Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class Social Science Book Solutions Geography Chapter 4 Our Agriculture Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Social Science Geography Chapter 4 Our Agriculture
SST Guide for Class 8 PSEB Our Agriculture Textbook Questions and Answers
I. Answer the following questions in 1-15 words:
Question 1.
What do you understand by Agriculture?
Answer:
Agriculture includes raising crops, cattle rearing, and other agricultural activities. It also includes dairy farming, poultry, bee-hiving, fishing, floriculture, gur production, flour mills, etc.
Question 2.
Which factors affect Agriculture?
Answer:
The following factors affect agriculture:
- Climate
- Relief
- Type of soil
- Irrigation
- Method of cultivation
- Marketing
- Means of transportation and
- Banking facilities.
Question 3.
Write a brief note on plantation farming.
Answer:
It includes the cultivation of single crop on large farms.
Question 4.
Write the names of cereal crops.
Answer:
Main cereal crops are Rice, Wheat, Maize, Jowar, Bajra, Pulses and Oilseeds.
![]()
Question 5.
What is puddling?
Answer:
For rice cultivation, seeds are planted in the fields. The field is levelled and filled with water. This is called puddling the field where rice plants are transplanted.
Question 6.
What products are prepared from Maize?
Answer:
Glucose, starch, alcohol and vegetable oil is prepared from Maize.
Question 7.
How many types of cotton are there on the basis of the length of staple?
Answer:
- Long staple cotton (Best Type)
- Medium staple cotton
- Short staple cotton.
Question 8.
Which are the things that can be made from jute?
Answer:
Bags, ropes, strings, etc. and shoes are prepared from jute.
Question 9.
How does the tea plant look like?
Answer:
Tea plant is a bush. Its leaves provide tea.
Question 10.
Write the names of three types of coffee.
Answer:
- Arabica
- Robusta
- Liberica.
![]()
Question 11.
What is the percentage of people engaged in agriculture in U.S.A. and Punjab?
Answer:
- U.S.A.-More than 30% people
- Punjab-58% people.
II. Answer the following questions in 50-60 words :
Question 1.
After writing the types of Agriculture differentiate between intensive and extensive agriculture.
Answer:
Types of Agriculture :
- Sedentary Agriculture
- Shifting Agriculture
- Dry Farming
- Wet Farming
- Intensive Farming
- Extensive Farming
- Mixed Farming
- Horticulture
- Individual Agriculture
- Co-operative Farming
- Collective Farming
- Plantation Agriculture
- Subsistence Agriculture
- Commercial Farming.
The distinction between Intensive and Extensive Farming :
- Intensive farming is done on small farms while extensive farming is done on large farms.
- Irrigation and fertilizers are used in intensive farming while machines are used in extensive farming.
- Intensive farming is done in Punjab while extensive farming is done in U.S.A.
Question 2.
Differentiate between subsistence and commercial type of farming.
Answer:
1. Subsistence Farming: Majority of farmers in the country practise subsistence farming. It is characterised by small and scattered land-holdings and use of primitive tools. As the farmers are poor, they do not use fertilisers and high yielding variety of seeds in their fields to the extent they should do. These result into low productivity. Important cash crops like sugarcane, oilseeds, cotton and jute are grown. The subsistence agriculture has given way to commercial agriculture to some extent.
2. Extensive Farming: Extensive farming is bush or tree farming. It is a single crop farming of rubber, tea, coffee, cocoa, spices, coconut and fruit crops. It is capital-intensive and demands good managerial ability, technical know-how, sophisticated machinery, fertilisers, irrigation and transport facilities. Extensive farming is done in U.S.A. and Canada.
![]()
Question 3.
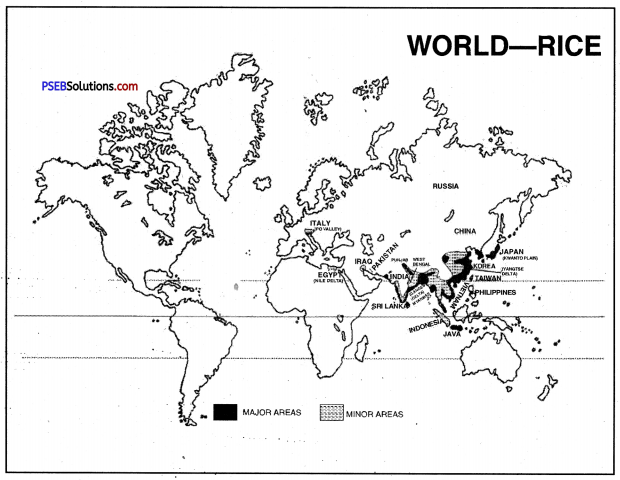
Which are main Rice producing areas?
Answer:
Cultivation of Rice. Rice is grown in deltas, flood-plains, coastal-plains and some terraced fields in the mountainous areas as well. It is one of the crops for which a lot of human labour is required. All operations including the preparation of seedling beds, ploughing, planting, weeding, harvesting and separation of grain are done by human labour.
