Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class Science Book Solutions Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water
PSEB 8th Class Science Guide Pollution of Air and Water Textbook Questions and Answers
Exercises
Question 1.
What are the different ways in which water gets contaminated?
Answer:
There are many different ways in which water gets contaminated such as :
- By washing, bathing or other household activities.
- By sewage
- By toxic chemicals thrown by industries.
- By silt.
- By garbage and dead bodies dumped in water resources.
- By fertilizers, insecticides, pesticides etc.
- By deposition of minerals or metals in the river bed.
Question 2.
At an individual level, how can you help reduce air pollution?
Answer:
Steps taken to reduce air pollution at an individual level.
- Automobile use is to be reduced and is maintained properly. Unleaded petrol or diesel must be used.
- Burning of leaves, tyres etc. must be stopped.
- Plant trees or vegetation around the residential areas.
- Use of public transport.
Question 3.
Clear, transparent water is always fit for drinking. Comment.
Answer:
It is not a correct statement. Clear, transparent water may appear clean, but it is not pure. It may contain dissolved impurities and many microorganisms. These microorganisms may be carriers of diseases. So, water fit for drinking is clean, clear, transparent, odourless, devoid of germs and dissolved impurities. Best way to get pure water is boiling. Boiling kills the germs and boiled water can be used for drinking purposes.
Question 4.
You are a member of the municipal body of your town. Make a list of measures that would help your town to ensure the supply of clean water to all its residents.
Answer:
List of measures to obtain clean water.
- Industrial waste must be treated before throwing into water resources.
- Sewage must be treated by physical and chemical methods before dumping in water resources.
Question 5.
Explain the differences between pure air and polluted air.
Answer:
Differences between Pure air and Polluted air.
| Pure air | Polluted air |
| 1. The air is clear and transparent. | 1. The air is dirty and translucent. |
| 2. No smoke and dust particles can be seen. | 2. Smoke and dust particles are in high amounts. |
| 3. No odour is there. | 3. It may have foul smell. |
| 4. Microorganisms are absent. | 4. Microorganisms are present. |
![]()
Question 6.
Explain circumstances leading to acid rain. How does acid rain affect us?
Answer:
Acid Rain. When NO2, N2O, SO2 and SO3 produced from the incomplete combustion of fossil fuels and by smelting of non-ferrous metals combine with water to form HNO3, H2SO3 and H2SO4 and fall down in the form of rain, it is called acid rain. It destroys crops, wild plants, steel rail tracks and electrical equipment. It causes irritation of eyes, nose and throat.
Question 7.
Which of the following is not a greenhouse gas?
[а] Carbon dioxide
[b] Sulphur dioxide
[c] Methane
[d] Nitrogen.
Answer:
[d] Nitrogen.
Question 8.
Describe the ‘Green House Effect’ in your own words.
Answer:
Green House Effect. Carbon dioxide is present in the atmosphere in very small proportion. It helps in photosynthesis process. It is also absorbed by oceans to form carbonate rocks. It also produces greenhouse effect. The heating of the earth due to trapped radiations is called greenhouse effect. Our sun emits light consisting of ultraviolet and infrared radiations. Ultraviolet radiations are absorbed by ozone layer, but infrared radiations pass through the atmosphere and reaches the surface of the earth.
Some of the rays are reflected back. The carbon dioxide absorbs these reflected rays. Since infrared radiations have a heating effect, the atmosphere gets heated up. There are four gases which can trap the infrared radiations. These are carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapour (H2O), ozone (O3) and methane (CH4). Out of these four, carbon dioxide is uniformly distributed in the atmosphere so it contributes mainly towards the greenhouse effect. The name greenhouse is derived from glasshouse in which green plants are kept.
Question 9.
Prepare a brief speech on global warming. You have to make in your class.
Answer:
Global Warming. Global warming as the name suggests is the increase in temperature of the globe i.e. the average temperature of the atmosphere has increased. Few gases like CO2, methane, ozone are responsible for it.
The quantity of these gases is increasing day by day in the atmosphere. If this is not checked in time, the temperature will have a big rise and there will be hazards all around us. Such as, glaciers will melt, lower area will get submerged in water, rainfall will be affected, sea level will rise affecting production of crops, forests, etc and it will also affect the lifestyle of living organisms. So special and immediate measures are to be taken to stop global warming.
Question 10.
Describe the threat to the beauty of the Taj Mahal.
