Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class History Book Solutions Map Questions Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB 12th Class History Map Questions
Battles of Guru Gobind Singh Ji:
Question 1.
(a) On the given outline map of Punjab show any five places of battles of the pre-Khalsa and post-Khalsa period of Guru Gobind Singh Ji.
(b) Write an explanatory note in about 20-25 words each on these battles.
Or
(a) On the given outline map of Punjab show any five places of Guru Gobind Singh Ji’s battles in the given outline map of Punjab.
(b) Write an explanatory note in about 20-25 words each on the battles as shown in the map.
Or
(a) On the given outline map of Punjab, show five important places where the battles of Guru Gobind Singh Ji were fought.
(b) Write an explanatory note in about 100 words about these battles.
Or
(a) On the given outline map of Punjab, show five battle places of Guru Gobind Singh Ji.
(b) Explain these battle places in about 20-25 words each.
Or
(a) On the given outline map of Punjab showing the rivers depict five places of the battles of Guru Gobind Singh Ji.
(b) Write an explanatory note in about 20-25 words each about these battles.
Answer:
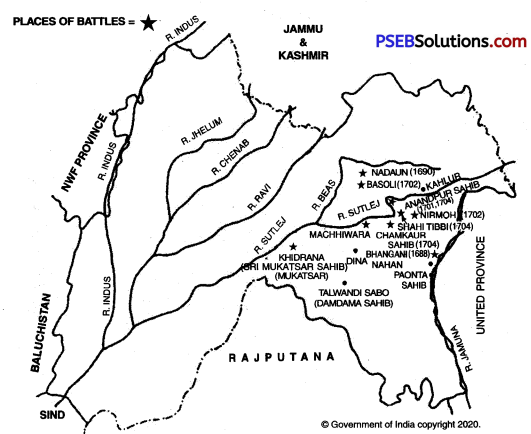
Guru Gobind Singh Ji held the Guruship from 1675 to 1708 A.D. He had to fight many battles against the Hill Chiefs and the Mughals. The battles of Guru Gobind Singh Ji are divided into two phases—the battles of pre-Khalsa period and the battles of post-Khalsa period.
![]()
Battles of Pre-Khalsa Period:
1. Battle of Bhangani 1688 A.D.: The Hill Chiefs were alarmed to see the military preparations of Guru Gobind Singh Ji. Consequently, they under the combined leadership of Bhim Chand, the ruler of Kahlur and Fateh Shah, the ruler of Srinagar attacked on September 22, 1688 A.D. the Sikh army at Bhangani. Pir Buddhu Shah of Sadhaura rendered valuable help to Guru Gobind Singh Ji in this battle. The armies of Hill Chiefs were forced to flee the field. This grand victory indeed infused a new spirit among the Sikhs.
2. Battle of Nadaun 1690 A.D.: After the battle of Bhangani, the Hill Chiefs refused to pay the annual Khiraj (tax) to the Mughals. Therefore, an army under the command of Alif Khan was sent against the Hill Chiefs. He attacked the army of Bhim Chand at Nadaun on March 20, 1690 A.D. Guru Gobind Singh Ji sided with Bhim Chand in this battle. Their joint army pushed back the Mughal army. Alif Khan had to run away from the battlefield to save his life. After this battle, the Hill Chiefs again made a treaty with the Mughals.
Battles of Post-Khalsa Period:
3. First Battle of Sri Anandpur Sahib, 1701 A.D. : Guru Gobind. Singh Ji laid the foundation of Khalsa Panth at Sri Anandpur Sahib in 1699 A.D.-As a result, people started coming to the fold of Sikhism in a large number. The Hill Chiefs saw in it, a great danger to their freedom. So, Bhim Chand, the ruler of Kahlur asked Guru Gobind Singh Ji to vacate the fort of Anandpur Sahib. When Guru Gobind Singh Ji declined to do so, Bhim Chand along with a few other Hill Chiefs invaded the fort of Anandpur Sahib in 1701 A. D. When they got no success they made peace with Guru Gobind Singh Ji.
4. Battle of Nirmoh, 1702 A.D.: After the first battle of Anandpur Sahib, Guru Gobind Singh Ji went to a village, Nirmoh near Kiratpur Sahib. Joining hands with the Mughal army, Bhim Chand attacked the army of Guru Gobind Singh Ji. The Sikhs, under the command of Guru Gobind Singh Ji, gave a crushing defeat to the joint army.
