Punjab State Board PSEB 11th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Ex 3.4 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Ex 3.4
Question 1.
Find the principal and general solutions of the equation, tan x = √3
Answer.
tan x = √3
It is known that:
tan \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) = √3 and
tan (\(\frac{4 \pi}{3}\)) = tan ( π + \(\frac{\pi}{3}\))
= tan \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) = √3
Therefore, the principal solutions are x = \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) and \(\frac{4 \pi}{3}\).
Now, tan x = tan \(\frac{\pi}{3}\)
⇒ x = nπ + \(\frac{\pi}{3}\), where n ∈ Z
Therefore, the general solution is x = nπ + \(\frac{\pi}{3}\), where n ∈ Z.
![]()
Question 2.
Find the principal and general solutions of the equation: sec x = 2
Answer.
sec x = 2
It is known that:
sec \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) = 2 and
sec \(\frac{5 \pi}{3}\) = sec (2π – \(\frac{\pi}{3}\))
= sec \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) = 2
Therefore, the principal solutions are x = \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) and \(\frac{5 \pi}{3}\).
Now, sec x = sec \(\frac{\pi}{3}\)
cos x = cos \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) [∵ sec x = \(\frac{1}{\cos x}\)]
⇒ x = 2nπ ± \(\frac{\pi}{3}\), where n e Z
Therefore, the general solution is x = 2nπ ± \(\frac{\pi}{3}\), where n ∈ Z.
![]()
Question 3.
Find the principal and general solutions of the equation cot cot x = – √3.
Answer.
cot x = – √3

![]()
Question 4.
Find the principal and general solutions of cosec x = – 2
Answer.
cosec x = – 2
It is known that:
cosec \(\frac{\pi}{6}\) = 2
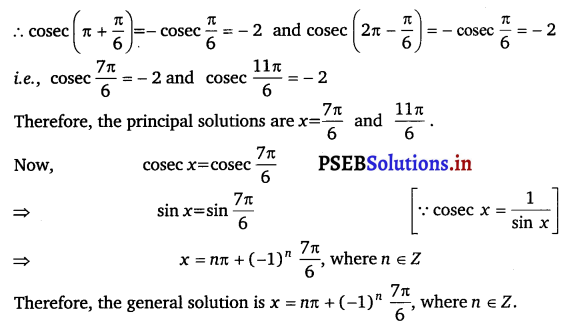
![]()
Question 5.
Find the general solution of the equation: cos 4x = cos 2x
Answer.
cos 4x = cos 2x
cos 4x – cos 2x = 0
– 2 sin \(\left(\frac{4 x+2 x}{2}\right)\) sin \(\left(\frac{4 x-2 x}{2}\right)\) = 0
[∵ cos A – cos B = 2 \sin \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \sin \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\(\)]
sin 3x sin x = 0
sin 3x = 0or sin x = 0
3x = nπ or x = nπ, where n ∈ Z
x = \(\frac{n \pi}{3}\) or x = nπ, where n ∈ Z.
![]()
Question 6.
Find the general solution of the equation cos 3x + cosx – cos 2x = 0
Answer.
cos 3x + cos x – cos 2x = 0
2 cos \(\left(\frac{3 x+x}{2}\right)\) cos \(\left(\frac{3 x-x}{2}\right)\) – cos 2x = 0
[∵ cos A + cos B = 2 \(\cos \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)]
2 cos 2x cos x – cos 2x = 0
cos 2x (2 cos x – 1) = 0
cos 2x = 0 or 2 cos x – 1 = 0
cos 2x = 0 or cos x = \(\frac{1{2}\)
∴ 2x = (2n + 1) \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) or cos x = cos \(\frac{\pi}{3}\), where n ∈ Z
x = (2n + 1) \(\frac{\pi}{4}\) or x = 2nπ ± \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) where n ∈ Z.
![]()
Question 7.
Find the general solution of the equation sin 2x + cos x = 0
Answer.
sin 2x + cos x = 0
⇒ 2sin x cos x + cos x = 0
⇒ cos x (2 sin x + 1) = 0
⇒ cos x = 0 or 2 sin x + 1 = 0
Now, cos x = 0
⇒ x = (2n + 1) \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) , where n ∈ Z.
or 2 sin x + 1 = 0
⇒ sin x = – \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= – sin \(\frac{\pi}{6}\)
= sin (π + \(\frac{\pi}{6}\))
= sin \(\frac{7 \pi}{6}\)
x = nπ + (- 1)n \(\frac{7 \pi}{6}\) where n ∈ Z
Therefore, the general solution is (2n + 1) \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) or nπ + (- 1)n \(\frac{7 \pi}{6}\) where n ∈ Z.
![]()
Question 8.
Find the general solution of the equation sec2 2x = 1 – tan 2x.
Answer.
sec2 2x = 1 – tan 2x
1 + tan2 2x = 1 – tan 2x
tan2 x + tan 2x = 0
=> tan 2x (tan 2x + 1) = 0
=> tan 2x = 0 or tan 2x + 1 = 0
Now, tan 2x = 0
=> tan 2x = tan 0
2x = nπ + 0, where n ∈ Z
x = \(\frac{n \pi}{2}\), where n ∈ Z
or tan 2x + 1 = 0
= tan 2x = – 1
= – tan \(\frac{\pi}{4}\)
= tan (π – \(\frac{\pi}{4}\))
= tan \(\frac{3 \pi}{4}\)
2x = nπ + \(\frac{3 \pi}{4}\) where n ∈ Z
x = \(\frac{n \pi}{2}+\frac{3 \pi}{8}\), where n ∈ Z
Therefore, the general solution is \(\frac{n \pi}{2}\) or \(\frac{n \pi}{2}+\frac{3 \pi}{8}\) where n ∈ Z.
![]()
Question 9.
Find the general solution of the equation sin x + sin 3x + sin 5x = 0
Answer.
sin x + sin 3x + sin 5x = 0
⇒ (sin x + sin 5x) + sin 3x = 0
\(\left[2 \sin \left(\frac{x+5 x}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{x-5 x}{2}\right)\right]\) + sin 3x = 0
[∵ sin A + sin B = 2 sin \(\sin \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)]
2 sin 3x cos (2x) + sin 3x = 0
2 sin 3x cos 2x + sin 3x = 0
sin 3x (2 cos 2x +1) = 0
sin 3x = 0 or 2 cos 2x + 1 = 0
Now sin 3x = 0
⇒ 3x = nπ, where n ∈ Z
i.e., x = \(\frac{n \pi}{3}\) where n ∈ Z
or 2 cos 2x + 1 = 0
cos 2x = \(-\frac{1}{2}\)
= – cos \(\frac{\pi}{3}\)
= cos (π – \(\frac{\pi}{3}\))
cos 2x = cos \(\frac{2 \pi}{3}\)
⇒ 2x = 2nπ ± \(\frac{2\pi}{3}\), where n ∈ Z
⇒ x = nπ ± \(\frac{\pi}{3}\), where n ∈ Z
Therefore, the general solution is \(\frac{n \pi}{3}\) or nπ ± \(\frac{\pi}{3}\), where n ∈ Z.