Rice requires high temperature of over 20°C to germinate, bloom and mature. Rainfall of 100 cm to 150 cm is required. Paddy is cultivated mainly in India, China, Japan, Bangladesh, Indonesia, Thailand and Myanmar.
In India rice is cultivated most widely in Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal and Andhra Pradesh. Other producers are Assam, Tamil Nadu, Orissa and Punjab.
In Punjab, rice is grown in districts of Amritsar, Gurdaspur, Ferozepur, Jalandhar, Patiala and Ludhiana.
Question 4.
Explain the conditions required for cultivation of cotton and jute.
Answer:
Cotton. Cotton requires cloud free sunny days and uniformly high temperature. It grows best in areas where the temperature is between 30°C to. 40°C. Cotton plants require rainfall of 60 to 100 cm. Alluvial and black soils are best suited for cotton plants.
Jute. Jute fibre is obtained from the bark of the jute plant stem.
The jute plant originated in the Indian subcontinent. It grows best in well drained sandy loam and requires warm and humid climate. Jute plant requires temperature of more than 25°C and rainfall of over 150 cm per year.
Question 5.
Write a note on cotton production in Punjab.
Answer:
Punjab and Haryana together produce 25% cotton of India. The major producers are Ferozepur and Sangrur districts. B.T. cotton has been successfully grown in Punjab. Malwa region is also called white gold.
Question 6.
Write about protection of tea and coffee plants.
Answer:
Tea. Tea plants are planted on cleared slope. So that on well drained slopes, water should not stand in the roots of plants. Fertilizers are used for growth of tea plants. Tea plant needs pruning for its proper growth.
Coffee. Coffee saplings are grown in Nursery and then transplanted in the fields. The plants require use of fertilizers, pruning, and irrigation. Sunny weather is required during growth. The tree is pruned to keep it upto a height of 8 feet.
Question 7.
Write a note on the uses of machines in agricultural operations in U.SA.
Answer:
Two types of farms are functioning in the United States viz.,
- specialized farms and
- mixed farms.
A specialized farm concentrates on a particular type of crop or livestock, whereas a mixed farm raises a variety of crops. About 95 per cent of farms in the USA are specialized farms. Mostly cereal grains such as corn, wheat, sorghum, rice, barley, oats and rye are grown in specialized farms. However, specialized farms also produce crops such as cotton, groundnut, sugarcane, tobacco, vegetables and fruits. Nearly half the specialized farms in the USA are livestock farms. These livestock farms rear meat animals, raise milk cows, chickens and turkeys. In the mixed farms, farmers produce a variety of crops and rear livestock. The United States is the world’s leader in international agricultural goods market.
III. Answer the following questions in about 125-130 words :
Question 1.
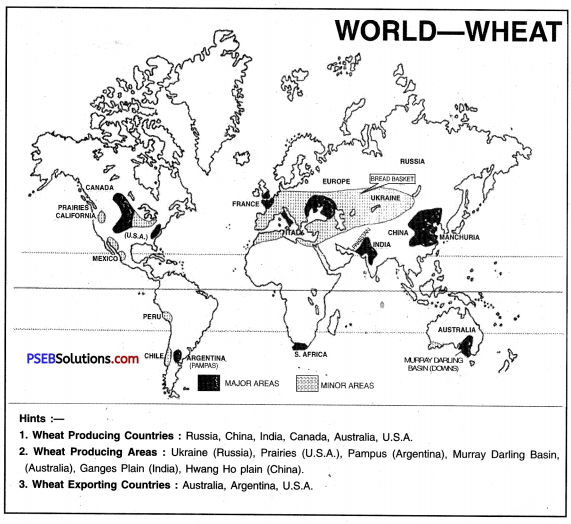
After writing about conditions for the growth of wheat explain the areas of wheat production. (P.B. 2009)
Answer:
Geographical conditions of growth. Wheat needs a cool and wet climate during growing season and a warm dry climate during harvesting season. It requires a rainfall of 50 cm to 75 cm. It is a rabi crop. It grows best in winter due to winter rainfall and regular irrigation. It does not depend on destiny like rice crop. Wheat grows best on loamy soils. Mechanisation and use of chemical fertilizers give higher yields.
Production. Wheat is one of the oldest cereal crops cultivated in the world. Wheat is grown in temperate regions with rainfall ranging between 30 cm to 80 cm.
Three countries: the United States of America, Russia and China are the major producers of wheat. The world’s largest producer is China. Other leading producers are India, Ukraine, France, Canada, Pakistan and Argentina. Winter wheat and spring wheat belts of USA and Canada are quite famous.
Wheat cultivation is mainly carried on in fertile soils or loamy soils. Different climatic conditions and sowing seasons across the world have led to harvesting of wheat in every month of the year in one or the other part of the world. It is grown in Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra and Bihar. India is the second largest producer of wheat in the world. The production and yield in Punjab has increased due to Green Revolution, Better seeds, fertilizers and irrigation is used. ,
Question 2.
