Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class Science Book Solutions Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
PSEB 8th Class Science Guide Coal and Petroleum Textbook Questions and Answers
Exercises
Question 1.
What are the advantages of using CNG and LPG as fuels?
Answer:
Advantages of LPG:
LPG is considered to be a better fuel because of the following reasons:
- LPG has a high calorific value. Its calorific value is about 50 kJ/g. This means that when 1 gram of LPG burns in a gas stove, it produces about 50 kilo-joules of heat energy.
- It burns with a smokeless flame and so does not cause pollution.
- LPG does not produce any poisonous gases on burning.
- LPG is easy to handle and convenient to store.
- It undergoes complete combustion.
- LPG is a very neat and clean domestic fuel.
Advantage of CNG:
It does not cause air pollution.
Question 2.
Name the petroleum product used for surfacing of roads.
Answer:
Bitumen.
![]()
Question 3.
Describe how coal is formed from dead vegetation. What is this process called ?
Answer:
Formation of coal from dead vegetation:
About 300 million years ago, the forests got buried under the soil. They were compressed by soil deposits and temperature also rose as they sank deeper and deeper. Due to this high temperature and pressure coal was formed from dead vegetation by process of carbonisation.
Question 4.
Fill in the blanks.
(a) Fossil fuels are …………….. , …………… and ……………
(b) Process of separation of different constituents from petroleum is called ………………… .
(c) Least polluting fuel for vehicle is ………………..
Answer:
(a) Coal, petroleum, natural gas.
(b) refining.
(c) CNG (Compressed natural gas).
Question 5.
Tick True/False against the following statements.
(a) Fossil fuels can be made in the laboratory.
Answer:
False
(b) CNG is more polluting fuel than petrol.
Answer:
False
(c) Coke is almost pure form of carbon.
Answer:
True
(d) Coal tar is a mixture of various substances.
Answer:
True
(e) Kerosene is not a fossil fuel.
Answer:
True
Question 6.
Explain why fossil fuels are exhaustible natural resources.
Answer:
Fossil fuels are formed from remains of dead organisms and it took million of years to get these organisms converted into fuels. The known reserves of these fuels are limited and so, these are exhaustible fuels.
Question 7.
Describe the characteristics and uses of coke.
Answer:
Characteristics of Coke:
- It is tough, porous and black substance.
- It is pure form of carbon.
Uses of Coke:
- It is used to manufacture artificial graphite.
- It is used in manufacture of calcium carbide required for manufacture of acetylene gas. Acetylene gas is the basic raw material for manufacture of acetic acid and P.V.C.
- It is used in manufacture of water gas and producer gas used as an important fuel.
- Water gas is not single gas. It is a mixture of equal volumes of carbon monoxide and hydrogen.
- Producer gas is produced by passing controlled amount of air over red hot coke. Producer gas is in fact a mixture of one part of carbon monoxide and two parts of nitrogen by volume.
- It is used to extract metals like copper, iron, zinc, lead, tin etc., from their ores.
- Since coke does not produce any smoke, hence it is used as a household fuel.
Question 8.
Explain the process of the formation of petroleum.
Answer:
Formation of Petroleum.
Petroleum is formed from the bacterial decomposition of the remains of animals and plants which got buried under the sea millions of years ago. When these organisms died, they sank to the bottom and got covered by sand and clay. Over a period of millions of years, these remains got converted into petroleum oil by heat, pressure and catalytic action. The hydrocarbons formed rose through porous rocks until they were trapped by impervious rocks forming an oil trap. Natural gas is found above the surface of petroleum oil.
![]()
Question 9.