Answer:
Taj Mahal is one of the seven wonders of the world. It is a white building made up of white marbles. The monument is being threatened by air pollution. The area surrounding Taj is congested with many harmful gases such as Sulphur dioxide, Nitrogen oxides etc.
This is being emitted by burning of fossil fuels by industries established around the Taj. These gases dissolve in rainwater to form acid rain. This acid rain falls on marble, react with it and dissolves and tarnishes it. If no steps are taken to minimise the fall of acid rain, one day marble monument will remain no more and all the marble will get damaged.
Question 11.
Why does the increased level of nutrients in the water? effect the survival of aquatic organisms?
Answer:
With increased quantities of nutrients (nitrates, phosphates etc.) the algae flourish in the water. When this algae die, decomposers decompose it, using oxygen present in water. Thus, there is decrease in oxygen level in water, which affect the survival of aquatic organisms.
![]()
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Pollution of Air and Water Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Ankush noticed that air pollution has increased in the market due to vehicles. Which gas is emitted by vehicles in a large quantity that causes air pollution?
(a) Carbon monoxide
(b) Carbon dioxide
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b).
Question 2.
Which of the following is greenhouse gas?
(a) Carbon dioxide
(b) Carbon monoxide
(c) Oxygen
(d) Hydrogen
Answer:
(a) Carbon dioxide.
Question 3.
The source of air pollution is:
(a) Burning forests
(b) Gas emitted by automobiles
(c) Smoke of burning wood
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(d) All of these.
Question 4.
Which of the gas present in air contains 78%?
(a) Oxygen
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Carbon dioxide
(d) Argon.
Answer:
(b) Nitrogen.
![]()
Question 5.
Which fuel is being used in vehicles in big cities like Delhi?
(a) L.P.G.
(b) Biogas
(c) C.N.G.
(d) Natural gas.
Answer:
(c) C.N.G.
Question 6.
Which diseases are caused due to polluted water?
(a) Cholera
(b) Typhoid
(c) Jaundice
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these.
Question 7.
The cause of diseases related to respiration in children is :
(a) Oxygen
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Water vapour
(d) Smog
Answer:
(d) Smog.
Question 8.
The ordinary chemical method to purify the water is :
(a) Boiling
(b) Filtering
(c) Chlorination
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(c) Chlorination
![]()
Question 9.
When was Ganga cleanliness planning started?
(a) In 1965
(b) In 1975
(c) In 1995
(d) In 1985.
Answer:
(d) In 1985.
Question 10.
Which gas reduces the capacity of absorption of oxygen in blood?
(a) Nitrogen
(b) Carbon monoxide
(c) Carbon dioxide
(d) Oxygen.
Answer:
(b) Carbon monoxide
Question 11.
What is the percentage of population which does not get the required water?
(a) 40%
(b) 30%
(c) 25%
(d) 15%
Answer:
(c) 25%
Question 12.
Which of the following is not greenhouse gas?
(a) Carbon dioxide
(b) Sulphur dioxide
(c) Methane
(d) Nitrogen.
Answer:
(d) Nitrogen.
![]()
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Who is responsible for deterioration of quality of atmosphere?
Answer:
Man and his activities.
Question 2.
What conditions of environment are lacking these days?
Answer:
Clear sky, fresh air, clean water etc.
Question 3.
What is composition of air?
Answer:
Composition of Air. Air is mixture of gases containing 78% nitrogen, 21% of oxygen and 1% of other gases such as carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, water vapour, argon, ozone, methane etc.
Question 4.
Which is the main air pollutant?
Answer:
Smoke.
![]()
Question 5.
What are the main causes of smoke?
Answer:
Causes of smoke :
- Automobiles
- Burning of fuels
Question 6.
Name natural air pollutants.
Answer:
Smoke, dust.
Question 7.
Which disease is caused by air pollution?
Answer:
Respiratory problems.
Question 8.
Which gases are released by vehicles?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, smoke etc.
Question 9.
Which gas reduces the capacity of the blood to carry oxygen?
Answer:
Carbon monoxide.
Question 10.
What is smog?
Answer:
Smog. Smog is made up of smoke and fog.
![]()
Question 11.
Name some Breathing/Respiratory Problems.
Answer:
Respiratory problems- Asthma, Cough, Wheezing in children etc.
Question 12.
Which chemicals are used in refrigerators, air conditioners, perfumes etc?
Answer:
Chloro-fluoro carbons.
