Punjab State Board PSEB 7th Class Social Science Book Solutions Geography Chapter 2 The Internal and External Face of the Earth Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB 7th Class Social Science Solutions Geography Chapter 2 The Internal and External Face of the Earth
SST Guide for Class 7 PSEB The Internal and External Face of the Earth Textbook Questions and Answers
I. Give answers to the following questions approximately in 1-15 words.
Question 1.
How many shells of the earth are there? Name them.
Answer:
Lithosphere, Mantle and Core. These are called Sial, Sima and Nife in that order.
Question 2.
How many types of Rocks are found on the earth?
Answer:
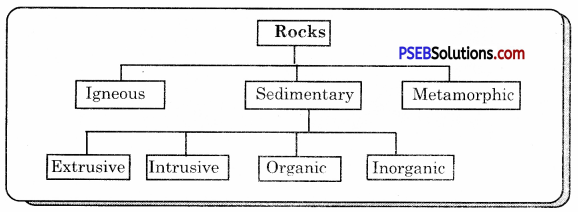
Igneous rocks, Sedimentary rocks, Metamorphic rocks.
Question 3.
Write down about the Mantle part of the Earth.
Answer:
Below the earth’s crust is Mantle. Its normal thickness is 2900 kms deep down to earth’s interior.
Question 4.
By which name the inner most part of the earth is called? What are the components of this part?
Answer:
The core of the earth is called ‘Nife’. It is made up of Nikel and Iron (Ferrous).
![]()
Question 5.
How can we avoid soil erosion?
Answer:
- By planting more and more trees.
- By adopting developed means of agriculture.
- By decreasing the grazing area of cattle.
II. Give answers to the following questions approximately in 50-60 words.
Question 1.
What are igneous rocks? How many types are there of these rocks? Write about the Intrusive rocks.
Answer:
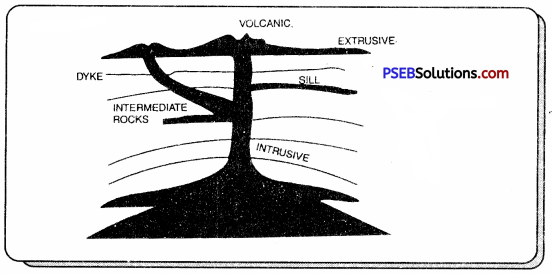
Igneous shell is the shell which is made up by cooling of Magma and Lava. These rocks are of two types: Intrusive/Extrusive.
Sometimes Magma get cold and slowly solidifies inside the earth’s surface, these are called Intrusive Igneous Rocks. While sometimes Magma gets cold and solidifies near the earth’s surface then these rocks are called Extrusive Igneous Rocks.
Question 2.
What are the sedimentary rocks? How many types are there of these rocks?
Answer:
- They are called secondary rocks.
- They form from deposits or sediments obtained from weathering and erosion of other rocks.
- They contain fossils.
- They are always layered.
- Sandstone, shale, gravel and conglomerate are examples of these rocks.
- On the basis of construction, layered rocks are of two types:
(i) Fossil layered rocks.
(ii) Non-fossil layered rocks.
Question 3.
Write about Metamorphic rocks, give specific example of these rocks.
Answer:
Metamorphic Rocks: These rocks are formed by ‘metamorphism’ or change of form of igneous and sedimentary rocks. The change takes place in hardness, colour, texture and composition of minerals in rocks deep inside the earth due to pressure and temperature. Thus original igneous rock like mica may be changed to schist, granite to gneiss and sedimentary rocks like limestone to marble, sandstone to quartzite and peat to coal.
Characteristics:
- They are very hard.
- They contain useful materials and minerals like building materials, marbles, gems, rubies and sapphires. Taj Mahal is made of white marble.
Question 4.
What kind of mineral is mica, for what purpose is it used?
Answer:
Mica is a non-metallie mineral: It has a great importance. This mineral is very useful in manufacturing eletromic goods. It is also used in making other things like lamps, chimneys, paints, radars, rubber, poper, transparent sheets and aeroplanes.
![]()
Question 5.
Which material is called as ‘Liquid Gold’? Give brief introduction.
Answer:
Mineral oil is known as Liquid Gold. This name has been given because of its increasing use and importance. It, is also called Petroleum or driving energy. It is also extracted from earth like other minerals. It is made up of two words- Petra and Oliuin. In Latin language Petra means rock and Olium means oil i.e. oil received from rocks. It is a fossil fuel which is made up of animals leftovers being pressed inside Sedimentary rocks.
