Punjab State Board PSEB 10th Class Computer Book Solutions Chapter 5 Desktop Publishing Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 10 Computer Science Chapter 5 Desktop Publishing
Computer Guide for Class 10 PSEB Desktop Publishing Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Programs that can be used to create books, magazines, newspapers, flyers, pamphlets, and many other kinds of printed documents.
(a) Desk Publishing
(b) DeskTop Publishing
(c) Top Publishing
(d) Publishing
Answer:
(b) DeskTop Publishing
Question 2.
That enable us to see on the display screen exactly what will appear when the document is printed:
(a) WYSWJKI
(b) WKSWUG
(c) WUSIWUG
(d) WYSIWYG
Answer:
(d) WYSIWYG
![]()
Question 3.
A printer that works like a photocopy machine:
(a) Laser
(b) InkJet
(c) Line
(d) Drum
Answer:
(a) Laser
Question 4.
……….. is a visual representation of objects.
(a) Charts
(b) Graphics
(c) Frames
(d) Fonts
Answer:
(b) Graphics
Question 5.
Printer that print image by pressing an inked ribbon against the paper using a hammer or pins.
(a) Ink-jet
(b) Impact
(c) Non impact
(d) Laser
Answer:
(b) Impact
PSEB 10th Class Computer Book Chapter 5 Desktop Publishing
![]()
2. Fill in the Blanks
1. Arial, Helvetica, Times, and Verdana etc. are examples of …………… and they have same …………. .
Answer:
Typeface, Design
2. A Gutter margin setting adds extra space to the …………….margin or margin of a ………… document that we plan to bind.
Answer:
Side, Top
3. In web pages the content is ………… not designed for ………… .
Answer:
Viewable, Print
4. Laser printers use …………. that stores an ……………. at a time.
Answer:
Buffers, Entire page.
![]()
3. True or False
1. DTP stands for Desk Top Publishing.
Answer:
True
2. Desktop publishing hardware and software is also used to design and produce web pages.
Answer:
True
3. In Ink-Jet Printer, the ink cannot be absorbed into the paper and dries instantly.
Answer:
False.
4. The dot-matrix printer uses print heads containing from 19 to 124 pins.
Answer:
False.
![]()
4. Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Which printer can typically print the range of 1,200 to 6,000 lines per minute?
Answer:
Line Printer
Question 2.
Which printer can be either two or three-dimensional.
Answer:
Computer Graphics
Question 3.
Which printer has a special coating on it to which toner (an ink powder) sticks?
Answer:
Laser Printers
Question 4.
A set of characters of the same design is called?
Answer:
Typeface
Question 5.
The area between the main content of a page and the page edges is called?
Answer:
Margins
![]()
5. Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is Desktop Publishing?
Answer:
An application of compute that is enables small companies and individuals
to produce reports, visiting cards, calendar, advertising, magazines etc. to near typeset quality. Modern systems, which simulate many of the professional typesetting functions, consist of a personal computer using DTP software.
Question 2.
What are the various types of printers?
Answer:
The various types of printers are:
- Impact printer
- Non-impact printers
- Thermal printers
Question 3.
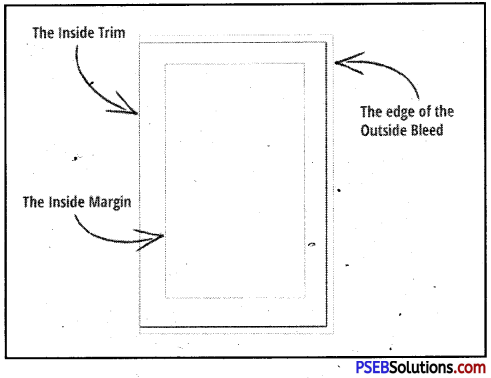
What is margin?
Answer:
Margins are the distance between the text from left and right edges, top and bottom edges. Margins are normally 1 inch, but you can adjust it according to your need.
Question 4.
What do you mean by Gutter Position?
Answer:
A gutter margin setting adds extra space to the side margin or top margin of a document that we plan to bind. A gutter margin helps ensure that text isn’t hidden by the binding.
![]()
Question 5.
What are Graphics?
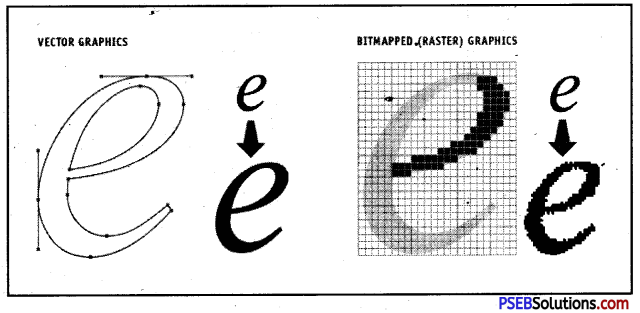
Answer: A graphic is an image or visual representation of an object. Computer graphics are simply images displayed on a computer screen. Computer graphics can be either two or three-dimensional. There are two main types of 2D graphic:
- Bitmap or Raster graphics
- Vector graphics
Question 6.
Explain the working of Laser Printer.
Answer:
A laser printer works like a photocopy machine. Laser printers produce images on paper by directing a laser beam at a mirror which again directs the beam onto a drum. The drum has a special coating on it to which toner (an ink powder) sticks. Using patterns of small dots, a laser beam conveys information from the computer to a positively charged drum to become neutralized. From all those areas of drum which become neutralized, the toner detaches. As the paper rolls by the drum, the toner is transferred to the paper printing the letters or other graphics on the paper. A hot roller bonds the toner to the paper.
Question 7.
Explain WYSIWYG feature.
Answer:
WYSIWYG, is an acronym for What You See Is What You Get. The term is used in computing to describe a system in which content displayed during editing appears very similar to the final output, which might be a printed document, web page, slide presentation or even the lighting for a theatrical event.
6. Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the difference between Vector Graphics and Bitmap Graphics?
Answer:
The difference between vector and bitmap graphics is as follows:
| Vector Graphics | Bitmap Graphics |
| 1. Vector Graphics are passed on Vector Paths | 1. They are based on Pixels |
| 2. They do not lose quality | 2. They lose quality when expended |
| 3. The file size is less | 3. The file size is more. |
| 4. These are used in advanced programmes | 4. These are used for basic programmes |
Question 2.
What is the difference between Impact and Non-Impact printers?
Answer:
The differences between impact and non impact printers are as follows:
| Impact Printer | Non-Impact Printers |
| 1. They produces noise. | 1. They do not produce noise. |
| 2. A head is strike on page. | 2. No head is striked. |
| 3. They are not costly. | 3. They are costly. |
| 4. A ribbon is used. | 4. No ribbon is used. |
| 5. They are slower in speed. | 5. They are faster in speed. |
| 6. The printing quality is low. | 6. Their printing quality is high. |
| 7. They use continous paper sheets. | 7. They use individual paper sheets. |
| 8. Example are Dot Matrix, Chain. | 8. Example are Laser, Inkjet. |
![]()
Question 3.
Explain any two types of Impact printers.
Answer:
Following are the two types of impact printers:
1. Impact Printers:
An impact printer has a head that contains pins to make contact with the paper. It usually forms the print image by striking its pins on a inked ribbon against the paper. Following are some examples of impact printers. The dot-matrix printer uses print heads containing from 9 to 24 pins. These pins produce patterns of dots on the paper to form the individual characters.
The 24 pin dot-matrix printer produces more dots that a 9 pin dot-matrix printer, which results in much better quality and clearer characters. The general rule is: the more pins, the clearer the letters on the paper. The pins strike the ribbon individually as the print mechanism moves across the entire print line in both directions, i.e, from left to right, then right to left, and so on. The user can produce a color output with a dot-matrix printer (the user will change the black ribbon with a ribbon that has color stripes). Dot-matrix printers are inexpensive and typically print at speeds of 100¬600 characters per second.
2. Daisy-Wheel Printers:
In order to get the quality of type found on typewriters, a daisy-wheel impact printer can be used. It is called daisy wheel printer because the print mechanism looks like a daisy; at the end of each “Petal” is a fully formed character which produces solid line print. A hammer strikes a “petal” containing a character against the ribbon, and the character prints on the paper. Its speed is slow typically 25-55 characters per second.
PSEB 10th Class Computer Guide Desktop Publishing Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Which is graphic Software among following?
(a) Adobe Illustrator
(b) Corel Draw
(c) Inter Space
(d) All of Above
Answer:
(d) All of Above
![]()
Question 2.
Which one is Photo Editing software?
(a) Adobe Photoshop
(b) Coral PaintShop
(c) Both of These
(d) None of These
Answer:
(c) Both of These
Question 3.
How many types are there of 2D Graphics?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 1
(d) 4
Answer:
(a) 2
Question 4.
What is the type of Laser Printer?
(a) Impact
(b) Non Impact
(c) Both of These
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Non Impact
Fill in the Blanks
1. ………….. means spacing between two or more lines.
Answer:
Leading
2. Frame …………..related information or graphics.
Answer:
group
3. WYSIWYG means …………… .
Answer:
what you see is what I get.
4. We can …………. document in many ways.
Answer:
print.
5. Faster color laser printer can print …………. pages/min.
Answer:
100.
![]()
True/False
1. Header is written on the bottom of the page.
Answer:
False
2. MS-Word is a DTP software.
Answer:
True
3. We don’t need to planning for preparing a document.
Answer:
False
4. Style include bullet effects.
Answer:
True
5. Spacing between two or more lines are called scaling.
Answer:
False
![]()
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the full form of WYSIWYG?
Answer:
What You See Is What You Get
Question 2.
Which is the best printing?
Answer:
Laser Printing
Question 3.
The printing in which ink is settled on paper is called?
Answer:
Offset Printing
![]()
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by Desktop Publishing?
Answer:
An application of computer that is enables small companies and individuals to produce reports, visiting cards, calendar, advertising, magazines etc. to near typeset quality. Modern systems, which simulate many of the professional typesetting functions, consist of a personal computer using DTP software.
Question 2.
What are the various methods of printing?
Answer:
There are two methods of printing:
1. Offset Printing:
Ink sit on the surface of the paper, nearly all modem printing is offset. Most short-run-jobs are now being done digitally. Instead of the offset printing as personal, for business use it becomes better and Cheaper.
2. Laser Printing:
A laser printer is a common type of printer that produces high quality text and graphics. Laser printer uses non-impact photo copier technology.
![]()
Question 3.
What do you mean by Scaling, Tracking & Leading?
Answer:
1. Scaling:
There are a number of ways for adjusting text in a document. This term refers to that, without changing the points of any font we can increase or decrease its width.
2. Tracking:
Tracking simple means to increase or decrease the character space in a word or multiple words. It can also measure in points.
3. Leading:
It simply shows the line space between two or more lines. It can also measure in points or depends upon the desktop publishing software.
Question 4.
What are Margins?
Answer:
Margins are the distance between the text from left and right edges, top and bottom edges. Margins are normally 1 inch, but you can adjust it according to your need.
Question 5.
What do you mean Document Planning?
Answer:
Document planning mean to set the following:
- Page layout
- Style
- Margin
- Hader and Fotter
- Font
![]()
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are fonts?
Answer:
A font is a set of printable or displayable text character s in a specific style and size or we can say that a font is a specific typeface of a certain size and style. A typeface is a set of characters of the same design. These characters include letters, numbers, punctuation marks, and symbols. Some popular typefaces include Arial, Helvetica, Times, and Verdana. While most computers come with a few dozen typefaces installed, there are thousands of typefaces available.

