Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 8 The d-and f-Block Elements Important Questions and Answers.
PSEB 12th Class Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 8 The d-and f-Block Elements
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why first ionisation enthalpy of Cr is lower than that of Zn?
Answer:
Ionisation enthalpy of Cr is less than that of Zn configuration. In case of zinc, electron comes out from completely filled 4s-orbital. So, removal of electron from zinc requires more energy as compared to the chromium.
Question 2.
Zn, Cd and Hg are soft metals. Why?
Answer:
Because they have one or more typical metallic structures at normal temperatures.
Question 3.
Although fluorine is more electronegative than oxygen, but the ability of oxygen to stabilise higher oxidation states exceeds that of fluorine. Why?
Answer:
Oxygen can form multiple bonds with metals, while fluorine can’t form multiple bond with metals. Hence, oxygen has more ability to stabilise higher oxidation state rather than fluorine.
![]()
Question 4.
Mn shows the highest oxidation state of + 7 with oxygen but with fluorine it shows the highest oxidation state of +4. Why?
Answer:
This is due to ability of oxygen to form pπ – dπ bond.
Question 5.
Mn2O7 is acidic whereas MnO is basic.
Answer:
Mn has +7 oxidation state in Mn2O7 and +2 in MnO. In low oxidation state of the metal, some of the valence electrons of the metal atom are not involved in bonding. Hence, it can donate electrons and behave as a base. On the other hand, in higher oxidation state of the metal, valence electrons are involved on bonding and are not available. Instead effective nuclear charge is high and hence it can accept electrons and behave as an acid.
Question 6.
Copper atom has completely filled d-orbitals in its ground state but it is a transition element. Why?
Answer:
Copper exhibits +2 oxidation state wherein it has incompletely filled d orbitals (3d9 4s0) hence a transition elements.
![]()
Question 7.
Why is zinc not regarded as a transition element?
Answer:
As zinc atom has completely filled d-orbitals (3d10) in its ground state as well as oxidised state, therefore, it is not regarded as transition element.
Question 8.
Zn2+ salts are white while Cu2+ salts are coloured. Why?
Answer:
Cu2+(3d94s0) has one unpaired electron in d-subshell which absorbs radiation in visible region resulting in d-d transition and hence Cu2+ salts are coloured. Zn2+(3d104s0) has completely filled d-orbitals. No radiation is absorbed for d-d transition and hence Zn2+ salts are colourless.
Question 9.
The second and third row of transition elements resemble each other much more than they resemble the first row. Explain, why?
Answer:
Due to lanthanoid contraction, the atomic radii of the second and third row transition elements is almost same. So, they resemble each other much more as compared to first row elements and show similar character.
![]()
Question 10.
Why does copper not replace hydrogen from acids?
Answer:
Because Cu shows E⊖ positive value.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why do transition elements show variable oxidation states? How is the variability in oxidation states of d-block different from that of the p-block elements?
Answer:
In transition elements, the energies of (n – 1)d orbitals and ns orbitals are nearly same. Therefore, electrons from both can participate in bond formation and hence show variable oxidation states.
In transition elements, the oxidation states differ from each other by unity e.g., Fe2+ and Fe3+, Cu+ and Cu2+ etc., while in p-block elements the oxidation state differ by units of two, e.g., Sn2+ and Sn4+, Pb2+ and Pb4+ etc. In transition elements, the higher oxidation states are more stable for heavier elements in a group e.g., Mo(VI) and W(VI) are more stable than Cr(VI) in group 6 whereas in p-block, elements the lower oxidation states are more stable for heavier elements due to the inert pair effect, e.g., Pb(II) is more stable than Pb(IV) in group 16.
![]()
Question 2.
When a chromite ore (A) is fused with sodium carbonate in free excess of air and the product is dissolved in water, a yellow solution of compound (B) is obtained. After treatment of this yellow solution with sulphuric acid, compound (C) can be crystallised from the solution. When compound (C) is treated with KC1, orange crystals of compound (D) crystallise out. Identify A to D and also explain the reactions.
Answer:
K2Cr2O7 is an orange compound. It is formed when Na2Cr2O7 reacts with KCl. In acidic medium, yellow coloured \(\mathrm{CrO}_{4}^{2-}\) (chromate ion) changes into dichromate.
The given process is the preparation method of potassium dichromate from chromite ore.
A = FeCr2O4; B = Na2CrO4; C = Na2Cr2O7; D = K2Cr2O7
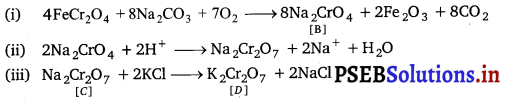
Question 3.
Mention the type of compounds formed when small atoms like H, C and N get trapped inside the crystal lattice of transition metals. Also give physical and chemical characteristics of these compounds.
Answer:
When small atoms like H, C and N get trapped inside the crystal lattice of transition metals.
(a) Such compounds are called interstitial compounds.
(b) Their characteristic properties are :
- They have high melting point, higher than those of pure metals.
- They are very hard.
- They retain metallic conductivity.
- They are chemically inert.
![]()
Question 4.
On the basis of lanthanoid contraction, explain the following:
(i) Nature of bonding in La2O3 and Lu2O3.
