Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class Social Science Book Solutions Geography Chapter 3 Minerals and Energy Resources Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Social Science Geography Chapter 3 Minerals and Energy Resources
SST Guide for Class 8 PSEB Minerals and Energy Resources Textbook Questions and Answers
I. Answer the following questions in 1-15 words :
Question 1.
Write the definition of mineral resources.
Answer:
Minerals are natural substances that are made up of one or more elements. These are found in the interior of the earth. These have a definite chemical composition. These are identified by their physical and chemical qualities.
Question 2.
Where do iron-ore is found in India?
Answer:
- Bihar: Singhbhum.
- Orissa: Mayurbhanjh.
- Chhattisgarh: Durg and Bastar.
- Karnataka: Bellary, Dharwar, Kudremukh.
Question 3.
What are the uses of copper?
Answer:
Copper is used for making utensils, coins, electrical wires and electronics. Their sheets are also made.
Question 4.
Name the famous gold mines in India.
Answer:
In Karnataka, Kolar and Hutti.
In Andhra Pradesh: Ramgiri.
![]()
Question 5.
How should we use atomic minerals?
Answer:
Atomic minerals should be used carefully. These should be used for the development of the country and not for destruction and pollution.
Question 6.
What are the non-conventional sources of energy?
Answer:
Water power, solar energy, wind power, geothermal energy and tidal energy.
Question 7.
Name the four types of coal.
Answer:
- Anthracite
- Bituminous
- Lignite
- Peat.
Question 8.
What are multipurpose projects?
Answer:
The dams built mainly for power generation are called multi- purpose projects as these provide many benefits at the same time.
II. Answer the following questions in 50-60 words :
Question 1.
Which are the countries from where iron ore is mainly found? Write down the different types of iron ore :
Answer:
Countries: Russia and its neighbouring countries, Australia, Brazil, U.S.A. produce large quantities of iron ore. India produces 5% iron ore in the world.
Types of Iron ore :
- Magnetite
- Haematite
- Limonite
- Siderite.
![]()
Question 2.
Write down a note on the importance of Bauxite.
Answer:
Aluminium is extracted from Bauxite. It makes up about 8 per cent of the earth’s crust. It is light, strong and a very good conductor of electricity. It is largely used in various industries like transportation (aircraft, ship building, automobiles), chemical industries, electrical goods, machines, etc. It is used in making utensils, coins, furniture, sheets, packing material, photo-frames, pipes, etc. It is the basis of our telecommunication systems as it is used in radios, telegraphs, televisions and electrical wires. Due to its wide uses, it has been described as the ‘champion of metals’ or ‘the metal of the twentieth century’.
Question 3.
What is the importance of natural gas in our life and name the major areas in our country where it is found?
Answer:
Natural gas is produced in areas producing petroleum. When an oil well is dug, Natural gas is found in upper layers.
Use: It is used in homes for cooking, in vehicles and in industry.
Production: All the petroleum-producing countries produce Natural gas. The U.S.A. is the leading producer in the world. Russia, Middle East, Canada, Uzbekistan are other producers. Natural gas is produced in some parts of India. These include the Krishna-Godavari basin, Bay of Bengal-Orissa region and Barmer region of Rajasthan. Gulf of Cambay and Kutch region in Gujarat is a potential area. About 75% of the production of India comes from Bombay High.
Question 4.
Name the important factors which are favourable for the generation of Hydroelectricity?
Answer:
The development of water power (Hydro-electric power) depends upon the following factors:
- Uneven relief. Mountainous areas provide quite good sites for the development of water power. Such areas provide rapids or falls.
- Abundant rainfall. Fairly = heavy rainfall uniformly distributed throughout the year is necessary for water power development.
- Presence of huge rivers and waterfalls. There should be some large rivers like Indus or Nile to provide large and regular supply of water.
- Presence of lakes. The presence of lakes along the course of a river helps to regulate water flow naturally.