Question 2.
What do you mean by WYSIWYG?
Answer:
A WYSIWYG is a system in which content (text and graphics) can be edited in a form closely resembling its appearance when printed or displayed as a finished product, such as a printed document, web page, or slide presentation. WYSIWYG is especially popular for desktop publishing.
With desktop publishing, we can increase productivity, minimize production cost, enhance the appearance of our documents, improve the level of creativity, reduce the time taken for printing and produce customized documents. The best part about DTP is that we can create professional-looking documents, without the need for graphic designer.
![]()
Question 3.
What are different types of printers? Discuss working of Laser printer.
Answer:
Printer:
A printer is an external output device that takes data from a computer and generates output on a paper in the form of graphics/text. There are two types of printers.
Impact Printers:
An impact printer has a head that contains pins to make, contact with the paper. It usually forms the print image by striking its pins on a inked ribbon against the paper. Following are some examples of impact printers:
1. Dot-Matrix Printers:
The dot-matrix printer uses print heads containing from 9 to 24 pins. These pins produce patterns of dots on the paper to form the individual characters. The 24 pin dot-matrix printer produces more dots that a 9 pin dot-matrix printer, which results in much better quality and clearer characters.The general rule is, the more pins, the clearer the letters on the paper.
The pins strike the ribbon individually as the print mechanism moves across the entire print line in both directions, i.e, from left to right, then right to left, and so on. The user can produce a color output with a dot-matrix printer (the user will change the black ribbon with a ribbon that has color stripes). Dot-matrix printers are inexpensive and typically print at speeds of 100-600 characters per second.