Question 6.
Write down the importance of the soil on the earth.
Answer:
Soil is a valuable natural resource. Its importance is in its fertility. Many human and economic activities depend upon soil. Most of the civilizations have flourished near the fertile soil beds of Nile and Indus rivers, Tigris, Euphrates and Yangste valleys. Even today fertile valleys and rivers attract dense population. India has been able to produce foodgrains for its large population on the strength of its fertile soil.
III. Write the answers to the following questions approximately in 125-130 words.
Question 1.
Write in detail about the rocks available on the earth.
Answer:
On the basis of their formation rocks are of three chief types as shown in the diagram, namely— Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic.
1. Igneous: These rocks are formed from cooling and solidification of molten material rising from interior of the earth called magma. When cooling and solidification happens just near the ground or above the ground they are called Extrusive Igneous Rocks. If cooling and solidification happens inside the earth, these rocks are called Instrusive Igneous Rocks. Basalt and Rhyolite are examples of extrusive igneous rocks and granite and gabro are examples of intrusive igneous rocks.
Igneous Rocks
Characteristics:
- When igneous rocks are exposed on the surface of the earth they are weathered and provide materials for other types of rocks. As a result the igneous rocks are called Primary Rocks.
- These rocks contain crystals whose size depends on rate of cooling.
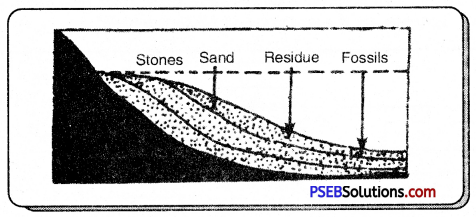
2. Sedimentary Rocks: The material for sedimentary rocks may be derived from weathering and erosion of all types of rocks- igneous, metamorphic or old sedimentary rocks. They may contain fossils formed from remains of dead plants and animals.
There are two types of sedimentary rocks: inorganic and organic,
(a) Organic Sedimentary rocks are formed from organic matter derived from plant and animal remains, shell and skeletons of dead marine animals, decayed and decomposed plant and animal life as well as direct precipitation of minerals in solution of water.
(b) Inorganic Sedimentary rocks are formed due to weathering and erosion of all types of old rocks, clay, sand and mud deposited in oceans and lakes.
Characteristics:
- They have a layering arrangement.
- They may contain fossils.
- They may have ripple marks left by water.
- They are softer than any other rock.
- They are pervious or water can easily enter.
- There are no crystals in sedimentary rocks.
- Secondary ores of bauxite, manganese and other minerals are found in secondary rocks. Only sedimentary rocks are sources of fossil fuels. They also provide rich soils and materials for building and construction industry.
3. Metamorphic Rocks: Igneous and sedimentary when subjected to pressure and heat form sedimentary rocks. Examples- sandstone, granite, gnesis. Metamorphic rocks are made up by two ways and are found deep inside the surface of the earth.
The two ways are:
- Transformation by heat. It happens because of hot magma, which solidifies the rocks that comes into its contact.
- Transformation by pressure. Sometimes the pressure of upper rocks transforms the structure of lower rocks.
![]()
Question 2.
What are minerals? Which minerals are available on the earth? Classify them and write about the metallic minerals.
Answer:
The substances that create rocks are known as minerals. These are extracted through mining. The classification is”as follows :
- Metallic minerals: It contains the particles of metals. It includes iron, copper, tin, aluminium, gold, silver, etc.
- Non-metallic minerals: These don’t contain the particles of metals. These are sulphur, gypsum, abhrak, phosphorus, potassium, etc.
- Power minerals: These minerals give us energy, which helps us to run our factories and motor vehicles. Coal, petroleum, natural gas are main power minerals.
Metallic minerals :
1. Iron: The iron ore is used from a small nail to a very big ship. The whole industrial machinery, motor vehicles, rails, agriculture machinery all are based on iron ore. The iron and steel has brought revolution in the industrial sector. In India it is produced mainly in Orissa, Jharkhand, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Karnataka and Goa.
2. Copper: Copper is the earliest found metal in the human history. From the industrial point of view, after iron comes the place of copper. The metallic age started with the use of copper. Many utensils are made of copper. In today’s age its importance has increased. It is a good conductor of electricity so, it is used for making electric cables. Telephone cables, railway engines, aeroplane and watches, etc. contain the use of copper. Chile, in South America, is the biggest producer of copper in the world followed by USA. In African continent there are maximum stores of copper. India, Japan, Australia also produces copper. In India, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan are known for copper.