- Nearness to market. The consuming areas should be near the power stations to avoid the loss during transmission.
III. Answer the following questions in about 125-130 words :
Question 1.
What are energy resources? What is their contribution towards the development of the country? Write in detail about any two energy resources.
Answer:
Coal: Coal is the prime source of energy. It is often called the ‘Mother of Industries’. It has been the basis of industrial revolution. Coal is used as a raw material in iron and steel, chemical industries. India ranks seventh in the world as regards coal reserves. The total proven coal reserves are nearly 214,000 million tonnes. These reserves will not last long. The major states known for coal reserves are Jharkhand, Bihar, Orissa, West Bengal, Chhattisgarh, M.P., Andhra Pradesh and Maharashtra. Coal production is 330 million tonnes (4% of world).
Distribution: India has two types of coalfields :
(a) Gondwana coalfields (98%)
(b) Tertiary coalfields (2%).
(a) Gondwana coalfields: These belong to the period of Gondwana age. Nearly 3/ 4th of coal deposits are found in Damodar valley (Damuda series). Godavari, Mahanadi, Son and Wardha valley have also coal deposits.
- W. Bengal. West Bengal has the oldest coalfield of India at Raniganj. It covers an area of 1267 sq. km.
- Jharkhand and Bihar. These two states produce 50% coal of India. The major coalfields of Jharia, Bokaro, Karanpura, Daltonganj are found in Damodar valley. Coking coal from this coalfield is supplied to steel centres of Jamshedpur, Asansol, Durgapur and Bokaro.
- Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh have Son valley coalfields of Suhagpur, Korba, Rampur, Tatapani, Singrauli.
- Petroleum: In about 10 lakh sq. km oil-bearing rocks are found in India. The oil reserves in India are estimated to be about 4000 million tonnes.
The first oilfield in India was discovered in 1867 at Makum in Assam. At present the production is as below (334 lakh tonnes) :
- Assam: In Assam oil is produced in Digboi, Moran, Naharkatiya and Sibsagar regions.
- Gujarat: In Gujarat oil is produced in the Gulf of Cambay region at Kalol, Ankleshwar, Lunej, etc.
- Maharashtra: Oil has struck in the off-shore region at Bombay High along the coast of Mumbai. It is the leading producer of crude oil in India. North Basin and South basin are the important oilfields.
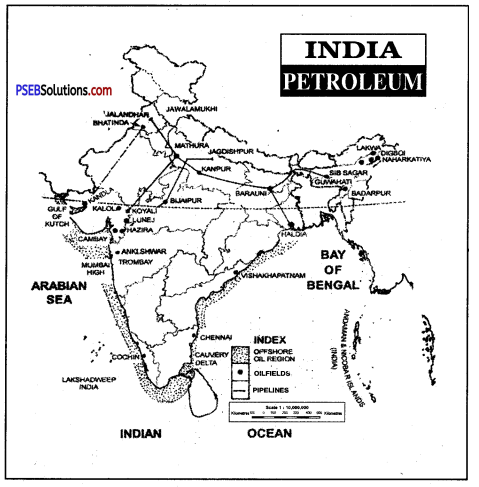
The production of oil in India is increasing everywhere under the organization of Oil and Natural Gas Commission.
![]()
IV. Map Skill
Question 1.
