Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class Science Book Solutions Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
PSEB 8th Class Science Guide Materials: Metals and Non-Metals Textbook Questions and Answers
Exercises
Question 1.
Which of the following can be beaten into thin sheets?
(a) Zinc
(b) Phosphorus
(c) Sulphur
(d) Oxygen.
Answer:
(a) Zinc.
Question 2.
Which of the following statements is correct?
(а) All metals are ductile.
(b) All non-metals are ductile.
(c) Generally, metals are ductile.
(d) Some non-metals are ductile.
Answer:
(a) All metals are ductile.
![]()
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks.
(a) Phosphorus is very ……………… non-metal.
(b) Metals are …………. conductor of heat and ……………… .
(c) Iron is ……………… reactive than copper.
(d) Metals react with acids to produce ……………………. gas.
Answer:
(a) reactive.
(b) good, electricity.
(c) more.
(d) Hydrogen.
Question 4.
Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false.
(а) Generally, non-metals react with acids.
(b) Sodium is a very reactive metal.
(c) Copper displaces zinc from zinc sulphate solution.
(d) Coal can be drawn into wires.
Answer:
(a) True
(b) True
(c) False
(d) False
Question 5.
Some properties are listed in the following Table. Distinguish between metals and non-metals on the basis of these properties. (From Board M.Q.P.)
| Properties | Metals | Non-metals |
| 1. Appearance | ||
| 2. Hardness | ||
| 3. Malleability | ||
| 4. Ductility | ||
| 5. Heat Conduction | ||
| 6. Conduction of electricity |
Answer:
Differences between metals and non-metals.
| Properties | Metals | Non-metals |
| 1. Appearance | Silvery or grey in colour. | Different coloured non-metals. |
| 2. Hardness | Solid at room temperature. | Solid, liquid or gas at room temperature and brittle. |
| 3. Malleability | Can be beaten into sheets. | Non-malleable. |
| 4. Ductility | Can be drawn into wires. | Non-ductile. |
| 5. Heat Conduction | Present. | Absent. |
| 6. Conduction of electricity | Possible. | Not Possible. |
Question 6.
Give reasons for the following :
(a) Aluminium foils are used to wrap food items.
(b) Immersion rods for heating liquids are made up of metallic substances.
(c) Copper cannot displace zinc from its salt solution.
(d) Sodium and potassium are stored in kerosene.
Answer:
(a) Aluminium foils are used to wrap food items because aluminium is malleable and less reactive to air and water.
(b) Immersion rods for heating liquids are made of metallic substances because metals are good conductors of heat and electricity.
(c) Copper is less reactive than zinc. As a result it cannot replace zinc from its salt solution.
(d) Sodium and potassium are very reactive metals. They react with air and water to form respective oxides and hydroxides. So, they are kept in kerosene.
Question 7.
Can you store lemon pickle in aluminium utensil ? Explain.
Answer:
No. Lemon pickle cannot be stored in aluminium utensils because acid present in lemon pickle reacts with aluminium to produce poisonous chemicals, which can cause food poisoning or other health hazards.
Question 8.
Match the substances given in Column A with their uses given in Column B.
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) Gold | (a) Thermometers |
| (ii) Iron | (b) Electric wire |
| (iii) Aluminium | (c) Wrapping food |
| (iv) Carbon | (d) Jewellery |
| (v) Copper | (e) Machinery |
| (vi) Mercury | (f) Fuel |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) Gold | (d) Jewellery |
| (ii) Iron | (e) Machinery |
| (iii) Aluminium | (c) Wrapping food |
| (iv) Carbon | (f) Fuel |
| (v) Copper | (b) Electric wire |
| (vi) Mercury | (a) Thermometers. |
![]()
Question 9.
What happens when
(a) Sulphuric acid is poured on a copper plate ?
(b) Iron nails are placed in copper sulphate solution ?
Write word equations of the reactions involved. (From Board M.Q.P.)
Answer:
(a) When sulphuric acid is poured on copper plate, Hydrogen gas is given out.

(b) When iron nails are placed in copper sulphate solution, iron displaces copper from its salt to form iron sulphate

Question 10.
Saloni took a piece of burning charcoal and collected the gas evolved in a test tube.