3. Bauxite: It is derived from aluminium. It is a light metal and is used in making aeroplanes. Moreover trains, motor vehicles, buses and electric cables also contain bauxite. The products made up of this metal do not get rusty. So, these products can be used for fairly long time.
Maximum bauxite is available in Australia. In India it is found in Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand.
Question 3.
What are mineral fuels? Give details of any mineral fuel.
Answer:
These minerals give us energy and required ignition run factories and motor vehicles. Main power minerals are coal, mineral oil and natural gas.
Out of this coal and mineral oil have special importance the description is as follow :
1. Coal: Coal is the main power mineral. These days the use of coal has decreased. Now it is used in thermal plants for producing electricity. The coal used for this purpose is stone coal. This coal was made in the sedimentary rocks deep inside the earth. It took crores of years in this process. Most of the coal stock in the world is found in 35° to 65° latitude. 90% of world coal is found in China, USA, Russia and European countries. Besides there are large stocks of coal in South America, Africa, North America and Asian sub-continent. Japan and Thailand also have stock of coal.
India produces 5% of coal. Damodar Valley is the main coal-production belt. Madhya Pradesh and West Bengal are coal-rich states.
2. Mineral Oil: It is known as Liquid Gold. Its name has been given because of its use and importance. Its called petroleum or driving force. Because it is extracted from earth like other minerals so it is called mineral oil. It is given the name of petroleum because it is made up of two words— Petra+Olium. Petra stands for rocks and olium means oil. So the literal meaning of Petroleum is oil received from rocks. It is fossil fuel. Most of the Petroleum that we get from inside the earth is in raw form. After refinement of thfs unrefined raw form, we get many products like Petrol, diesel, kerosene oil, gas, grease, wax, etc.
Most of the oil stock in the world is in South-west Asia, which includes areas like Saudi Arab, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait and United Arab Emirates.
![]()
Question 4.
Write in detail about the soils available in India.
Answer:
Soil is an important resource that becomes the basis of agriculture and foodgrains production. In India, six types of soils are found of which the following four types are major :
- Alluvial soil
- Black soil
- Red soil
- Laterite soil.
1. Alluvial Soil: This soil is derived from sediments of rivers and is confined to river basins and coastal plains. Alluvium is very fertile because it is renewed every year during floods or deposition work of rivers. It contributes enormously to growth and development of agriculture in India. It is found in the states of Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Orissa, Bengal, Rajasthan and coastal areas of Brahmaputra valley and Peninsular India.
2. Black Soil: This lava soil is also known as Regur soil or Black Cotton soil. It is black because it is formed in its place of origin. It is found in parts of Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, North Karnataka, Southern Tamil Nadu and parts of Madhya Pradesh.
3. Red Soil: The presence of iron oxide is responsible for reddish colour. When fertilisers are added these soil become very productive for growing crops like rice, millets, cotton and sugarcane. Red soils are found in Malwa region, Chhotanagpur plateau, parts of Chhattisgarh, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Orissa.
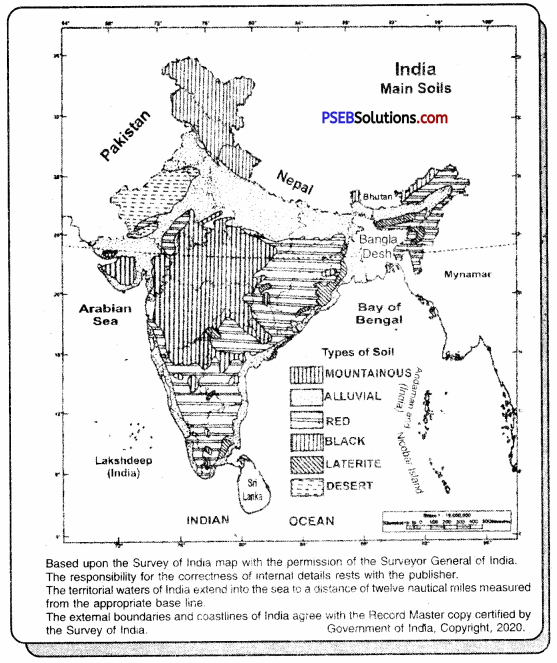
4. Laterite Soils. These are not very fertile soils. They occur in high places of plateau region where rainfall leaches nutrients in the soil. Laterite rock is best suited for building purposes rather than for agriculture. These soils are found in parts of Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh. Orissa, Bengal and Summits of Western and Eastern Ghats.
