Punjab State Board PSEB 10th Class Science Book Solutions Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds
PSEB 10th Class Science Guide Carbon and its Compounds Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Ethane, with the molecular formula C2H6 has :
(a) 6 covalent bonds
(b) 7 covalent bonds
(c) 8 covalent bonds
(d) 9 covalent bonds.
Answer:
(b) 7 covalent bonds
Question 2.
Butanone is a four-carbon compound with the functional group :
(a) carboxylic acid
(b) aldehyde
(c) ketone
(d) alcohol.
Answer:
(c) ketone
Question 3.
While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, it means that :
(а) the food is not cooked completely
(b) the fuel is not burning completely
(c) the fuel is wet
(d) the fuel is burning completely.
Answer:
(b) the fuel is not burning completely
Question 4.
Explain the nature of the covalent bond using the bond formation in CH3Cl.
Answer:
The formation of CH3Cl can be represented as :
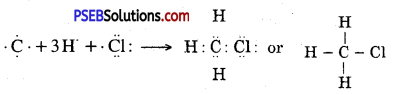
Carbon forms single covalent bonds with three H- atoms and one Cl – atom by sharing one electron pair with each C-H bonds are non-polar. But C – Cl bond is polar because C and H leave almost same electronegativity whereas Cl has more electronegativity than carbon.
![]()
Question 5.
Draw the electron dot structures for :
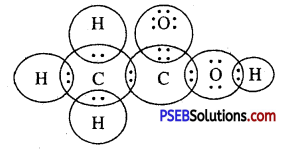
(a) ethanoic acid
Answer:
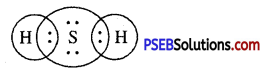
(b) H2S
Answer:
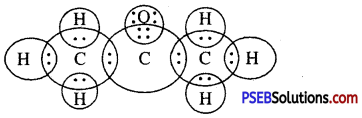
(c) propanone
Answer:
(d) F2.
Answer:

Question 6.
What is an homologous series? Explain with an example.
Answer:
A series of compounds having similar structural formulae, same functional group and hence similar chemical properties is called a homologous series. In the homologous series any two adjacent members differ by CH2 unit in their molecular formulae.
For example homologous series of aldehydes (or alkanals) can be represented as :
| H – CHO | Methanal |
| CH3 – CHO | Ethanal |
| CH3 – CH2 – CHO | Propanal |
| CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CHO | Butanal |
| CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CHO | Pentanal and so on. |
Question 7.
How can ethanol and ethanoic acid be differentiated on the basis of their physical and chemical properties?
Answer:
Differences between ethanol and ethanoic acid
| Ethanol | Ethanoic acid |
| 1. It is a colourless liquid having a pleasant smell. | 1. It is colourless liquid having vineger like smell. |
| 2. It has no action with a litmus solution. | 2. It turns blue litmus solution red. |
| 3. It has no action with sodium hydrogen carbonate solution. | 3. It decomposes sodium hydrogen carbonate solution giving brisk effervescence of carbon dioxide gas. |
Question 8.
Why does micelle formation take place when soap is added to water? Will a micelle be formed in other solvents such as ethanol also?
Answer:
Soap molecule has two ends, one is hydrophilic, and it dissolves in water, while the other end is hydrophobic, and it dissolves in hydrocarbons. When soap is at the surface of water , the hydrophobic ‘tail’ of soap will not be soluble in water and the soap will align along the surface of water with the ionic end in water and the hydrocarbon ‘tail’ pointing out of water.
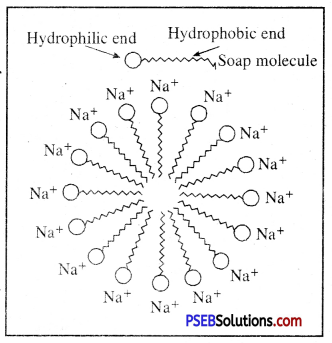
Inside water, these molecules have a unique orientation which keeps the hydrocarbon portion out of the water. This is achieved due to the formation clusters of molecules in which the hydrophobic tails are in the interior of the cluster and the ionic ends are on the surface of the cluster. This formation is called a micelle.
