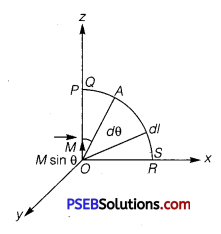
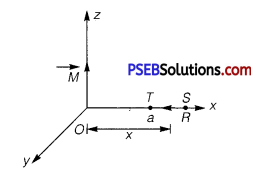
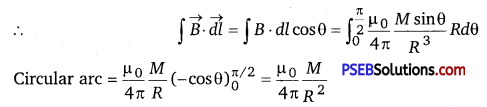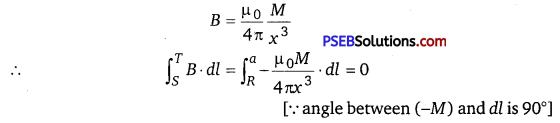Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class Physics Important Questions Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Important Questions and Answers.
PSEB 12th Class Physics Important Questions Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Very short answer type questions
Question 1.
What is reflection?
Answer:
When a light ray incident on a smooth surface bounces back to the same medium, it is called reflection.
Question 2.
State new cartesian sign conventions used for mirrors.
Answer:
- All the distances are measured from the pole of the mirror.
- All the distances measured in the direction of incident ray are taken as positive and the distances measured opposite to the incident ray are taken as – ve.
- All heights measured perpendicular to the principal axis in the upward direction are taken as + ve and those measured in downward direction are taken as – ve.
Note: Direction of incident light is always to be shown falling from left to right. So distance of the object and real image is always -ve while that of virtual image is always + ve, height of real image is always – ve while that of the virtual image and the size of real object are always + ve.
Question 3.
How does focal length of a lens change when red light incident on it is replaced by violet light? Give reason for your answer.
Answer:
The refractive index of the material of a lens increases with the decrease in wavelength of the incident light. So, focal length will decrease with a decrease in wavelength according to the formula.
\(\frac{1}{f}=(\mu-1)\left(\frac{1}{R_{1}}-\frac{1}{R_{2}}\right)\)
Thus, when we replace red light with violet light then due to increase in wavelength the focal length of the lens will decrease.
![]()
Question 4.
Define refraction of light.
Answer:
It is defined as the process of bending of light from its path when it travels from one medium to the another.
Question 5.
State
(a) Laws of reflection.
(b) Laws of refraction.
Answer:
(a) The following are the two laws of reflection :
(i) Angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection.
(ii) The incident ray, reflected ray and normal to the surface at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
(b) The following are the two laws of refraction :
(i) The ratio of the sine of angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is always constant for a given pair of media.
i.e., \(\frac{\sin i}{\sin r}\) = constant = aµb
where aµb is called relative refractive index of medium b w.r.t. a.
(ii) The incident ray, refracted ray and the normal to the refracting surface at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
Question 6.
(i) What is the relation between critical angle and refractive index of a material?
(ii) Does critical angle depend on the colour of light? Explain.
Answer:
(i) Refractive index (µ) = \(\frac{1}{\sin C}\)
where, C is the critical angle.
(ii) Since, refractive index depends upon the wavelength of light, the critical angle for a given pair of media is different for different wavelengths (colours) of light.
Question 7.
Under what condition does a biconvex lens of glass having a certain refractive index act as a plane glass sheet when immersed in a liquid?
Answer:
A biconvex lens will act like a plane sheet of glass if it is immersed in a liquid having the same index of refraction as itself. In this case, the focal length 1/f = 0 or f→ ∞.
Question 8.
A biconvex lens made of a transparent material of refractive index 1.25 is immersed in water of refractive index 1.33. Will the lens behave as a converging lens? Give reason.
Answer:
No, it will behave as a diverging lens.
On Using thin lens maker formula
\(\frac{1}{f_{w}}=\left(\frac{n_{g}}{n_{m}}-1\right)\left(\frac{1}{R_{1}}-\frac{1}{R_{2}}\right)\)
On Using sign convention R1 = +ve, R2 = -ve and ng = 1.25 and nm = 1.33
\(\left(\frac{1}{R_{1}}+\frac{1}{R_{2}}\right)\) +ve,value and \(\left(\frac{1.25}{1.33}-1\right)\) =-ve value Hence fw = -ve , so it behaves as a diverging lens.