IV. Activities:
Question 1.
Make a model of the earth showing its layers.
Answer:
Do it yourself.
![]()
Question 2.
Is soil erosion a serious problem? Discuss it in your class.
Answer:
Soil erosion is a global problem. Deforestauon, overgrazing bv animals are the main causes. The rate of soil erosion in India is the highest. It takes a long time to form fertile soils, but in a short time soil erosion removes the soil.
PSEB 7th Class Social Science Guide The Internal and External Face of the Earth Important Questions and Answers
I. Multiple Choice Questions :
Question 1.
The rock which is made up of molten magma is :
(a) Igneous
(b) Sedimentary
(c) Metamorphic
(d) Sedentary.
Answer:
(a) Igneous.
Question 2.
Which of the following is an example of sedimentary rocks?
(a) Basalt
(b) Granite
(c) Gabro
(d) Sandstone.
Answer:
(d) Sandstone.
Question 3.
Deccan plateau is made up of :
(a) Basalt
(b) Gabro
(c) Slate
(d) Granite.
Answer:
(a) Basalt.
![]()
Question 4.
Where is the deepest mine found on earth?
(a) In South Africa
(b) In North Africa
(c) In South America
(d) In Australia.
Answer:
(a) In South Africa.
Question 5.
Laterite soils are found :
(a) Karnataka
(b) Punjab
(c) U.P.
(d) Bihar.
Answer:
(a) Karnataka.
Fill in the Blanks :
Question 1.
__________ is a dark substance formed in soils.
Answer:
Humus
Question 2.
__________ rocks have more sand.
Answer:
Porous
Question 3.
Limestone is changed into __________ under great heat and pressure of the above layers of the rocks.
Answer:
Marble
![]()
Question 4.
When magma reaches earth surface, it is called __________
Answer:
Lava
Question 5.
Sedimentary rocks are called __________ rocks .
Answer:
Secondary.
True / False :
Question 1.
The innermost layer of the earth is called core.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
The combined form of natural minerals is called rocks.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
Sial made up of Silica and Alumina.
Answer:
False
Question 4.
Sulphur, Gypsum are non-metallic minerals.
Answer:
True
![]()
Question 5.
Coal, Petrol, Natural gas etc. are considered power resources.
Answer:
True.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How is volcanic mountain formed? Give an example.
Answer:
In the lower layers of earth, there is so much heat which results in cuts on earth’s surface, and the hot substance from deep inside earth comes out in the form of . ‘Lava’. When after cooling and solidifying, this lava takes the shape of a mountain then it is called a volcanic mountain. The example is Fugeyama volcanic mountain of Japan.
Question 2.
What is the difference between Porous and Non-porous rocks?
Answer:
Porous rocks have more sand while Non-porous rocks have more of soil in these.
Question 3.
Classify rocks on the basis of absorption.
Answer:
Two types of Rocks: Absorbing and Non-absorbing. While Absorbing rocks easily soak water but non-absorbing rocks don’t easily absorb water.
![]()
Question 4.
Name two classifications of rocks on the basis of chemical structure.
Answer:
- Acidic Rocks
- Base Rocks.
Question 5.
What is difference between Lava and Magma?
Answer:
Inside the earth’s surface: Molten substance is called Magma. When it comes outside through pores/cutting in earth’s surface, it is called Lava.
Question 6.
What do you mean by primary rocks? Write their features.
Answer:
Igneous rocks are formed by the solidification of lava. Lava cools rapidly and solidifies on the surface of earth. Crystals are formed due to the cooling of lava. These rocks are intrusive as well as extrusive. It is believed that the earth was in a molten state in the beginning. Igneous rocks were the first rocks to be formed due to cooling and solidification of molten matter. Hence, these are called Primary rocks.
The importance of Igneous rocks
Igneous rocks supply different types of minerals. Granite is used for house-building and idol-making. Basalt is used for road-making. Monuments are made from these hard rocks.
Question 7.
What are the factors on which the qualities of metamorphatic rocks depend?
Answer:
The quality depends on the base rocks i.e. if the metamorphatic rocks are made up of igneous rocks then their qualities are like igneous rocks, and if these are made up of sedimentary rocks then these are like sedimentary rocks.