(а) How will she find the nature of the gas ?
(b) Write down word equations of all the reactions taking place in this process.
Answer:
(a) To test the nature of the gas:
1. Take blue/red litmus solution turnwise into the jar of gas collected. It will turn blue litmus red while red litmus will remain unaffected. This shows that gas is acidic in nature.
2. Add some water to the jar. The liquid for turns blue litmus red showing acidic nature of the gas.
(b) When a charcoal is burnt, it reacts with oxygen to form an acidic oxide called
carbon dioxide.

The acidic oxide, carbondioxide, dissolves in water to form an acid called Carbonic acid
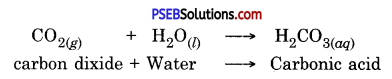
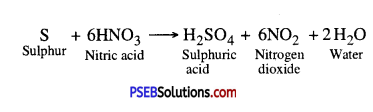
Question 11.
One day Reeta went to a jeweller’s shop with her mother. Her mother gave an old gold jewellery to the goldsmith to polish. Next day when they brought the jewellery back, they found that there was a slight loss in its weight. Can you suggest a reason for the loss in weight ?
Answer:
Jewellers usually use a chemical solution named aquaregia for cleansing the jewellery. This solution is capable of dissolving gold in it. So, loss in weight is found.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
In order to keep the flow of electricity continue in circuit, which of the following items should be used in place of iron nail in the given circuit. (From Board M.Q.P.)
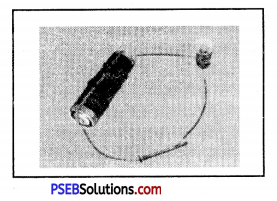
(a) Graphite
(b) Plastic
(c) Wood
(d) Rubber.
Answer:
(a) Graphite.
Question 2.
Sodium metal is stored ………………….
(a) In water
(b) In kerosene oil
(c) In Air
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) In kerosene oil.
Question 3.
When strip of iron is placed in moist air then after some days a layer is deposited over it which has colour:
(a) Green
(b) Red
(c) Dirty
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Red.
Question 4.
Which of the following statements is correct ?
(a) All metals are ductile
(b) All non-metals are ductile.
(c) Generally metals are ductile
(d) Some non-metals are ductile.
Answer:
(c) Generally metals are ductile.
![]()
Question 5.
Which of the following is a non-metal ?
(a) Iron
(b) Carbon.
(c) Gold
(d) Calcium.
Answer:
(b) Carbon.
Question 6.
Phosphorus is stored in:
(a) Water
(b) Air
(c) Oil
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(a) Water
Question 7.
The metal which is found in liquid form is:
(a) Copper
(b) Silver
(c) Mercury
(d) Sodium.
Answer:
(c) Mercury.
Question 8.
Which metal is a good conductor of electricity and heat ?
(a) Sodium
(b) Potassium
(c) Copper
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(c) Copper.
Question 9.
The best conductor of electricity is:
(a) Copper
(b) Lead
(c) Aluminium
(d) Silver.
Answer:
(d) Silver
Question 10.
Red colour makes the solution of litmus blue because of:
(a) Metal oxide
(b) Sulphur dioxide
(c) Carbondioxide i
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(a) Metal oxide.
Question 11.
Non-metal on the base of hardness is:
(a) Iron
(b) Aluminium
(c) Copper
(d) Coal.
Answer:
(d) Coal.
![]()
Question 12.
Which of the following gas is released when a metal react with acids ?
(a) Oxygen
(b) Hydrogen
(c) Sulphur dioxide
(d) Nitrogen
Answer:
(b) Hydrogen.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name the property because of which metals can be beaten into thin layers or sheets.
Answer:
Malleability.
Question 2.
What is ductility ?
Answer:
Ductility. The property by which metals can be drawn into wires, is called ductility.
Question 3.
Name the most ductile metal.
Answer:
Silver.
Question 4.
Name the metal which exists in the liquid state.
Answer:
Mercury.
Question 5.
Name one metal which is poor conductor of electricity.
Answer:
Lead.
Question 6.
Which metal is used in thermometer ?
Answer:
Mercury.
![]()
Question 7.
Which metal and non-metal is liquid at ordinary temperature ?
Answer:
Metal – Mercury
Non-Metal – Bromine.
