Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class Science Book Solutions Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals
PSEB 8th Class Science Guide Reproduction in Animals Textbook Questions and Answers
Exercises
Question 1.
Explain the importance of reproduction in organisms.
Answer:
Importance of Reproduction.
It is the ability of living organism to produce the youngones of its own kind. Reproduction helps to increase the population of species. It is an important biological process for existence and continuity of a species. It also involves the transmission of genetic material from parents to offsprings.
Question 2.
Describe the process of fertilization in human beings.
Answer:
Fertilization.
The testes produce the male gametes called sperms. Millions of sperms are produced by the testes. Though sperms are very small in size, each has a head, a middle piece and a tail.
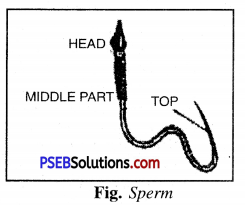
The first step in the process of reproduction is the fusion of a sperm and an ovum or an egg. Millions of sperms from the male are transferred into female body. The sperms swim in the oviduct with the help of their tails to reach egg. When they come in contact with the egg,- one of the sperms may fuse with the egg. Such fusion of the egg and the sperm is called fertilization. During fertilization, the nuclei of the sperm and the egg fuse to form a single nucleus which result in the formation of a fertilized egg called zygote. Zygote is the beginning of a new individual.
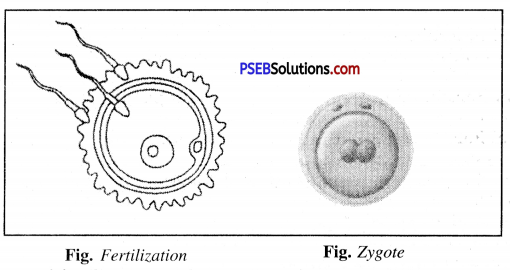
The process of fertilization is the meeting of an egg cell from the mother and a sperm cell from the father. So the new individual inherits some characteristics from the mother and some from the father.
![]()
Question 3.
Choose the most appropriate answer.
(a) Internal fertilization occurs:
(i) in female body.
(ii) outside female body.
(iii) in male body.
(iv) outside male body.
Answer:
(i) In female body.
(b) A tadpole develops into an adult frog by the process of:
(i) fertilization
(ii) metamorphosis
(iii) embedding
(iv) budding.
Answer:
(ii) metamorphosis.
(c) The number of nuclei present in a zygote is
(i) none
(ii) one
(iii) two
(iv) four.
Answer:
(ii) one
Question 4.
Indicate whether the following statements are True [T] or False [F]:
(a) Oviparous animals give birth to young ones.
Answer:
False
(b) Each sperm is a single cell.
Answer:
True
(c) External fertilization takes place in frog.
Answer:
True
(d) A new human individual develops from a cell called gamete.
Answer:
False
(e) Egg laid after fertilization is made up of a single cell.
Answer:
True
(f) Amoeba reproduces by budding.
Answer:
False
(g) Fertilization is necessary event in asexual reproduction.
Answer:
False
(h) Binary fission is a method of asexual reproduction.
Answer:
True
(i) A zygote is formed as a result of fertilization.
Answer:
True
(j) An embryo is made up of a single cell.
Answer:
False
Question 5.
Give two differences between a zygote and a foetus.
Answer:
Differences between a zygote and a foetus
| Zygote | Foetus |
| 1. The fusion of sperm and egg is called a zygote. | 1. The stage of embryo in which cell body parts are identifiable is called foetus. |
| 2. It is single celled structure. | 2. It is a multicellular structure. |
Question 6.
Define asexual reproduction. Describe two methods of asexual reproduction in animals.
Answer:
Asexual Reproduction.
The type reproduction in which only a single parent is involved is called asexual reproduction.
