Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class Science Book Solutions Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
PSEB 8th Class Science Guide Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Textbook Questions and Answers
Exercises
Question 1.
Explain why some fibres are called synthetic.
Answer:
Some fibres are called synthetic fibres because they are not obtained from natural sources. They are made by human beings. The raw materials used for preparing synthetic fibres are petrochemicals, which in turn are produced from fossil fuel, petroleum.
Question 2.
Mark (✓) the correct answer.
Rayon is different from synthetic fibres because
(a) it has a silk-like appearance
(b) it is obtained from wood pulp
(c) its fibres can also be woven like those of natural fibres.
Answer:
(b) It is obtained from wood pulp.
![]()
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words.
(а) Synthetic fibres are also called …………… or ……………….. fibres.
(b) Synthetic fibres are synthesised from raw material called ………………. .
(c) Like synthetic fibres, plastic is also a ………………… .
Answer:
(a) Man made, artificial
(b) Petrochemicals
(c) Synthetic.
Question 4.
Give examples which indicate that nylon fibres are very strong.
Answer:
Parachutes, ropes for climbing, tents made of nylon.
Question 5.
Explain why plastic containers are favoured for storing food.
Answer:
Advantages of using plastic containers for storing food:
- They do not react with food, air and water.
- They are strong and light in weight.
- They can have different sizes, shapes and colours.
Question 6.
Explain the difference between thermoplastic and thermosetting plastics.
Answer:
Differences between the Thermoplastics and Thermosetting Plastics
| Thermoplastics | Thermosetting plastics |
| 1. It can bend easily. | 1. It cannot bend but breaks. |
| 2. On heating, it gets deformed. | 2. Heating has no affect on it. |
| 3. It can be used again and again. | 3. It cannot be reused. |
| 4. It can be moulded into various shapes on heating. Examples : Polythene, PVC. | 4. It can be moulded only once, on heating.
Examples : Bakelite, Melamine. |
Question 7.
Explain why the following are made of thermosetting plastics.
(а) Saucepan handles
(b) Electric plugs/switches/plug boards
Answer:
(a) Saucepan handles are made of thermosetting plastics because plastic is bad conductor of electricity, fire resistant and heat tolerant.
(b) Electric plugs/switches/plugboards are made of thermosetting plastics because this plastic is bad conductor of electricity and durable.
Question 8.
Categorise the materials of the following products into ‘can be recycled’ and ‘cannot be recycled’.
Telephone instruments, plastic toys, cooker handles, carry bags, ball point pens, plastic, bowls, plastic covering on electric wires, plastic chairs, electrical switches.
Answer:
Can be recycled. Plastic toys, carrybags, ball point pens, plastic bowls, plastic chairs, plastic covering on electric wires.
Cannot be recycled. Telephone instruments, cooker handles, electrical switches.
Question 9.
Rana wants to buy shirts for summer. Should he buy cotton shirts or shirts made from synthetic material ? Advise Rana, giving your reason.
Answer:
Rana should buy cotton shirts.
Preference of cotton clothes to synthetic materials in summers.
- Cotton clothes are porous while synthetic materials are non-porous or air resistant.
- Cotton clothes soak sweat and give a dry feeling while synthetic clothes have little water absorbing property.
![]()
Question 10.
Give examples to show that plastics are non-corrosive in nature.
Answer:
Plastics are non-corrosive in nature. Plastics do not react with air, water etc. so, they do not get corroded.
For example –
- Different chemicals are stored in plastic bottles.
- Water is kept into plastic bottles.
- Pickles and food items are stored in plastic containers.
Question 11.
Should the handles and bristles of a toothbrush be made of the same material ? Explain your answer.
Answer:
No, different materials should be used for making handles and bristles of toothbrush because bristles help in cleaning teeth and handle is just for support. Bristles must be soft and delicate and powerful while handle should be hard and rigid.
Question 12.
‘Avoid plastics as far as possible’. Comment on this advice.
Answer:
Plastics are not environment friendly. They release poisonous gases on burning. They are non-biodegradable, so pollute soil or water in which they are dumped. Therefore, use of plastic should be avoided as far as possible.