Question 8.
Write two properties of metals.
Answer:
Malleability and Ductility.
Question 9.
Name two metals which are good conductors of both heat and electricity.
Answer:
Copper and Aluminium are good conductors of both heat and electricity.
Question 10.
Name three metals which occur in the native state.
Answer:
- Silver
- Gold
- Platinum occur in the native state.
Question 11.
List two metals which are easy to cut.
Answer:
- Sodium
- Potassium.
Question 12.
What is that property, which allows metals to be drawn into wires, called ?
Answer:
Ductility.
Question 13.
Which metals are used to make electric wires ?
Answer:
Copper and Aluminium.
![]()
Question 14.
Which metal is constituent of haemoglobin ?
Answer:
Iron.
Question 15.
Write a chemical reaction of Iron with Oxygen.
Answer:
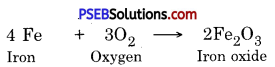
Question 16.
Write the chemical equation for the reaction of Zn with Oxygen.
Answer:

Question 17.
The set of metals in order of their increasing chemical reactivity is given below:
Silver, copper, lead, iron, zinc, magnesium and sodium.
(a) Which of the above metals is stored in kerosene ?
(b) Which metals will react with cold water ?
(c) Which gas will be liberated when metals react with cold water ?
(d) Which of the metals will react with oxygen when heated ?
(e) Which of the metals becomes black in the presence of hydrogen sulphide, H2S ?
(f) Which of the metals burns with white bright flame in oxygen ?
Answer:
(a) Sodium
(b) Sodium and Magnesium
(c) Hydrogen
(d) Magnesium
(e) Silver
(f) Magnesium.
Question 18.
Name five metals which are used in daily life.
Answer:
Metals used in daily life.
- Aluminium
- Iron
- Copper
- Zinc
- Tin.
Question 19.
Name five metals which are used in our industrial processes.
Answer:
Metals used in Industrial Processes.
- Aluminium
- Iron
- Copper
- Nickel
- Zinc.
Question 20.
Why do Sodium, Zinc, Magnesium and Aluminium not occur in their pure state ?
Answer:
Because these react with air, water and acids.
![]()
Question 21.
Name atleast two metals which do not react with air, water and acids.
Answer:
- Gold
- Platinum.
Question 22.
Of what property, are metals used in jewellery ?
Answer:
Metallic lustre.
Question 23.
What is the colour of copper metal ?
Answer:
Eeddish-brown colour.
Question 24.
Of Iron, Copper and Magnesium, which metal can be cut easily ?
Answer:
Magnesium.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the difference between a metal and a non-metal ? What is the total number of naturally occurring elements ?
Answer:
Metals have metallic lustre, are malleable, ductile, good conductors of heat and electricity, hard and combine with oxygen to form basic oxides.
Non-metals have dull lustre, not malleable and non-ductile, bad conductors of heat and electricity, brittle and combine with oxygen to form acidic oxides. The total number of naturally occurring elements is 92.
Question 2.
Why is Potassium metal not stored in water ?
Answer:
Potassium is a reactive metal. It reacts with air even at room temperature. Also it reacts with water at room temperature and catches fire. Hence, it is not stored in water but kept under kerosene oil.
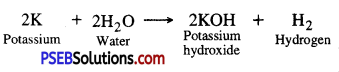
Question 3.
State two physical properties on the basis of which metals may be distinguished from non-metals.
Answer:
- Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity. Non-metals are bad conductors of heat and electricity.
- Metals have a shiny appearance, that is, they show a metallic lustre. Nonmetals have a dull lusture. They generally do not reflect light well.
![]()
Question 4.
State one chemical property which may be used to distinguish a metal from a non-metal.
Answer:
Metals when burn, combine with oxygen to form metallic oxides which are basic in nature, whereas non-metals combine with oxygen to form acidic oxides. This property can be used to distinguish a metal from a non-metal.
Question 5.
Why is sodium stored in kerosene oil ?
Answer:
Sodium is highly reactive metal. It readily combines with oxygen when exposed to air and sometimes it even catches fire. It also reacts with water forming its hydroxide. To prevent its oxidation, sodium is stored under kerosene oil.
Question 6.