![]()
Question 9.
Define total internal reflection.
Answer:
It is defined as the process of reflection of light that takes place when a ray of light travelling from denser to rarer medium gets incident at the interface of the two media at an angle greater than the critical angle for the given air of media.
Question 10.
State the criteria for the phenomenon of total internal reflection of light to take place.
Answer:
Following are the criteria for total internal reflection
- Light must pass from a denser to a rarer medium.
- Angle of incidence must be greater than critical angle.
Question 11.
Define mirage.
Answer:
It is defined as an optical illusion that occurs in deserts and coal tarred roads appear to be covered with water but on approaching at that place no water is obtained. In deserts thirsty animals observe virtual images of trees on hot sand so expecting a pond of water there but on reaching there, they do not get water pond and hence called optical illusion.
Question 12.
Why diamond sparkles?
Answer:
The critical angle for diamond is low i.e., 23° and its refractive index is 2.47. The faces of diamond are cut in such a way that when a ray of light entering from a face undergoes multiple total internal reflections from its different faces. Due to small value of the critical angle, almost all light rays entering the diamond suffer multiple total internal reflection and thus it shines brilliantly.
Question 13.
What are optical fibres? Give their one use.
Answer:
Optical fibres are thousands of very fine quality fibres of glass or quartz. The diameter of each fibre is of the order of 10-4 cm having refractive index of material equal to 1.7. These are coated with a thin layer of material having µ = 1.5.
They are used in transmission and reception of electrical signals by converting them first into light signals.
Question 14.
Write the relationship between angle of incidence ‘i’ angle of prism ‘A’ and angle of minimum deviation for a triangular prism.
Answer:
i = \(\frac{A+\delta_{m}}{2}\)
where, δm = angle of minimum deviation.
Question 15.
Define dispersion of light. What is its cause?
Answer:
It is defined as the process of splitting up of white light into its constituent colours on passing through a prism.
We know that for small angled prism,
δ = (µ -1)A.
Also according to Cauchy’s formula, we know that µ ∝ \(\frac{1}{\lambda^{2}}\)
Thus µ of the material of prism is different for different colours, so δ is also different for different incident colours.
Thus due to different values of angle of deviation, each colour occupies different direction in emergent beam of light and thus constituent colours of white light get dispersed. λv < λr, so δv > δr.
The violet colour deviates more than the red colour.
![]()
Question 16.
Explain the rainbow.
Answer:
The rainbow is an example of the dispersion of sunlight by the water drops in the atmosphere. This is a phenomenon due to combined effect of dispersion, refraction and reflection of sunlight by spherical water droplets of rain. The conditions for observing a rainbow are that the sun should be shining in one part of the sky (say near western horizon) while it is raining in the opposite part of the sky (say eastern horizon). An observer can therefore see a rainbow only when his back is towards the sun.
Question 17.
Why does the Sun look reddish at sunset or sunrise?
Answer:
During sunset or sunrise, the sun is just above the horizon, the blue colour gets scattered most by the atmospheric molecules while red light gets scattered least, hence Sun appears red.
I ∝ \(\frac{1}{2^{4}}\) and λB << λR.
Question 18.
Will the focal length of a lens for red light be more, same or less than that for blue light? (NCERT Exemplar)
Answer:
As the refractive index for red is less than that for blue, parallel beams of light incident on a lens will be bent more towards the axis for blue light compared to red. Thus the focal length for red light will be more than that for blue.
Question 19.
An unsymmetrical double convex thin lens forms the image of a point object on its axis. Will the position of the image change if the lens is reversed? (NCERT Exemplar)
Answer:
No, the reversibility of the tens makes equation.