Question 13.
Match the terms of Column A correctly with the phrases given in Column B.
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) Polyester | (a) Prepared by using wood pulp |
| (ii) Teflon | (b) Used for making parachutes and stockings |
| (iii) Rayon | (c) Used to make non-stick cookwares |
| (iv) Nylon | (d) Fabrics do not wrinkle easily |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) Polyester | (d) Fabrics do not wrinkle easily |
| (ii) Teflon | (c) Used to make non-stick cookwares |
| (iii) Rayon | (a) Prepared by using wood pulp |
| (iv) Nylon | (b) Used for making parachutes and stockings |
Question 14.
‘Manufacturing synthetic fibres is actually helping conservation of forests’. Comment.
Answer:
Natural fibres are obtained from natural resources i.e. natural plants. But synthetic fibres are obtained from other materials. So, synthetic fibres are not dependent on natural vegetation or crops grown in the field. Thus manufacturing synthetic fibres actually helps conservation of forests.
Question 15.
Describe an activity to show that thermoplastic is poor conductor of electricity.
Answer:
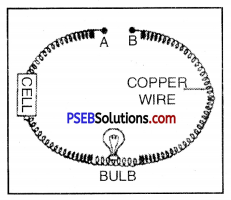
Activity.
Take a few samples of thermoplastic such like polythene, PVC, Nylon, Polystyrene etc.
Now set up the circuit as shown in fig. and insert a piece of Nylon between the two terminals A and B of copper wire. If bulb starts glowing then it is good conductor otherwise it is a bad conductor. Repeat the experiment using different samples of thermoplastics.
In each case, bulb would not glow indicating that thermoplastics are bad conductor of electricity.
![]()
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
In the following diagram, a boy is seen using rope for going up a rock. Tell rope made of which material is most suitable for this purpose ?

(a) Cotton
(b) Wood
(c) Nylon
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Nylon.
Question 2.
Which of the following is called artificial silk ?
(a) Rubber
(b) Teflon
(c) Rayon
(d) Polythene.
Answer:
(c) Rayon.
Question 3.
…………… is used for making polyester clothes.
(a) P.E.T.
(b) Acrvline
(c) Terrylene
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Terrylene.
Question 4.
Today while studying in the class Nisha came to know that there is such a type of plastic which melts when heated. Name this plastic. (From Board M.Q.P.)
(a) Plastic
(b) Thermoplastic
(c) Acrylic
(d) All of the above.
Answer:
(b) Thermoplastic.
Question 5.
Which out of the following is natural fibre ?
(a) Rayon
(b) Terylene
(c) Wool
(cl) Nylon.
Answer:
(c) Wool.
Question 6.
Which out of the following fibres is made by man ?
(a) Cotton
(b) Wool
(c) Rayon
(d) Silk.
Answer:
(c) Rayon.
Question 7.
Which out of the following is biodegradable ?
(a) Metal
(b) Plastic
(c) Paper
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(c) Paper.
![]()
Question 8.
Which of the following material is used to make ropes ?
(a) Cotton
(b) Wool
(c) Nylon
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(c) Nylon.
Question 9.
Which type of thermoplastic is used to make switches, which is poor conductor of heat and electricity ?
(a) Nylon
(b) Backelite
(c) Melamine
(d) Polythene
Answer:
(b) Backelite.
Question 10.
Which out of the following is thermoplastic ?
(a) Nylon
(b) Polythene
(c) Acrylic
(d) Backelite
Answer:
(d) Backelite.
Question 11.
Synthetic fibres are made from small units called:
(a) Cell
(b) Molecules
(c) Polymer
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(c) Polymer.
Question 12.
Sericulture is the bringing up of which creature ?
(a) Sheep
(b) Goat
(c) Hare
(d) Silk worm
Answer:
(d) Silk worm
Question 13.
Natural Polymer is:
(a) Rayon
(b) Cotton
(c) Nylon
(d) Polyster
Answer:
(b) Cotton.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name few natural fibres.