Methods of asexual reproduction in animals
1. Binary Fission.
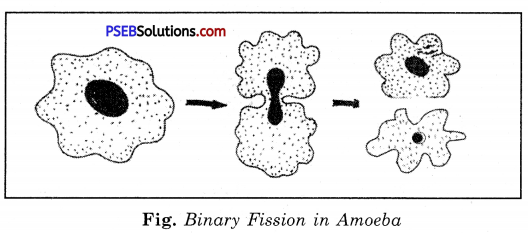
Binary fission involves an equal or nearly equal longitudinal or transverse splitting of the body of the parents into two parts each of which grows to parental size and form. This method of reproduction occurs regularly among protozoa (Amoeba, Paramecium etc.) in which it is essentially the process of cell division which results in the complete separation of the daughter cells. It has also been observed among multicellular animals as an sea anemones in the form of longitudinal fission or as transverse fission among planarians.
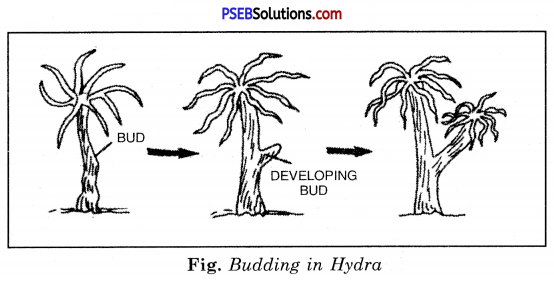
2. Budding.
Budding is a form of asexual reproduction in which new individual arises from a relatively small mass of cells that initially forms a bud on the parental body. The bud may assume parental form either before separation from the body of the parent as in external budding or after separation as in internal budding. External budding is common among sponges, coelenterates (e.g. Hydra), flatworms and tunicates. But in some coelenterate as in Obelia, it gives rise to medusae rather than to the parental.
Question 7.
In which female reproductive organ does embryo get embedded ?
Answer:
Uterus (Uterine wall).
![]()
Question 8.
What is metamorphosis ? Give examples.
Answer:
Metamorphosis. The drastic changes that take place during the development of an animal is called metamorphosis.
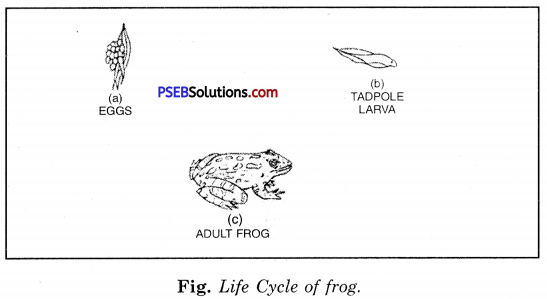
In the above figure, we see the different stages of development of frog. We find three distinct stages –
(i) Egg (ii) tadpole larva (iii) adult frog.
We see that tadpole larva is totally different from its adults.
Tadpole has gills for respiration because it lives outside the water. The sudden changes come in the body of tadpole like gills are replaced lungs. These sudden changes are called metamorphosis.
Example of animals in which metamorphosis take place are : Frog, silkworm.
Question 9.
Differentiate between internal fertilization and external fertilization.
Answer:
Differences between external fertilization and internal fertilization
| External fertilization | Internal fertilization |
| 1. The fusion of male gamete (sperm) and female gamete (ovum) occurs outside the body. | 1. The fusion of gametes occurs inside the body. |
| 2. Both individuals discharge their gametes outside the body. | 2. Only the male discharge gametes into genital tract of female. |
| 3. Development occurs outside the body. | 3. Development may occur inside the body. |
| 4. Example : Frog. | 4. Example : Human, cattle, shark, birds. |
Question 10.
Complete the crossword puzzle using the hints given below.
Across
1. The process of the fusion of the gametes.
6. The type of fertilization in hen.
7. The term used for bulges observed on the sides of the body of Hydra.
8. Eggs are produced here.
Down
2. Sperms are produced in these male reproductive organs.
3. Another term for the fertilized egg.
4. These animals lay eggs.
5. A type of fission in amoeba.
Answer:
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Reproduction in Animals Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
A hydra on fission produces two or more hydra. What is this type of asexual reproduction called ?
(a) Budding
(b) Binary Fission
(c) Vegetative reproduction
(d) Gamete.