What are the conditions required for the growth of Tea and Coffee? Explain the main areas of tea and coffee production in India.
Answer:
Geographical Conditions of Growth of Tea. Tea is a plant of both tropical and temperate areas.
- Temperature. Tea requires uniformly high temperatures (20° – 30°C) throughout the year. Frost is harmful for tea leaves.
- Rainfall. An annual rainfall of 150 cm is essential for the growth of tea.
- Soil. Tea requires a deep acidic and fertile soil.
- Land. Tea is grown on gently sloping, well drained hill slopes and valley-sides.
- Labour. Tea is a labour intensive crop. It requires cheap, skilled labour for picking tea-leaves.
Conditions for Growth of Coffee. One-third of the world population drinks coffee, the second largest beverage after tea. There are two types of coffee plants. Coffee Arabica or Mocha and Coffee Robusta. Robusta is the main variety produced in the world.
The coffee plant requires warm climate and moderate rainfall. Both strong sunshine and snowfall are harmful to the plant. During its growth, coffee plant requires rainfall of 100 cm to 150 cm and temperatures between 15°C and 25°C. Irrigation is required where the annual rainfall is less than 100 cm.
Areas of Cultivation of Tea. More tea is produced in Northern India than Southern India. Tea is grown on an area of 4.21 lakh hectares.
The average yield is 1540 kg per hectare. Assam produces about 50% tea of India.
1. Assam. Assam is the largest producer of tea in India. Tea is grown on the valley sides of Brahmaputra and Duar region.
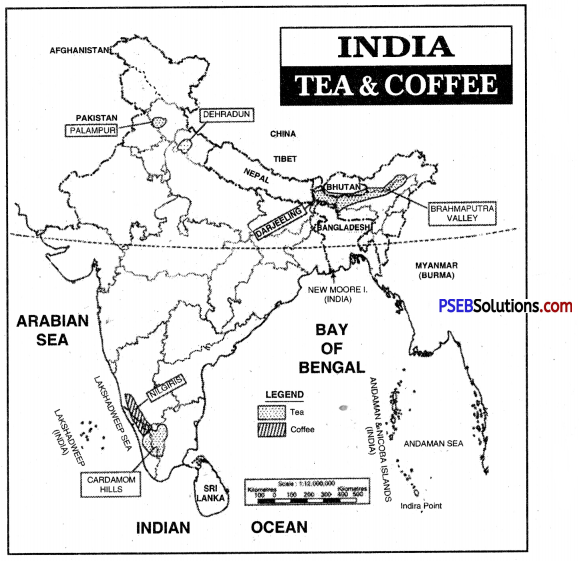
2. West Bengal. Tea is grown in Darjeeling and Jalpaiguri districts in West Bengal. Darjeeling tea has a special flavour. This flavour is due to slow growth under high humidity and low temperature.
3. Southern India. Tea is grown on the slopes of Nilgiris, Cardamom and Anamalai hills, Coimbatore (Tamil Nadu), Malabar coast (Kerala), Coorg region (Karnataka) and Ratnagiri (Maharashtra) are important areas of tea production. Areas of Cultivation of Coffee.
Karnataka is the largest coffee producing state of India.
(а) Karnataka. Coffee is grown in the districts of Chikamanglur, Coorg, Hassan, Shimoga (Nilgiris) in Karnataka state. High rainfall, sunshine, protected slopes, well- drained soils favour the cultivation of coffee.
(b) Arcot, Tinevelley, Madurai, Coimbatore districts of Tamil Nadu grow coffee.
(c) In Kerala, Cardamom hills covering the districts of Palghat and Thiruvananthapuram.
![]()
Question 3.
Write down the process involved in Jute production. Write in detail the uses and distribution of Jute in the world.
Answer:
Jute: Jute is an industrial fibre. It is the cheapest fibre. It has commercial importance. It is also called ‘golden fibre’. It is used in the making of carpets, ropes, covers and linoleum. It is used for packing many agricultural commodities. Jute is called ‘Brown Paper of Whole-sale trade’. Jute fibre has softness, strength and length.
Conditions of Growth: Jute is a plant of hot-wet tropical areas.
- Temperature. It requires uniformly high temperature (27°C) throughout the year.
- Rainfall. Jute requires well distributed heavy rainfall (150 cm).
- Soil. It is grown on flood plains and deltas. Fertilizers are also used.
- Clean Water. Jute needs an ample supply of clean water for washing.
Area and Production: The jute is grown on an area of about 8 lakh hectares. The total production is about 93 lakh bales (each bale = 180 kg). The average yield is 2014 kg per hectare.
India is the largest producer of jute in the world. Due to partition of India 75% of jute producing areas remained in East Pakistan (now Bangladesh). There was shortage of raw jute for jute mills in India. Now India is self-sufficient in jute production. Coarse jute called Mesta is also grown.
Areas of Cultivation
- West Bengal. West Bengal is the largest producer of jute in India. Jute is grown in Ganges delta. Murshidabad, Burdwan, Nadiad, Hooghly are the main jute producing districts.