Answer:
Cotton, wool, silk.
![]()
Question 2.
Name a natural polymer.
Answer:
Cellulose.
Question 3.
Name a fibre which is silk like but man made.
Answer:
Rayon.
Question 4.
Which fibre is obtained from woodpulp ?
Answer:
Rayon.
Question 5.
In which year, Nylon was made ?
Answer:
In 1931.
Question 6.
Which fibre was made from coal, air and water ?
Answer:
Nylon
Question 7.
Of which fibre, parachutes and tents are made of ?
Answer:
Nylon
Question 8.
What is PET ?
Answer:
PET. It is a form of Polyester.
![]()
Question 9.
Why do parachutes and ropes for climbing rocks are made of Nylon ?
Answer:
Due to its strength.
Question 10.
Give few characteristics of plastics.
Answer:
Plastics can be recycled, reused, coloured, melted, rolled into sheets or made into wires.
Question 11.
What are Polythene and PVC ?
Answer:
Thermoplastics.
Question 12.
Bakelite is an example of which type of plastic ?
Answer:
Thermosetting plastic.
Question 13.
Where is Teflon used ?
Answer:
For making kitchen cookware and tape sealing.
Question 14.
Which of these fibres is costly-wool, rayon ?
Answer:
Wool.
Question 15.
Why does hot water deform plastic bottles ?
Answer:
Because they are made of thermoplastic, which melts on heating.
![]()
Question 16.
Which thermosetting material is versatile, heat resistant and fireproof ?
Answer:
Melamine.
Question 17.
Why is plastic used in cars, aircrafts etc. instead of metals ?
Answer:
Because it is lighter than metals.
Question 18.
Why are plastic containers convenient to use ?
Answer:
Plastic containers are light, cheap, strong and can be handled easily.
Question 19.
Which synthetic fibre resembles wool ?
Answer:
Acrylic.
Question 20.
Give two reasons for prefering synthetic fibres over natural fibres.
Answer:
- Durability and
- affordability.
Question 21.
Give one disadvantage of synthetic fibres.
Answer:
They melt on heating.
Question 22.
Which substances are non-biodegradable ?
Answer:
Non-biodegradable substances: Those substances which cannot be decomposed by bacteria are called non-biodegradable substances.
![]()
Question 23.
Which material or thing is responsible for choking drains and death of herbivores ?
Answer:
Polythene bags.
Question 24.
What is 4R principle ?
Answer:
- Reduce,
- Reuse,
- Recycle and
- Recover.
Question 25.
Plastics are non-biodegradable. Are they environment friendly or environment non-friendly ?
Answer:
Environment non-friendly.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are polymers ? Give an example of natural polymer. Are polymers found in nature ?
Answer:
Polymer.
A Polymer is a long chain consisting of lakhs of small units (molecules). It is made by combining together small molecules of chemical substances. Cellulose is natural polymer.
Polymers are found in nature. As for example, cotton is a natural fibre which in fact is cellulose. Cellulose is made up of large units of glucose. Similarly, wood pulp is cellulose from which rayon is manufactured. Therefore, rayon also a polymer.
Question 2.
What are synthetic fibres ?
Answer:
Synthetic Fibres.
The fibres other than natural fibres which are made by human beings are called synthetic fibres.
These are made of very large units which in turn are made up of similar small units.
Question 3.
Give few examples of synthetic fibres.
Answer:
Rayon, Nylon, Polyester, Plastic, Acrylic, Terylene etc. are synthetic fibres.
Question 4.
Give uses of Rayon and Nylon.
Answer:
Rayon is used to make clothes, bedsheets and carpets.
Nylon is used to make clothes, socks, ropes, tents, tooth brushes, belts, sleeping bags, curtains, parachutes etc.
![]()
Question 5.
List the characteristics of synthetic fibres which make them popular dress material.
Answer:
Characteristics of Synthetic Fibres:
Synthetic fibres possess the following unique characteristics:
- They are durable.
- They are less expensive.
- They dry up quickly.
- They are readily available.
- They are easy to maintain.
- It is easy to wash and does not wrinkle.