Answer:
(a) Budding.
Question 2.
The following diagram is of which organism ?
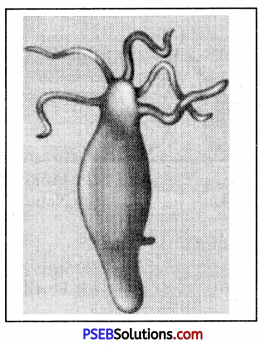
(a) Amoeba
(6) Paramecium
(c) Hydra
(d) Frog
Answer:
(c) Hydra.
![]()
Question 3.
The following diagram shows the life cycle of which organism ?
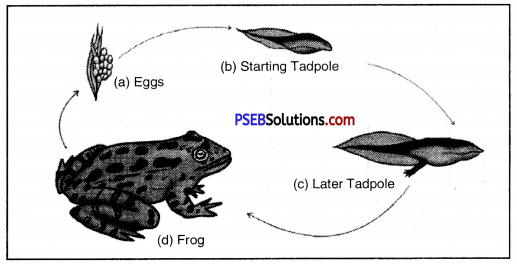
Answer:
Life cycle of a frog.
Question 4.
The following Diagram shows which process of asexual reproduction of amoeba ?
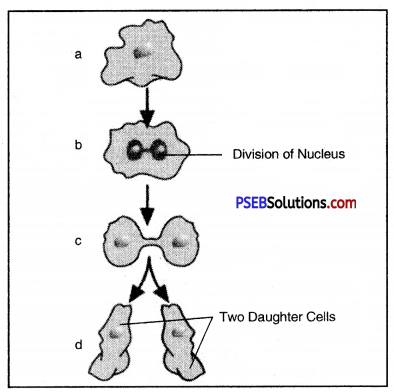
(a) Budding
(b) Binary fission
(c) Asexual reproduction
(cl) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Binary fission
Question 5.
Female gamete is called:
(a) Sperm
(b) Egg
(c) Zygote
(d) Fertilization
Answer:
(b) Egg.
Question 6.
An amoeba on fission produces two amoeba. What type of asexual reproduction is this ?
(a) Budding
(b) Binary fission
(c) Gametes
(d) Vegetative reproduction.
Answer:
(b) Binary fission.
Question 7.
Internal fertilization is:
(a) Inside the body of female
(b) Outside the body of female
(c) Inside the body of male
(d) Outside the body of male.
Answer:
(a) Inside the body of female.
Question 8.
By which process one tadpol is developed into adult ?
(a) Fertilization
(b) Metamorphosis
(c) Stagnation
(d) Budding.
Answer:
(b) Metamorphosis.
Question 9.
The number of nucleus found in gamete is:
(a) None
(b) One
(c) Two
(d) Four
Answer:
(b) One.
![]()
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
1. The process of ……………… ensures continuity of life on earth.
2. The male and female gametes in the flower are called ………………. and ………………… respectively.
3. In ……………….. reproduction, one individual can make many new individuals from its body parts.
4. ………………….. grow throughout life, but ………………… grow only upto a certain age.
5. A multicellular animal starts its life from a ……………………. through sexual reproduction.
Answer:
1. reproduction
2. pollen, egg
3. asexual (vegetative)
4. plants, animals
5. zygote.
Question 2.
Which part of the body:
(a) produces sperms ?
(b) produces ova ?
(c) passes sperms from a man to a woman ?
Answer:
(a) Testis
(b) Ovaries
(c) Penis.
Question 3.
How many methods of reproduction are there in the plants and animals ?
Answer:
Two:
- asexual
- sexual.
Question 4.
How many parents are needed in asexual reproduction ?
Answer:
Only one parent is needed in asexual reproduction.
Question 5.
How many parents are needed in sexual reproduction ?
Answer:
Two parents are needed in sexual reproduction.
Question 6.
What are the specialised cells present in the sex organs ?
Answer:
Gametes.
Question 7.
Name two animals which reproduce by binary fission.
Answer:
- Amoeba
- Paramecium.
Question 8.