2. Daisy-Wheel Printers:
It is called daisy-wheel printer because the print mechanism looks like a daisy; at the end of each “Petal” is a fully formed character which produces solid-line print. A hammer strikes a “petal” containing a character against the ribbon, and the character prints on the paper. Its speed is slow typically 25-55 characters per second.

3. Line Printers:
Line printers, or line-at-a-time printers, use special mechanism. that can print a whole line at once; it can typically print the range of 1,200 to 6,000 lines per minute. Drum, chain, and band printers are line-at- a-time printers.
Non-Impact Printers:
Non-impact printers do not use a striking device to produce characters on the paper; and because these printers do not hammer against the paper its much quieter. Following are some non-impacted printers:
1. Ink-Jet Printers:
Ink-jet printers work in the same fashion as dot matrix printers in the form images or characters with little dots. However, the dots are formed by tiny droplets of ink. Ink-jet printers form characters on paper by spraying ink from tiny nozzles through an electrical field that arranges the charged ink particles into characters at the rate of approximately 250 characters per second. The ink is absorbed into the paper and dries instantly. Various colors of ink can also be used.

2. Laser Printers:
A laser printer works like a photocopy machine. Laser printers produce images on paper by directing a laser beam at a mirror which again directs the beam onto a drum. The drum has a special coating on it to which toner (an ink powder) sticks. Using patterns of small dots, a laser beam conveys information from the computer to a positively charged drum to become neutralized. From all those areas of drum which become neutralized, the toner detaches. As the paper rolls by the drum, the toner is transferred to the paper printing the letters or other graphics on the paper. A hot roller bonds the toner to the paper.

Laser printers use buffers entire page at a time. When a whole page is loaded, it will be printed. The speed of laser printers is high and it print quietly without producing much noise. Many home-use laser printers can print eight pages per minute, but faster and print approximately 21,000 lines per minute, or 437 pages per minute (if each page contains 48 lines). When high speed laser printers were introduced they were expensive.