Question 13.
What is ill effect of chloro-fluoro carbons?
Answer:
Chloro-fluoro carbons (CFCs) damage the ozone layer.
Question 14.
Why is ozone layer important?
Answer:
It protects the earth from UV radiation of the sun.
Question 15.
What is the source of suspended solid particles in air?
Answer:
Sources of solid particles in air:
- Burning of petrol, diesel in automobiles,
- Industrial processes such as steelmaking and mining
- Power plants.
Question 16.
What is the effect of suspended particles in air?
Answer:
They reduce the visibility.
Question 17.
Which industries are responsible for acid rain around Taj in Agra?
Answer:
Rubber processing, Automobile, Chemical, Mathura oil refinery.
Question 18.
Which are acid gases?
Answer:
Acid-gases. Sulphur dioxide, Sulphur trioxide, Nitrous oxide.
![]()
Question 19.
Name two clean fuels.
Answer:
LPG and CNG.
Question 20.
Which gas has tendency to trap sun radiations and warm the atmosphere?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide.
Question 21.
Name some greenhouse gases.
Answer:
Green House gases. Methane, ozone, water vapours, nitrous oxide, carbon dioxide.
Question 22.
Which protocol has been signed to minimize greenhouse effect?
Answer:
The Kyoto protocol.
Question 23.
Name few alternate fuels.
Answer:
Alternate fuels. Solar energy, Hydropower, Wind energy.
Question 24.
When is Van Mahotsav celebrated in India?
Answer:
In the month of July of every year.
Question 25.
How should dry leaves be disposed?
Answer:
Dry leaves must be put in compost pit to obtain compost.
![]()
Question 26.
Which characteristics of water can get changed?
Answer:
Smell, colour and acidity.
Question 27.
Name few water pollutants.
Answer:
Water pollutants. Sewage, toxic chemicals, silt; insecticides, weedicides etc.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Give two examples of air pollutants.
Answer:
Examples of air pollutants:
- Oxides of Sulphur and Nitrogen.
- Radioactive fallout.
Question 2.
What are the major sources of air pollution?
Answer:
The major sources of air pollution are as follows :
- Industries. Paper and pulp industries, steel plants, petroleum refineries and chemical plants.
- Automobiles
- Smoke.
Question 3.
What is sewage?
Answer:
Sewage. The release of huge quantities of municipal and domestic wastes is called sewage. They contain certain organic wastes, toxic substances, which damage biological activities.
![]()
Question 4.
Why is the sewage water called polluted water?
Answer:
Sewage water contains human urine and faeces, cloth washings and industrial wastes. This water is totally unfit for drinking, washing and for other purposes. It lacks oxygen. It gives foul smell. It can lead to spread of water-borne diseases. Hence, the sewage water is called polluted water.
Question 5.
How should air pollution be controlled?
Answer:
Steps to control air pollution :
- Combustible solid wastes should tie burnt in incinerators.
- Automobiles must be either made to eliminate the use of gasoline and diesel oil or complete combustion is obtained in the engine so that harmful products are not emitted.
- Excessive and undesirable burning of vegetation should be stopped.
Question 6.
How can pollution of river water be controlled?
Answer:
Pollution of river water can be controlled by :
- Mechanical and chemical treatment of sewage at its origin and then allowing the clean, harmless effluents (industrial waste) to flow into the river.
- Shifting of present chemical factories and banning the construction of new factories on the river banks.
Question 7.
In what way chloro-fluoro carbons are harmful?
Answer:
Chloro-fluoro carbons deplete the ozone layer in the atmosphere which protects earthly organisms from harmful ultraviolet radiations.
Question 8.
How does carbon monoxide act on humans?
Answer:
Haemoglobin of the blood absorbs carbon monoxide. This in turn reduces oxygen-carrying capacity of blood. The non-availability of sufficient oxygen to the tissues results in death.
![]()
Question 9.
Which metals are harmful for health?
Answer:
Lead, Arsenic, Mercury.
Question 10.
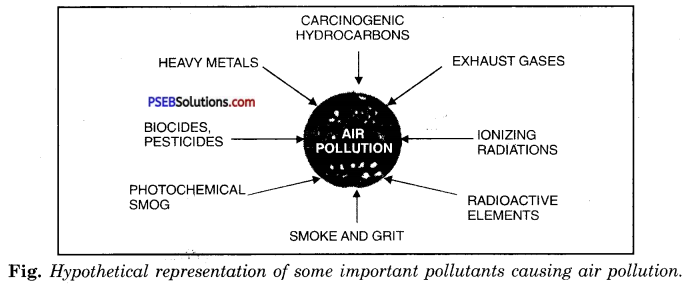
Depict the important pollutants of air.