Such micelles can be formed in other polar solvents like ethanol.
Question 9.
Why are carbon and its compounds used as fuels for most applications?
Answer:
Carbon and its compounds are used as fuels for most applications because they bum producing a large amount of heat and light.
![]()
Question 10.
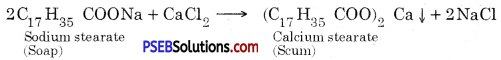
Explain the formation of scum when hard water is treated with soap.
Answer:
When soap is added to hard water, the soluble calcium and magnesium salts present in it react with soap to give insoluble calcium salt of soap which produces scum.
Question 11.
What change will you observe if you test soap with litmus paper (red and blue)?
Answer:
Soap solution will turn red litmus paper blue because soap is alkaline in nature.
Question 12.
What is hydrogenation? What is its industrial application?
Answer:
The addition of hydrogen to unsaturated hydrocarbons in the presence of catalysts like palladium, platinum, nickel etc. to give saturated hydrocarbons is called hydrogenation.
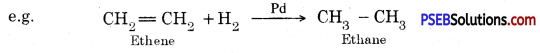
This reaction is used for hydrogenation of liquid vegetable oils using a nickel catalyst to get artificial or vanaspati ghee.
Question 13.
Which of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition reaction : C2H6, C3H8, C3H6, C2H2 and CH4.
Answer:
Out of C2H6, C3H8, C3H6, C2H2 and CH4; C3H6 and C2H2 undergo addition reactions because they contain multiple bonds.
Question 14.
Give a test that can be used to differentiate chemically between butter and cooking oil.
Answer:
Distinction between Butter and Cooking oil:
| Butter | Cooking Oil |
| 1. It is solid at room temperature. | 1. It is liquid at room temperature. |
| 2. Mix equal volumes of HgCl2 solution in 50% alcohol and 5% iodine solution in alcohol. To this add lg of butter. Violet colour does not fade away. | 2. Mix equal volumes of HgCl2 solution in 50% alcohol and 5% solution of iodine in alcohol. To this add 1 ml of cooking oil. Violet colour fades away. |
| 3. Take 2 g of butter in a test tube. To this add 1ml of cone. HCl and a few drops of 2% furfural solution in alcohol. Shake and allow to stand for 5 – 10 minutes. No rose red coloration appears. | 3. Take 2 g of cooking oil in a test tube. To this add 1 ml of cone. HCl and a few drops of 2% .furfural solution in alcohol. Shake it and allow to stand for 5 – 10 minutes. Rose red coloration is obtained. |
Question 15.
Explain the mechanism of the cleansing action of soaps.
Answer:
Mechanism of cleansing action of Soap:
Soaps are sodium or potassium salts of higher fatty acids e.g. sodium palmitate, C15H31COO–Na+, sodium stearate, C17H35COO–Na+ etc. A molecule of soap consists of two parts :
- a long chain hydrocarbon part (C15H31–, C17H35 …. etc.) which is soluble in oil and
- ionic part on polar group, – COO–Na+ which is soluble in water. Thus a molecule of soap can be represented as :
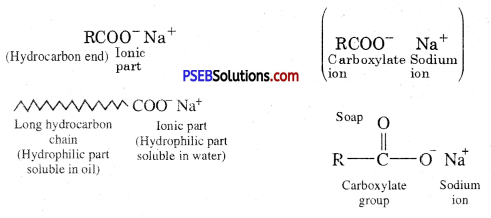
The long hydrocarbon chain is insoluble in water but soluble in oil and greases whereas the ionic or polar part is soluble in water. Soap has a capacity to clean a dirty piece of cloth whereas ordinary water cannot. The dirty clothes contain greasy and oily substance (dirt). Soap molecules dissociate in water to give carboxylate ion (RCOO–) and cation (Na+). When soap added to dirty clothes dipped in water, the hydrocarbon part of carboxylate group dissolving in greasy or oily dirt particles where the polar (COO–) group remain attached to water. In this way each oil droplet acquires negative charge.
