provides definite shape and prevents evaporation of water. |
Question 4.
Which cell organelle is called “suicidal bag” and why ?
Answer:
Lysosome is commonly called suicidal bag of cell. It is so as it contains hydrolytic enzymes which help in digestion of foreign food or bacteria (by heterophagy) ; or reserve food or certain cell organelles (by autophagy) ; or the whole cell after the cell death (by autolysis).
![]()
Question 5.
Which cell organelle is called “power house” of the cell ? Write about its function briefly.
Answer:
Mitochondrion is commonly called “power house” of the cell because it is site of oxidative breakdown of glucose in aerobic cell respiration to produce energy- rich ATP molecules. One mole of glucose, in aerobic respiration, produces 36 ATP molecules.
Question 6.
Define the following terms :
(a) Protoplasm
(b) Cytoplasm
(c) Nucleoplasm.
Answer:
(a) Protoplasm is the physical basis of life and lies inside the cell membrane. It includes both cytoplasm and nucleoplasm.
(b) Cytoplasm lies between the cell membrane and nucleus. It contains various types of cell-organelles and cell-inclusions. It undergoes cyclosis. It is the site of protein synthesis, glycolysis, etc.
(c) Nucleoplasm lies inside the nucleus and contains only nucleoli and chromatin fibres. It does not undergo cyclosis. It forms spindle during cell division.
Question 7.
Draw a labelled diagram of plant and animal cell.
Answer:
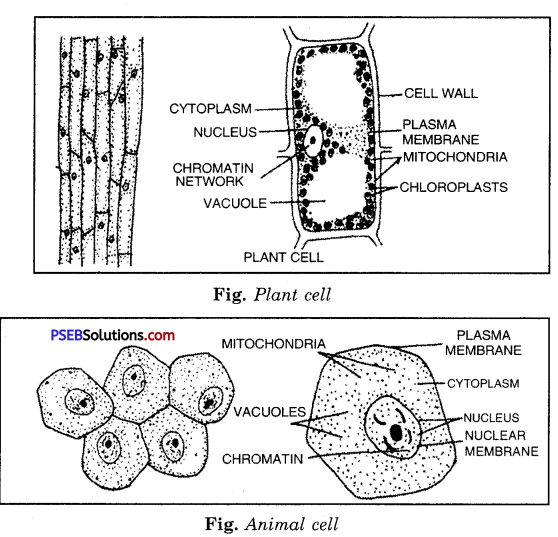
Question 8.
Describe the variations in shape and size of cells.
Answer:
The cells are generally round or spherical in shape. However, there is lot of variations in shape of cells. These can be cuboidal and columnar. Some of the animal cells are long and branched as in nerve cells.
![]()
Question 9.
What are unicellular and multicellular organisms ?
Answer:
Unicellular Organisms. The organism whose body is made of only a single cell is called a unicellular organism, e.g. Amoeba, Paramecium, Chlamydomonas, Yeast, Euglena etc.
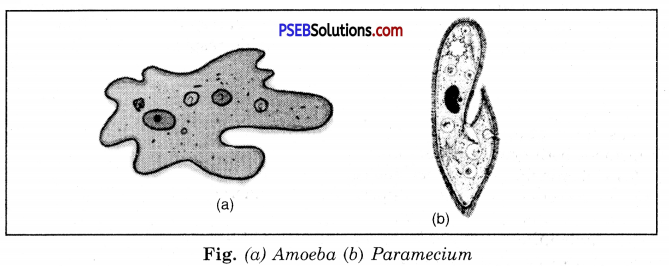
Multicellular Organisms. The organisms whose body is made of many cells is called a multicellular organisms, e.g. Man, Hydra, Dog, Elephant etc.
Question 10.
WTiat are organs and organ systems ?
Answer:
Organ. A group of tissues which perform a definite function of the body is called an organ.
Organ System. A group of organs which do a big job is called an organ system.
Question 11.
Draw the diagrams of different kinds of cells.
Answer:
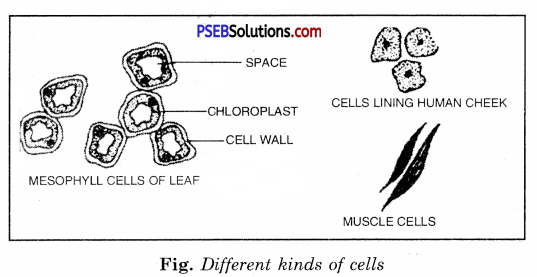
Question 12.
How was the first cell discovered?
Answer:
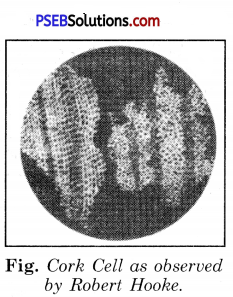
Robert Hooke in 1665 observed slices of cork under a simple magnifying device. Cork is part of the bark of a tree. He took thin slices of cork and observed them under his microscope. He noticed partitioned boxes or compartments in the cork slice. These boxes appeared like a honey comb.
He also noticed that one box was separated from the other by a wall or partition. Hooke coined the term ‘cell’ for each box. Cell in Latin means ‘hollow space.’
Question 13.
Discuss about the various shapes of cells.