In which organisms do the buds remain attached to the parent organisms ?
Answer:
Sponges, Corals.
![]()
Question 9.
What is zygote ?
Answer:
Zygote. Zygote is the first structure formed after union of sperm and egg.
Question 10.
What is fertilization ?
Answer:
The fusion of male gamete and female gamete is known as fertilization.
Question 11.
Which is the larger-sperm or ovum ?
Answer:
Ovum or egg.
Question 12.
Name two hermaphrodites.
Answer:
- Earthworm
- Leech.
Question 13.
Name two animals in which fertilization is external.
Answer:
- Frog
- Fish.
Question 14.
Define metamorphosis.
Answer:
Metamorphosis. The drastic changes which transform a larva into an adult is called metamorphosis.
Question 15.
What is gonad ? Name the male and female gonads of human body.
Answer:
Gonad.
The reproductive organ that produces special sex cells called gametes, is called gonad.
Male gonad. The male gonad testis produces male gametes, called sperms.
Female gonad. It is the ovary and produces female gametes called ova.
Question 16.
Name the male and female gametes of man.
Answer:
Male gamete – Sperm : Female gamete – Ovum.
![]()
Question 17.
Give one example each of animal showing external fertilization and another of internal fertilization.
Answer:
External fertilization – Frog;
Internal Fertilization – Human.
Question 18.
What is the function of sperm duct ?
Answer:
Sperm duct (vas deferens). It conducts sperms from testes to urethra.
Question 19.
What is hymen ?
Answer:
Hymen. In the case of virgins at the orifice of vagina present a thin membranous diaphragm called hymen. It is perforated to pass menstrual discharge.
Question 20.
In which type of asexual reproduction takes place in Hydra ?
Answer:
Budding.
Question 21.
Define cloning.
Answer:
Cloning. It is the production of an identical cell, any other part, or a complete organism.
Question 22.
Name the sheep which was cloned successfully by Ian Wilmont at the Roslin Institute in Edenburgh, Scotland.
Answer:
Dolly sheep.
Question 23.
Name the first mammal to be cloned.
Answer:
A sheep named Dolly which was born on 5th July, 1996.
![]()
Question 24.
What is reproduction ?
Answer:
Reproduction. To produce young ones of their own kind is called reproduction.
Question 25.
What is the function of tail of sperm in man ?
Answer:
For movement.
Question 26.
What is ovulation ?
Answer:
Production of eggs from the ovaries is called ovulation.
Question 27.
What is a test tube baby ?
Answer:
The babies produced by an artificial fertilization outside the body are called test tube babies.
Question 28.
Give full form of I.V.F.
Answer:
Invitro fertilization.
Question 29.
Where does test tube baby develops ?
Answer:
In uterus.
Question 30.
What are oviparons animals ?
Answer:
Egg laying animals are called oviparous animals.
![]()
Question 31.
What are viviparous animals ?
Answer:
Young ones producing animals are called viviparous animals.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the difference between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction ?
Answer:
Differences between Asexual and Sexual reproduction:
| Asexual reproduction | Sexual reproduction |
| 1. New individuals are formed from a single parent. | 1. Two parents are involved in the formation of new individual. |
| 2. It does not require the production of sex organs. | 2. Sex organs are pre-requisite for it. |
| 3. It does not involve meiosis. | 3. It involves meiosis at one or the other stage. |
| 4. It does not involve fusion of cells. | 4. It involves formation and fusion of gametes. |
| 5. New individual develops from one cell. | 5. New individual develops from fusion product of two gametes. |
| 6. New individuals are genetically similar to the parents. | 6. New individuals are generally different from either of the two parents. |
| 7. It does not introduce variability. | 7. It introduces variability. |
Question 2.
What is sexual reproduction ? Discuss sexual reproduction in animals.
Answer:
Sexual reproduction.
Union of male and female individuals to accomplish fertilization is called sexual reproduction.
Sexual reproduction in animals.