\(\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{f}=(n-1)\left(\frac{1}{R_{1}}-\frac{1}{R_{2}}\right)\)
= -(n-1) \(\left(\frac{1}{R_{2}}-\frac{1}{R_{1}}\right)\)
On reversing the lens, values of R1 and R2 are reversed and so their signs.
Hence, for a given position of object (u), position of image (v) remains unaffected.
Question 20.
Why danger signals are of red light?
Answer:
Scattering of light is inversely proportional to the fourth power of wavelength of incident light. As red light has longer wavelength as compared to other visible colours, so its scattering is least and thus red light signals can be seen from a longer distance.
Short answer type questions
Question 1.
Will the focal length of a lens for red light be more, same or less than that for blue light? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
As the refractive index for red is less than that for blue parallel beams of light incident on a lens will be bent more towards the axis for blue light compared to red.
In other words, μb > μr By lens maker’s formula,
\(\frac{1}{f}=\left(n_{21}-1\right)\left(\frac{1}{R_{1}}-\frac{1}{R_{2}}\right)\)
Therefore, fb < fr
Thus, the focal length for blue light will be smaller than that for red.
Question 2.
Define power of a lens. Write its units. Deduce the relation \(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{f_{1}}+\frac{1}{f_{2}}\) for two thin lenses kept in contact coaxially.
Answer:
The power of a lens is equal to the reciprocal of its focal length when it is measured in metre. Power of a lens,
P = \(\frac{1}{f(\text { metre })}\)
Its SI unit is dioptre (D).
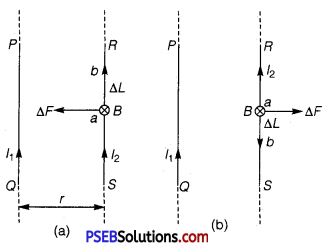
Consider two lenses A and B of focal lengths, f1 and f2 placed in contact with each other. An object is placed at a point O beyond the focus of the first lens A. .
The first lens produces an image (real image) at I1 which serves as a virtual object for the second lens B producing the final image at I.
Since, the lenses are thin, we assume the optical centres P of the lenses to be coincident. For the image formed by the first lens A, we obtain
\(\frac{1}{v_{1}}-\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{f_{1}}\) ……………………………. (1)
For the image formed by the second lens B, we obtain
\(\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{v_{1}}=\frac{1}{f_{2}}\) …………………………………. (2)
Adding eqs. (1) and (2), we obtain
\(\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{f_{1}}+\frac{1}{f_{2}}\) …………………………. (3)
If the two lenses system is regarded as equivalent to a single lens of focal length f, we have
\(\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{f}\) ……………………………… (4)
From eqs. (3) and (4), we obtain
\(\frac{1}{f_{1}}+\frac{1}{f_{2}}=\frac{1}{f}\) .
![]()
Question 3.
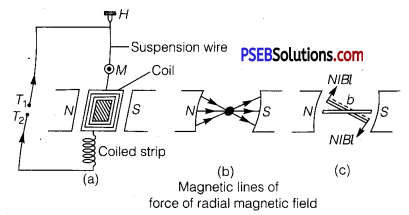
(a) Draw a schematic labelled ray diagram of a reflecting type telescope (cassegrain).
(b) The objective of telescope is of larger focal length and of larger aperture (compared to the eyepiece). Why? Given reasons.
(c) State the advantages of reflecting telescope over refracting telescope.
Answer:
(a)
(b) In normal adjustment, magnifying power of the telescope, M = \(\frac{f_{0}}{f_{e}}\)
(i) If focal length of the objective lens is large in comparison to the eyepiece, magnifying power increases.
(ii) Resolving power of the telescope RP = \(\frac{D}{1.22 \lambda}\)
D being the diameter of the objective. To increase the resolving power of the telescope, large aperture of the objective lens is required.
Advantages
- There is no chromatic aberration in a mirror.
- Brighter image.
- High resolving power.
- Large magnifying power.
Question 4.
How is the working of a telescope different from that of a microscope?
Answer:
Difference in working of telescope and microscope
- Objective of telescope forms the image of a very far off object at or within the focus of its eyepiece. The microscope does the same for a small object kept just beyond the focus of its objective.