Question 8.
What is soil?
Answer:
The uppermost layer of the earth’s crust is called soil. It consists of a thin layer of loose material of rock waste. The soil consists of mineral particles, organic matter (humus), water, air and living organisms (bacteria).
![]()
Question 9.
What are the two elements in soil?
Answer:
The soil has two elements minerals and excreta. The soil contains minerals in good quality and these are derived from basic rocks. The excreta comes from the dead animals. It increase the fertility of soil.
Question 10.
Which soil is known as cotton soil?
Answer:
Black soil is known as cotton soil. It is ideal for cotton agriculture.
Question 11.
Name the types of soils found in India.
Answer:
Alluvial soil, black soil, red soil, laterite soil, dry soil, mountain soil.
Question 12.
Write two features of Alluvial soil.
Answer:
- This soil contains potassium, phosphoric acid and lime.
- It contains less of nitrogen and bio substance.
Question 13.
Write two features of black soil.
Answer:
- It is made up of the flow of lava.
- It is useful for cotton agriculture.
Question 14.
Write the names of places in India where black soil is found.
Answer:
It is found in the deccan pleateu as well as Maharashtra, Sourastra, Malwa and Southern Madhya Pradesh Plateau.
Question 15.
Write two features of Laterite soil.
Answer:
- Laterite soil is less fertile.
- It is only useful for grass and bushes.
![]()
Question 16.
How can the acid soil be made useful for agriculture?
Answer:
By putting together the irrigation facilities.
Question 17.
What is meant by tectonic plate movements?
Answer:
The earth’s interior is very dynamic. The lithosphere is broken into seven very large and several small plates. This deformation in the earth’s crust and structures produced by this deformation are called tectonics. This model or theory that explains this distribution, evolution and causes of earth’s crustal features is known as the theory of plate tectonics.
Question 18.
What are kqown as rocks? Name the rock-forming materials.
Answer:
Bocks are the chief materials of earth’s crust. Rock-forming materials are known as minerals.
Question 19.
How can we identify mineral which form the rocks?
Answer:
We can identify minerals in rocks by their colour, texture, lustre and hardness. Some minerals like salt can also be identified by tasting but it is not a good method. It can endanger human life.
Question 20.
Name the three groups of rocks on the basis of their formation.
Answer:
The three groups of rocks on the basis’ of their formation are igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic.
![]()
Question 21.
Why are the Igneous rocks called Primary Rocks?
Answer:
It is believed that the earth was in a molten state in the beginning.’Igneous rocks were the first rocks to be formed due to cooling and solidification of molten matter. Hence, these are called Primary rocks.
Question 22.
Why are fossils preserved in Sedimentary and not in Igneous, rocks?
Answer:
Fossils are remains of vegetation and animals buried under the sediments. The sedimentary rocks are stratified rocks and are found in layers. These fossils are preserved in between these layers. But in Igneous rocks, the fossils are destroyed due to high temperature of lava.
Question 23.
What part do rocks play in Geography?
Answer:
Rocks influence different types of landforms. Different types of minerals are found in rocks. Rocks are used for building purposes. Rocks are the basis of soil formation.
Question 24
How are Igneous rocks formed?
Answer:
Igneous rocks are formed by the solidification of lava. Lava cools rapidly and solidifies on the surface of earth. Crystals are formed due to the cooling of lava. These rocks are intrusive as well as extrusive.
![]()
Question 25.
What is the importance of Igneous rocks?
Answer:
Igneous rocks supply different types of minerals. Granite is used for house-building and idol-making. Basalt is used for road-making. Monuments are made from these hard rocks.
Question 26.
What do you mean by ‘Deccan trap’?
Answer:
Deccan trap is an extensive area in the N.W. part of India covering about 5 lakh sq. km. It has been formed by lava flows. Lava has solidified to form Basalt. It is useful for cotton cultivation.
Question 27.
Why are sedimentary rocks classfied as belonging to secondary group? How are these rocks formed?
Answer:
The secondary rocks are those which are derived from other rocks. The sedimentary rocks are formed from weathering and erosion of igneous, metamorphic and even other sedimentary rocks.
Question 28.
What are known as fossils? In which types of rocks can fossils be found?
Answer:
Fossils are the remains of dead plants and animals trapped in rocks. They are found in sedimentary type of rocks.
![]()
Question 29.
Why the ‘Sial’ layer is known by this name?