- Assam. Jute is grown in Goalpara, Kamrup and Tezpur districts in Brahmaputra valley.
- Bihar. Jute is grown in Terai districts of Purnea and Champaran. The major producers of Jute in the world are China, India, Bangladesh, Thailand and Brazil.
Question 4.
What are the similarities and variations in the agriculture of Punjab and the U.S.A.?
Answer:
(A) Agriculture in the U.S.A.-A Glance :
- Agriculturally, the U.S.A. is a developed country. About 3% of the total population is engaged in agriculture,
- The main reason behind this is that all the activities of agriculture are carried on by machines and. not by men.
- Agricultural activities are carried on about 20% part of the land,
- The main agricultural areas include North-West, North-East, interior plains and coastal plains of the country. Different types of crops are grown in different parts of the country,
- The farmers of the U.S.A. have large landholdings as compared to that of India. The farm size is very big. The average farm size in U.S.A. is 700 acres. Due to the large size of the fields, extensive type of agriculture is practised.
- Machines are used at a very large scale. It is almost impossible to work in farms without machines,
- In a farm, only one type of crop is cultivated. From the sowing of crop to the taking of the crop to markets or stores, every work is done with the help of machines,
- Insecticides and pesticides are properly utilized. The farmer of U.S.A. practice agriculture like a businessman and not like a mere farmer.
(B) Agriculture in Punjab (India)-A Glance :
- Punjab in comparison to other states of India, is much advanced in agriculture. The agriculture sector contributes 35% to the total income of the country. About 58% population of the state is engaged in agriculture,
- The soils here are fertile in nature. To maintain the fertility of the soils, the farmer also uses fertilisers,
- The farmers of Punjab do not have too much of land. Landholding mostly range between 5 to 25 acres. Some farmers possess even less land. Six percent farmers of the state have more than 25 acres of land.
- The farmer grows, different types of crops in his fields. The variations in crops mainly depend on climate, size of landholding, type of soil, irrigation facilities and requirements of the farmer.
- According to the size of the land holding the farmer uses tractor or combine harvester,
- Almost all the net sown area comes under irrigation. The farmer of Punjab also uses insecticides and pesticides at a large scale to get more production. Though the farmer of Punjab uses the machines, even then the contribution of labourers is too much. This we can estimate from the number of people working in the agricultural sector. In U.S.A. only 3% of population is engaged in agriculture whereas in Punjab 58% people are working in the agriculture sector,
- The farmer of Punjab (except a few big farmers) does not practice agriculture like a businessmen. He sows a number of crops in his fields. Two-2 crops are taken at the same time,
- The agriculture of Punjab is an intensive type of agriculture. Therefore, the yield per acre is more than that of the U.S.A.
IV. Map Skill
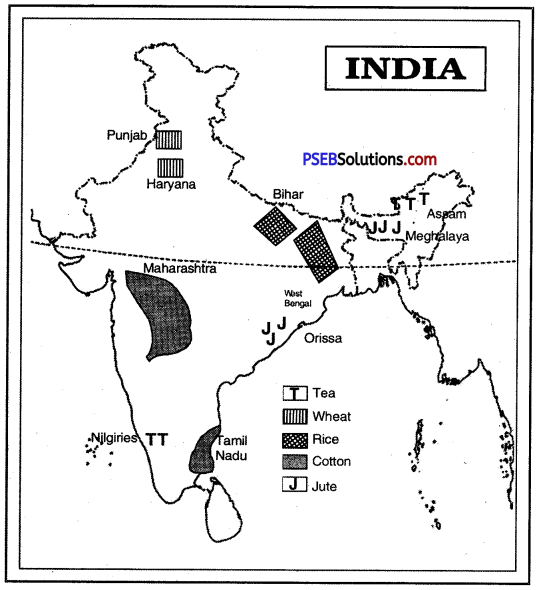
Question 1.
Show two place’s each of following crops on outline map of India. Tea, Wheat, Rice, Cotton, Jute.
Answer:
![]()
V. Activity
Question 1.
Name three each of Kharif and Rabi crops mentioning geographical conditions need for each.
Answer:
| Crop | Temp | Rainfall | Soils |
| 1. Wheat | 10°-20°C | 50-100 cm | Clay soil |
| 2. Rice | 20°-30°C | 100-200 cm | Alluvial soil |
| 3. Maize | 18°-27°C | 50-100 cm | Levelled plain |
| 4. Cotton | 20°-30° | 50-100 cm | Simple slope |
| 5. Tea | 20°-30°C | 150-300 cm | Sloping |
| 6. Jute | 29°-35°C | 120-150 cm | Alluvial soil |
PSEB 8th Class Social Science Guide Our Agriculture Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions :
Question 1.
Commercial rearing of silkworm is called
(a) Commercial farming
(b) Pisciculture
(c) Sericulture
(d) Viticulture.
Answer:
(c) Sericulture.
Question 2.