In sexual reproduction, there are two parents. The parents have sex organs which produce sex cells. Females produce eggs while males produce sperms. Sperms are produced by sex organs called testes. Female sex cells are called eggs or ova (singular ovum). Ova are produced by sex organ called ovaries. A sperm enters an egg. This is called fertilization. A fertilized egg divides many times. The cells develops into an embryo which later develops into an adult.
Question 3.
What are the organs in human beings which produce the gametes ?
Answer:
The male organs in human beings are a pair of testis. The female organs in human beings are a pair of ovaries.
Question 4.
Name two organisms which produce by two types of asexual methods. What are the methods ?
Answer:

Question 5.
What are gametes ? What is the difference between the unisexual and hermaphrodite ?
Answer:
Gametes.
Gametes are the reproductive cells which are produced by the sex organs of the body. There are two types of gametes-male and female. Due to the union of gametes, fertilization takes place.
Unisexual organism are those which have only one kind of sex organs either male or female.
Hermaphrodite are those organisms which have both kinds of sex organs.
![]()
Question 6.
What is hermaphrodite ? Give two examples.
Answer:
The organisms which can produce both the male and female gamete are called hermaphrodites or bisexual. Examples:
- Earthworm
- Hydra.
Question 7.
In how many ways can a tissue grow in size ?
Answer:
Growth means getting bigger in size. The tissue can grow in size by:
- Increasing the size of the cells.
- Increasing the number of cells.
Question 8.
What are the basic features in the process of asexual reproduction ?
Answer:
Basic features of asexual reproduction
- Only one parent is involved.
- All the cell divisions are mitotic.
- All the offsprings are genetically similar to the parent.
- The reproductive unit is a fragment or specialised part of the parent.
Question 9.
How is process of binary fission different from budding ?
Answer:
Differences between binary fission and budding
| Binary | Budding |
| 1. Only two young ones are formed. | 1. Large number of buds may be formed, each growing into new individual. |
| 2. Example : Amoeba, Euglena. | 2. Examples : Sponges, Hydra. |
Question 10.
Define ovulation.
Answer:
Ovulation.
Release of ovum (unfertilized egg) from the ovary is called ovulation. Egg is released on 14th day of 28-day menstrual cycle.
Question 11.
What is reproduction ? What are its basic types ?
Answer:
Reproduction.
All organisms born on this earth show characteristics life cycle, involving birth, growth, maturation, reproduction and death. Reproduction is one of the most important processes by which continuation of the species from one generation to another generation can take place. Older and aged organisms are replaced by new and younger organisms by reproduction. There are two basic types of reproduction. Reproduction is of two types:
A. Asexual reproduction
B. Sexual reproduction.
Question 12.
Name the various organs of male reproductive system in man.
Answer:
Male reproductive organs of man
- A pair of testes
- A pair of epididymis
- A pair of vas deferentia
- A pair of seminal vesicles
- Urethra
- Penis
- Male reproductive glands
(Cowper’s gland and prostate gland).
![]()
Question 13.
Name the various organs of female reproductive system.
Answer:
Female reproductive system is composed of organs given ahead :
- A pair of ovaries
- A pair of fallopian tubes
- Uterus
- Vagina
- Vulva
Question 14.
Differentiate the following:
(i) Sperm and Ovum
(ii) Vas deferens and Fallopian tube
(iii) Male urethra and Female urethra
(iv) Foetus and Embryo.
Answer:
(i) Differences between Sperm and Ovum
| Sperm | Ovum |
| 1. The sperm is active. | 1. The ovum is inactive. |
| 2. The sperm is capable of movement. | 2. The ovum is stationary. |
| 3. It has a locomotory organ (tail). | 3. It has no locomotory organ. |
| 4. It is smaller in size. | 4. It is bigger in size due to presence of yolk. |
(ii) Differences between Vas deferens and Fallopian tube
| Vas deferens | Fallopian tube |
| 1. Vas deferens is a part of male reproductive system. | 1. Fallopian tube is a part of female reproductive system. |
| 2. It serves to conduct the sperm from the testis to the urethra. | 2. It serves to conduct the ovum from the ovary to the uterus. |
(iii) Differences between Male Urethra and Female Urethra
| Male urethra | Female urethra |
| In male the urethra serves to carry the urine as well as semen outside. | In female urethra serves to carry only the urine as the urethra and the vaginal apertures are separate. |
(iv) Differences between Foetus and Embryo
| Foetus | Embryo |
| 1. The mammalian embryo which has recognisable appearance of main features of fully developed animal is called as foetus. | 1. In early stage of development (from the fertilized egg), the developing animal is called as embryo. |
| 2. In humans after two months of gestation the embryo is called foetus. | 2. It is the early stage of development, before it emerges from the egg or from the uterus of the mother. In humans, the term is restricted to the stages between second to eighth week after conception. |
Question 15.
