Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class Social Science Book Solutions History Chapter 14 Handicraft and Industry Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Social Science History Chapter 14 Handicraft and Industry
SST Guide for Class 8 PSEB Handicraft and Industry Textbook Questions and Answers
I. Answer the following questions :
Question 1.
Write down the two reasons for the decline of small-scale industries in India.
Answer:
- The main protectors of these industries were local rulers, their family members, and officials.
- When the British started conquering local kingdoms, then cottage industries were bound to decline.
- People of new classes didn’t like the goods made in cottage industries of India.
- They were under the impact of the British. That’s why they liked the goods made in Europe instead of goods made in India.
Question 2.
Why the goods made by small-scale industries were expensive in India?
Answer:
Goods made by cottage industries of India were more expensive because more labour was required to manufacture these goods.
Question 3.
Where and when the first cotton industry was set up in India?
Answer:
First industry (factory) of cotton textile in India was set up in 1853 A.D. at Bombay.
Question 4.
Where and when the first jute industry was set up in India?
Answer:
First Jute industry in India was established in 1854 A.D. at Sarampur (Bengal).
![]()
Question 5.
Where and when the first coffee garden was set up?
Answer:
First coffee garden in India was started in 1840 A.D. in South India.
Question 6.
Where afiid when the first tea garden was set up?
Answer:
First tea-garden in India was established in 1852 A.D. at Assam.
Question 7.
Write down the reasons of decline of small scale industries in India in the 19th century.
Answer:
Indian villages were self-dependent before the establishment of the British rule in India. People of villages such as blacksmiths, farmers, carpenters, cobblers, potters, etc. collectively made things to fulfil needs of the village. Their cottage industry or their art was their means of income. But after the advent of the British rule in the country, rural people also started using goods made in the British factories because they were cheap as well as of good quality. So the small scale industries of villages and Indian cities started to decline and people became unemployed.
Question 8.
Write down the importance of modern Indian industries.
Answer:
Economic and Social life of India was greatly affected by the development of modern industries in India. It led to the emergence of two classes i.e. capitalists and labourers. Capitalists started to exploit the labourers. They gave less wages by taking more work from the labourers. So government passed the Factory Acts to improve condition of labourers. Many new cities came into being with industrial development. These cities became centres of modern life and culture.
Question 9.
Write a note on Indigo industry.
Answer:
Indigo was required by the British for textile industry in England. That’s why they encouraged the cultivation of indigo in India. It was started in Bihar and Bengal in laterpart of 18th century. Europeans established large gardens of Indigo where Indian were employed. 35 Lakh hectare land was there in 1825 under the cultivation of indigo. But this cultivation of indigo started declining in 1879 A.D. when manufacture of artificial indigo started. As a result only 3-4 Lakh hectare remained under the cultivation of indigo in 1915 A.D.
![]()
Question 10.
Write down a note on Coal Mines.
Answer:
All the new factories, established by the British in India, were run by coal. Coal was also required to run the railway. That’s why special care was given to take out coal from mines. In 1854 A.D. only two coal mines were there in Raniganj district of Bengal. But this number increased to 56 in 1880 and to 123 in 1885 A.D.
II. Fill in the Blanks :
Question 1.
The kings of princely states used to use the things made by industries.
Answer:
small scale
Question 2.
New generation did not the goods prepared by small scale industries.
Answer:
like
![]()
Question 3.
All new factories were run by
Answer:
power.
III. Write True or False in the brackets given after each statement:
Question 1.
All workers became unemployed due to the decline of small scale industries in towns and villages.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Industrial revolution occurred in England in the 19th century.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
The rates of the small scale commodities were high.
Answer:
True
Question 4.
Indian raw material began export to England in the 18th century.
Answer:
True
![]()
IV. Match the words :
Question 1.
| A | B |
| 1. Assam | (i) Sarampur (Bengal) |
| 2. Jute Industry | (ii) Raniganj |
| 3. Coal Mining Industry | (iii) Tea Company |
| A | B |
| 1. Assam | (iii) Tea Company |
| 2. Jute Industry | (i) Sarampur (Bengal) |
| 3. Coal Mining Industry | (ii) Raniganj |
Answer:
V. Things To Do :
Question 1.
Dear student! a potter will be making the utensils of clay. You go to him and know how he is doing his professions?
Answer:
Do it yourself.
Question 2.
If any weaver is weaving the cloth in any village or near the village then you go to him and know how cloth is prepared by him?
Answer:
Do it yourself.
PSEB 8th Class Social Science Guide Handicraft and Industry Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions :
Question 1.
Which of these was a cause of decline of small scale industries in India?
(а) Abolition of native princely states
(b) High rates of small scale commodities
(c) Better finishing of machine-made goods
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(d) All of these.
![]()
Question 2.
When was the first Cotton factory established in India?
(a) 1853 A.D.
(b) 1854 AD.
(c) 1855 A.D.