Farming in which the produce is consumed by the farmer’s household is called :
(a) Subsistence
(b) Extensive
(c) Intensive
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(a) Subsistence.
Question 3.
What does golden filament means?
(a) Cotton
(b) Jute
(c) Silk
(d) Wool.
Answer:
(b) Jute.
![]()
Question 4.
Which country is the largest producer of rice in the world?
(a) India
(b) Brazil
(c) China
(d) U.S.A.
Answer:
(c) China.
Question 5.
India is largest producer of _________
(a) Tea
(b) Coffee
(c) Rice
(d) Cotton.
Answer:
(a) Tea.
Question 6.
For what purpose the following machine is used?

(а) For drilling
(b) For showing wheat / rice
(c) For harvesting
(d) For growing vegetables.
Answer:
(c) For harvesting.
Question 7.
In the following picture a plant is shown, name the areas in which plant is found.
(а) Tropical
(b) Temperate
(c) Tropical & temperate
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Tropical & Temperate.
Question 8.
What is the name of farming of fruit shown in this picture?

(а) Horticulture
(b) Sericulture
(c) Pisciculture
(d) Viticulture.
Answer:
(d) Viticulture.
Question 9.
Which of the following crops does this picture resemble?

(a) Paddy (Rice)
(b) Wheat
(c) Maize
(d) Cotton.
Answer:
(a) Paddy (Rice).
![]()
Question 10.
What type of crops can be grown on the part of land with plenty of black soil?
(a) Sugarcane
(b) Wheat
(c) Cotton
(d) Jute.
Answer:
(c) Cotton.
Fill in the Blanks :
Question 1.
_________ agriculture is done with machines in sparsely populated areas.
Answer:
Extensive
Question 2.
_________ is called cultivation of grapes.
Answer:
Viticulture
Question 3.
Shifting cultivation is also called _________
Answer:
Slash and burn
Question 4.
Coarse grain are also called _________
Answer:
Millets
![]()
Question 5.
Agricultural activity in India is a _________
Answer:
primary activity.
True/False :
Question 1.
Production of fruit and flower is called viticulture.
Answer:
False
Question 2.
Punjab state is the largest producer of wheat.
Answer:
False
Question 3.
Arabica is a variety of coffee.
Answer:
True
Question 4.
Flax is a fibre crop.
Answer:
True
![]()
Question 5.
Russia is a leading producer of coffee.
Answer:
False.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by agriculture?
Answer:
The word ‘agriculture’ is derived from the Latin words ‘ager’ or ‘agri’ and ’culture’. Ager means soil and culture means cultivation or tilling the soil. Agriculture, thus, means cultivation of soil. But in broader sense, agriculture is growing crops and rearing of livestock. Livestock include animals (cattle, sheep and goat) and birds that are reared for human use.
Question 2.
What are the different forms of the word ‘culture’?
Answer:
The word cuture has many variants like :
- Agriculture. Science and art of cultivation on soil, raising crops or livestock.
- Sericulture. Commercial rearing of silkworms.
- Pisciculture. Breeding of fish for commercial gains.
- Viticulture. Cultivation of grapes.
- Horticulture. Growing of vegetables, fruits or flowers for commercial use.
Question 3.
What is Sedentary Agriculture?
Answer:
When a farmer practises settled agriculture at a fixed place, it is called sedentary agriculture. Crops can be grown every year at the same field. Organic fertilizers and chemical fertilizers are used to increase the fertility of the soil.
Question 4.
What is mixed farming?
Answer:
In mixed farming, foodgrains, fruit, vegetables are grown along with cattle farming. Fisheries and. bee-hiving is also done. It increases the income of farmers.
![]()
Question 5.
What is the main characteristic of plantation farming?
Answer:
Crops are grown on large farms. Tea, coffee, rubber are plantation crops which give yield for many years.
Question 6.
Enlist the fibre crops and the beverage crops.
Answer:
Fibre Crops. Cotton, jute, flax.
Beverage Crops. Tea, coffee, cocoa.
Question 7.
Why the people of rich countries prefer wheat to rice?
Answer:
Wheat contains protein, carbohydrate and vitamins. Therefore, wheat is preferred to rice.
Question 8.
State the conditions of growth, temperature, rainfall and land required for maize.
Answer:
- Temperature: 18°C – 27°C, Frost free season.
- Rainfall: 50 cm to 100 cm.
- Land: Level or rolling.
![]()
Question 9.
What are oilseeds? What is their importance?
Answer:
The seeds which provide oil are called oilseeds. These include til, sunflower, rapeseed, etc. These provide us food and meet our daily needs.
Question 10.
Which sources provide fibre? For which purpose fibre from sheep is used?
Answer:
Fiber is obtained from plants and animals. Wool from sheep is used for woollen clothes.
Question 11.
What is the use of cotton fibre?
Answer:
Cotton fibre is used as a raw material for textile industry. It makes fight and strong clothes.
Question 12.
Explain the term ‘farm system’.
Answer:
Agriculture or farming or cultivation is s system called farm system.