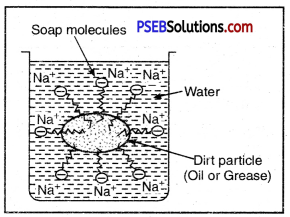
The cleansing action of Soap
These negative charged oil droplets called micelles cannot coalesce and hence form a stable emulsion water. These small droplets along with dirt can be easily washed away with water. Thus the soap helps in removing greasy dirt by producing a stable oil in wrater type emulsion. Also the soap reduces surface tension of water. Hence cloth is wetted more effectively and is cleaned.
Science Guide for Class 10 PSEB Carbon and its Compounds InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What would be the electron-dot structure of carbon dioxide which has the formula CO2?
Answer:
In carbon dioxide, carbon atoms are bonded with two oxygen atoms. The atomic number of carbon is 6, and it has four electrons in the outer shell.
To make an octet it requires four electrons. Oxygen requires only two electrons in the outer shell. Therefore electron-dot structure will be :
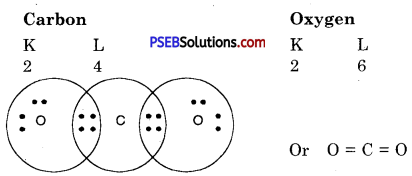
Every oxygen atom is joined to carbon atom by double bond.
Question 2.
What would be the electron-dot structure of a molecule of sulphur which is made up of eight atoms of sulphur? (HINT. The eight atoms of sulphur are joined together in the form of ring.)
Answer:
The atomic number of sulphur is 16
![]()
Sulphur has 6 electrons in the outermost shell and to complete an octet it requires 2 electrons.
∴ Sulphur atom will share 2 electrons. It’s chemical formula is S8.
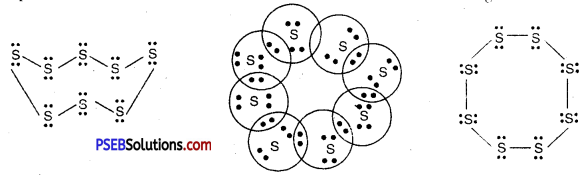
![]()
Question 3.
How many structural isomers can you draw for pentane?
Answer:
Three ; n-Pentane, iso-pentane, neo-pentane.
Structural isomers can be drawn for pentane.
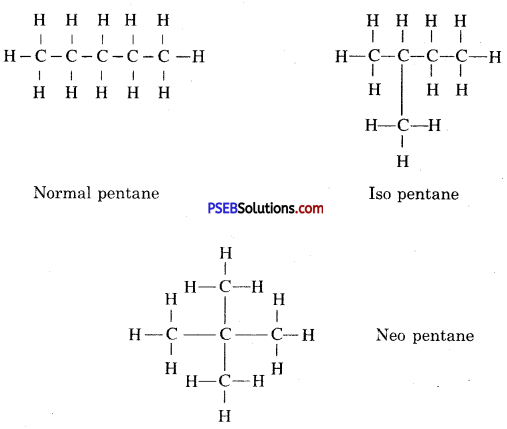
Question 4.
What are the two properties of carbon which lead to the huge number of carbon compounds we see around us?
Answer:
- Catenation: The carbon atoms have an astonishing property to combine and form bond with other carbon atoms to form long chain compounds. This property is known as catenation. In this, either long chain of carbon are in ring form or the carbon atoms join in single, double or triple bond.
- Tetravalency: Carbon has four electrons in the outermost shell. That is why its valency is four and it has got capacity to make bonds with other elements. Oxygen, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Sulphur, Chlorine and many other elements can make new compounds with the help of carbon.
Question 5.
What will be the formula and electron dot structure of cyclopentane?
