Punjab State Board PSEB 11th Class Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry Important Questions and Answers.
PSEB 11th Class Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
In what regions of the atmosphere, the temperature increases with altitude and in which regions it decreases?
Answer:
Temperature increases with altitude in stratosphere and thermosphere while it decreases in troposphere and mesosphere.
Question 2.
Name three natural sources of air pollution.
Answer:
Volcanic eruptions, forest fires and pollen grains of flowers.
![]()
Question 3.
How are NO and NO2 formed in the atmosphere?
Answer:
NO is formed by the reaction of N2 and O2 during lightning or combustion of fossil fuels. It is further oxidised to NO2.
Question 4.
What is anoxia or asphyxiation?
Answer:
Acute oxygen starvation in the body (due to CO poisoning) is called anoxia or asphyxiation.
Question 5.
Name the gas that caused the Bhopal gas tragedy.
Answer:
Methyl isocyanate (MIC).
Question 6.
What is the size range of particulates?
Answer:
5 nm to 500000 nm. ,
Question 7.
What is the composition of ‘London smog’?
Answer:
Fog of H2SO4 droplets deposited on the particulates.
Question 8.
What is the nature of ‘London smog’ and why?
Answer:
Reducing, because of the presence of SO2 and carbon soot which are good reductant.
Question 9.
What should be the tolerable limit of fluoride ions in drinking water? What happens if it is higher than 10 ppm?
Answer:
1 ppm or 1 mg dm-3. If higher than 10 ppm, it is harmful to bones and teeth.
![]()
Question 10.
Name three methods generally used in green chemistry.
Answer:
Use of sunlight and microwaves, use of sound waves and use of enzymes.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
(i) What do you mean by sink? Give one example.
(ii) What is the sink for hydrocarbons and why?
Answer:
(i) Medium present in the environment that take up some amount of certain pollutants is called sink e.g., oceans act as sink for SO2, CO2 and NOx.
(ii) Chemical and photochemical reactions act as sink for hydrocarbons as these get decomposed in these reactions.
Question 2.
Green plants use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis and return oxygen to the atmosphere, even then carbon dioxide is considered to be responsible for green house effect. Explain why?
Answer:
The amount of CO2 produced due to human activity such as burning of fossil fuels like coal, natural gas, petroleum, etc., and production of lime from limestone is much more than that consumed during photosynthesis. The consumption in photosynthesis has further decreased due to deforestation.
Question 3.
(i) What are the reactions involved in removingS02 from the
atmosphere by passing it through a solution containing citrate ions?
(ii) What is the most important sink of CO pollutant?
(iii) How are fuel gases from industries freed from oxides of nitrogen and sulphur?
Answer:
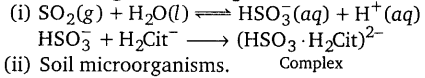
(iii) By scrubbing them with cone. or with alkaline solutions like
Ca(OH)2 and Mg(OH)2.
Question 4.
What are biodegradable and non-biodegradable pollutants?
Answer:
Biodegradable pollutants are those which are decomposed by micro-organisms such as bacteria, e.g., sewage, cow-dung, discarded vegetables etc.
Non-biodegradable pollutants are those which cannot be decomposed by microorganisms e.g., mercury, aluminium, lead, copper, DDT etc.
Question 5.
Oxidation of sulphur dioxide into sulphur trioxide in the absence of a catalyst is a slow process but this oxidation occurs easily in the atmosphere. Explain how does this happen? Give chemical reaction for the conversion of SO2 into SO3.
Answer:
The presence of particulate matter in polluted air catalyses the oxidation of SO2 to SO3.
The oxidation of sulphur dioxide into sulphur trioxide can occur both photochemically or non-photochemically. In the near ultraviolet region, the SO2 molecules react with ozone photochemically.
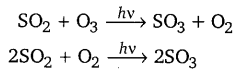
Non-photochemically, SO2 may be oxidised by molecular oxygen in presence of dust and soot particles.
![]()
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Account for the following
(i) Ozone layer is necessary for life.
(ii) The temperature of thermosphere is 1500°C but a person would not feel warm in it.
(iii) Increased SO2 concentration causes chlorosis.
(iv) CO2 keeps the earth warm.
(v) The pH of normal rain water is 5.6.
Answer:
(i) Ozone absorbs about 99% of harmful UV radiations coming from the sun and thus protects human beings from adverse effect of UV radiations. Thus, its presence is necessary for life.
(ii) This is because the pressure in the thermosphere is very low.
(iii) Because increased SO2 concentration retards the rate of formation of chloroplast.
(iv) CO 2 have tendency to absorb most of the heat radiation that are emitted by objects of the earth. Thus, it keeps the earth warm.
(v) This is because dissolution 0f CO2 from atmosphere furnish H+ ions to the rain water.
H2O(Z) + CO2(g) ⇌ H2CO3(aq)
H2CO3(aq) ⇌ H+(aq) + \(\mathrm{HCO}_{3}^{-}\) (aq)
![]()
Question 2.
How can you apply green chemistry for the following:
(i) to control photochemical smog.
(ii) to avoid use of halogenated solvents in dry cleaning and that of chlorine in bleaching.
(iii) to reduce use of synthetic detergents.
(iv) to reduce the consumption of petrol and diesel.
Answer:
(i) Certain plants e.g., Pinus, Juniparus, Quercus, Pyrus and Vitis can metabolize nitrogen oxide (NO) and therefore, their plantation could help in reducing photochemical smog.
(ii) Liquefied CO2 with a suitable detergent is used for dry cleaning and H202 (hydrogen peroxide) is used for the purpose of bleaching clothes in the process of laundary which gives better results and makes use of lesser amount of water.
(iii) Soaps are 100% biodegradable so that they should be used in place of detergents. Now a days biodegradable detergents are available. Therefore, they should be used in place of non-biodegradable hard detergents.
(iv) CNG (compressed natural gas) should be used as it causes much less pollution. Moreover, electrical vehicles should be used to reduce the consumption of petrol and diesel.