- Inputs. Include seeds, fertilisers, water, machinery, and labour.
- Operations. Ploughing, sowing, irrigation, weeding, and harvesting.
- Outputs. Crops, wool, dairy, products, poultry, etc.
Question 13.
Name the main states producing cotton. Account for large production in these states.
Answer:
Maharashtra, Gujarat and Andhra Pradesh produce more than 60% cotton of India. The large production is due to fertile black soils in these states.
Question 14.
Why is tea grown on hill slopes?
Answer:
Tea needs uniform supply of water throughout the year. Water should not stagnate in the roots of tea bush. Hill slopes are well-drained.
Question 15.
How is coffee powder prepared? Which element of it produces excitement in our bodies?
Answer:
Coffee seeds are dried, roasted and grinded to make powder. It contains Caffeine which produces excitement in our bodies.
Question 16.
How is coffee plant grown?
Answer:
Coffee plant is grown in nurseries. After six months, it is transplanted in fields. It starts giving fruit after 3-4 years.
Question 17.
Agricultural development is uneven in different parts. Give one example.
Answer:
Many parts of Africa are not agriculturally developed. But in U.S.A., agriculture is a commercial and profitable occupation.
![]()
Question 18.
What is Green Revolution?
Answer:
The increase in agricultural production by introducing scientific methods like; new varieties of seeds, use of fertilizers and good water supply is called green revolution. The increase was in the yields of certain crops like wheat and rice.
Question 19.
Which activities are included in Agriculture?
Answer:
Dairy farming, poultry, honey bee keeping, pisciculture, gur making, flour milks, floriculture all occupations are a part of agriculture.
Question 20.
State two characteristics of Extensive farming.
Answer:
- Size of farms is very large.
- Yield per acre is less and machines are used for agriculture.
Question 21.
What is the position of Punjab in production of rice?
Answer:
Per hectare yield of rice in Punjab is the highest in India. Punjab produces about 12.2 per cent of total rice of the country. Punjab ranks second in rice production.
Question 22.
If a person has cultivated crops like Tea, Coffee and Cocoa, then identify the types of these crops.
Answer:
Beverage crops.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Discuss the main characteristics of shifting cultivation.
Answer:
Shifting Agriculture. In this type of agriculture, first of all, a piece of forest land is cleared by felling trees and burning of trunks and branches. After the land is cleared, crops are grown for two to three years and then the land is abandoned as the fertility of the soil decreases. The farmers then move to new areas and the process is repeated. Dry paddy maize, millets and vegetables are the crops commonly grown in this type of farming. The per hectare yield is low.
Question 2.
Distinguish between dry land farming and wetland farming.
Answer:
Dry land farming. It is practised in areas where the rainfall is low and irrigation facilities are inadequate. Here, emphasis is laid on the conservation of moisture and on crops like jowar, bajra and pulses, which need less water. In dry farming, only one crop is grown in the kharif season.
Wet land farming. It is practised in the areas where rainfall is more than 200 cm per year. It is mostly practised in S.E. Asia. In India, it is practised in West Bengal, Orissa and coastal areas. The main crop is Rice, Sugarcane. Multiple Cropping is done in different seasons.
Question 3.
Distinguish between Individual and Cooperative farming.
Answer:
Individual farming. In this farming, the farmer is the owner of the land. The use of tools, fertilizers and management is in the hands of the farmer. The total income is the personal income of the farmer.
Co-operative farming. In this, the Govt, is the owner of the land. A part of the income goes to the government as tax. The rest of income is divided among the labourers and farmers. This type of agriculture was practised in U.S.S.R.
Question 4.
Write a note on Collective farming.
Answer:
In this type, the farmers join together to form a collective organisation. All the farmers cultivate their own land. The accounts of production is in the hands of the organisation. The decisions are taken for the benefit of farmers. All the profit is distributed among farmers in the ratio of their lands. In India, this type of farming is encouraged by the government.
![]()
Question 5.
Describe the favourable conditions for growth of Rice.
Answer:
- Temperature: 20°C to 30°C.
- Rainfall: 100-200 cm (Irrigation in dry areas)
- Soils: Alluvial, clay, loamy and delta or black soils.
- Land: Level land suitable for irrigation.
- Labour: Cheap and skilled labour.
Question 6.
Describe the cultivation of maize in India and world.
Answer:
Maize: Maize is known as Makka in India, corn in the United States of America, India and Europe. It originated from the American continent. It was introduced in Europe by Columbus and other explorers. It was Native Americans who taught colonizers how to grow maize.
Maize is used as foodgrains and as fodder. It is grown mainly in Russia, Canada and parts of South America. The United States of America is the largest producer. China is the second-largest producer followed by Brazil, Mexico, Argentina and India.
India: Most of Maize is grown in Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka and Rajasthan. U.P, Himachal Pradesh, J & K, Maharashtra, Punjab and Gujarat are also the producers of Maize. In Punjab, Rupnagar, Amritsar, Hoshiarpur, Jalandhar produce maize.
Question 7.