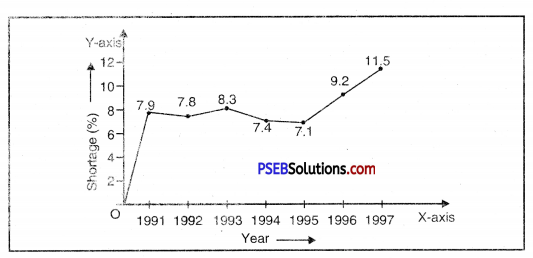
The following table shows the total power shortage in India from 1991-1997. Show the data in the form of a graph. Plot shortage percentage for the years on the Y-axis and the year on the X-axis.
| S. No. | Year | Shortage % |
| 1 | 1991 | 7.9 |
| 2 | 1992 | 7.8 |
| 3 | 1993 | 8.3 |
| 4 | 1994 | 7.4 |
| 5 | 1995 | 7.1 |
| 6 | 1996 | 9.2 |
| 7 | 1997 | 11.5 |
Answer:
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Coal and Petroleum Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Gurmeet’s mother uses cylinder to cook chapatti on gas burner at home. Name the gas in cylinder.
(a) Air
(b) Oxygen
(c) L.P.G.
(d) C.N.G.
Answer:
(c) L.P.G.
Question 2.
Monika read in a newspaper that a man became unconscious because of burning coal in a closed room. The teacher told her that during burning coal, a gas is produced which causes death of a person. Name
this gas.
(a) Oxygen
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Carbon-monoxide
(d) Hydrogen.
Answer:
(c) Carbon-monoxide.
Question 3.
The example of fossil fuel is:
(a) Air
(b) Sunlight
(c) Water
(d) Coal
Answer:
(d) Coal
Question 4.
Which out of the following is used as fuel in households ?
(a) Diesel
(b) Petrol
(c) Kerosene oil
(d) Bitumen.
Answer:
(c) Kerosene oil.
Question 5.
The purest form of carbon is:
(a) Coaltar
(b) Coal gas
(c) Diamond
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(c) Diamond.
Question 6.
Which out of the following is the least pollution causing fuel ?
(a) Petrol
(b) Coal
(c) Kerosene oil
(d) C.N.G.
Answer:
(d) C.N.G.
![]()
Question 7.
Which is the natural solid fuel ?
(a) Coal
(b) Coke
(c) L.P.G.
(d) Coal tar
Answer:
(a) Coal.
Question 8.
Which among the following is the best domestic fuel ?
(a) Petrol
(b) Coal
(c) Kerosene oil
(d) C.N.G.
Answer:
(d) C.N.G.
Question 9.
Which of the following is the fossil fuel ?
(a) Air
(b) Hydrogen gas
(c) Water
(d) Coal.
Answer:
(d) Coal.
Question 10.
Which out of the following is the non renewable source of energy ?
(a) Air
(b) Sunlight
(c) Coal
(d) Forests
Answer:
(c) Coal
Question 11.
Which out of the following is called black gold ?
(a) Diesel
(b) Coal
(c) Bitumen
(d) Petroleum.
Answer:
(d) Petroleum.
Question 12.
Which out of the following is limited natural resource ?
(a) Air
(b) Sunlight
(c) Natural gas
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(c) Natural gas.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name some natural materials.
Answer:
Air, water, soil, forests, minerals etc.
![]()
Question 2.
Name some man-made materials.
Answer:
Glass, cement, clothes, houses etc.
Question 3.
Define the term fossil fuel. Name three fossil fuels.
Answer:
Fossil fuels.
These are the fuels which are formed in nature from the dead remains of organisms over millions of years ago.
Examples. Coal, natural gas, petroleum etc.
Question 4.
How is coke prepared ?
Answer:
Coke is prepared by the destructive distillation of coal. The gases, and other substances present in coal are given off on heating. The black residue left behind is coke.
Question 5.
Name two products formed by Destructive distillation of Coal.
Answer:
- Coal gas
- Coal tar.
Question 6.
Name some products formed as a result of Fractional distillation of Petroleum.
Answer:
Asphalt, petrol, diesel oil, paraffin wax, fuel oil, kerosene oil.
Question 7.
Name three products of petroleum.
Answer:
Fertilizer, Insecticide, Artificial rubber.
Question 8.
What will happen if fossil fuels are used up at a fast rate ? Give reasons.
Answer:
Fossil fuel will get exhausted because the earth cannot recreate them rapidly.
![]()
Question 9.
Coal, petroleum, natural gas are example of which type of fuel ?
Answer:
Fossil fuel.
Question 10.
What is petroleum ?