- The final image formed by a telescope is magnified relative to its size as seen by the unaided eye while the final image formed by a microscope is magnified relative to its absolute size.
- The objective of a telescope has large focal length and large aperture while the corresponding parameters for a microscope have very small ‘ values.
Question 5.
For a glass prism (μ = \(\sqrt{3}\) ) the angle of minimum deviation is equal to the angle of the prism. Find the angle of the prism. (NCERT Exemplar)
Answer:
At minimum deviation μ = \(\frac{\sin \left[\frac{\left(A+\delta_{m}\right)}{2}\right]}{\sin \left(\frac{A}{2}\right)} \)
Given, δm = A
∴ μ = \(\frac{\sin A}{\sin \frac{A}{2}}=\frac{2 \sin \frac{A}{2} \cos \frac{A}{2}}{\sin \frac{A}{2}}=2 \cos \frac{A}{2}\)
∴ \(\cos \frac{A}{2}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \text { or } \frac{A}{2}=30\)
⇒ A = 600.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
(a) Draw a ray diagram for formation of image of a point object by a thin double convex lens having radii of curvature R1 and R2. Hence, derive lens maker’s formula for a double convex lens. State the assumptions made and sign convention used.
(b) A convex lens is placed over a plane mirror. A pin is now positioned so that there is no parallax between the pin and its image formed by this lens-mirror combination. How will you use this observation to find focal length of the lens? Explain briefly.
Answer:
(a) Lens Maker’s Formula: Suppose L is a thin lens. The refractive index of the material of lens is n2 and it is placed in a medium of refractive index n1. The optical centre of lens is C and X’ X is principal axis. The radii of curvature of the surfaces of the lens are R1 and R2 and their poles are P1 and P2.
The thickness of lens is t, which is very small. O is a point object on the principal axis of the lens. The distance of O from pole P1 is u. The first refracting surface forms the image of O at I’ at a distance v’ from P1.
From the refraction formula at spherical surface, \(\frac{n_{2}}{v^{\prime}}-\frac{n_{1}}{u}=\frac{n_{2}-n_{1}}{R_{1}}\) ……………………………….. (1)
The image I’ acts as a virtual object for second surface and after refraction at second surface, the final image is formed at I.
The distance of I from pole P2 of second surface is v. The distance of virtual object (I’) from pole P2 is (v’ -t).
For refraction at second surface, the ray is going from second medium (refractive index n2) to first medium (refractive index n1), therefore, from refraction formula at spherical surface
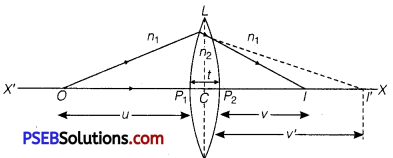
\(\frac{n_{1}}{v}-\frac{n_{2}}{\left(v^{\prime}-t\right)}=\frac{n_{1}-n_{2}}{R_{2}}\) ……………….. (2)
For a thin lens t is negligible as compared to v’, therefore from eq. (2)
\(\frac{n_{1}}{v}-\frac{n_{2}}{v^{\prime}}=-\frac{n_{2}-n_{1}}{R_{2}}\) ……………………………….. (3)
Adding equation (1) and (3),we get
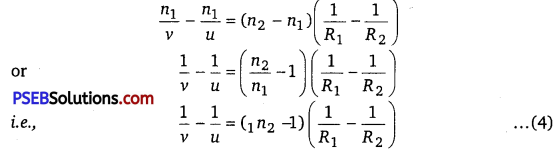
where, 1n2 = \(\frac{n_{2}}{n_{1}}\) is refractive index of second medium (te. medium of lens) with respect to first medium. If the object O is at infinity, the image will be formed at second focus i.e., if u = ∞, v = f2 =f
Therefore, from equation (4)
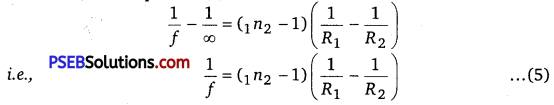
This formula is called Lens-Maker’s formula. If first medium is air and refractive index of material of lens be n, then 1n2 = n, therefore, the modified equation (5) may be written as
\(\frac{1}{f}=(n-1)\left(\frac{1}{R_{1}}-\frac{1}{R_{2}}\right)\) ………………………………. (6)
(b) Focal length = distance of the pin from the mirror.