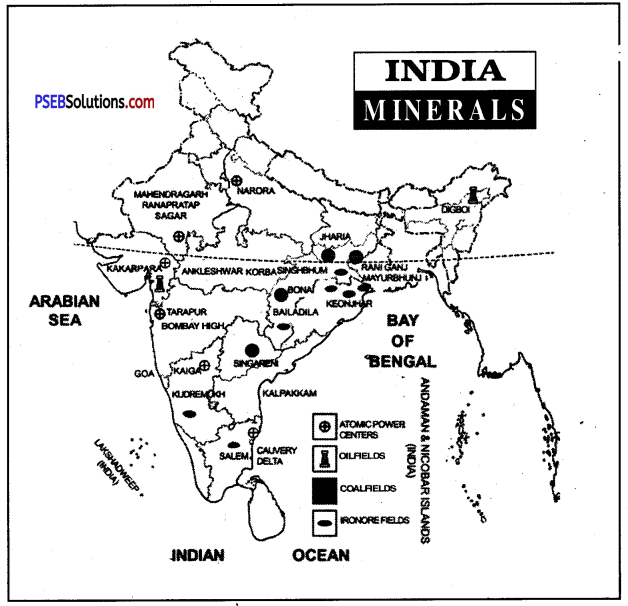
Show one important area of minerals and energy resources on map of India
1. Iron ore
2. Manganese
3. Gold
4. Mica
5. Coal
6. Petroleum.
Answer:
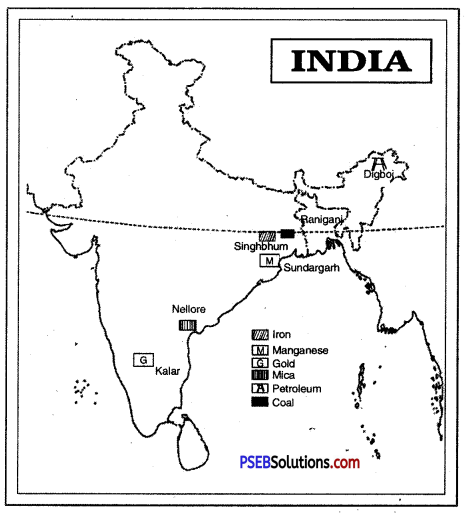
V. Activity
Question 1.
Prepare a list of atleast ten minerals.
Answer:
| S.No. Name of the minerals | Name of state of India in which mineral is found | Use of the mineral |
| 1. Iron ore | Jharkhand | Iron steel industries |
| 2. Manganese | Madhya Pradesh | Steelmaking |
| 3. Gold | Karnataka | Jewellery |
| 4. Copper | Jharkhand | Electrical industries |
| 5. Mica | Bihar | Chemical Industries |
| 6. Uranium | Jharkhand | Utensils |
| 7. Bauxite | Andhra Pradesh | Chemical |
| 8. Coal | Jharkhand | Power |
| 9. Petroleum | Assam | Power |
| 10. Hydroelectricity | Maharashtra | Power |
PSEB 8th Class Social Science Guide Minerals and Energy Resources Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions :
Question 1.
Which one of the following is not a type of mining?
(a) Open cast
(b) Shaft
(c) Drilling
(d) Shaft.
Answer:
(d) Shaft.
Question 2.
Which is the hardest mineral?
(a) Diamond
(b) Granite
(c) Basalt
(d) Gatbro.
Answer:
(a) Diamond.
![]()
Question 3.
Which is the first metal discovered by man?
(a) Copper
(b) Silver
(c) Gold
(d) Iron.
Answer:
(a) Copper.
Question 4.
Name the diamond which is rarest diamond.
(a) Green diamond
(b) White diamond
(c) Pink diamond
(d) Brown diamond.
Answer:
(a) Green diamond.
Question 5.
Which is a ferrous mineral?
(a) Bauxite
(b) Iron
(c) Mica
(d) Coal.
Answer:
(b) Iron.
Question 6.
What is the name of mining shown in the picture?
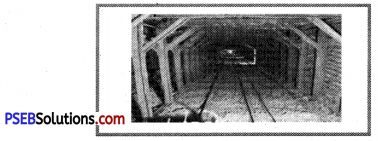
(a) Open Cast
(b) Shaft
(c) Drilling
(d) Shaft mining.
Answer:
(d) Shaft mining.
Question 7.
Which source of energy is the activity in the picture associated with?
Or
Seeing the picture tell the source to which it belongs.