Answer:
Sial has more of Silicon and Aluminium, That is why it is called Sial (Si+Al).
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is humus? How is it formed? What is its significance in soil formation?
Answer:
Humus. Humus is a dark substance formed in soils. It is a dead organic matter formed by decay of animals and plants. Trees, shrubs, grass and bacteria help in the formation of humus. In warmer climates, humus is destroyed by countless bacteria. In colder areas soils are rich in humus and it is collected in the soil. Tropical humid soils are poor in humus because it is consumed by bacteria.
Humus is vital to the fertility of soils. It provides nitrogen, phosphorus and calcium to the soils. It sustains other forms of life. It helps the weathering of minerals to add to fertility of soils. It increases water holding capacity of soils.
Question 2.
What is a bad land topography?
Answer:
A highly dissected land surface is known as bad larid. In sloping areas, gully erosion results in soil erosion. These gullies develop a ravine land a bad land topography. This topography consists of ridges, earth pillars, ravines, escarpments, etc. This topography is found in Chambal Valley of Madhya Pradesh in India.
Question 3.
What is soil-erosion?
Answer:
Soil-erosion. It is the destruction and removal of top soil by running water, wind, etc. So erosion has become a serious problem in many areas Soil formation is a slow process and takes thousands of years to develop, but it may be removed in the matter of a few years.
![]()
Question 4.
What is soil erosion? Name its types.
Answer:
Soil erosion. Soil erosion is the destruction and removal of top soil by running water, wind, etc. Soil formation is a slow process and takes thousands of years to develop soil; but it may be removed in a matter of few years.
Types of Soil Erosion :
Soil erosion is of three types :
- Sheet erosion: When the surface soil is washed away by rain or blown away by the wind.
- Gully erosion: When torrential rain forms deep gullies on sloping land.
- Wind erosion: When strong winds blow away fine soil in arid areas.
Question 5.
What are the causes of soil erosion?
Answer:
Causes of Soil Erosion :
- Steep slopes: Steep slopes increase the rapidity and intensity of soil erosion.
- Torrential rainfall: Heavy rainfall forms gullies and ravines leading to a bad land topography.
- Strong winds: Winds, through the process of deflation, blow away layers of fine soil.
- Overgrazing: Overcropping and shifting cultivation renders the soil infertile.
- Deforestation: Deforestation exposes the area to soil erosion. Reckless cutting of trees has resulted in soil erosion by chos of the Shiwaliks.
Question 6.
State the method of soil management.
Answer:
Various methods are being practised for soil management :
- Afforestation” Reforestation in old areas and afforestation in new areas are required to hold the soil. Surface run-off can be checked. Advance of deserts can be checked by planting trees along the margins of deserts.
- Controlled grazing” This number of animals to be grazed on slopes should be according to the carrying capacity of the pastures. It gives time for the grass to grow again.
- Terraced agriculture” Terraced cultivation on slopes should be practised to check the flow oT rain water.
- Contour ploughing” Contour ploughing, terracing and bunding is done to check soil erosion on slopes. Ploughing is done at right angles to the slopes.
![]()
Question 7.
Distinguish between Sial and Sima.
Answer:
The distinction between Sial and Sima :
| Sial | Sima |
| 1. Sial is the uppermost layer on the Earth. | 1. Sima is the layer found below sial. |
| 2. It consists of silica and aluminium. | 2. It consists of silica and magnesium. |
| 3. It is a lighter layer with a density of 2.75. | 3. It is a havier layer with a density of 5. |
| 4. Continents are made of sial. | 4. Ocean floors are made of sima. |
Question 8.
How are rocks useful to man?
Answer:
- Building materials: Rocks like granite, sandstone, slate and limestone are used in building roads and houses. Marble is used in more expensive building decoration.
- Fossils: Fossils are found in sedimentary rocks. They are very useful to us because they tell us about the past environment, about animals and plants that are no longer found on earth.
- Tools and implements: Since early civilization, rocks and stone have been used to make tools and implements. Clay bricks have been used for house construction and stones for the construction of pyramids, temples and buildings.
- Fertilizers: Potash, nitrates and phosphates found in sedimentary rocks are used in the manufacturing of fertilizers.
Question 9.
Classify the minerals available in the earth’s crust.
Answer:
Three classifications are there:
- Metallic Minerals: These have particles of metals like iron, copper, aluminium, gold, silver, etc.
