Punjab State Board PSEB 7th Class Science Book Solutions Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric
Science Guide for Class 7 PSEB Fibre to Fabric Intext Questions and Answers
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 24)
Question 1.
Name any two natural fibres obtained from plants.
Answer:
Natural Fibres obtained from Plants : (1) Cotton, (2) Bamboo.
Question 2.
Name any two natural fibres obtained from animals.
Answer:
Natural fibres obtained from animals : (1) wool, (2) silk.
![]()
Question 3.
Name any three animals which provide us wool.
Answer:
Animals that provide wool : (1) sheep, (2) yak, (3) goat.
Question 4.
Why do some animals have a thick coat of hairs ?
Answer:
The hair of some animals is dense because the wool-giving sheep that are found in cold regions have a dense coat of hair over their body, so that they can keep their body warm in winter. Hair traps a lot of air. This air is a poor conductor of heat and prevents the body heat to escape to the surrounding environment and thus keeps the sheep warm.
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 29)
Question 1.
What difference in smell you notice on burning silk thread, thread and wool ?
Answer:
The process of burning of silk gives a smell like burning of meat. When cotton thread bums, it gives smell like burning of paper but the burning of wool gives strong smell like burning of hair.
Question 2.
What type of ash is formed in the above activity ?
Answer:
The ash left after burning of cotton thread is of grey colour. The burning of silk thread and woollen thread produces ash like hollow bead of black colour.
Question 3.
Does the smell of burning of silk thread is same as the smell of burning woollen thread ?
Answer:
No. The smell of burning of silk thread is just like burning of hair while the smell of burning of wool thread is like cooking meat.
PSEB 7th Class Science Guide Fibre to Fabric Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Fill in the Blanks:
(i) Wool is obtained from the …………….. of sheep, goat and yak.
Answer:
hairs
(ii) Long hair on the body protect animals from ………………
Answer:
cold
(iii) Removal of fleece from the skin of animal is called ………………
Answer:
shearing
![]()
(iv) Rearing of silkworm is called ………………….
Answer:
sericulture
(v) The process of unwinding the filaments from the boiled cocoons, is called ………….. .
Answer:
reeling
2. Match the Column ‘A’ with Column ‘B’:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Scouring
2. Sericulture 3. Protein 4. Mulberry leaves 5. Lohi |
(a) Food of silkworm
(b) Sheeps found in Rajasthan and Punjab (c) Silk fibre made up of (d) Rearing of silkworms (e) Cleaning sheared fleece |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Scouring
2. Sericulture 3. Protein 4. Mulberry leaves 5. Lohi |
(e) Cleaning sheared fleece
(d) Rearing of silkworms (c) Silk fibre made up of (a) Food of silkworm (b) Sheep found in Rajasthan and Punjab |
3. Choose the Correct Answer:
Question (i)
The fibre which is not produced by animals:
(a) Angora Wool
(b) Wool
(c) Jute
(d) Silk
Answer:
(c) Jute.
Question (ii)
Wool is commonly obtained from:
(a) Sheep
(b) Goat
(c) Yak
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(a) Sheep.
Question (iii)
Washing of sheared hair is called:
(a) Scouring
(b) Sorting
(c) Shearing
(d) Dyeing
Answer:
(a) Scouring.
Question (iv)
Wool is chemically:
(a) Fat
(b) Protein
(c) Carbohydrate
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Fat.
Question (v)
The animal that does not yield wool is:
(a) Alpaca
(b) Woolly dog
(c) Camel
(d) Goat
Answer:
(b) Woolly dog.
![]()
4. Write True or False:
(i) Air is a bad conductor of heat.
Answer:
True
(ii) Air trapped in long hair does not allow body heat to escape from body.
Answer:
True
(iii) In Tibet and Ladakh, wool is obtained from yak.
Answer:
False
(iv) Rearing of silk moths is called apiculture.
Answer:
True
(v) The cover around the body of caterpillar is called cocoon.
Answer:
False
(vi) Tassar silk and moonga silk are produced by silk moth who have been feeding on non-mulberry trees.
Answer:
False
5. Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Question (i)
Names any two plant fibres and animal fibres.
Answer:
Fibres obtained from plants : (1) Husk fibre, (2) Cotton.
Fibres obtained from animals : (1) Wool, (2) Silk.
![]()
Question (ii)
What is sericulture ?
Answer:
Sericulture. Cultivation of silkworms to obtain silk is called sericulture.
Question (iii)
Name the common animals who yield fleece.
Answer:
(1) Yak, (2) Sheep, (3) Camel (4) Goat
6. Short Answer Type Questions:
Question (i)
What do you understand by Angora and Kashmere wool ?
Answer:
North Angora wool. It is obtained from goats found in mountainous places like Jammu and Kashmir.
Kashmere Wool. Kashmere wool is woven into pashmina shawls.
Question (ii)
Write the states where the following breeds of sheep are found : Lohi, Bakharwal, Nali and Marwari.