(а) Hydroelectricity
(b) Solar energy
(c) Wind energy
(d) Nuclear (Atomic) energy.
Answer:
(a) Hydroelectricity.
Fill in the Blanks :
Question 1.
The __________ metals do not contain metals.
Answer:
Non-Metallic
![]()
Question 2.
Gondwana coalfields belong to the period of __________ age.
Answer:
Gondwana
Question 3.
Biogas is produced in __________ areas.
Answer:
Rural
Question 4.
Khetri is famous for __________
Answer:
Copper
Question 5.
In Gujarat oil is produced in the __________ region.
Answer:
Gulf of camboy.
True/False :
Question 1.
Energy generated by Tides is called Tidal energy.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
West Bengal has the oldest coalfield of India.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
Iron is a non-ferrous mineral.
Answer:
False
Question 4.
Jharia is famous for Atomic energy.
Answer:
False
Question 5.
Gold metal is used for decoration.
Answer:
True.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Into how many categories can minerals be classified? Give two examples of each.
Answer:
Minerals are grouped into three categories :
- Metallic Minerals. Iron ore, tin.
- Non-metallic Minerals. Diamond, Gypsum.
- Atomic Minerals. Uranium, Thorium.
![]()
Question 2.
Distinguish between Ferrous and Non-ferrous minerals.
Answer:
| Ferrous minerals | Non-ferrous minerals |
| 1. The metallic minerals which contain iron content are called ferrous minerals (Fe). | 1. The minerals which do not contain iron (ferrous) content are called non-ferrous minerals (Nfe). |
| 2. Iron, Manganese, Chromite, Cobalt, etc. are ferrous minerals. | 2. Copper, Lead, Zinc, Aluminium are non-ferrous minerals. |
Question 3.
What are the uses of Manganese?
Answer:
- It is used for manufacturing bleaching powder.
- It is used in insecticides.
- It is used for making paints and batteries.
Question 4.
Where does India rank in the production of manganese in the world? Where is it found in India?
Answer:
India ranks second in world production of Manganese. In India the main producing areas are Karnataka, Orissa, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, West Bengal and Goa.
Question 5.
What is Bronze? What is its use?
Answer:
It is a hard and strong product. Tin and copper are mixed to make it. It is used in making tools and weapons.
Question 6.
Where is copper found in the world ? Name the copper producing areas in India.
Answer:
USA, Russia, Chile, Zambia, Canada and Zaire are the main producers of copper. In India copper is found in Singhbhum (Jharkhand), Balaghat (Madhya Pradesh) and Jhunjhunu, Alwar (Rajasthan).
![]()
Question 7.
Which two states of India are large producer of Bauxite? Name two copper producing areas of these states.
Answer:
Jharkhand and Rajasthan are Bauxite producing states of India. Copper is mined at Singhbhum and Khetri.
Question 8.
What are the uses of Gold?
Answer:
Gold is a valuable metal :
- It is used for making ornaments and articles for decoration.
- It is used for gold plating, teeth covers and medicines.
Question 9.
What are the uses of copper?
Answer:
Copper is a soft and brown-coloured metal. It has been used by man for a very long time. It is mixed up with tin to be known as Bronze. It is used in the production of utensils, coins, electric wires.
Question 10.
Which minerals are used to produce atomic energy?
Answer:
Uranium, Thorium, Lithium and Zircon are used to produce atomic energy.
Question 11.
Why is petroleum called Rock oil?
Answer:
Petroleum or ‘mineral oil is called rock oil because it is formed in sedimentary rocks. It is called crude oil.
Question 12.
Which country is the largest producer of Gold in the world? And how much?
Answer:
South Africa is the largest producer of gold in the world. It produces about 70% gold of the world.
![]()
Question 13.
What is Mica? Why is it used in electrical goods industry?
Answer:
Mica is black or brown or white transparent material. It is a non-metallic .mineral. It is non-conductor of electricity. So it is used in electrical goods industry.