Answer:
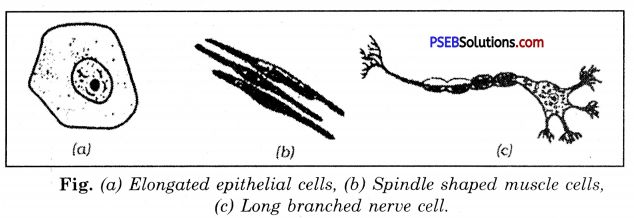
Generally cells are round, spherical or elongated. Some cells are long and pointed at both ends. They exhibit spindle shape. Cells sometimes are quite long and thread like. Some are branched like the nerve cell or neuron.
![]()
Question 14.
Differentiate between unicellular and multicellular organisms.
Answer:
Differences between unicellular and multicellular organisms.
| Unicellular Organisms | Multicellular Organisms |
| 1. These organisms are made of only one cell. | 1. These organisms are made of many cells. |
| 2. All functions of body are performed by only a single cell. | 2. Each function of the body is performed by a group of special cells. |
| 3. Cilia are found.
Examples. Amoeba, Paramecium etc. |
3. Cilia are not found.
Examples. Almost all animals. |
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe the structure of a typical cell in detail.
Answer:
Structure of cell
A cell is the basic unit of life. It is capable of performing all functions of life and to fulfil all the functions, cell is made up of different parts. Basically, a cell is formed of three parts:
1. Cell membrane or plasma membrane
2. Nucleus.
3. Cytoplasm.
The cytoplasm is surrounded by cell membrane and nucleus constitutes the protoplasm of a cell. The typical structure of plant and animal cells are shown ahead:
1. Cell Membrane.
It is a delicate, thin membrane. It is also called plasma membrane. It forms the outermost layer in animals but in plant cells an additional membrane is present. It is called cell membrane in animal’s cell and cell wall in plant’s cell. Cell membrane has following functions:
(i) It provides shape to the cell.
(ii) It allows the flow of some substances into the cell and out of the cell.
(iii) It acts as a barrier to protect internal parts.
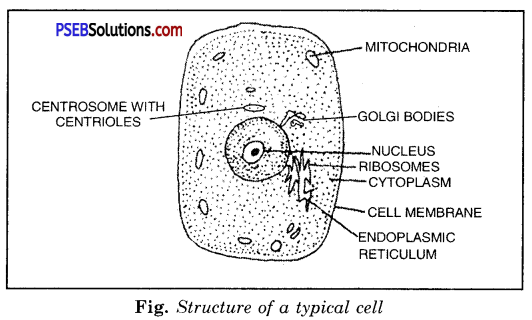
2. Nucleus.
The oval or spherical structure, which is the controlling centre of all activities of the cell is called nucleus. Nucleus is made up of following parts:
(i) Nuclear Membrane. It is the membrane having pores which separates contents of nucleus from cytoplasm.
(ii) Nucleoplasm. The fluid present in nucleus is called nucleoplasm.
(iii) Nucleolus. Small spherical body made up of nucleoprotein. RNA is also present in nucleus.
(iv) Chromatin Material. Several thread like structures forming a network are present in nucleoplasm. Chromatin material is in the form of chromosomes which carries genes on it.
The nucleus has following functions:
Chromatin material of nucleus transmits characters from one generation to other.
It contains informations for carrying out all basic functions.
3. Cytoplasm.
The jelly like fluid inside the membrane of cell is cytoplasm. All tiny structures performing different functions, are present in it. These are called organelles.
It also contains water, sugar, minerals, lipids, proteins etc. The various cell organelles present in cytoplasm are:
(i) Mitochondria. They are commonly called Tower house of the cell’ because they help in release of energy from food. They also store energy. Mitochondria (singular mitochondrion) are oval or rod shaped organelle bounded by two membranes.
(ii) Endoplasmic Reticulum. A complex network of membranes which are present either attached to nucleus or free from it are endoplasmic reticulum. Its network extends from nuclear membrane to cell membrane. It helps in protein synthesis and also in transport of various substances.
(iii) Plastids. These organelles are present only in plant cells. These are of three types:
(а) Chloroplasts. Green coloured plastids are chloroplasts. The green colour is due to the presence of pigment chlorophyll. They are commonly known as ‘Kitchen of the’ cell’ because chloroplasts are the site of photosynthesis i.e. process of making food.
(b) Leucoplasts. Colourless plastids are called leucoplasts. These are present in the roots and underground modified stems.
(c) Chromoplasts. These are coloured plastids. These are present mainly in flowers, petals and fruits.
(iv) Golgi Bodies. These are membrane-bound, piles of many flattened sacs. In plants, Golgi bodies are known as dictyosomes. They are mainly secretory in function.
(v) Vacuoles. The fluid-filled organelles present in a cell are vacuoles. In-plant cells, vacuoles are few in number and larger in size whereas, in animals, they are more in number and smaller in size. They maintain the turgidity of plants cells. Vacuoles also serve as a waste deposit bin in which unwanted materials may be diverted.
(vi) Lysosomes. Small spherical bodies having a single membrane are lysosomes. They sacrifice their own selves to destroy and digest various materials. They are also called ‘suicidal bags’. Plant cells do not have lysosomes.
(vii) Ribosomes. These are small rounded bodies that are present free or attached with the endoplasmic reticulum. They perform the function of protein synthesis.
(viii) Centrosome. It is a rod-like structure. It occurs close to the nucleus and helps in cell division.
