This PSEB 10th Class Computer Notes Chapter 5 Desktop Publishing will help you in revision during exams.
PSEB 10th Class Computer Notes Chapter 5 Desktop Publishing
Desktop publishing is a term coined after the development of a specific type of software. It’s about using that software to combine and rearrange text and images and creating digital files. Desktop publishing (also known as DTP) combines, a personal computer and WYSIWYG(What You See Is What You Get) page layout software to create publication documents on a computer for either large scale publishing or small scale local multifunction peripheral output and distribution.
![]()
Desktop Publishing:
The term “desktop publishing” is commonly used to describe page layout skills. However, the skills and software are not limited to paper and book publishing. The same skills and software are often used to create graphics for point of sale displays, promotional items, trade show exhibits, retail package designs and outdoor signs. Desktop publishing refers to the act of using software on a personal computer to combine mixed-media elements such as text, photos, or charts into printable documents.
Once created, these documents can either be printed on a home printer or outsourced to a professional printing service. One of the key features is the ability to preview a page layout before prior to printing, via a feature called What You See Is What You Get (WYSIWYG), pronounced wizzy-wig. While this Was once taught through advanced education programs, advancements in software means that the process is less difficult to master than in past decades.
Definition of DTP
Desktop publishing is the process of using a computer and specific types of software to combine text, images and artwork to produce documents properly formatted for print or visual consumption.
DTP opened visual communication to all with the advent ofdesktop publishing software and affordable desktop computers, a wide range of people, including non-designers and others without graphic design experience, suddenly had the tools to become desktop publishers.
Freelance and in-house graphic designers, small business owners, secretaries, teachers, students and individual consumers do desktop publishing. Non-designers can create visual communications for commercial digital printing, printing on a printing press, and for desktop printing at home or in the office.
![]()
Visual Communication using DTP
Now, anyone can do desktop publishing. We dont need any professional for that. Designing and printing both are included in desktop publishing but usually it is considered a process of creating a digital file of product only.
Desktop-Publishing Software:
The primary software used in desktop publishing is page layout software and web design software. Graphics software, including drawing software, a photo editor and word processing software, are also important tools of the graphic designer or desktop publisher. The list of available software is lengthy, but some software is seen on just about everyone’s must-have list depending on what they are trying to accomplish.
Page Layout Software for Printing:
- Adobe InDesign
- PagePlus Series from Serif
- QuarkXpress
Page Layout Software for Office:
1. Microsoft Office Suite Apple iWork Suite
Graphics Software:
- Adobe Illustrator
- Corel Draw
- Inkscape
Photo Editing Software:
- Adobe Photoshop
- Corel PaintShop Pro
Web Design Software:
- Adobe Dreamweaver CC
- Adobe Muse
![]()
Word Processing and Desktop Publishing:
The similarities between the two are:
- Both deal with text that can be formatted.
- Both can work with tables and pictures.
- Both have many similar features like WordArt, Clip Art, and text styles.
The Differences between DTP and Word Processing:
Word processing involves creation, editing, and printing of text while desktop publishing involves production of documents that combine text with graphics. Word processing is difficult to layout and design as compared to desktop publishing. Thus, desktop publishing is used to work on things like newsletters, magazines, adverts, and brochures where layout is important. Word processing documents are common for simple memos, letters, manuscripts, and resumes.
The difference between desktop publishing and word processing software is as follows:
| Desktop Publishing | Word Processing |
| 1. DTP involves production of documents that combine text and graphics.
2. Layout designing is easy. 3. Main products are newsletter, magazines adverts etc. 4. They involve more graphics. 5. Its products are coloured mainly. |
Word processors deals with creation, edition of text.
Layout designing is difficult. Main products are documents and resumes. They involve more text. They are used to get black and white documents. |
Wysiwyg Feature:
A WYSIWYG is a system in which content (text and graphics) can be edited in a form closely resembling its appearance when printed or displayed as a finished product, such as a printed document, web page, or slide presentation. WYSIWYG is especially popular for desktop publishing.
With desktop publishing, we can increase productivity, minimize production cost, enhance the appearance of our documents, improve the level of creativity, reduce the time taken for printing and produce customized documents. The best part about DTP is that we can create professional-looking documents, without the need for graphic designer.
![]()
Graphics:
A graphic is an image or visual representation of an object. Therefore, computer graphics are simply images displayed on a computer screen. Graphics Eire often contrasted with text, which is comprised of characters, such as numbers and letters, rather than images.
Computer graphics can be either two or three-dimensional. Early computers only supported 2D monochrome graphics, meaning they were black and white. Eventually, computers began to support color images. While the first machines only supported 16 or 256 colors, most computers can now display graphics in millions of colors.
Bitmap or Raster Graphics
Bitmap graphics consist of many tiny dots called pixels. It is possible to edit each individual pixel using bitmap graphics software like Adobe Photoshop. Examples of bitmap graphics are a digital photograph or a scanned image. The amount of detail we can draw depends on the number of pixels per square inch (PSI). Since the computer has to store information about every single pixel in the image, the file size of a bitmap graphic is often quite large. When we resize a bitmap graphic, it tends to lose its quality.
Vector Graphics
Vector graphics are based on control points which are connected by lines and curves called vector paths or vectors. Vector paths can be used to make shape objects. It is possible to edit each shape object separately, for example, to change the shape, outline type (stroke), fill, size or position.
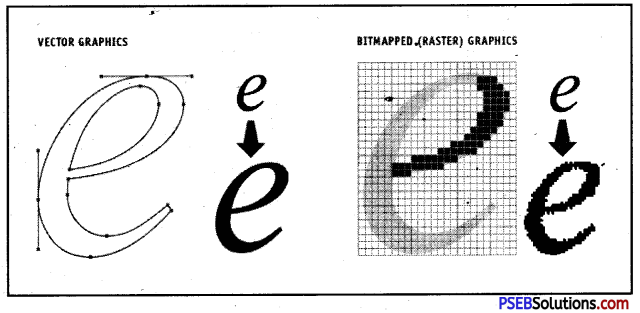
The difference between vector and bitmap graphics is as follows :
| Vector Graphics | Bitmap Graphics |
| 1. Vector Graphics are passed on Vector Paths
2. They do not lose quality 3. The file size is less 4. These are used in advanced programmes |
They are based on Pixels
They lose quality when expended The file size is more. These are used for basic programmes |
Margins:
A margin is the area between the main content of a page and the page edges. The margin helps to define where a line of text begins and ends. A page to include top, Bottom, Left and Right margin.
The default margins are usually defined as one inch on all sides. However, depending on the requirement, the margins may vary. These margins create a frame around the content of the page so that the text does not run all the way to the edges. The white space along the edges of the document makes the page look cleaner and the text is easier to read.
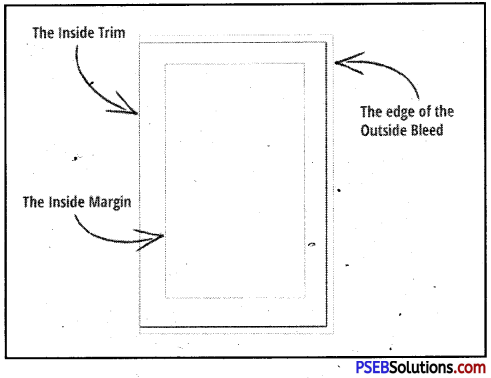
Gutter Position
A gutter margin setting adds extra space to the side margin or top margin of a document that we plan to bind. A gutter margin helps ensure that text isn’t hidden by the binding.
![]()
Fonts:
A font is a set of printable or displayable text character s in a specific style and size or we can say that a font is a specific typeface of a certain size and style. A typeface is a set of characters of the same design. These characters include letters, numbers, punctuation marks, and symbols. Some popular typefaces include Arial, Helvetica, Times, and Verdana. While most computers come with a few dozen typefaces installed, there are thousands of typefaces available.