Question 14.
Describe the different methods of extracting minerals.
Answer:
Taking out minerals from rocks is called mining :
- Open cast mining: Minerals at shallow depths are taken out by removing the surface layer.
- Shaft Mining: Minerals at depth are taken out by making deep bores.
- Drilling: Deep wells are bored to take out petroleum.
- Quarrying: Minerals at surface are dug out.
Question 15.
Most industries are concentrated around coal mines.
Answer:
Most industries are concentrated around coal mines because coal is an important source of energy. It is key mineral and fuel for the industries. It is used as a power resource in many industries. Many industries use it as a raw material. So most industries are concentrated around coal mines.
Question 16.
Petroleum is referred to as “black gold”. Why?
Answer:
Nowadays petroleum is a major source of energy in the world. Many byproducts such as kerosene, fuel, lubricating oils etc. are obtained from it. Petrochemical products have become very useful. Petroleum is used in agro-industry, paints, perfumes, transport, etc. So it is rightly called the “black gold”.
Question 17.
Distinguish between conventional and non-conventional sources of energy.
Answer:
| Conventional Sources | Non-conventional Sources |
| 1. The sources of energy which have been used since a long time are called the conventional sources of energy. . | 1. The sources of energy which have not been commonly used are called non conventional sources of energy |
| 2. Wood, fuel, coal, petroleum gas and water power are conventional sources of energy. | 2. Wind, tidal power, Geothermal energy, bio gas, solar energy are non conventional sources of energy. |
Question 18.
Distinguish between
(i) Thermal power and Hydel power.
Answer:
Thermal Power and Hydel Power
| Thermal Power | Hydel Power |
| 1. It is expensive. | 1. It is comparatively cheaper. |
| 2. It is a limited resource. | 2. It is an unlimited resource. |
| 3. It creates problems of atmospheric pollution. | 3. It is non polluted. |
| 4. The electricity generated by coal or petroleum is called thermal power. | 4. The electricity generated by running water is called hydel power. |
(ii) Anthracite coal and Bituminous coal.
Answer:
Anthracite coal and Bituminous coal
| Anthracite coal | Bituminous coal |
| 1. It is the best quality of coal. | 1. It is the low quality of coal. |
| 2. It causes very less pollution. | 2. It causes more pollution. |
| 3. It gives more energy. | 3. It gives less energy. |
| 4. It is found only in J & K. | 4. It is found in West Bengal, Orissa, Chhattisgarh and Jharkhand. |
![]()
Question 19.
How should the natural resources be conserved?
Answer:
The natural resources should be used carefully in a planned manner. No resource should be wasted. These should be used so that the future generations can also use these.
Question 20.
Distinguish between Metallic and Non-metallic minerals.
Answer:
| Metallic Minerals | Non-Metallic Minerals |
| 1. Metals are malleable i.e., they can be beaten into sheets. | 1. They are brittle in nature and cannot be beaten into sheets. |
| 2. They are good conductors of heat and electricity. | 2. They are bad conductors of heat and electricity. |
| 3. All metals are solids. | 3. They may be solids, liquids and gases. |
| 4. For Example iron, copper. | 4. For Example sand, diamonds. |
Question 21.
‘Human civilisations are associated with discovery of minerals.’ Give example.
Answer:
Mining is an age-old activity. The use of minerals is marked with different stages of human civilisation. During 5000 B.C., copper age existed. During 3000 B.C., Bronze age and during 1400 B.C., iron age were developed.
Question 22.
What are the alternative sources of energy?
Answer:
There are other sources of energy as well. They include hydropower, geothermal, nuclear, solar and wind. These are also referred to as the alternative energy sources.
Question 23.
Many African countries have large potential of water resources but they have not used it to generate hydro-electricity.
Answer:
Large amount of capital is required for making dams on rivers, fixing machines and turbines and buying of transmission lines. So in spite of the water resources they are not used to generate hydro-electricity.