Explain the following:
(а) Acidic oxides
(b) Basic oxides.
Answer:
(a) Acidic Oxides. These are the oxides of non-metals and give acids when dissolved in water.
Examples : CO2, SO2 etc.
(b) Basic Oxides. These are the oxides of metals and give alkaline or basic solutions in water.
Examples : Sodium oxide, Calcium oxide etc.
Question 7.
Explain the occurrence of metals in nature.
Answer:
Occurrence of Metals in Nature. Metals occur in the nature in free as well as in combined state.
1. Free or Native State. The metals which are not attacked by air and moisture generally occur in the free or native state e.g. metals like gold, platinum etc.
2. Combined State. Metals generally occur in nature in the form of compounds
such as oxides, sulphides etc. These metals are said to occur in the combined state, e.g. Aluminium oxide.
Question 8.
What do you understand by ductility and malleability of a metal ? Give examples of two metals which are both ductile and malleable.
Answer:
Ductility.
It is the property of metals by virtue of which metals can be drawn into thin unbroken wires. Metals exhibiting this property are called ductile.
Examples : Copper, Aluminium, Silver, Gold.
Malleability. It is the property of metals by virtue of which Metals which can be beaten into thin sheets and twisted or bent without breaking. Metals showing this property are called malleable.
Examples : Gold, Silver, Aluminium.
Examples of two metals which are both malleable and ductile :
Aluminium and Gold.
Question 9.
Silver does not combine easily with oxygen but silver jewellery tarnishes after some time. How ?
Answer:
Silver does not combine easily with oxygen of the air. But it readily combines with sulphur compounds such as hydrogen sulphide present in the air to form a black coating of silver sulphide. Therefore, silver jewellery tarnishes after some time.
Question 10.
Why do gold ornaments look new even after several years of use ?
Answer:
Gold does not tarnish. That is, it never corrodes as it is non-reactive. It is unaffected by air, water and acids. This is why gold ornaments look new even after several years of use.
![]()
Question 11.
Magnesium and copper metals are heated directly over a flame. Which of these will burn in air ? Which is more reactive ?
Answer:
When magnesium and copper are heated directly over a flame, magnesium will burn in air. Magnesium is more reactive.
Question 12.
CuSO4 + Fe → FeSO4 + Cu
FeSO4 + Zn → ZnSO4 + Fe
On the basis of the above reactions, indicate which is the most reactive and which is the least reactive metal out of zinc, copper and iron ?
Answer:
In the first reaction, iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution, therefore, iron is more reactive than copper. In the second reaction zinc displaces iron from iron sulphate, therefore, zinc is more reactive than iron. Therefore, zinc is the most reactive metal while copper is the least reactive.
Question 13.
Why are pickles, chutney and citrus fruits not stored in iron and aluminium utensils ?
Answer:
Certain foodstuffs, particularly citrus fruits, chutney, pickles and curd, which contain acids tend to attack kitchen utensils made of aluminium and iron forming poisonous salts. Iron and aluminium utensils are, therefore, not used to store pickles, chutney and citrus fruits.
Question 14.
What would you observe when a strip of zinc is dipped in the solution of copper sulphate ?
Answer:
Zinc being more reactive would replace copper from its salt solution i.e. copper sulphate.
Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu
Question 15.
Can copper displace iron from iron sulphate solution ? Give reasons.
Answer:
No, because copper is less reactive than iron. As a result, it can’t replace iron from its salt solution i.e. iron sulphate. Only more reactive metals can replace less reactive metals from their salt solutions. Vice-versa is not possible i.e., less reactive metals cannot replace more reactive metals from their salt solutions.
Question 16.
Why does aluminium vassel lose its lusture after sometime ?
Answer:
Aluminium is a reactive metal. During its use, it comes in contact with air and water when it forms dull coating of aluminium oxide on its surface. Hence the vessel loses its shine.
![]()
Question 17.
Why aluminium metal is preferred to copper for making cooking utensils ? Give two reasons.
Answer:
Because of the following two reasons, aluminium is preferred to copper for making cooking utensils.
- It is very light and is a good conductor of heat.
- It is not readily attacked by acids present in the food materials to be cooked.
Question 18.
What is corrosion ? What are the different ways to reduce corrosion ?