Write a note on ‘test tube babies’.
Answer:
Test tube babies.
Actually this name is a wrong name because babies cannot grow in test tubes. In some women oviducts are blocked. These women unable to bear babies because sperms can not reach the egg for fertilization. In such cases, doctors collect freshly released egg and sperms and keep them together for a few houjs for in vitro fertilization (fertilization outside the body). After the zygote develops for about a week, it is placed in the mother’s uterus. Complete development takes place in the uterus and the baby is born like any other baby.
Question 16.
How does fertilization take place in frog ?
Answer:
In frog fertilization takes place outside the body of female. So this type of fertilization is called external fertilization.
During spring or rainy season, frogs and toads move to ponds. As the eggs are laid, the male frog deposits sperms over them. Each sperm swims randomly in water with the help of its long tail. The sperms come in contact with the eggs. This results in fertilization.
![]()
Question 17.
Why animals which undergo external fertilization such as frog and fish lay eggs in hundreds while a hen lays only one egg at a time ?
Answer:
Frog and fish release hundred of eggs and millions of sperms. But all the eggs are not fertilized because eggs and sperms get exposed to water movement, wind and rainfall. Some animals found in water may feed on eggs. Thus production of large number of eggs are necessary to ensure fertilization.
Question 18.
What are oviparous and viviparous animals ?
Answer:
Oviparous animals. The animals, which lay eggs are called oviparous animals. Frog, butterfly, hen, crow etc.
Viviparous animals. The animals which give birth to young ones are called viviparous animals, e.g. man, dog, cow, cat etc.
Question 19.
What is Menstruation ?
Answer:
Menstruation.
The rhythmic changes in the uterus which occur about every 28 days throughout the reproductive cycle of women except the pregnancy is called menstrual cycle. The female sex hormones initiate the thickening of the uterine wall for the implantation of a fertilized ovum. If the ovum is not fertilized, the lining wall is broken down and discharged from the body. This is called menstruation. Normally the menstrual cycle starts at the age of 10-14 years and stops at the age of 45-50 when menopause is reached.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are gonads ? Briefly explain male reproductive system.
Answer:
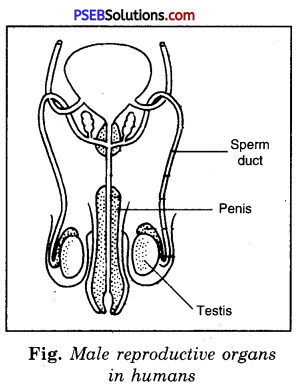
Gonads.
The primary sex organs which produce gametes are called gonads. Male gonads are testes and female gonads, ovaries.
Male reproductive system. The male reproductive system of man consist of following organs:
1. A pair of testes.
The male gonads (primary sex organs) are a pair of testes. They are paired organs and are located outside the body cavity in a pouch called scrotum. It helps in keeping the testes at a cooler temperature than the body temperature essential for maintenance and function of spermatogenic tissue. It measures 4 cm, 3 cm and 2.5 cm in length, thickness and width. Each testis is formed of large number of seminiferous tubules, they produce sperms and glandular cells which produce sex hormone, testosterone.
2. A pair of epididymis.
At the end of each seminiferous tubule is a very small tubule called the vas efferens. The vasa efferentia lead into epididymis. In the epididymis sperms are stored.