The rays from the object after refraction from lens should fall normally on the plane mirror. So, they retrace their path. Hence, rays must be originating from focus and thus distance of the pin from the plane mirror gives focal length of the lens.
![]()
Question 2.
(a) Draw the labelled ray diagram for the formation of image by a compound microscope. Derive an expression for its total magnification (or magnifying power), when the final image is formed at the near point. Why both objective and eyepiece of a compound microscope must have short focal lengths?
(b) Draw a ray diagram showing the image formation by a compound microscope. Hence, obtain expression for total magnification when the image is formed at infinity.
Answer:
(a) Compound Microscope: It consists of a long cylindrical tube, containing at one end a convex lens of small aperture and small focal length. This is called the objective lens (0). At the other end of the tube another co-axial smaller and wide tube is fitted, which carries a convex lens (E) at its outer end. This lens is towards the eye and is called the eyepiece. The focal length and aperture of eyepiece are somewhat larger than those of objective lens. Cross-wires are mounted at a definite distance before the eyepiece. The entire tube can be moved forward and backward by the rack and pinion arrangement.
Adjustment: First of all the eyepiece is displaced backward and forward to focus it on cross-wires. Now the object is placed just in front of the objective lens and the entire tube is moved by rack and pinion arrangement until there is no parallax between image of object and cross wire. In this position, the image of the object appears quite distinct.
Working: Suppose a small object AB is placed slightly away from the first focus Fo‘of the objective lens. The objective lens forms the real, inverted and magnified image A’ B’, which acts as an object for eyepiece. The eyepiece is so adjusted that the image A’B’ lies between the first focus Fe‘ and the eyepiece E. The eyepiece forms its image A”B” which is virtual, erect and magnified. Thus the final image A”B” formed by the microscope is inverted and magnified and its position is outside the objective and eyepiece towards objective lens.
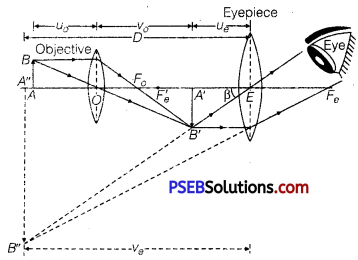
The magnifying power of a microscope is defined as the ratio of angle (β) subtended by final image on the eye to the angle (α) subtended by the object on eye, when the object is placed at the least distance of distinct vision, i.e., Magnifying power,
M = \(\frac{\beta}{\alpha}\)
As object is very small, angles a and 1 are very small and so tan α = α and tan β = β. By definition the object AB is placed at the least distance of distinct vision.
∴ α = tan α = \(\frac{A B}{E A}\)
By sign convention, EA = – D,
∴ α = \(\frac{A B}{-D}\)
and from figure
β = tan β = \(\frac{A^{\prime} B^{\prime}}{E A^{\prime}}\)
If ue is distance of image A’ B’ from eyepiece E, then by sign convention, EA’ = -ue
and so, β = \(\frac{A^{\prime} B^{\prime}}{-u_{e}}\)
Hence, magnifying power,
M = \(\frac{\beta}{\alpha}=\frac{A^{\prime} B^{\prime} /\left(-u_{e}\right)}{A B /(-D)}=\frac{A^{\prime} B^{\prime}}{A B} \cdot \frac{D}{u_{e}}\)
By sign conventions, magnification of objective lens
\(\frac{A^{\prime} B^{\prime}}{A B}=\frac{v_{o}}{\left(-u_{o}\right)}\)
∴ M = \(-\frac{v_{o}}{u_{o}} \cdot \frac{D}{u_{e}}\) ………………………………….. (2)
Using lens formula \(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{u}\) for eyelens,
(i.e. using f = fe’ V = -ve, U = -ue ) we get
\(\frac{1}{f_{e}}=\frac{1}{-v_{e}}-\frac{1}{\left(-u_{e}\right)}\)
or \(\frac{1}{u_{e}}=\frac{1}{f_{e}}+\frac{1}{v_{e}}\)
Magnifying power,
M = \(-\frac{v_{o}}{u_{o}} D\left(\frac{1}{f_{e}}+\frac{1}{v_{e}}\right)\)
or M = \(-\frac{v_{o}}{u_{o}}\left(\frac{D}{f_{e}}+\frac{D}{v_{e}}\right)\)
When final image is formed at the distance of distinct vision, Ve = D
∴ Magnification,
M= – \(\frac{v_{o}}{u_{o}}\left(1+\frac{D}{f_{e}}\right)\)
For greater magnification of a compound microscope, fe should be small. As fo < fe’ so f0 is small.