Answer:
Air pollutants.
Question 11.
Write the harmful effects of greenhouse effect.
Answer:
Harmful effects of Greenhouse effect. The greenhouse effect will increase the temperature of earth’s surface. It will make the life of men and animals uncomfortable. The scientists have estimated that the sea level will rise by 100 m if the global temperature rises by 3-6°C due to greenhouse effect. If it happens, the coastal regions and many islands will be submerged causing great damage.
Question 12.
Why is Ganga river more polluted at Kanpur?
Answer:
At Kanpur, the amount of water and flow is comparatively less and slow. Near about 5000 industries of Kanpur discharge toxic chemicals into the river. People bath, wash clothes, defecate, throw garbage, flowers, worship material and polythene bags in the river.
![]()
Question 13.
How is ozone layer help to us?
Answer:
Ozone layer of atmosphere is very important for all living organisms. It absorbs the harmful ultraviolet rays radiated from the sun which otherwise can give rise to fatal diseases like skin cancer in humans. These rays are also harmful for crops.
Question 14.
Explain the ozone layer.
Answer:
Ozone layer. The ozone gas found in the stratosphere of atmosphere is known as ozone layer. It protects us from ultraviolet rays of the sun. A poisonous substance chlorofluorocarbon is used in refrigerators and air conditioners which attenuates the ozone layer. This is known as depletion of ozone layer.
Question 15.
Which types of problems can arise with an increase in global warming? Write about three problems.
Answer:
Global warming can create following problems.
- Summers will become more hot and dry and winters will be damp and colder.
- Glaciers will melt down due to increase in global warming and level of sea will rise by two feet.
- Water supplies would become disrupted and droughts would be more common.
Question 16.
How the industries located on the bank of Ganga river contribute to pollute it?
Answer:
There ae established industries in very big number in the cities and towns located on the bank of Ganga river. Only in Kanpur, there are more than 5000 industrial units which are adding fertilizers, detergents, poisonous waste of leather and paint industries, sewage, insecticides and garbage etc. in Ganga Paper factories, sugar mills and other chemical factories are polluting the water of Ganga by discharging their wastes in huge amount.
Question 17.
What instructions are issued by government for industries to maintain the cleanliness of holy rivers like Ganga?
Answer:
Oil refineries, textile and sugar mills, paper factories and chemical factories discharging their industries wastes directly into the rivers. As a result, the water of rivers is becoming poisonous. To check it government have passed regulations. According to these regulations, industries are to treat the waste produced for discharging it into water, but quite often the rules are not followed.
![]()
Question 18.
How can you help to reduce air pollution. Suggest any two measures.
Answer:
Steps to control air pollution
- Combustible solid wastes should be burnt in incinerators.
- Automobiles must be either made to eliminate the use of gasoline and diesel oil or complete combustion is obtained in the engine so that harmful products are not emitted.
Question 19.
List sources of noise pollution in your surroundings. Explain how noise pollution is harmful for human beings.
Answer:
Sources of noise pollution :
- Sounds of vehicles.
- Loudspeakers.
- Working Machines.
- Bursting of crackers.
- Desert coolers.
- Radios and televisions at high volumes.
- Kitchen appliances.
- Hawkers.
Harmful effects of noise pollution :
- Lack of sleep.
- Hypertension.
- Anxiety.
- Partial deafness.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What steps would you suggest for minimising the air pollution around you?
Answer:
The air pollution can be minimised by the following steps :
- Using alternative sources of energy, that are non-polluting such as solar energy, wind energy etc.
- Using lead-free fuels, such as Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) for running cars, buses, trucks etc. The vehicles must be regularly checked for pollution.
- Setting factories away from residential areas and their chimneys must have filters.
- Planting more and more trees, as they purify air.
- Not using bags made of plastic, instead using cloth and jute bags.
- Recycling materials, such as paper, metal etc.
- Avoiding burning of dried leaves, tree branches, paper, garbage etc. as the smoke released causes pollution.
- Saving electricity as it would amount to burning of less fossil fuels.
