Punjab State Board PSEB 11th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 17 Breathing and Exchange of Gases Important Questions and Answers.
PSEB 11th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 17 Breathing and Exchange of Gases
Very short answer type questions
Question 1.
Why do cells need a constant supply of oxygen?
Answer:
Cells continuously need oxygen for the metabolic reactions that releases energy from molecules. This energy is used by cells for various functions of body.
Question 2.
Give the name of the organ that produces sound.
Answer:
Larynx.
Question 3.
A fluid filled double membranous layer surrounds the lungs. Name it. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
This layer is called pleural membrane and pleural fluid is found in between the two.
Question 4.
Which component of the respiratory system help in generation of pressure gradient for breathing? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
The diaphragm and a specialised set of muscles external and internal intercostals between the ribs.
Question 5.
Define Residual Volume (RV). [NCERT Exemplar] Or State the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal breathing. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Residual Volume (RV): It is the volume of air remaining in the lungs even after a forcible expiration. It is about 1100-1200 ml.
![]()
Question 6.
What is the RQ for glucose and proteins?
Answer:
Glucose RQ= 1
Proteins RQ = 0.85
Question 7.
Why is it advisable to do nasal breathing rather than mouth breathing?
Answer:
Nasal breathing is advisable because it is healthier as the air inhaled gets filtered in the nose so cleaner air goes to the lungs.
Question 8.
A major percentage of O2 (97%) is transported by RBCs in the blood. How does the remaining 3% of O2 transported? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
In dissolved state through plasma.
Question 9.
What is the amount of O2 supplied to tissues through every 100 mL of oxygenated blood under normal physiological conditions? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Around. 5 mL.
Question 10.
Cigarette smoking causes emphysema. Give reason. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Cigarette smoking cause damages to the alveolar walls due to alveolar sacs remaining filled with air leading to decreased respiratory surface for exchange of gases.
Question 11.
What causes snoring?
Answer:
Partial blocking of upper respiratory tract by tongue leading to turbulence of airflow causes a rough rattling inspiratory noise called snoring.
Question 12.
Give the name of some common respiratory disorders.
Answer:
Asthma, emphysema, occupational lung disorders (e.g., Silicosis and asbestosis).
![]()
Short answer type questions
Question 1.
Explain the structure of thoracic chamber.
Answer:
Anatomically, thoracic chamber is an air-tight chamber. The thoracic chamber is formed dorsally by the vertebral column, ventrally by the sternum, laterally by the ribs, and on the lower side by the dome-shaped diaphragm. The anatomical setup of lungs in thorax is such that any change in the volume of the thoracic cavity will be reflected in the lung (pulmonary) cavity. Such an arrangement is essential for breathing, as we cannot directly alter the pulmonary volume.
Question 2.
Explain various steps of respiration.
Answer:
Steps of Respiration
- Breathing or pulmonary ventilation by which atmospheric air is drawn in and CO2-rich alveolar air is released out.
- Diffusion of gases (O2 and CO2) across alveolar membrane.
- Transport of gases by the blood.
- Diffusion of O2 and CO2 between blood and tissues.
- Utilization of O2 by the cells for catabolic reactions and resultant release of CO2.
Question 3.
Give a brief account of exchange of gases during respiration.
Answer:
Alveoli are the primary sites of exchange of gases. Exchange of gases also occur between blood and tissues. O2 and CO2 are exchanged in these sites by simple diffusion mainly based on pressure/concentration gradient.
Solubility of the gases as well as the thickness of the membranes involved in diffusion are also some of the important factors that can affect the rate of diffusion. Pressure contributed by an individual gas in a mixture of gases is called partial pressure and is represented as pO2 for oxygen and pCO2 for carbon dioxide.
![]()
Question 4.
What do you understand by occupational respiratory disorders?
Answer:
In some industries, workers may inhale harmful dust. For example, workers in stone-crushing plant may inhale silica dust. When there is long-term exposure to such situations, lungs can develop inflammation, which leads to fibrosis and ultimately to serious damage to lungs.
Long answer type questions
Question 1.
Explain the mechanism of expiration under normal conditions.
Answer:
Expiration: It is a passive process by which CO2 is expelled out from the lungs. It takes place when the intra-pulmonary pressure is higher than the atmospheric pressure.
The movement of following muscles are involved :
(a) Diaphragm: The muscle fibres of the diaphragm relax making it convex, decreasing volume of the thoracic cavity.
(b) Internal intercostal muscles: These muscles contract thus, pulling the ribs downward and inward, decreasing the thoracic volume.
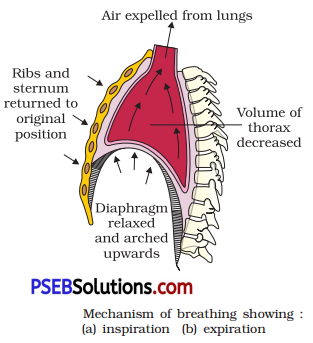
The overall volume of the thoracic cavity thus decreases thereby reducing the pulmonary volume.
Ribs and sternum returned to original position (lowered)
As a result, the intrapulmonary pressure increases slightly above the atmospheric pressure. This inturn causes the expulsion of the air from the lungs. The process of expiration is simpler than inspiration.