Answer:
Molecular formula of cyclopentane = C5 H2 × 5 = C5H10
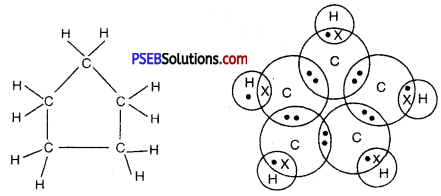
Question 6.
Draw the structures for following compounds :
Are structural isomers possible for bromopentane?
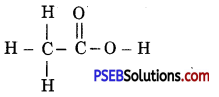
(i) Ethanoic acid
Answer:
Ethanoic acid (CH3COOH)
(ii) Bromopentane
Answer:
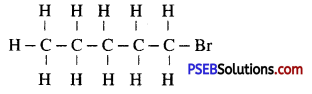
Due to exchange of position of carbon with bromine, many isomers of bromopentane are possible.
For example :
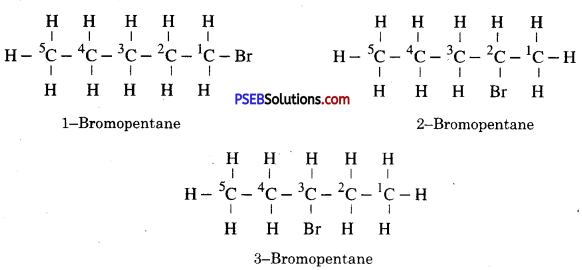
(iii) Butanone
Answer:
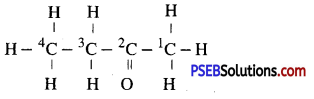
(iv) Hexanal.
Answer:
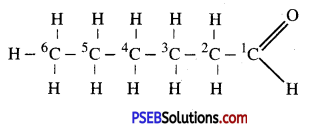
Question 7.
How would you name the following compounds?
(i) CH3 – CH2 – Br
Answer:
Bromoethane
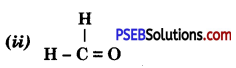
Answer:
Methanal
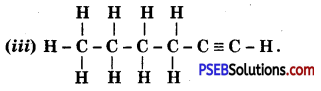
Answer:
Hex-1-yne.
![]()
Question 8.
Why is the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid an oxidation reaction?
Answer:
This is because in this reaction oxygen gets added to ethanol.
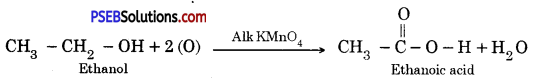
Question 9.
A mixture of oxygen and ethyne is burnt for welding. Can you tell why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used?
Answer:
A mixture of ethyne and air is not burnt for welding. This is because air also contains nitrogen along with oxygen. Nitrogen will also burn in oxygen producing oxides of nitrogen such as nitre oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) which cause pollution.
Question 10.
How would you distinguish experimentally between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid?
Answer:
The following two tests are used :
- Litmus test: Treat the given compound with blue litmus solutions. If the blue litmus solution turns red, it is a carboxylic acid and if does not turn red, it is an alcohol.
- Sodium bicarbonate test: Add some sodium bicarbonate solution to the given compound. If their is a brisk evolution of a colourless and odourless gas (CO2) which turns freshly prepared lime water milk, it is carboxylic acid and if their is no effervescence, it is an alcohol.
Question 11.
What are oxidising agents?
Answer:
- The substances which can oxidise other substances by giving oxygen are called oxidising agents.
- Examples: Alkaline potassium permanganate solution, acidified potassium dichromate solution, etc.
Question 12.
Would you be able to check if water is hard using a detergent?
Answer:
No, we can’t check whether the water is hand or soft using a detergent.
Question 13.
People use a variety of methods to wash clothes. Usually after adding the soap, they ‘beat’ the clothes on a stone, or beat it with a paddle, scrub with a brush, or the mixture is agitated necessary to get clean clothes?
Answer:
This is because when soap molecules dissolve in the dirt, the dirt is somewhat loosened from the clothes, and in order to remove it from clothes, the clothes have to be beaten on a stone or beaten with a paddle or scrubbed with a brush or mixture has to be agitated in washing machines.