- Reducing the use of aerosols (i.e. particles of solid, or liquid matter) that can remain suspended in air from a few minutes to many months depending on particle size and weights, such as perfumes, deodorants etc.
- Avoiding smoking and encouraging others also to do the same.
![]()
Question 2.
Describe the role of sewage as water pollutant.
Answer:
Sewage can be classified into domestic sewage and industrial wastes. Domestic sewage is one of the most primary sources of water pollution. The industrial wastes also play major role in the pollution of water.
Sewage pollutes rivers, lakes and even oceans. Polluted waters are contaminated with infectious agents for cholera, typhoid, dysentery, jaundice and skin diseases.
In sewage water, there is depletion of oxygen, because the same is required for degradation of sewage. Reduced availability of oxygen causes suffocation and kills many aquatic animals especially fishes. Polluted water becomes unfit for drinking and cooking. The poisonous substances which get dissolved in water, make it unsuitable for aquatic life. It is unfit for agricultural operations also. Scum and sludge get collected and make the water unfit for boating and other recreational purposes.
Question 3.
Write a short note on air pollution.
Answer:
Air Pollution. Air is never found pure due to natural and man-made pollution. An undesirable change in the physical, chemical and biological characteristics of air is called air pollution. The substances which pollute the air are called air pollutants. The common air pollutants are carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide, oxides of nitrogen and suspended particulate matter.
The air pollution is caused by natural processes and human activities. Air pollution has very adverse effects on human beings. It affects raw materials, industrial processes, living conditions and cultural assets like historical monuments. It is posing main dangers to our lives.
Question 4.
Define acidic gases. Give examples. Can you observe its effects on newly constructed buildings made of marble?
Answer:
The gases which combine with water to form acids are called acidic gases.
Example: Sulphur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen dioxide (NO2). Effects on buildings made of marble.
The acidic gases (SO2 and NO2) react with water present in the air and get converted to acids :
2SO2 + O2 + 2H2O → 2H2SO4 Sulphuric acid
4NO2 + O2 + 2H2O → 4HNO3 Nitric acid
The acids come down to earth with rainwater. The rain containing acids is called acid rain. The acid damages the marble stone (CaCO3) by dissolving it.
CaCO3 + H2SO4 → CaSO4 + CO2↑ + H2O
CaCO3 + 2HNO3 → Ca(NO3)2 + CO2 ↑+ H2O Marble stone
Therefore, acidic gases damage the buildings made of marble.
Question 5.
Explain ozone depletion.
Answer:
Ozone Depletion:
Ozone layer acts as protector of life on earth. Due to human activities, CFCs produced by man depletes the ozone layer, more ultraviolet radiations reach the surface of earth. It is termed ozone depletion.
Effects of ozone depletion.
- UV radiation strikes the earth and these radiations cause skin cancer and damage to eye.
- These ultraviolet radiations damage the defence (immune) system of the body.
- It may lead to variations in global rainfall.
- It causes ecological disturbances such as floods, shortage of food etc.
Question 6.
Describe the sources of water pollution.
Answer:
Sources of water pollution:
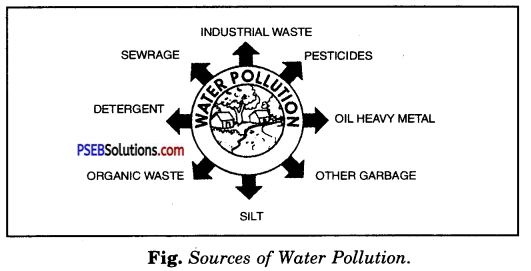
Following are the sources of water pollution-
1. Domestic effluent. In this case, wastewater is discharged into public sewerage system such as-
- Human and animal excreta
- Plenty of organic matter in the form of food residue
- Detergents
- A large number of bacteria.
2. Industrial effluent. Industries usually discharge wastewater into ponds, lakes, and rivers. Industrial wastewater contains heavy metals as mercury, lead, copper, arsenic, and cadmium.
3. Pesticides and fertilizers. The surface water runoff from the field with inorganic fertilizers, pesticides, insecticides, bring heavy loads of pollutants into natural water bodies. Pesticides like DDT are non-biodegradable.
4. Waste Heat. Waste heat is a rise in the temperature of water by human activity. Thermal power plants, refineries, etc. discharge hot water into nearly lakes, sea, etc. The sudden rise in the temperature of the water has very harmful effects on aquatic organisms, such as fish and algae.