- Non-Metallic Minerals: These don’t contain particles of metal like Sulphur, Abhrak, Gypsum, Potassium, etc.
- Power Minerals: We get power and energy from such minerals which drive vehicles and run factories for us. Coal, Petrol, Natural gas, etc. are considered power minerals.
![]()
Question 10.
In which category Mica is classified, for what purpose is it used?
Answer:
It is a non-metallic mineral. It has many uses:
- Used in electric goods making industry.
- Used mostly in lamp chimneys, colours, rubber, paper, medicines, vehcies and transparent sheet industry, etc.
- Slim sheets of this mineral are put in electric motors as insulator.
Comparison Type Questions
Question 1.
Distinguish between Rocks and Minerals.
Answer:
The distinction between rocks and minerals :
| Rock | Minerals |
| 1. They are solid materials that make up earth’s crust. | 1. They are solid and crystalline materials that for m the rocks. |
| 2. Rocks have physical properties but do not have any definite chemical make-up. | 2. They have physical properties and chemical make-up. |
| 3. Rocks differ from each other on the basis of mineral content arid mode of formation. | 3. Minerals differ from each other on the basis of elements or compounds of which they are constituted. |
| 4. Based on formation, rocks can be divided into 3 main groups: igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic. | 4. Based on formation there are above 2000 minerals that combine in different ways .to form rocks. |
Question 2.
Distinguish between Igneous and Sedimentary rocks.
Answer:
The distinction between Igneous and Sedimentary rocks :
| Igneous Rocks | Sedimentary Rocks |
| 1. They are called primary rocks. | 1. They are called secondary rocks. |
| 2. They are formed from the cooling and solidification of lava. | 2. They form from deposits or sediments obtained from weathering and erosion of other rocks. |
| 3. They do not contain any fossils. | 3. They contain fossils. |
| 4. They are rarely layered. | 4. They are always layered. |
| 5. Basalt, rhyolite, granite and gabbro are examples of these rocks. | 5. Sandstone, shale, gravel and conglomerate are examples of these rocks. |
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe the process of soil formation and the factors influencing it.
Answer:
The physical, chemical and organic changes that take place in the exposed rock over a long period of time lead to formation of soils.
Following factors influence this process of soil formation :
- Climate: Weathering depends on and is influenced by climate. It is the climate that causes disintegration of rock on account of differences in temperature and moisture.
- Rock Types: Parent rock and its type determines the rate of weathering and erosion. For example, sedimentary rock may be disintegrated quickly as well as cause form ation of soil and be a source of humus content in soil,
- Vegetation: Roots of plants help in weathering. The vegetation also provide materials for decomposition and formation of soils.
- Slope of land: Slope of land and general topography affect deposition and erosion of materials oi weathering. They may also form transported and residual soils.
- Time: The changes that lead to formation of soil are spread over thousands to millions of years. -The soils also undergo drastic changes with the passage of time.
![]()
Question 2.
With the help of a diagram, describe the interior of the earth.
Answer:
A diagram showing the interior of the earth is given ahead :
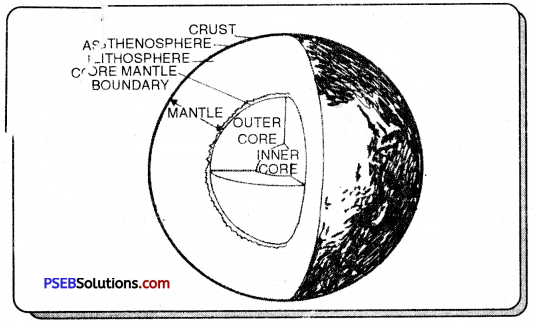
From the diagram it will be noticed that density goes on increasing towards the interior of the earth. Three main divisions of the interior of the earth are crust, mantle and core. Each of these three divisions has upper and lower part. Like density, temperature and pressure increase with the increase in depth inside the earth.
Crust: The thickness of the crust is 4-7 km below the seafloor and about 35 km below the continents. Beneath the mountain, the crust is 70 km thick. Continents are however made of a lighter material and rise above the oceanic crust.
Mantle: It extends upto 2900 km. The upper part is only about 100 km thick forming part of the lithosphere. The lower Mental is in a semi-plastic state.
Core: It has a radius of 3470 km and its upper part is in a liquid state and the lower part has enormous heat and is highly compressed, therefore at a solid rate. Iron and nickel are said to be the constituents of the Inner Core.