Answer:
Petroleum. Petroleum is thick viscous crude oil with an unpleasant odour.
Question 11.
Which type of rocks store petroleum in them ?
Answer:
Impervious (non-porous) rocks.
Question 12.
Which process is used for refining petroleum ?
Answer:
Fractional distillation.
Question 13.
How is petroleum gas produced ?
Answer:
It is produced in the form of uncondensed gas during fractional distillation of crude petroleum oil.
Question 14.
What is the use of bitumen ?
Answer:
Road surfacing.
Question 15.
Which liquid fuel is used in stoves, lamps and jet air-crafts ?
Answer:
Kerosene oil.
Question 16.
Which product of petroleum is used for dry cleaning ?
Answer:
Petrol.
![]()
Question 17.
Name few exhaustible natural resources.
Answer:
Forests, wild life, minerals, coal etc.
Question 18.
Give examples of in-exhaustible natural resources.
Answer:
Air, water, sunlight etc.
Question 19.
Which natural material is available at a blacksmith’s place ?
Answer:
Coal.
Question 20.
What is main component of coal ?
Answer:
Carbon.
Question 21.
Which process converts dead vegetation into coal ?
Answer:
Carbonisation.
Question 22.
What happens when coal is heated or burn in air ?
Answer:
Carbondioxide gas is released.
Question 23.
Which condition is necessary for destructive distillation ?
Answer:
Absence of oxygen.
Question 24.
What is the latest use of coal-gas ?
Answer:
As a source of heat energy.
![]()
Question 25.
What is destructive distillation ?
Answer:
Destructive Distillation – The process of heating coal in the absence or limited supply of air is called destructive distillation.
Question 26.
What are hydrocarbons ?
Answer:
Hydrocarbons. The compounds of carbon and hydrogen are called Hydrocarbons.
Question 27.
What are Petrochemicals ?
Answer:
Petrochemicals.
These are the substances obtained from Petrol and Natural gas. These are largely used for the manufacture of detergents, synthetic fibres and plastics etc.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write two differences between Exhaustible and In-exhaustible Resources.
Answer:
Differences between Exhaustible and In-exhaustible Natural Resources.
| Exhaustible Natural Resources | In-exhaustible Natural Resources |
| 1. Limited quantity in nature. | 1. Limitless or unlimited quantity in nature. |
| 2. Gets exhausted on consumption.
Examples: Forests, wild life. |
2. Cannot exhaust on consumption i.e. can be retrieved back.
Examples: Air, Sun energy. |
Question 2.
Where is petroleum found in India ?
Answer:
In India, petroleum is found in the states of Gujarat and Assam. It is also obtained from reservoirs buried deep under the sea bed near Mumbai. This oil-bearing region is called Bombay-High. Recently, oil has also been discovered in Godavari and Kaveri basins.
Question 3.
What are the major products of Petroleum refining ?
Answer:
During refining of petroleum following fractions are produced:
- Natural gas, Petrol,
- Naphtha,
- Kerosene oil,
- Gas oil (diesel),
- Lubricating oil/waxes,
- Fuel oil and
- Bitumen.
Question 4.
What are the products of coal ?
Answer:
Coal on heating in the absence of air gives coal gas, coal tar, and coke. Coal gas is also a good fuel. Coal tar gives important chemicals such as benzene, toluene, naphthalene, anthracene etc.
![]()
Question 5.
What is coal gas ? How is it formed ? Give its uses.
Answer:
Coal Gas. Coal gas is a mixture of methane, hydrogen and carbon monoxide.
When coal is heated in the absence of air, coal gas is formed.
Uses.
- It is used as a fuel.
- It is used for providing reducing atmosphere in metallurgical operations.
Question 6.
Give few uses of coal.
Answer:
Uses of Coal:
- As a fuel to cook food.
- To produce steam to run an engine.
- To produce electricity in Thermal Power plants.
- As a fuel in industry.
Question 7.
What is coal tar ? What are its uses ?
Answer:
Coal Tar. Coal tar is a black thick liquid with unpleasant smell. It is a mixture of about 200 substances, which are used as starting materials for the manufacturing of various daily need ithins such as paints, dyes, plastics, films, perfumes, explosives, drugs etc.