Answer:
Corrosion. Metals when exposed to moist air get covered with dull layer.
This layer can be easily removed giving place to the next such layer to be formed. In this way, metal is eaten up or corroded and the process is called corrosion.
Ways to reduce corrosion:
- By covering the metal with paint
- By applying oil or grease on the surface of metal.
- By coating the metal with some other metal which is not easily corroded by passing electricity.
- By making an alloy.
Question 19.
Sodium occurs in the combined state where as Gold in its native state, why ?
Answer:
Sodium is the most reactive metal. It readily combines with air and water to form its compounds. So it occurs as compound. On the other hand Gold is the noble metal and is not attacked by air, water or acids so it exists in its native form.
Question 20.
Does copper rust ? What will happen if copper is exposed to moist air ?
Answer:
Copper does not rust. When copper is exposed to moist air for long, it acquires a dull green coating. The green material so formed is a mixture of Copper hydroxide [CU(OH)2] and Copper carbonate [CuCO3], The following reaction takes place:
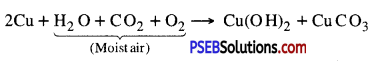
Question 21.
Give reasons for the following:
(i) Aluminium is used in making parts of aeroplane.
(ii) Copper is used in making electric wires.
(iii) Silver is used in making mirrors.
(iv) Graphite is used as an electrode in the Dry cell.
(v) Iron is used in constructing bridges and dams.
Answer:
(i) Aluminium being light and strong metal is used in making parts of aeroplanes.
(ii) Copper is a good conductor of electricity. So, it is used for making electric wires.
(iii) Silver is very shining white metal and has, therefore, high reflecting power.
(iv) Graphite is a good conductor, so it used for making electrode in dry cells.
(v) Iron being strong and rigid metal is used in the construction of bridges and dams.
![]()
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Give general physical properties of metals.
Answer:
General physical properties of metals:
- Metals have a shiny appearance, i.e. they show metallic lustre.
- Metals are generally hard and their hardness varies from metal to metal.
- Most metals are malleable, i.e. they can be hammered into thin sheets.
- Metals are ductile and, therefore, can be drawn into wires.
- Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity. Electricity flows most readily through gold, silver, copper and aluminium.
- Metals are generally sonorous i.e. metals make sound when hit with an object.
- All metals except mercury exist in solid form at room temperature.
- Metals have high melting points.
Question 2.
Give general physical properties of non-metals.
Answer:
General physical properties of non-metals:
- Lustre. Non-metals possess dull lustre, i.e., they do not reflect light well. Exceptions are graphite and diamond.
- Conductivity. Non-metals are poor conductors of heat and electricity. Exception is graphite.
- State. Non-metals may occur as solids or liquids or gases at room temperature. For example Sulphur, Carbon and Iodine are solids. Bromine is a liquid. Chlorine and nitrogen are gases.
- Malleability. Non-metals are not malleable but they are brittle. Non-metals break into small pieces when hammered.
- Hardness. Non-metals are generally not hard but diamond is exception. Diamond is the hardest known substance.
- Ductility. Non-metals cannot be drawn into wires and are, therefore, not ductile
- Melting and Boiling Point. Non-metals have low melting and boiling points. A majority of non-metals are gases. Exception is graphite which has a high melting point.
Question 3.
How do metals react with acids ?
Answer:
Reaction of metals with acids :
1. Active metals like zinc, magnesium, iron etc. which lie above hydrogen in the electrochemical series or activity series can displace hydrogen from dilute mineral acids such as hydrochloric acid and sulphuric acid.
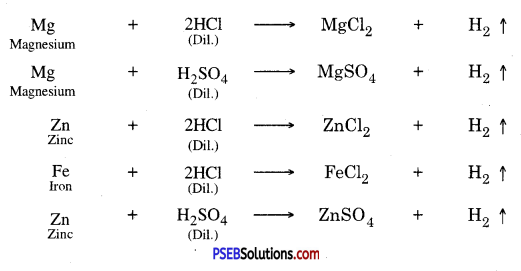
2. The metals which lie below hydrogen don’t displace hydrogen from dilute mineral acids such as hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid etc.
For example, copper does not react with dil. HCl.
Question 4.