![]()
Question 24.
Name four main belts where iron ore is found.
Answer:
The four main iron ore belts are :
- Orissa – Jharkhand belt
- Durg – Bastar Chandarpur belt
- Bellary – Chick Manglur belt
- Maharashtra – Goa belt.
Question 25.
‘Mineral conservation can delay a crisis.’ Explain.
Answer:
Due to growing population, the use of minerals is increasing at an alarming rate. Minerals will not last long. We need to find substitutes, reduce consumption, recycle mineral resources. It can delay a mineral crisis.
Question 26.
Classify the following metals :
(i) Ferrous
Answer:
Ferrous: Iron and Manganese
(ii) Non-ferrous
Answer:
Non-ferrous: Copper and Lead
(iii) Light metal
Answer:
Light metal: Aluminium
(iv) Rare metals.
Answer:
Rare metals: Zirconium.
Question 27.
List three basic ways through which energy is-obtained.
Answer:
Energy is the capacity to do work. It can be obtained by :
- Direct heating like fire, sun, etc.
- Electricity
- Stored energy in the form of a battery.
![]()
Question 28.
Describe the different types of coal.
Answer:
- Peat: Peat is the first stage of coal development. It is dark brown in colour. It has about 35 per cent carbon content.
- Lignite: Lignite is the next stage of coal formation, which has almost 50 per cent carbon.
- Anthracite: Lignite becomes sub-bituminous, bituminous and eventually anthracite coal. Anthracite has more than 85 per cent carbon. It is the best quality of coal. It is very hard, compact, black in colour. It ignites slowly and bums with short blue flame.
Question 29.
Describe the formation of coal.
Answer:
Coal is a black or brown rock consisting mainly of carbon. Coal is formed by the decomposition of vegetation of last ages. Most of coal deposits were formed in carboniferous age about 300 million years ago.
Question 30.
Describe natural gas as a source of conventional energy.
Answer:
- Natural gas is found with petroleum deposits.
- It is released when crude oil is brought to the surface.
- It is used as a domestic and industrial fuel.
- Russia, Norway, UK and the Netherlands are the major producers of natural gas in the world.
- Jaisalmer, Krishna-Godavari delta. Tripura and some areas off shore in Mumbai have natural gas resources in India.
- Very few countries in the world have sufficient natural gas reserves of their own.
Question 31.
Describe solar energy.
Answer:
Solar Energy:
- Sun provides heat and light energy every day.
- Solar energy trapped from the sun is used in solar cells to produce electricity.
- These cells are joined into solar pan&b to generate power for heating and lighting purpose.
- The technology of utilising solar energy benefits tropical countries with abundant sunshine.
- Solar energy is also used in solar heaters, solar cookers, solar dryers along with community lighting and traffic signals.
Question 32.
Explain wind energy.
Answer:
- Wind is an inexhaustible source of energy.
- Windmills have been used for grinding grain and lifting water since times immemorial.
- At present high speed wind rotate the windmill which is connected to a generator to produce electricity.
- Wind farms are clusters of wind mill. They are located in coastal regins and in mountains passes where strong and steady win blows.
- Wind farms are found in Netherland, Germany, Denmark, UK, USA and Spain, ‘ They are known for wind energy production.
![]()
Question 33.
Give an account of nuclear power.
Answer:
Nuclear power:
- Nuclear power is obtained frm energy stored in the nuclei of atoms of naturally occurring radioactive fuels like uranium and thorium.
- These fuels undergo nuclear fission in nuclear reactors and emit power.
- USA and Europe are the greatest producers of nuclear power.
- In India: Rajasthan and Jharkhand have large deposits of uranium.
- Thorium is found in large quantities in the monozite sands of Kerala.
- Nuclear power stations in India are located in Kalpakkam (Tamil Nadu), Tarapur (Maharashtra), Ranapratap Sagar near Kota (Rajasthan), Narora (Uttar Pradesh) and Kaiga (Karnataka).
