Punjab State Board PSEB 5th Class Welcome Life Book Solutions Chapter 5 Love with Nature and Environment Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 5 Welcome Life Chapter 5 Love with Nature and Environment
Welcome Life Guide for Class 5 PSEB Love with Nature and Environment Textbook Questions and Answers
(a) Avoid using Plastic Bags :
Story/Master with Bag
Children had been whispering mutually for three days. They were curious to know that why did the new teacher carry his diary and tiffin in a cloth bag? They have given him the name’ Master with a Bag’. Today, Rana asked hesitantly, “Sir, how beautiful the plastic bags are I but you only bring a cloth bag?”
![]()
The Master smiled a little. All students were looking at him carefull. The master started speaking politely, “Dear children, I had guessed from your mutual whispers that you wanted to ask something, but were not asking. I will tell this story but first of all, always keep in mind that never ever hesitate to ask anyone a question. The students who ask questions are the smartest students and they get all kind of knowledge.”
“Yes Sir”, all students speak loudly.
“Well done! You are all very wise, innocent too…” the master continued, “If I want to sum up the talk of cloth bag in one sentence, then I can say that it’s my habit. I keep cloth bag with myself if I have to buy something from market and I never ever take a plastic bag……………”
“Why, Sir? plastic bags are much beneficial, use and throw away….” asked Sukha while standing.
“Children, These plastic bags are very dangerous…!”
“How?” asked Rani kaur.
“There is not only one but many side effects of these plastic bags….” The master began to tell. All students listened in amazement. The master continued the talk, “As Sukha Singh said, use and throw away, first listen to the disadvantages of this thing. They are blown away by the wind and get trapped in the drains. The drainage of water stops. The water stagnates in the street and flies and mosquitoes breed, and this way we get sick.
“You’re right Sir, many days ago there was water in our street like this and the same plastic bags were stuck in the drain…” said Hargun.
“Absolutely! Listen, these bags are sometimes swallowed by animals when we throw away the peels of vegetables and unleavened bread in these bags….”
“What would happen to the animals if they ate them?” Gurleen stood up and asked.
“These are indigestible son, how many animals have died just by eating them. Throwingthem in canals and drains kill aquatic creatures…”
![]()
“Really!” all were amazed.
“Sir, they should be set on fire then?” advised Pardeep. Once everyone liked his point.
“But children, when we set it on fire, it emits a lot of dangerous gases, which pollute the environment…”
“Then yes, they should be buried in the soil. Then they will not fly away and block the drains again Also the animals will not get killed by eating these and bad gasses will not be emitted on burning,” said Seerat Kaur.
“You’re right, Seerat! But now listen to the thing about burying these. They do not rot for thousands of years. They remain lying in the soil In this way the fertility of the soil will decrease….our crops will stop growing. These flowers will not grow”
“Oh yes, then you’re right, we will stop using these bags from today…” said several children together.
“Very Good! Very good students! Then tell, how will you bring vegetables, sugar and tea from the shop…?”
“In the cloth bags…” said all together.
“In the cloth bags…” said all together.
“So students! You understand that plastic bags and plastic items including food and drink cup-plates, water bottles etc they pollute our natural resources.”
“Yes, air, water, soil, sunshine are our natural resources and they spoil them” saidGiandeep.
“That’s right! You’ll no longer use these dangerous plastic items yourself and will urge your parents and neighbors not to use it….”
“Yes….” said all the children loudly.
“Sir, listening to your words, I just made a couplet sitting may I recite?” asked Rane politely.
![]()
“Tell me, son.”
“ਸਾਫੇ…..ਸਾਫੇ…..ਸਾਫੇ
ਮਿੱਤਰੋ ਅਸੀਂ ਨਹੀਂ ਵਰਤਣੇ
ਮੋਮਜਾਮੇ ਦੇ ਲਿਫ਼ਾਫ਼ੇ…’
“Clean…….clean…….clean
Friends we’ll never use
plastic polythene…….”
Oral Question-Answers:
Question 1.
Why did the teacher use cloth bag?
Answer:
Because plastic bags have a lot of disadvantages.
Question 2.
What are the disadvantages of plastic bags?
Answer:
- Animals can die after eating them.
- They decrease the fertile power of soil.
- They block the water in drains. That is why streets are filled with water and mosquitoes breed.
- After burning plastic, poisonous gases are produced.
Question 3.
Should vegetable peels, unleavened bread and kneaded flour be thrown away in plastic bags?
Answer:
No, animals can eat these eatables with polythenes and can die. Because polythenes are not digestable for animals.
Question 4.
Why should we nottake plastic items?
Answer:
Because plastic things pollute the natural resources.
Question 5.
Which talks of teacher did you like in this story?
Answer:
The teacher told us that we should not use plastic things. They pollute our natural resources and he also told us that we should keep all the things in cloth bags.
![]()
Question 6.
How can we survive from plastic bags?
Answer:
We can protect ourselves from plastic bags while keeping cloth bags with us in the market.
Question 7.
Plastic bags increase the fertility of soil or decrease?
Answer:
Decreases.
Question 8.
Using plastic improves our health or makes us sick?
Answer:
We can become sick while using plastic.
Question 9.
Drainage, ditches and sewerage drainage are properly working with plastic envelopes or not?
Answer:
No, they create obstacles in the drainage of water.
Question 10.