How do metals react with water ?
Answer:
Reaction of metals with water. Different metals have different reactivities with water. All metals react with water under different conditions to produce hydrogen gas.
1. Active metals like Na, K react with water at room temperature.
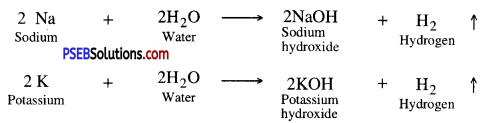
The reaction is so violent and exothermic that the evolved hydrogen catches fire.
2. Less active metals like Mg, Zn, Al, react with boiling water.
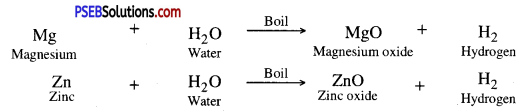
3. Metals like Fe, Ni react very mildly with steam

![]()
Question 5.
Which of the following displacement reaction cannot occur ?
(a) CUSO4(aq) + Fe → FeSO4(aq) + Cu
(b) FeSO4(aq) + Zn → ZnSO4(aq) + Fe
(c) ZnSO4(aq) + Pb → PbSO4(aq) + Zn
(d) 2AgNO3(aq) + Cu → Cu(NO3)2 + 2Ag
(e) MgSO4(aq) + Cu → CuSO4 + Mg
Answer:
A more reactive metal (placed higher in the activity series) can displace the less reactive metal from its solution. Out of the above five reactions.
(c) cannot occur because zinc is more reactive than lead.
(e) cannot occur because magnesuim is more reactive than copper.
Question 6.
Name three metals that you come across in your daily life and also give their uses.
Answer:
We come across directly or indirectly the following metals in our daily life:
- Iron
- Copper
- Aluminium
1. Uses of Iron :
- Iron mixed with other metals is largely used in making trains, automobiles and other machine parts.
- Iron mixed with cement is used in constructing big buildings and dams.
- Iron is used in making bridges and boilers for industry.
2. Uses of Copper:
- It is used for making cooking utensils,
- It is used in making photoframes, coins and statues.
- It is used for making electrical wires.
3. Uses of Aluminium:
- It is used for making aeroplanes
- It is used for making electric wires and parts of electric gadgets.
- Aluminium foils are used as packing material.
Question 7.
Distinguish between metals and non-metals on the basis of their chemical properties.
Answer:
Distinction between Metals and Non-metals
| Property | Metals | Non-Metals |
| Chemical Properties-
1. Nature of Ions |
Metals are electr-opositive elements and lose electrons to become electro-positive ions. | Non-metals are electro-negative elements and gain electrons to form negative ions. |
| 2. Nature of Oxides | Form basic oxides | Form acidic oxides. |
| 3. Reaction with Water | Mostly displace hydrogen. | Do not react with water. |
| 4. Reaction with Acids | Metals above hydrogen in the activity series displace hydrogen from | Non-metals do not react with dilute acids. |
| 5. Nature of Hydrides | Metals react with hydrogen to form ionic hydrides. | Form covalent hydrides. |
| 6. Nature of Chlorides | Metals combine with chlorine to form solid ionic chlorides which conduct electricity. | Non-metals combine with chlorine to form covalent chlorides which do not conduct electricity. |
Question 8.
Give general chemical properties of non-metals.
Answer:
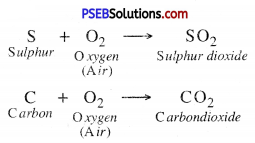
1. Reaction with Air or Oxygen. Non-metals react with air or oxygen to form their corresponding oxides which are acidic in nature. These oxides turn blue litmus red.
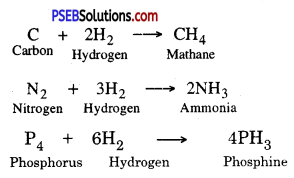
2. Reaction with Hydrogen. Non-metals like carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorous react with Hydrogen to form different compounds.
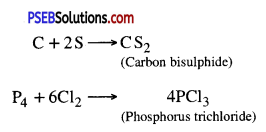
3. Reaction with other non-metals. Non-metals react with other non-metals to form compounds
4. Reaction with Acids. Non-metals react with acids to form corresponding oxyacids.