Hence, for greater magnification both f0 and fe should be small with f0 to be smaller of the two.
(b) If image A’B’ is exactly at the focus of the eyepiece, then image A”B” is formed at infinity.
If the object AB is very close to the focus of the objective lens of focal length f0, then magnification M0 by the objective lens
Me = \(\frac{L}{f_{0}}\)
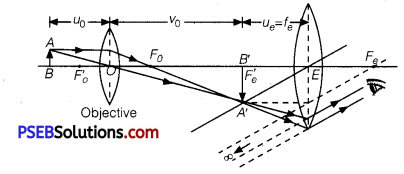
where, L is tube length (or distance between lenses L0 and Le) Magnification Me by the eyepiece
Me = \(\frac{D}{F_{e}} \)
where, D = Least distance of distinct vision
Total magnification, m = M0 Me = \(\left(\frac{L}{f_{o}}\right)\left(\frac{D}{f_{e}}\right)\)
Question 3.
Explain with the help of a labelled ray diagram, how is image formed in an astronomical telescope. Derive an expression for its magnifying power.
Or
Draw a ray diagram showing the image formation of a distant object by a refracting telescope. Define Its magnifying power and write the two important factors considered to increase the magnifying power. Describe briefly the two main limitations and explain how far these can be minimised in a reflecting telescope.
Answer:
Astronomical (Refracti ng) Telescope
Construction: It consists of two co-axial cylindrical tubes, out of which one tube is long and wide, while the other tube is small and narrow. The narrow tube may be moved in and out of the wide tube by rack and pinion arrangement. At one end of wide tube an achromatic convex lens L1 is placed, which faces the object and is so-called objective (lens). The focal length and aperture of this lens are kept large. The large aperture of objective is taken that it may collect sufficient light to form a bright image of a distant object. The narrow tube is towards eye and carries an achromatic convex lens 12 of small focal length and small aperture on its outer end. This is called eye-lens or eyepiece.
The small aperture of eye lens is taken so that the whole light refracted by it may reach the eye. Cross-wires are fitted at a definite distance from the eye lens. Due to large focal length of objective lens and small focal length of eye lens, the final image subtends a large angle at the eye and hence the object appears large. The distance between the two lenses may be arranged by displacing narrow tube in or out of wide tube by means of rack and pinion arrangement.
Adjustment: First of all the eyepiece is moved backward and forward in the narrow tube and focused on the cross-wires. Then the objective lens is directed towards the object and narrow tube is displaced in or out of wide tube until the image of object is formed on cross-wires and there is no parallax between the image and cross-wires. In this position, a clear image of the object is seen. As the image is formed by refraction of light through both the lenses, this telescope is called the refracting telescope.
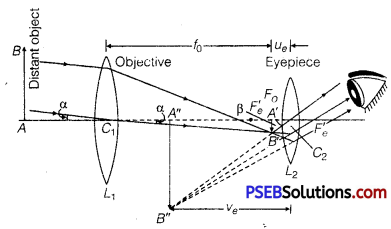
Working: Suppose AB is an object whose end A is on the axis of telescope. The objective lens (L1) forms the image A’B’ of the object AB at its second principal focus F0.