Question 34.
How is geothermal energy used?
Answer:
Geothermal Energy
- Heat energy obtained from the earth is known as geothermal energy.
- The temperature in the interior of the earth increases with increase in depth.
- This heat energy comes on the surface in the form of hot springs. This heat energy is used to generate power.
Question 35.
Rajan lives in West Bengal. Which cereal crop should he sow in his field to maximise his profit?
Answer:
Rice.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe the production of mica in world and in India.
Answer:
U.S.A., Russia, India, France, Argentina and South Korea are the main producers of Mica. India is the leading producer of mica in the world. But the production of mica is decreasing in India.
It is due to two factors :
- The demand for mica is decreasing in the world.
- The use of substitutes is increasing.
90% of the production of Mica in India comes from three states of Andhra Pradesh, Rajasthan and Jharkhand. Other producers are Bihar, Gujarat, Kerala, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Himachal Pradesh. The main districts are Nellore, Vishakhapatnam, Krishna (Andhra Pradesh), Jaipur, Udaipur, Bhilwara (Rajasthan), Gaya (Bihar), Hazaribagh (Jharkhand).
![]()
Question 2.
What is Nuclear Energy? Name the areas in India producing nuclear minerals.
Answer:
The energy generated by nuclear minerals is called nuclear energy. Uranium, Thorium, Lithium are nuclear minerals.
Areas of Production :
- Uranium. Singhbhum, Hazaribagh (Jharkhand), Gaya (Bihar) Saharanpur (U.P.) and Udaipur (Rajasthan).
- Thorium. Kerala, Jharkhand, Bihar, Rajasthan and Tamil Nadu.
- Lithium. Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Chhattisgarh, Kerala.
Question 3.
Describe the importance of Natural Resources in our day to day life. Name the main areas of Natural Resources.
Answer:
Natural resources are free gifts of nature. These are very important for our lives. These are the index of a country’s progress and strength. These are called ‘the backbone of a country.
Areas of Natural Resources:
- India’s 30% of the total area is covered with mountains. These have huge water and forest resources.
- About 27% of the total area is covered with plateaus. These are storehouses of minerals.
- About 43% of the total area is covered with plains. These have fertile soils and agriculture is well developed. These are ‘granaries’ of India.
Question 4.
Describe the Non-conventional sources of energy produced in India.
Answer:
Non-conventional sources of energy. Today non-conventional sources of energy include wind, tides, geothermal heat, biogas, farm and animal waste including human excreta.
All these sources are renewable or inexhaustible.
1. Wind energy: It can be used for generating electricity. It is estimated that wind alone can provide 2000 MW of electricity. The states of Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra and Orissa are better placed in regard to this energy. Areas with constant and high speed winds are suitable for the purpose.
2. Tidal energy: The Gulfs of Kutch and Cambay are ideally suited to develop electricity from the energy produced by high tides entering to narrow creeks.
3. Geo-thermal energy: India is not rich in this source. However, efforts are on to utilize natural energy of the hot springs at Manikaran in Himachal Pradesh.
4. Energy from urban waste: A pilot for demonstration purposes had already been set up in Delhi to treat solid municipal waste for conversion into energy. It produces nearly 4 MW energy every year. Sewage in cities is used for generating gas and electricity.
5. Biogas based power plants: Bagasse, farm wastes, rice husk are being used to produce electricity.
6. Farm animal and human wastes (Urja Gram): By using biomass, animal poultry waste and human excreta, gobar gas plants are being set up in villages.
7. Solar energy: Solar voltaic cells are used to generate solar energy.
![]()
Question 5.
Environmental aspects must be carefully looked into before building huge dams.
Answer:
- Dams create an imbalance in the earth’s equilibrium.
- Deforestation leads to environmental pollution.
- People are displaced.
- Cities/villages/towns are shifted causing untold hardships to people.