Printer:
A printer is an external output device that takes data from a computer and generates output on a paper in the form of graphics/text. There are two types of printers.
Impact Printers
An impact printer has a head that contains pins to make, contact with the paper. It usually forms the print image by striking its pins on a inked ribbon against the paper. Following are some examples of impact printers:
1. Dot-Matrix Printers. The dot-matrix printer uses print heads containing from 9 to 24 pins.
These pins produce patterns of dots on the paper to form the individual characters. The 24 pin dot-matrix printer produces more dots that a 9 pin dot-matrix printer, which results in much better quality and clearer characters.
The general rule is, the more pins, the clearer the letters on the paper. The pins strike the ribbon individually as the print mechanism moves across the entire print line in both directions, i.e, from left to right, then right to left, and so on. The user can produce a color output with a dot-matrix printer (the user will change the black ribbon with a ribbon that has color stripes). Dot-matrix printers are inexpensive and typically print at speeds of 100-600 characters per second.
2. Daisy-Wheel Printers. It is called daisy-wheel printer because the print mechanism looks like a daisy; at the end of each “Petal” is a fully formed character which produces solid-line print. A hammer strikes a “petal” con-taining a character against the ribbon, and the character prints on the paper. Its speed is slow typically 25-55 characters per second.
3. Line Printers. Line printers, or line-at-a-time printers, use special mecha¬nism. that can print a whole line at once; it can typically print the range of 1,200 to 6,000 lines per minute. Drum, chain, and band printers are line-at- a-time printers.
![]()
Non-Impact Printers:
Non-impact printers do not use a striking device to produce characters on the paper; and because these printers do not hammer against the paper its much quieter. Following are some non-impacted printers:
1. Ink-Jet Printers
Ink-jet printers work in the same fashion as dot-matrix printers in the form images or characters with little dots. However, the dots are formed by tiny droplets of ink.

Ink-jet printers form characters on paper by spraying ink from tiny nozzles through an electrical field that arranges the charged ink particles into characters at the rate of approximately 250 characters per second. The ink is absorbed into the paper and dries instantly. Various colors of ink can also be used.
2. Laser Printers
A laser printer works like a photocopy machine. Laser print¬ers produce images on paper by directing a laser beam at a mirror which again directs the beam onto a drum. The drum has a special coating on it to which toner (an ink powder) sticks. Using patterns of small dots, a laser beam conveys information from the computer to a positively charged drum to become neutralized. From all those areas of drum which become neutralized, the toner detaches. As the paper rolls by the drum, the toner is transferred to the paper printing the letters or other graphics on the paper. A hot roller bonds the toner to the paper.

Laser printers use buffers entire page at a time. When a whole page is loaded, it will be printed. The speed of laser printers is high and it print quietly without producing much noise. Many home-use laser printers can print eight pages per minute, but faster and print approximately 21,000 lines per minute, or 437 pages per minute (if each page contains 48 lines). When high speed laser printers were introduced they were expensive.