This image is real, inverted and diminished. This image A’ B’ acts as an object for the eyepiece L2 and lies between first focus fe‘ and optical centre C2 of lens L2.
Therefore, eyepiece forms its image A” B” which is virtual, erect and magnified.
Thus, the final image A” B” of object AB formed by the telescope is magnified, inverted and lies between objective and eyepiece.
Magnifying Power: The magnifying power of a telescope is measured by the ratio of angle (β) subtended by final image on the eye to the angle (α) subtended by object on the eye. i.e.,
Magnifying power M = \(\frac{\beta}{\alpha}\)
As α and β are very small angles, therefore, from figure.
The angle subtended by final image A” B” on eye.
β = angle subtended by image A’B’ on eye
= tanβ = \(\frac{A^{\prime} B^{\prime}}{C_{2} A^{\prime}}\)
As the object is very far (at infinity) from the telescope, the angle subtended by object at eye is same as the angle subtended by object on objective lens.
∴ α = tan α = \(\frac{A^{\prime} B^{\prime}}{C_{1} A^{\prime}}\)
∴ M = \(\frac{\beta}{\alpha}=\frac{A^{\prime} B^{\prime} / C_{2} A^{\prime}}{A^{\prime} B^{\prime} / C_{1} A^{\prime}}=\frac{C_{1} A^{\prime}}{C_{2} A^{\prime}}\)
If the focal lengths of objective and eyepiece be f0 and fe, distance of image A’B’ from eyepiece be ue, then by sign convention
C1A’ = +f0
C2A’ = – ue
∴ M = –\(\frac{f_{o}}{u_{e}}\) ……………………………… (1)
If ve is the distance of A” B” from eye-piece, then by sign convention, fe is positive, ue and ve are both negative. Hence, by lens formula = \(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{u}\)
we have
\(\frac{1}{f_{e}}=\frac{1}{-v_{e}}-\frac{1}{\left(-u_{e}\right)}\)
or
\(\frac{1}{u_{e}}=\frac{1}{f_{e}}+\frac{1}{v_{e}}\)
Substituting this value in eq. (1), we get
M = -f0 \(\left(\frac{1}{f_{e}}+\frac{1}{v_{e}}\right)\) …………………………. (2)
This is the general formula for magnifying power. In this formula, only numerical values of f0, fe and ve are to be used because signs have already been used.
Length of Telescope : The distance between objective and eyepiece is called the length (L) of the telescope. Obviously,
L = L1L2 =C1C2 = f0+ue …………………… (3)
Now there arise two cases :
(i) When the final image is formed at minimum distance (D) of distinct vision then ve =D
∴ M = -f0 \(\left(\frac{1}{f_{e}}+\frac{1}{D}\right)=-\frac{f_{o}}{f_{e}}\left(1+\frac{f_{e}}{D}\right)\) …………………………… (4)
Length of telescope L = f0 + ue
(ii) In normal adjustment position, the final image is formed at infinity: For relaxed eye, the final image is formed at infinity. In this state, the image A’B’ formed by objective lens should be at first the principal focus of eyepiece, i.e.,
ue = fe and ve
∴ Magnifying power,
M = – f0 \(\left(\frac{1}{f_{e}}+\frac{1}{\infty}\right)\) = –\(\frac{f_{o}}{f_{e}}\)
Length of telescope = f0 + fe
For large magnifying power, f0 should be large and fe should be small. For high resolution of the telescope, diameter of the objective should be large.
![]()
Factors for Increasing the Magnifying Power
1. Increasing focal length of objective
2. Decreasing focal length of eyepiece
Limitations
1. Suffers from chromatic aberration
2. Suffers from spherical aberration
3. Small magnifying power
4. Small resolving power
Advantages of Reflecting Telescope
1. No chromatic aberration, because mirror is used.
2. Spherical aberration can be removed by using a parabolic mirror.
3. Image is bright because no loss of energy due to reflection.
4. Large mirror can provide easier mechanical support.