(ii) Trends in the stability of oxosalts of lanthanoids from La to Lu.
(iii) Stability of the complexes of lanthanoids.
(iv) Radii of 4d and 5d block elements.
(v) Trends in acidic character of lanthanoid oxides.
Answer:
(i) As the size decreases covalent character increases. Therefore, La2O3 is more ionic and Lu2O3 is more covalent.
(ii) As the size decreases from La to Lu, stability of oxosalts also decreases.
(iii) Stability of the complexes increases as the size of lanthanoids decreases.
(iv) Radii of 4d and 5d block elements will be almost same.
(v) Acidic character of oxides increases from La to Lu.
Question 5.
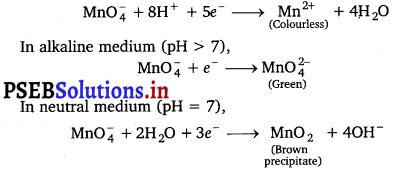
A solution of KMnO4 on reduction yields either a colourless solution of a brown precipitate or a green solution depending on pH of the solution. What different stages of the reduction do these represent and how are they carried out?
Answer:
Oxidising behaviour of KMnO4 depends on pH of the solution.
In acidic medium (pH < 7),
Question 6.
Identify the following:
(i) Oxoanion of chromium which is stable in acidic medium.
(ii) The lanthanoid element that exhibits + 4 oxidation state.
Answer:
(i) Cr2O7
(ii) Cerium
Question 7.
The magnetic moments of few transition metal ions are given below:
| Metal ion | Metal ion |
| Sc3+ | 0.00 |
| Cr2+ | 4.90 |
| Ni2+ | 2.84 |
| Ti3+ | 1.73 |
(at no. Sc = 21, Ti = 22, Cr = 24, Ni = 28)
Which of the given metal ions :
(i) has the maximum number of unpaired electrons?
(ii) forms colourless aqueous solution?
(iii) exhibits the most stable + 3 oxidation state?
Answer:
(i) Cr2+
(ii) Sc3+
(iii) Sc3+
![]()
Question 8.
Consider the standard electrode potential values (M2+/M) of the elements of the first transition series.
![]()
Explain:
(i) E0 value for copper is positive.
(ii) E0 value of Mn is more negative as expected from the trend.
(iii) Cr2+ is a stronger reducing agent than Fe2+.
Answer:
(i) E0 value for copper is positive because the high energy to transform Cu(s) to Cu2+(aq) is not balanced by its hydration enthalpy.
(ii) E0 value of Mn is more negative as expected from the trend because Mn2+ has d5 configuration i. e., stable half-filled configuration.
(iii) Cr2+ is a stronger reducing agent than Fe2+ because d4 to d3 occurs in case of Cr2+ to Cr3+ (more stable \(t_{2 g}^{3}\)) while it changes from d6 to d5 in case of Fe2+ to Fe3+.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write similarities and differences between the chemistry of lanthanoids and that of actinoids.
Answer:
Similarities between lanthanoids and actinoids :
- Both lanthanoids and actinoids mainly show an oxidation state of +3.
- Actinoids show actinoid contraction like lanthanoid contraction is exhibited by lanthanoids.
- Both lanthanoids and actinoids are electropositive.
Differences between lanthanoids and actinoids :
- The members of lanthanoid exhibit less number of oxidation states than the corresponding members of actinoid series.
- Lanthanoid contraction is smaller than the actinoid contraction.
- Lanthanoids except promethium cure non-radioactive metals while actinoids are radioactive metals.
![]()
Question 2.
(a) Assign reasons for the following:
(i) Zr and Hf have almost identical radii.
(ii) The ![]() , value for copper is positive (+0.34 V).
, value for copper is positive (+0.34 V).
(b) Although +3 oxidation state is the characteristic oxidation state of lanthanoids but cerium shows +4 oxidation state also. Why?
Answer:
(a) (i) This is due to filling of 4/ orbitals which have poor shielding effect (lanthanoid contraction).
(ii) This is because the sum of enthalpies of sublimation and ionisation is not balanced by hydration enthalpy.
(b) It is because after losing one more electron Ce acquires stable 4f0 electronic configuration.
Question 3.
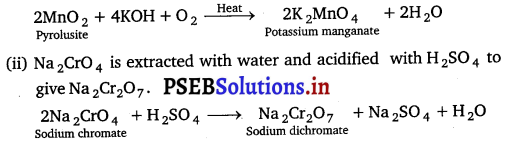
(a) How do you prepare :
(i) K2MnO4 from MnO2?
(ii) Na2Cr2O7 from Na2CrO4?
(b) Account for the following :
(i) The enthalpy of atomisation is lowest for Zn in 3d series of the transition elements.
(ii) Actinoid elements show wide range of oxidation states.
Answer:
(a) (i) Pyrolusite is fused with KOH in the presence of atmospheric oxygen to give K2MnO4.
(b) (i) In the formation of metallic bonds, no electrons from 3d-orbitals are involved in case of zinc, while in all other metals of the 3d series, electrons from the d-orbitals are always involved in the formation of metallic bonds. That is why the enthalpy of atomisation of zinc is the lowest in the series.
(ii) This is due to comparable energies of 5f, 6d and 7s orbitals.