(d) 1856 A.D.
Answer:
(a) 1853 A.D.
Question 3.
Where was the first Jute industry set up in 1854 A.D.?
(a) Calcutta
(b) Sarampur
(c) Bokaro
(d) Jharia.
Answer:
(b) Sarampur.
Question 4.
What is Hectare?
(a) A measurement of height
(b) A measurement of Weight
(c) A measurement of land
(d) A measurement of air
Answer:
(c) A measurement of land.
Question 5.
When was Assam Tea company established?
(a) 1844 A.D.
(b) 1834 A.D.
(c) 1854 A.D.
(d) 1864 A.D.
Answer:
(b) 1834 A.D.
![]()
Question 6.
Where was first tea garden developed in 1852 A.D?
(a) Assam
(b) West Bengal
(c) Karnataka
(d) Meghalaya.
Answer:
(a) Assam.
Question 7.
When was first coffee garden established in India?
(a) 1820 A.D.
(b) 1830 A.D.
(c) 1840 A.D.
(d) 1850 A.D.
Answer:
(c) 1840 A.D.
Question 8.
Mahatma Gandhi believed that all Indians must make their cloth by knitting the yarn. In the given picture Mahatma Gandhi is knitting the yarn to make ________ cloth.
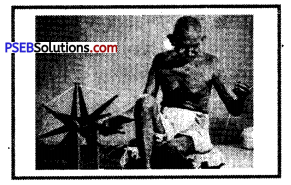
(a) Silk
(b) Khadi.
(c) Jute
(d) Polyster
Answer:
(b) Khadi.
Fill in the Blanks :
Question 1.
Kings of local kingdoms used products made by ________ industry.
Answer:
cottage
![]()
Question 2.
New generation never ________ the products of cottage industry.
Answer:
like
Question 3.
All new industries are run on ________
Answer:
coal.
Tick the Right (✓) or Wrong (✗) Answer :
Question 1.
Decline of Indian cottage industry led to the unemployment of artisons.
Answer:
(✓)
Question 2.
Industrial revolution in England started in 19th century.
Answer:
(✗)
Question 3.
Machine made goods are costly.
Answer:
(✗)
Question 4.
In 18th century, raw material from India was exported to England.
Answer:
(✓).
Match the Following :
Question 1.
| A | B |
| 1. Assam | (i) Sarampur (Bengal) |
| 2. Jute Industry | (ii) Raniganj |
| 3. Coal Mines | (iii) Tea Company |
Answer:
| A | B |
| 1. Assam | (iii) Tea Company |
| 2. Jute Industry | (i) Sarampur (Bengal) |
| 3. Coal Mines | (ii) Raniganj |
Question 1.Very Short Answer Type Questions
What was the economic condition of villages before the establishment of the British rule?
Answer:
Villages were self-dependent from economic point of view before the establishment of the British rule.
![]()
Question 2.
Why goods made by Indian artisans were unable to compete with goods made by machines?
Answer:
Goods made by Indian artisans were unable to compete with machine made goods because machine made goods were not only cheap but they were of good quality as well.
Question 3.
Why goods by cottage industries of India were not liked by people of new classes?
Answer:
Because they were under the impact of western culture.
Question 4.
Which things are made in Jute industry?
Answer:
Mats and sacks of jute.
Question 5.
Why coffee industry suffered huge loss?
Answer:
Indian coffee was in competition with the coffee of Brazil which was much better in quality as compared to the Indian coffee. That’s why coffee industry of India suffered huge loss.
![]()
Question 6.
Name six modern industries developed during the British rule in India.
Answer:
- Cotton Textile industry
- Jute industry
- Coal industry
- Indigo industry
- Tea
- Coffee.
Question 7.
Why were the Factory Acts passed?
Answer:
The Factory Acts were passed to improve the condition of labourers.
Question 8.
Clothes made of which thing were used by early man to keep himself warm?
Answer:
Clothes made by skin of animals.
Question 9.
Where were maximum jute factories opened and who opened them?
Answer:
Maximum Jute factories were opened in Bengal and they were opened by the Europeans.
Question 10.
Why was the cultivation of indigo reduced?
Answer:
The cultivation of indigo was reduced because of the introduction of synthetic indigo in 1879 A.D.
![]()
Question 11.
Why did the Coffee plantation industry suffer a lot?
Answer:
The coffee plantation industry suffered a lot because of the competition with Brazilian coffee.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How was the process of making of cloth developed in India? Which evidences have been found about making of cloth through excavation?
Answer:
Early man wore clothes made by skin of animals to keep himself warm. The process of making of cloth was invented quite late. It has been believed that grass was used to make clothes inTndia. Later on they came to know about use of thread on ‘Khaddi or Kargha’ or to make samples. With the passage of time, the technique of making clothes on charkha or kargha was improved.
Evidence: Archaeologists, who study ancient goods, have found evidences of coloured cotton cloth and making of thread from the excavations of Harappa and Mohenjodaro.