What did we understand from the above story?
Answer:
The above story makes us understand that we should not use the things of plastic and plastic bags.
![]()
Activity for Teacher:
The teacher can do it as a novella or role-play. It will become interesting in this way and all students will be included. Few oral questions can be asked on the basis of this story.
The teacher will assign work to the students that they will aware their parents and neighbors about the disadvantages of plastic bags and motivate them not use it. Whatever is told and how it is told, they will bring it in written form.
Students can do a meeting with their grand-parents to know that how did they bring things from the shop? Did they use these plastic bags?
PSEB 5th Class Welcome Life Guide Love with Nature and Environment Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions :
Question 1.
From how many days the children were doing whispering?
(a) From seven days
(b) From three days
(c) From two days
(d) From ten days.
Answer:
(b) From three days.
Question 2.
The plastic bags are harmful because :
(a) They create obstacles in drains.
(b) They decrease the fertile value of soil.
(c) Animals can die after eating them.
(d) All of the above.
Answer:
(d) All of the above.
![]()
Question 3.
Which students become intelligent?
(a) Those who do not hesitate from asking questions
(b) Those who remain quiet in the class
(c) Those who do not come to school
(d) All are correct.
Answer:
(a) Those who do not hesitate from asking questions
Question 4.
Which statement is not correct?
(a) The plastic bags are very useful.
(b) Animals can die after eating plastic bags.
(c) Plastic bags decrease the fertile power of soil.
(d) All are wrong.
Answer:
(a) The plastic bags are very useful.
Question 5.
……………………………….. is not a natural resource.
(a) Petrol
(b) Air
(c) Water
(d) Sunlight.
Answer:
(a) Petrol.
![]()
Fill in the blanks :
1. Those ……………………………….. who do not hesitate from asking questions, become intelligent.
2. Plastic bags are very ………………………………. .
3. ……………………………….. things pollute our natural resources.
Answer:
1. students
2. dangerous
3. plastic.
Tick Right (✓) or Wrong (✗) :
1. Children were whispering among themselves from the last five days.
2. The plastic bags decompose after one or two days.
3. There is not any harm of using plastic bags to the animals.
4. There are a lot of harms of using plastic bags.
Answer:
1. ✗
2. ✗
3. ✗
4. ✓
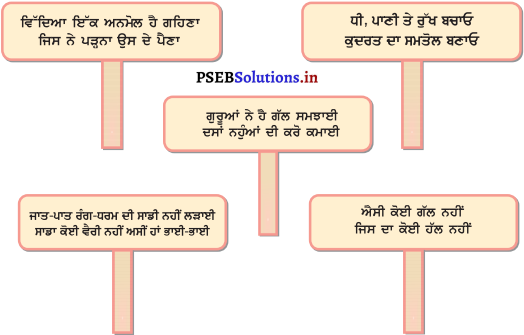
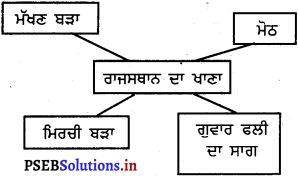
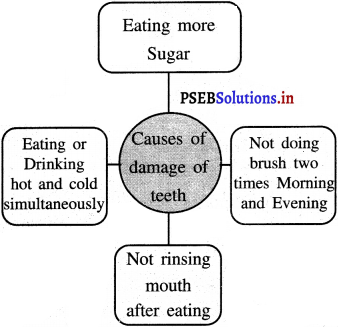
Mind Mapping :
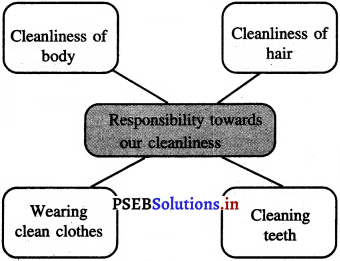
Answer:
![]()
Match the following :
1. Whispering among ourselves (a) Pollution
2. Decomposing of plastic (b) Three days
3. Natural Resources (c) Thousand years
4. Plastic things (d) Air.
Answer:
1. (b)
2. (c)
3. (d)
4. (a).
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Which students do become intelligent?
Answer:
Those who do not hesitate from asking questions.
Question 2.
What are the harms of burning plastic bags?
Answer:
A lot of poisonous gas is released and the environment is polluted while burning plastic bags.
Question 3.
What are the harms of dumping plastic bags in the soil?
Answer:
These plastic bags do not decompose even after thousand years and therefore decrease the fertile power of the soil.
![]()
Question 4.
What are the harms of plastic bags to the animals?
Answer:
Animal cannot digest these plastic bags and can die.
Question 5.
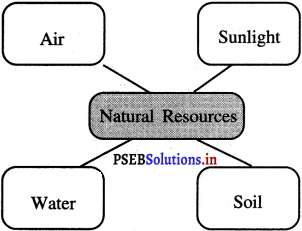
What are the natural resources?
Answer:
Natural resources are Air, Water, Soil, Sunlight etc.
Question 6.
Why should we plant trees?
Answer:
We should plant trees to purify the air.
Question 7.
Name the gas which is necessary for breathing.
Answer:
Oxygen is necessary for breathing.
Question 8.
Give one slogan related to trees.
Answer:
Save Trees, Save Environment.
![]()
Question 10.
Why should not we burn garbage?
Answer:
We should not burn garbage because it creates pollution.