Write a note on the agricultural development of Punjab.
Answer:
Punjab is one of the leading states of India in agriculture. This is due to :
- 58% people are engaged in agriculture. 35% of income comes from agriculture.
- Soils are fertile. Fertilizers are used.
- Mulitple cropping is done. Better seeds are used. Tractors and Harvesters are used.
- Irrigation is the basis of agriculture.
- Pesticides are used to protect crops.
- Machines are used on large farms.
Question 8.
Why agriculture is called the main stay of the Indian Economy?
Answer:
Indian’s main occupation is agriculture. Two-thirds of India’s population is engaged in agriculture. Agriculture is the main stay of the Indian Economy. Agriculture provides food to the teeming millions in India. It sustains 2/3 of our population. It provides raw material to agro-based industries. Agriculture along with forests and fisheries form 45% of our total national income. Our industrial structure is being built on the broad foundation of Indian agriculture. It is also a great earner of foreign exchange.
Question 9.
What are the main features of Agricultural development in India?
Answer:
- India is a vast country. More than 70% of its population is dependent upon agriculture for livelihood.
- The major foodgrains produced in India are rice and wheat.
- Most of farms are not more than one hectare of land.
- India is self-sufficient in the production of foodgrains .
- In India, half of the total cultivable land is irrigated.
Question 10.
What has been the impact of mechanisation on agriculture?
Answer:
The earlier farmers used simple tools. Gradually on-driven ploughs were introduced. But, now in modern times the techniques have been changed. Now in developed countries all farm operations have been mechanised. It has reduced the number of people engaged in agricultural work. Many people can now work in industries and services.
![]()
Question 11.
What is Agriculture?
Answer:
The word Agriculture is derived from two Latin words ‘agri’ and ‘culture’. ‘Agri’ means’soil and ‘culture’ means cultivation or tilling. Agriculture hence refers to the cultivation of soil for growing crops and rearing of livestocks.
Question 12.
Name the factors influencing agriculture.
Answer:
The factors which influence agriculture are :
- Relief
- Soil conditions
- Temperature
- Rainfall.
Question 13.
What is plantation agriculture?
Answer:
It is special type of commercial farming which requires large amount of labour, technical efficiency, very large estates and capital. In this type of agriculture a simple crop of tea, rubber, coffee, sugarcane, cashew, banana or cotton is grown. The produce may be processed on the farm itself or in nearby factories. A well developed transport . network is also required.
Tropical regions of the world are major plantation areas. Rubber in Malayasia, coffee in Brazil, tea in India and Sri Lanka are some examples.
Question 14.
Name the different varieties or crops in India.
Answer:
- Cereals
- pulses and oilseeds
- Fibre crops
- Beverage crops
- Cash crops
Question 15.
Discuss the different types of fibres.
Answer:
Vegetable fibers are obatained from seeds, barks, leaves and fruit cases.
Animals fibres are produced from insects; such as silkworm and animals such as camels, sheep, goats, yaks, Hamas, rabbits, guanacos, alpacas, vicunas and reindeers.
Mineral fibres such as glass is made from silica sand.
Synthetic fibres are derived from chemical treatment of natural cellulose, which is i made from wood pulp.
Question 16.
What do you know about commercial agriculture?
Answer:
In this type of agriculture the main aim is to produce the crop for sale in the market. It can be intensive or extensive agriculture. The farmers try to keep the cost of production low. The framework is done by machines. This type of agriculture is practised in the prairies of North America, Pampas of South America, Steppes of Russia, Western Europe and in some parts of India.
Question 17.
Write the features of Intensive Subsistence Agriculture.
Answer:
It is a type of subsistence agriculture and its features are :
- Intensive subsistence agriculture is done on small plot with simple tools.
- Done by farmer and his family as labour.
- Produce is used mainly by farmer so food grains are grown.
- Rice is the main crop. Other crops are wheat, maize, pulses etc are cultivated.
- Done mainly in thickly populated areas of south, southeast and east Asia.
![]()
Question 18.
Describe the main characteristics of shifting agriculture.
Answer:
- In shifting agriculture, a plot of land is cleared by felling trees and burning them.
- The ashes are then mixed with soil which works as a fertilizer.
- After the soil loses its fertility, the land is abandoned. Cultivators move to a new plot.
- It is practised in areas of heavy rainfall and quick generation of vegetation.
- It is mainly done in Amazon basin, Tropical Africa, Southeast Asia and northeast India.
- Crops like maize, yam, potatoes, and cassava are grown. This is also known as the ‘slash and burn’ agriculture.
Question 19.
Distinguish between :
(i) Subsistence farming and Commercial farming
Answer:
| Subsistence Farming | Commercial Farming |
| 1. The practice of farming in which the crops are grown for home consumption by the farmer. | 1. The practice of farming in which crops are grown for sale in the market or trade. |
| 2. It is practised on small farms with simple tools and old technology. | 2. It is practised on large farms with modern technology. |
| 3. For example The production of wheat in some parts of country. | 3. For example The production of sugarcane in U.P. |
(ii) Intensive farming and Extensive farming.