- Silting of lakes a problem.
Fill in the blanks :
Question 1.
Russia is rich in __________ resource.
Answer:
Natural gas
Question 2.
Processing of digging out of minerals is known as __________
Answer:
quarrying
Question 3.
Biogas is produced in __________ areas.
Answer:
rural
Question 4.
India __________ in ferrous minerals.
Answer:
is rich
Question 5.
Australia is the largest producer of __________ in the world.
Answer:
bauxite
![]()
Question 6.
China and India have large __________ are deposits.
Answer:
iron.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is Hydel power? How is it generated? Describe its production in India and world.
Answer:
Hydel power is generated through falling water. Dams are built on rivers, the water is dropped from a height to rotate turbines. Due to friction, turbines generate electricity.
Production: Many countries have sufficient water resources. These countries produce large quantities of Hydel power. U.S.A., Russia, Japan, Germany, Canada, England, France, Italy, Poland, Brazil and India are the main producers. U.S.A. produces 31% water power of the world.
Hydel power in India. India produces sufficient Hydel power. But India’s share is only 1% in world production. Rivers and canals are the main sources.
- Himalayan rivers
- Peninsular rivers.
Ganga, Brahmaputra and tributaries are snow fed and perennial rivers. So these have large capacity to generate water power with 18% of total potential of India. But peninsular rivers are seasonal and depend upon rainfall. So their capacity is low.
Distribution: All the states, except, Goa produce Hydel power. Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Punjab, Tamil Nadu, Orissa, Kerala states have large capacity. Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh are rich in Hydel power resources. We have to develop these resources.
Important: Projects,
- Nagarjun Sagar Dam-Karnataka.
- Ganga Hydro-electric system-U.P.
- Tata Hydro-electric Grid-Maharashtra.
- Hirakud Dam-Orissa.
- Pandoh Project-Himachal Pradesh.
- Bhakra-Nangal Project-Punjab.
![]()
Question 2.
Describe the economic importance of minerals. Explain the main types of minerals.
Answer:
Minerals. Mineral resources are of great use to man. Minerals have been called ‘The Gifts of Nature’. Mineral resources have been used since pre-historic times. Human civilisation has seen many ages like the stone age, copper age and iron age. Modern industrial and economic development depends upon the production and utilization of minerals.
Types of Minerals: There are 70 to 80 minerals found on the surface of the earth. These can be divided into three types :
- Non-Metallic Minerals. These include salt, mica, limestone, graphite, potash, gypsum.
- Metallic Minerals. These include iron, copper, aluminium, gold, silver. These can be melted into useful metals.
- Fuel Minerals. These include coal, oil and natural gas. These are called sources of power.
Importance of Minerals :
- Industries. Minerals form the basis of heavy industries like iron and steel. Minerals are called ‘vitamins’ of industry.
- Machinery. Minerals provide machinery for modern manufacturing.
- Transport. Minerals are used in the making of different means of transportation.
- Sources of Energy. Minerals provide energy to modern industries.
Question 3.
Describe the production of Petroleum in India.
Answer:
Production. In about 10 lakh sq. km. oil-bearing rocks are found in India. The oil reserves in India are estimated to be 50 crore metric tons.
The first oilfield in India was discovered in 1867 at Makum in Assam. At present the production is as under:
- Assam: In Assam, oil is produced in Digboi, Moran, Naharkatiya, and Sibsagar regions.
- Gujarat: In Gujarat, oil is produced in the Gulf of Cambay region at Kalol, Ankleshwar, Lunej, etc.
- Maharashtra: Oil has struck in the offshore region at Mumbai High along the coast of Mumbai. It is the leading producer of crude oil in India. North Basin and South Basin and Albet islands are the important oil fields.
- The production of oil in India is increasing everywhere under the organization of the Oil and Natural Gas Commission. The production of oil in India was estimated to be about 210 lakh tonnes in 2001.