3. A pair of vasa deferentia (Sing. Vas deferens).
Corpus epididymis continues as vas deferens. It is a muscular tube. It is about 30 cm long. It leaves the scrotum by inguinal canal passes over the urinary bladder and receives a duct from seminal vesicle to form ejaculatory Fig. Male reproductive organs duct.
4. Male Urethra.
It is about 7-9 inches long. It leaves the urinary bladder and is joined by ejaculatory duct. It passes through penis and opens at the tip. The tip of penis is called glans penis and is covered over by fold of skin which is known as prepuce.
5. Reproductive glands (Accessory or secondary glands). They are prostate gland and Cowper’s gland.
- Prostate gland. It surrounds the urethra and opens into by means of numerous fine ducts. It secretes milky alkaline secretion and form 15-30% of semen.
- Cowper’s gland. A pair of glands called Cowper’s gland are attached to urethra. They secrete a clear viscid muscus which is lubricatory in function.
- The seminal vesicles. They are paired tubular structures located behind the neck of bladder. Its secretion forms essential component of seminal fluid.
Question 2.
Briefly explain various parts of female reproductive system.
Answer:
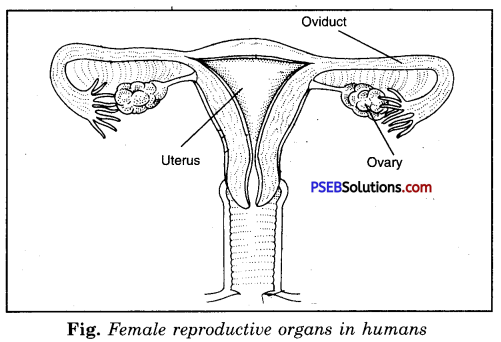
Reproductive system of woman. It consists of following organs:
1. A pair of ovaries.
There are present a pair of ovaries (primary female sex organ) measuring 3 cm, 2 cm and 1 cm in length, breadth and thickness. Each ovary is a small almond-like flattened body. Each ovary lies in the abdominal cavity on either side of the middle line. Ovaries produce female sex cells, ova and their glandular cells produce hormones. Each ovary is attached to dorsal abdominal wall by a fold of peritoneal membrane called mesovarium.
2. A pair of fallopian (uterine) tubes.
Each fallopian tube is about 5 inches long. It extends from the vicinity of the ovary to the uterus. The fallopian tube is retained in its position by a mesentery called mesometrium.
3. Uterus.
The uterus is hollow, muscular, thick walled organ. Its mucous membrane contains small gland cells and many capillaries. It receives ova and pass them on to vagina. The lower part of uterus is called cervix.
4. Vagina.
It is muscular tube measures 8 cm in length and lined with stratified epithelium. It receives the semen from the male during mating and during child birth, it conveys the child to the outside.
5. Vulva.
The opening of vagina to the outside alongwith labia majora and labia minora constitute the external female sex organs collectively called as vulva. Clitoris, homologous to penis is present at the junction of labia majora and labia minora.
Question 3.
Write a note on cloning.
Answer:
Cloning. It is the production of an identical cell or a complete organism. Dolly, a sheep, was successfully cloned. It was the first mammal to be cloned in 1996.

A cell was collected from the mammary gland of a female Finn Dorsett sheep. [Fig. (a)]. Simultaneously, an egg was obtained from a Scottish blackface ewe [Fig. (b)]. The nucleus was removed from the egg. Then, the nucleus of the cell from the Finn Dorsett sheep was inserted into the egg of the Scottish blackface ewe. The egg thus produced was implanted into the Scottish blackface ewe. Development of the egg took place normally and finally Dolly was born. Though Dolly was given birth by Scottish blackface ewe, it was found to be identical to the Finn Dorsett sheep from which the nucleus was taken. Because the nucleus of Scottish blackface ewe was removed, Dolly did not show any character of the Scottish blackface ewe. Unfortunately, Dolly died on 14th February 2003 due to certain lung diseases.
The cloned animals are also found to be born with severe abnormalities.