Answer:
| Types of Sheep | State where they are found |
| Lohi | Punjab, Rajasthan |
| Bakharwal | Jammu, Kashmir |
| Nali | Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan |
| Marwari | Gujarat |
Question (iii)
Write all the steps involved in processing fibres into wool.
Answer:
The Different Stages of Rise to the North
- Shearing or cutting
- Scouring
- Sorting
- Combing
- Dyeing
- Spinning or weaving.
Question (iv)
Why do some animals have a thick coat of hair ?
Answer:
The hair of some animals is dense because the wool-giving sheep that are found in cold regions have a dense coat of hair over their body, so that they can keep their body warm in winter.
Hair traps a lot of air. This air is a poor conductor of heat and prevents the body heat from circulating in the external environment which keeps the sheep warm.
![]()
Question (v)
How is silkmoth reared ?
Answer:
Rearing of Silkworm. The female silkworm lays hundreds of eggs at a time. These eggs are carefully collected on cloth strips or paper and kept in healthy conditions, at suitable heat and humidity conditions. The eggs are kept warm to a suitable temperature to allow the larvae to hatch. The larvae, called caterpillars or silkworms, are housed on mulberry leaves.
They eat these leaves day and night and increase in size considerably. Then these are kept in clean bamboo trays with fresh mulberry leaves. After 25-30 days, they stop eating and the caterpillars are moved to bamboo chambers to make cocoons. So the twigs are placed in a tray, with which the cocoons clrng. Caterpillar or silkworms form cocoons in which silkworm develop.
7. Long Answer Type Questions:
Question (i)
Write all the steps in processing silk from cocoons.
Answer:
The process of making silk from the cocoon. The cocoon has a continuous growth of insect inside it. Silk thread is obtained from the cocoon of the silkworm. Silk threads are used to make silk fabrics. These soft silk threads can be as strong as steel wires. There are many types of silkworms that look different from each other.
The different textures (rough, soft, shiny etc.) of silks like tusser silk, mooga silk, consa silk etc. are obtained from different types of insect cocoons. The most common silkworm is the mulberry silkworm. The silk obtained from this worm is very soft, shiny and flexible. It can be painted in beautiful colours. Sericulture or rearing of silkworms is a very old occupation in India. India produces a lot of silk commercially.
Question (ii)
Draw a labeled diagram and explain the life cycle silkmoth.
Answer:
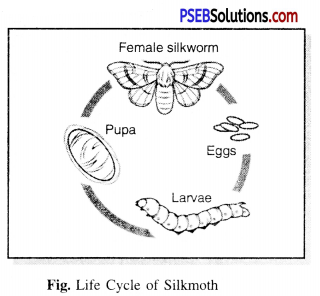
Life Cycle of Silkmoth. The life cycle of the silkworm is summarized in the following steps:
Step 1. The female silkworm lays eggs on the leaves of mulberry.
Step 2. The eggs give birth to larvae that take on an insect-like structure over the next two weeks called a caterpillar or silkworm.
PSEB Solutions for Class 7 Science Fibre to Fabric Important Questions and Answers
1. Fill in the Blanks:
(i) The wool is obtained from the …………….. of sheep, goat and yak.
Answer:
skin
(ii) Long hair on the body of animals protect them from ……………… .
Answer:
cold
(iii) The process of yielding wool from the skin of animal is known as ………………….. .
Answer:
shearing
![]()
(iv) Rearing silk worm is called ………………. .
Answer:
sericulture
(v) The process of removing threads from the boiled cocoon is called ………………….. .
Answer:
reeling.
2. Match the Column I with Column II:
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Scouring
2. Mulberry leaves 3. Yak Cocoon |
(a) Yields silk fibres
(b) Wool yielding animal (c) Food of silk worm. (d) Reeling (e) Cleaning sheared skin. |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Scouring
2. Mulberry leaves 3. Yak 4. Cocoon |
(e) Cleaning sheared skin.
(c) Food of silk worm. (b) Wool yielding animal (a) Yields silk fibres. |
3. Choose the Correct Answer:
Question (i)
We get from yak:
(a) silk
(b) cotton
(c) wool
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) wool.
Question (ii)
For making Pashmina shawls, wool is obtained from:
(a) Yak
(b) Camel
(c) Sheep
(d) Angora goat.
Answer:
(d) Angora goat.
Question (iii)
In South America wool is obtained:
(a) Llama and Angora goat
(b) Llama and yak
(c) Sheep and Llama
(d) Llama and Alpaca.
Answer:
(d) Llama and Alpaca.
Question (iv)
Bakharwal breed of sheep is found:
(a) In Punjab
(b) In Rajasthan
(c) In Haryana
(d) In Jammu and Kashmir.
Answer:
(d) In Jammu and Kashmir.
![]()
Question (v)
The sheep’s hair are mostly cut in:
(a) Summer
(b) Winter
(c) Both Summer & Winter
(d) Neither very hot or cold season.
Answer:
(a) Summer.
Question (vi)
Process of taking out silk yarn from cocoons:
(a) Rearing silk worms
(b) Sericulture
(c) Reeling
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Reeling.