These characteristics make them popular dress material.
Question 6.
What happens when different synthetic fibres like Nylon, Polyester and Acrylic burn in air ?
Answer:
On burning the different fabrics, the following results are obtained :
| 1. Nylon | Burns with difficulty, fabric shrinks from flame, forming hard beads, smells of burning hair. |
| 2. Polyester | Same as nylon, produces a black smoke on burning. |
| 3. Acrylic | Shrinks from flame forming a black bead and a sooty flame. |
Question 7.
Why plastic material like polythene is preferred over natural materials ?
Answer:
Advantages of Plastic material over Natural Material. Following are some advantages of plastic material (polythene etc.) over natural materials:
- It is cheaper and can be made on a large scale.
- It is light weight and can be easily transported.
- It is unbreakable, corrosion free, tough and flexible.
- It can be easily moulded.
Question 8.
Give uses of polythene.
Answer:
Uses of Polythene.
Polythene sheets are used for packing, satchels are used for packaging milk, polythene containers and pipes are used for storing and transporting water, oil and other materials. Polythene is also used as a water-proofing material.
Question 9.
Give some uses of PVC.
Answer:
Uses of PVC. PVC is used to make bottles, floor coverings, rain coats, soles of shoes, sandals and leather like materials.
Question 10.
What is blended fabric ? Why is it more comfortable to wear them than fabrics from pure synthetic fibres ?
Answer:
Blended Fabric (Polycot and Polywool).
It is a mixture of synthetic (man-made) and natural fibres such as terrycot (polyester and cotton fibres), terrywool etc. Pure synthetic fibres do not absorb sweat so well, so they stick to the body in hot weather. Some synthetic fibres catch fire very easily. To overcome this defect, synthetic fibres are mixed with natural fibres to make blended fabrics.
![]()
Question 11.
What are biodegradable and non-biodegradable substances ?
Answer:
Biodegradable Substances.
Substances which are decomposed by microbes (bacteria) are known as biodegradable substances. Bodies of dead animals, human excreta and many other substances are decomposed into simpler compounds or elements by bacteria. Such substances are biodegradable substances.
Non-biodegradable substancs.
Those substances which are not decomposed into simpler compounds by naturalprocessesor or bacteria are known as non-biodegradable substances.
Question 12.
What are natural and synthetic polymers ?
Answer:
1. Natural Polymers. The polymers which occur in nature and are obtained from plants and animals e.g. rubber, starch, cellulose, proteins etc. are called natural polymers.
2. Synthetic Polymers. The polymers which do not occur in nature and have been synthesised in laboratory are called synthetic polymers. These are also called manmade polymers e.g. polythene, poly-vinyl chloride, teflon, bakelite etc.
Question 13.
Suggest some ways to reduce the use of plastic materials.
Answer:
Plastic is non-biodegradable and is therefore, not environment friendly. The best way to reduce its use is to follow the 4R principle, which is as follows:
- Reduce – use less
- Reuse – use again
- Recycle – cycle again
- Recover – get again
Question 14.
Which way the plastic/polythene bags and wrappers thrown carelessly be harmful to animals ?
Answer:
The plastic/polythene bags and wrappers thrown carelessly after use are swallowed by stray animals. These plastic made materials are non-biodegradable either choke the respiratory canal of the animals or forms a lining in their stomach resulting in the cause of their death.
Question 15.
In which ways excessive use of plastic materials is harmful for environment and society ?
Answer:
Plastic is harmful for environment and the man in the following ways:
- Since Plastic is synthesised from petrochemicals so its excessive use would lead to exhaustion of non-renewable petrochemical the reserve of which is limited.
- Plastic is non-biodegradable and clogs the drains and sewage system if thrown carelessly after use which usually happens.
- Plastic does not burn completely and releases lots of poisonous fumes in the atmosphere causing air pollution.
- Sometimes carelessly thrown plastic/polybag are swallowed by animals resulting in their death.
Question 16.
Why it is not advised to wear polyester clothes while working in a kitchen ?