Answer:
| Intensive Farming | Extensive Farming |
| 1. Production is increased by using higher inputs and better agricultural techniques. | 1. Production is increased by bringing more and more land under cultivation. |
| 2. This is practised in areas which are thickly populated. | 2. This is practised in areas which are thinly populated. |
| 3. This is practised in areas where there is less land available. | 3. This is done in areas where abundant land is easily available. |
| 4. Livestock farming is little developed due to poor pastures. | 4. Livestock farming Supplements agriculture due to availability of grasslands. |
| 5. Farms are small in size. | 5. Farms are very large in size. |
Fill in the blanks :
Question 1.
Shifting agriculture is also known as _________
Answer:
Slash and burn
Question 2.
_________, soil and climate are vital factors for agricultural activities.
Answer:
Topography
Question 3.
Advertising is an example of _________ activities.
Answer:
Tertiary
![]()
Question 4.
Jute is grown intensively in _________ and _________
Answer:
India, Bangladesh
Question 5.
Coarse grains are also called _________
Answer:
Millets.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the importance of cotton? Explain the conditions of growth and areas of production of cotton and jute in India.
Answer:
Cotton. Cotton has been called ‘the universal fibre’. It is one of the most important fibres of all the fibres. It forms the basis of cotton textile industry. Cotton is the leading fibre crop of India. It is known from the writings of Herodotus that cotton has been in use in India since 3000 B.C.
Geographical Conditions of Growth
- Temperature. Cotton needs uniformly high summer temperature between 22°C to 32°C. It requires a warm climate with bright sunshine. Frost is harmful to cotton plants.
- Rainfall. Cotton needs light to moderate rainfall between 50 to 100 cm.
- Irrigation. In arid treas, irrigation is used. It increases the yield per hectare as in Punjab.
- Soils. Cotton grows best on rich, well-drained loamy soils or lava soils.
Types of Cotton:
- The long-staple cotton. This cotton has a length of 25 mm and above.
- The medium staple cotton. This cotton has a staple length between 18 mm to 25 mm.
- The short-staple cotton. This cotton has a fibre length of less than 18 mm.
Area of Cultivation
Southern India produces more cotton than Northern India. Gujarat is the leading
producer of cotton in India with a production of 25% of the total production in the country.
1. Black cotton soil region. This is the chief cotton-growing area of India on the ‘lava soil’ of N.W. Deccan Plateau. Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Madhya Pradesh are the major cotton-producing states.
2. Red soil region. Medium staple cotton is grown in the red soil areas including the states of Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh. The yield is low.
3. Alluvial soil region. Long-staple cotton is grown on the alluvial soils of Northern Plains. The states of Punjab, Haryana, and Rajasthan are the important producers. Punjab has the highest yield per hectare due to its warm climate, fertile soils, and facilities of irrigation.
World Production. The U.S.A. is the leading producer of cotton in the world. China ranks second. India ranks third. Other main producers are Russia, Mexico, Egypt, Sweden, and Pakistan. Egypt is known for long-staple cotton. In the U.S.A., cotton production is decreasing.
![]()
Question 2.
Describe the different types of Farming.
Answer:
1. Shifting Agriculture. This farming method is practised by primitive people living in dense forests. The land is prepared by felling trees and burning the trees. People move from one area to another when the soil loses its fertility.
2. Subsistence Farming. In this method, farmers use primitive tools to cultivate their lands. Farmers in these regions produce agricultural goods, which are just sufficient to satisfy their own needs.
3. Commercial Farming. When farmers use modern tools and equipment such as tractors, threshers, winnowers, etc., and produce crops mainly to sell them in the market, it is called commercial farming.
4. Extensive Farming. This method is practised in countries where the population is sparse and the availability of land is more. Farmers use machines to a great extent, as the size of land holdings is large.
5. Intensive Farming. In this method of farming, the same piece of land is used throughout the year continuously. The soil is also very fertile. Farmers use more labourers, seeds that can yield more, better manures, and ensure a regular water supply.
6. Irrigation Farming. It is the type of farming, which mainly depends on irrigation through canals, wells, and tanks. Farmers cultivate their lands throughout the year.
Some of the important river valleys of the world where this method is followed are, the Ganga valley and the Indus valley in India, the Nile valley in Egypt, the Xi Jiang valley in China, Missouri, and San Joaquin valley in the United States of America.
7. Rainfed Farming. In the regions where the rainfall is not only seasonal but also scanty, farmers use different measures to cultivate their lands and use the scarce amount of rainwater efficiently. This is known as rainfed farming.
8. Mono-crop Farming. When the farmers specialize in the production of a single crop or if the soil and other natural factors allow farmers to cultivate only one crop that farming is known as one-crop or mono-crop farming.
9. Double and Multi-crop Farming. When two or more crops are cultivated in a plot of land, it is known as double or multi-crop farming. In this method, farmers apply scientific methods—use seeds that can give high yield, and apply manures in an appropriate manner.