Coal tar is also used for road surfacing.
Question 8.
Name at least three constituents of petroleum and give their uses.
Answer:
Constituents of Petroleum
- Petrol
- Paraffin wax
- Diesel.
Uses of Petroleum:
- Petrol is used as a motor fuel and aviation fuel. It is also used for dry cleaning.
- Paraffin wax is used for making ointments, candles, vaseline etc.
- Diesel is used as a fuel for heavy motor vehicles and electric generators.
Question 9.
Define natural resource.
Answer:
Natural Resource. The resource that is obtained from nature is called natural resource.
Question 10.
What are the characteristics of a good fuel ?
Answer:
Characteristics of Good Fuel:
- It should be easily available.
- It should be cheap.
- It should be clean and should not produce poisonous gases and ash after burning.
- It should produce more energy.
- It should be easy to transport and store.
![]()
Question 11.
What is the difference between coal and coke ?
Answer:
Differences between Coal and Coke
| Coal | Coke |
| 1. It is a non-crystalline form of carbon | 1. It is an amorphous form of carbon. |
| 2. It is obtained bj? death and decay of plants which remain buried under the earth for years together. | 2. It is obtained by heating soft coal in the absence or limited siuply of air. |
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are fossil fuels ? How are they formed ? Why are they called non¬renewable sources of energy ?
Answer:
Petroleum, natural gas, coal etc., are main forms of fossil fuels. Millions of years ago, remains of animals, plants got buried under the earth before dinosaurs. These remains are called fossils. They remained inside the earth under huge pressure and high temperature in the absence of oxygen, these remains got converted into fossil fuel.
Fossils as a source of non-renewable source of energy.
Fossils were formed several hundred years ago under the earth. Man uses these for his various activities. These cannot be regained after use. So they are called non-renewable source of energy.
Question 2.
Describe the formation of
(a) Coal
(b) Petroleum.
Answer:
(a) Coal Formation.
Coal is believed to be formed from fossils which got buried inside the earth during earthquakes, volcanic eruptions etc., which occurred about 300 million years ago. These fossils were covered with sand, clay and water. In the absence of air and under high temperature and high pressure inside the earth, the fossils got converted into coal. This process of conversion of plants and animals buried inside the earth under high temperature and pressure to coal is called carbonisation. It is a very slow process and may have taken thousands of years.
(b) Formation of Petroleum.
It is believed that petroleum was formed and preserved in its crude state in the earth from the remains of dead microscopic marine plants (phytoplankton) which settled in muddy sediments at the bottom of sea millions of years ago. Prolonged sedimentation and cooking of these organic debris under pressure in the presence of natural catalysts, converted them into petroleum . For this reason, petroleum is also called fossil fuel.
Question 3.
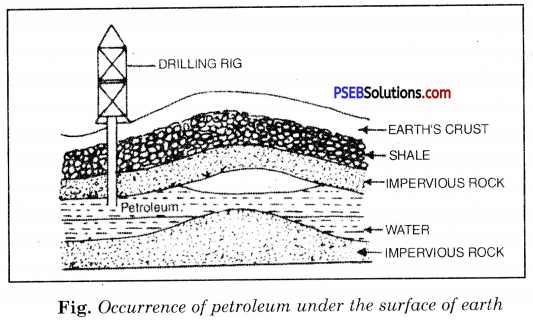
What is petroleum? How does it occur? How is it mined?
Answer:
Petroleum.
It is dark coloured viscous, foul-smelling, oily liquid. It is a complex mixture of several solid, liquid, and gaseous hydrocarbons mixed with water, salt, and earth particles.
Occurrence of Petroleum.
Petroleum occurs deep down under the earth between two impervious rocks (non-porous rocks) as shown in Fig. Natural gas occurs above the petroleum oil trapped under rocks.
The crude petroleum is obtained by drilling a hole into the earth’s crust and sinking pipes into it. When the pipe reaches the oil deposit, natural gas comes out with great pressure. After the pressure has subsided, the crude oil is pumped out of the oil well. This process of obtaining crude oil from its sources is called mining.