Question (vii)
Lohi breed of sheep is found in:
(a) Punjab and Rajasthan
(b) Punjab and Himachal
(c) Punjab and Gujarat
(d) Punjab and Jammu.
Answer:
(a) Punjab and Rajasthan.
4. State True or False:
(i) Pashmina Shawl is made from llama and alpaca wool.
Answer:
True
(ii) Wool is chemically a carbohydrate.
Answer:
False
(iii) Warm silk is obtained from leaf-eating insects.
Answer:
True
![]()
(iv) The wool obtained from the Marwari sheep (breed of Gujarat) is very soft.
Answer:
False
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How do hair help animals to keep them warm ?
Answer:
Hair trap a lot of air. As air is bad conductor of heat so it does not allow heat of the body to go to the surroundings and therefore, keeps the animal warm.
Question 2.
From where wool is derived ?
Answer:
Hairy skin of animals.
Question 3.
Name wool yielding animals.
Answer:
Yak, Sheep, Goat, Lama, Alpaca.
Question 4.
What is pashmina ?
Answer:
Pashmina is soft wool obtained from Kashmiri goat.
Question 5.
In which part of India is Yak wool commonly seen ?
Answer:
Tibet and Ladakh.
Question 6.
Which animal is commonly reared for wool ?
Answer:
Sheep.
![]()
Question 7.
What is called woollen thread ?
Answer:
Fiber.
Question 8.
In winter, which food is given to sheep ?
Answer:
Leaves, grains, dry fodder.
Question 9.
Which instrument is used for shearing ?
Answer:
Machine similar to those used by barbers.
Question 10.
In which season, fleece is sheared off ?
Answer:
Summer or hot season.
Question 11.
Name some Indian breed of sheep.
Answer:
Lohi, Rampur bushair, Nali, Marwari, Bakharwal, Patanwad.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write down the different steps for obtaining wool from sheep.
Answer:
Steps for obtaining wool
Shearing, scouring, sorting, drying, dyeing, spinning and weaving.
Question 2.
In which part of India, sheep are reared for wool ?
Answer:
Hills in Kashmir, Himachal, Uttranchal, Arunachal, Sikkim and plains of Haryana. Punjab, Rajasthan and Gujrat.
Question 3.
Why does shearing not hurt the sheep ?
Answer:
Hair grow on uppermost layer of the skin, which consists of dead cells. So sheep do not feel pain of the time of shearing.
![]()
Question 4.
Why is fleece scoured ?
Answer:
Fleece is scoured to remove dirt, grease and dust from it. This process is known as scouring
Question 5.
What happens when silk fibre and artificial silk thread is burned ?
Answer:
Burning of silk fibres produces no smell and no residue is left behind.
While burning of artificial silk thread produces pungent smell and a fluffy residue formed.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write in brief the process of obtaining silk ?
Answer:
Silk is obtained from silk moth which are reared and their cocoons are collected to get silk fibre. The process involves two steps:
(i) Rearing silk worms.
(ii) Processing silk.
(i) Rearing silk worms. The eggs layed by female silk moth are stored carefully on strips of cloth or paper and kept under hygienic conditions and suitable temperature and humidity.
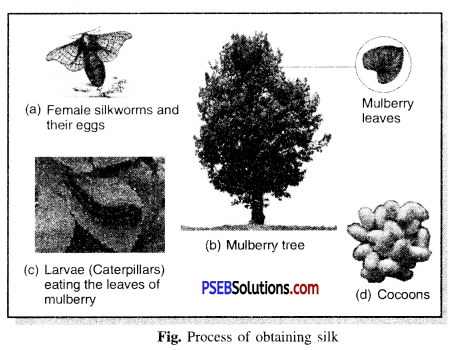
Sometimes eggs are warmed to hatch larvae and these larvae are fed on fresh leaves of mulberry tree. These larvae called caterpillars or silkworms eat day and night to grow into enormous sizes.
These larvae are kept in clean bamboo trays along with freshly chopped mulberry leaves. After 20 to 25 days, the caterpillass or silkworms stop eating and move to a tiny chamber of bamboo tray to spin cocoons. Inside cocoon, develops the silk moth.
(ii) Processing silk. A pile of cocoons is collected and kept under the sun. or boiled or exposed to steam to separate out the silk fibres. These silk fibres are reeled and then spun into silk threads which are woven to give silk cloth.
Question 2.
Describe in brief the steps involved in obtaining wool from sheep.
Answer:
Processing of silk involves the following steps:
(i) Boiling. First cocoons are first boiled in hot water then treated in ovens to kill larvae inside. If in case of larvae a not killed, they are allowed to grow. They will break the cocoon and thereby reducing the length of the silk fibre. The hot water softens the silk gum to the unwinding silk fibre as one continuous thread.
(ii) Reeling. It is the process of taking out the thread from the cocoon. Reeling is done with the help of special machines.
(iii) Throwing. In this step raw silk is twisted to produce thrown silk. It prevents the silk from splittings into individual fibres.
(iv) Deying. Thrown silk is then dyed for making coloured fabrics. Dyed Silk fibres are spun into silk threads, which are waven into silk clothes.