Answer:
Polyester is a synthetic fibre. It easily catches fire and melts so that it sticks to the body causing harmful and painful burns. That is why women are advised not to wear polyester clothes while working in kitchen.
Question 17.
As a sensible and responsible citizen what measures would you adopt in your individual capacity to keep public places free from plastic ?
Answer:
- I would not throw plastic carry bags in water bodies and on the road after use.
- While going to market for shopping I would take cotton or jute bag with me or I would insist on the shopkeeper to give me paper bag.
- I would use steel lunch box instead of one made from plastic.
![]()
Question 18.
Four students planned to climb the top of mountain. They have selected the rope according to the table shown below. Which student has selected the correct rope and why ?
| Name of the Students | Rope |
| Inderjeet | Cotton |
| Gopal | Silk |
| Saloni | Nylon |
| Karamjit | Wool |
Answer:
Saloni has choosen the correct rope because the rope of nylon is stronger than silk and wool.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Give uses of the following:
(a) Polyester fibres
(b) Teflon
(c) Polythene
(d) Polypropylene
Answer:
(a) Uses of Polyester Fibres:
- Polyester fibres are used in textile industry for making a variety of clothes, such as sarees, dress materials, curtain clothes, etc.
- Polyester fibres mixed with natural fibres are used for making blended textiles such as terrycot (mixed with cotton), terry wool (mixed with wool).
- It is used for making sails of sail boats.
- It is used for making water hoses for fire fighting operations.
(b) Uses of Teflon:
- It is used for coating inside of non-stick cooking utensils.
- It is used in the manufacture of seals and gaskets.
(c) Uses of Polythene:
- It is used in the manufacture of bags, toys and pipes.
- It is used for covering electric cables because it is a good electrical insulator.
(d) Uses of Polypropylene:
- It is used to prepare seat covers.
- It is used for making ropes, fishing nets etc.
Question 2.
State four important properties and uses of nylon fibres.
Answer:
Properties of Nylon Fibres:
- Nylon fibres are very strong.
- Nylon fibres absorb very less water. Therefore, these can be dried rapidly.
- Nylon is wrinkle resistant and keep permanent creases.
- Nylon fibres have high wear and tear resistance and therefore, have longer life.
Use of Nylon:
- Nylon is used for a large number of purposes where high strength fibres are required.
- Nylon is used for making parachute fabrics, fishing nets, tyrecord, ropes, stockings (socks) and other textiles.
- Nylon is mixed with wool to make long-lasting fabrics.
Question 3.
Give the properties common to Nylon and Polyester fibres.
Answer:
Properties of Nylon and Polyester Fibres:
- Nylon and polyester fibres are very strong threads in comparison to silk, cotton, and wool.
- Both the threads have excellent resistance to wrinkles.
- Both the threads absorb very little water, so they dry out quickly.
- They have the high abrasion resistance and are not attacked by moths.
- Ordinary chemicals have no effect on them.
- They are lightweight and fine in texture.
- They are insoluble in common solvents.
Question 4.
What is plastic? What are its different types? Give properties of plastics which render them as a material of choice. Also, give its uses.
Answer:
Plastic. It is a polymer like synthetic fibre.
Example. Polythene
Types of Plastic. All plastics do not have the same arrangement of units. There are two types of plastics: One has a linear arrangement of units and the other has a cross-linked arrangement of units.
Properties of Plastics:
- Plastic is not attacked by air and water. That is they are non-reactive and non¬corrosive.
- Plastic is light, strong, and durable.
- Some plastics can be easily deformed on heating and some others do not soften on heating.
- Plastics are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
Uses of Plastics:
- In Health Care Industry. Plastics find extensive use in the Health care industry for packaging tablets, threads used for stitching wounds syringes, doctor’s gloves, and many other instruments.
- In Kitchen Cookwares. Plastic is used for making special cookwares to be used in micro-ovens which can withstand high temperatures.
- In making non-stick cookwares on which Teflon, a kind of plastic is used, oil and water do not stick.
- Fire Proof Plastics. Melamine plastic is used for coating the uniforms of firemen. This makes the uniform flame resistant.