Except this, they have found charkhas, mats etc. from excavations of certain places of Kashmir. It tells us that people used to make clothes even 4,000 years ago.
Question 2.
Why did the textile industry decline in India? How it got new life or how was it revived?
Answer:
Indian clothes were famous all around the world. European traders came to India to do trade of cloth and pepper, cloves, cardamom and cinnamon. They established factories of cotton clothes in India. Production in these factories was being done with machines instead of ‘Khaddis’. But textile industry in India started declining after the advent of industrial revolution in England. But in the 20th century, Mahatma Gandhi encouraged the production of Khadi cloth through ancient means of producing clothes i.e. through ‘Charkha’. With this Indian cloth industry was revived.
Government made new economic policy with which cloth industry did enormous progress. Government has also given many facilities for the export and import of the cloth.
![]()
Question 3.
Write a note on Jute industry in India during the British rule.
Answer:
Jute industry makes sacks and mats of jute. This industry was mainly under control of European people. First jute industry in India was established at Serumpur (Bengal) in 1854 A.D. After this, most jute factories were established in the province of Bengal. This number of industries was increased up to 36 in the start of 20th century.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write down in detail the causes of decline of small scale industries.
Answer:
The main reasons of decline of cottage industries in India are given below :
1. End of Local Kingdoms of India: A number of Indian kingdoms were annexed by the British. That’s why cottage industries suffered a great loss because the things made by cottage industries were used by family members and kings of local kingdoms.
2. Expensive goods of Indian cottage industries: Goods made by the Indian cottage industries were more expensive because more labour was required to manufacture those products. On the other hand, goods made by machines were very cheap. That’s why the sale of goods made by cottage industries was declined. It lead to decline of Indian cottage industries.
3. Quality of machine-made goods. The quality of machine-made goods of the British ‘ industries was much better than the goods made by local cottage industries. That’s why the machine-made goods were liked by most of the Indians. This thing also led to decline of Indian cottage industries.
4. Interests of people of new classes. People of new classes were under the impact of western culture. With this, the things made by machines were of much better quality as compared to the local goods. That’s why the local goods were not ljked by the people of new generation.
5. Sending Indian raw material to England. Industrial Revolution came in Europe in 18th century. That’s why large industries were established over there. Lot of raw material was required to make goods in such industries. But England itself was unable to fulfill needs of its industries. That’s why the British rulers in India started to send raw material from India to England. It led to the shortage of raw material for the Indian manufacturers. So Indian industries started declining.
![]()
Question 2.
Write down in detail about modern Indian industries.
Answer:
Many new industries were established in India during the British rule but of which main industries are given below :
1. Cotton Textile Industries. First cotton textile industry in India was established at 1853 A.D. in Bombay. After this, many textile mills were established in 1877 A.D. in cotton-producing areas of Ahmedabad, Nagpur, etc. Till 1879 A.D. around 59 cotton textile mills were established in India in which around 43,000 people were employed. This number of textile mills was increased to 206 in 1905 A.D. Around 1,96,000 labourers were employed in these industries.
2. Jute Industry. Jute industry makes mats and sacks of jute. This industry was mainly under the European people. First jute industry in India was established at Sarampur (Bengal) in 1854 A.D. After this most jute factories were established in the province of Bengal. This number of industries was increased up to 36 in the beginning of 20th century.
3. Coal Mining. All the industries established by the British in India were running with coal. Coal was also required for railway. That’s why special care was given to take out coal from mines. In 1854 A.D. only two coal mines were there in Raniganj district of Bengal. But this number increased to 56 in 1880 and to 123 in 1885 A.D.
4. Indigo Industry. Indigo was required by the British for textile industry in England. That’s why they encourage cultivation of indigo in India. It was started in Bihar and Bengal in later part of 18th century. Europeans established large gardens of indigo where thousands of Indians were employed. 35 Lakh hectare land was there under the cultivation of Indigo. But this cultivation of indigo started to decline in 1879 A.D. when manufacture of artificial indigo started. As a result, only 3-4 Lakh hectare remained under the cultivation of indigo in 1915 A.D.
5. Tea. One company was established in Assam in 1834 A.D. the British planted the first Tea garden in Assam in 1852 A.D. Till 1920 A.D., around 7 Lakh hectare land was there under the cultivation of tea. Tea of around 34 crore Pounds was exported to foreign countries at that time. Later on, tea gardens were also planted in the mountains of Kangra and Nilgiri.
6. Coffee. The first coffee garden was planted in South India in 1840 A.D. Later on, the coffee gardens were planted in the regions of Mysore, Coorg, Nilgiri, and Malabar. This industry suffered a huge loss due to its competition with the coffee of Brazil.
7. Other Industries. Many new industries were established in India during the later part of the 19th century and the early part of the 20th century. Out of these industries steel, sugar, paper, matchstick, leather industries were more important.