5. Second Battle of Sri Anandpur Sahib, 1704 A.D.: The Hill Chiefs wanted to take revenge from Guru Gobind Sir gh Ji for their insult due to continuous defeats. Thus, they attacked the fort of Sri Anandpur Sahib for the second time, in collaboration with Mughal forces in 1704 A.D. The Sikhs put up strong resistance from within the fort. The royal army took false vows to assure Guru Gobind Singh Ji that they would not cause any harm, if he left the fort. So Guru Gobind Singh Ji decided to leave the fort.
6. Battle of Shahi Tibbi, 1704: As soon as, Guru Gobind Singh Ji came out of the fort, the royal army pursued them hotly. Consequently, there was confusion and consternation. A battle took place at Shahi Tibbi, where Bhai Udai Singh put up strong resistance along with his 50 companions and ultimately became martyrs.
7. Battle of Chamkaur Sahib, 1704 A.D.: Guru Gobind Singh Ji reached the fortress of Chamkaur Sahib along with his 40 Sikhs on 21st December, 1704 A. D. No sooner, did they reach there, a huge Mughal army besieged them on 22nd December, 1704 A.D. A pitched battle took place. In this battle, Ajit Singh and Jujhar Singh, the two elder sons of Guru Gobind Singh Ji fought with unparalleled example of bravery and ultimately became martyrs.
8. Battle of Khidrana, 1705 A.D.: On December 29,1705 A.D., Wazir Khan, the Mughal Faujdar of Sirhind, attacked Guru Gobind Singh Ji with a large army. In this battle, the Sikhs gave a crushing defeat to the Mughals. Those 40 Sikhs, who had parted company with Guru Gobind Singh Ji in the second battle of Sri Anandpur Sahib, also fought in this battle and became martyrs. Guru Gobind Singh Ji accorded them the boon of Mukti (salvation) on the request of their leader Maha Singh. As a result, Khidrana acquired the name of Sri Muktsar Sahib.
![]()
Important Battles of Banda Singh Bahadur:
Question 2.
(a) On the outline map of Punjab, show five places of military exploits of Banda Singh Bahadur.
(b) Explain these places in about 20-25 words.
Or
(a) On the given outline map of Punjab fill the places of five important battles of Banda Singh Bahadur.
(b) Write an explanatory note in about 20-25 words each on the places shown in the map.
Or
(a) On the given outline map of Punjab show five battle places of Banda Singh Bahadur.
(b) Explain these battles in about 20-25 words each.
Or
(a) On the given outline map of Punjab, showing rivers depict five important places of the Banda Singh Bahadur.
(b) Explain these places in about 20-25 words each.
Answer:
Banda Singh Bahadur fought many battles against the Mughals during 1709 to 1715 A.D. During these battles, Banda Singh Bahadur showed such feats that the Mughals began to tremble, on hearing his name. The main battles of Banda Singh Bahadur were as follows :
1. Attack on Sonepat : First of all Banda Singh Bahadur attacked Sonepat with his 500 Sikhs in November 1709 A.D. The ruler of Sonepat was so afraid of the Sikhs that he ran away to Delhi without facing them. This victory greatly enhanced the morale of the Sikhs.
2. Conquest of Samana : The executioners of Guru Tegh Bahadur Ji and the younger sons of Guru Gobind Singh Ji lived in Samana. Banda Singh Bahadur attacked Samana and slaughtered many Muslims. After this, he thoroughly plundered the whole town. It was the first and important conquest of Banda Singh Bahadur.
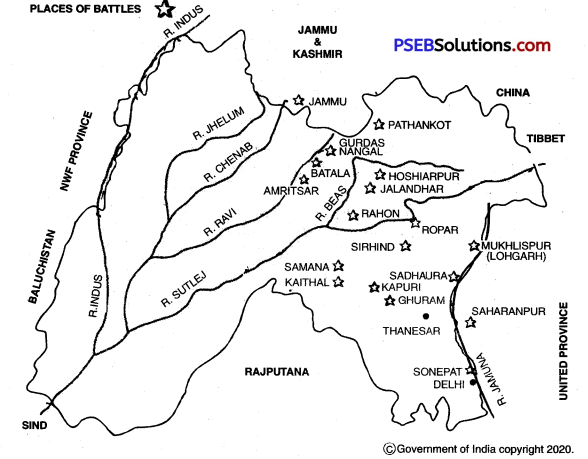
3. Conquest of Kapuri: The ruler of Kapuri, Qadam-ud-Din was very cruel. He ill-treated the Hindus. So, Banda Singh Bahadur attacked Kapuri, put to death Qadam-ud-Din and conquered the town.
4. Conquest of Sadhaura: Usman Khan the ruler of Sadhaura was notorious for his tyranny. He was a sworn enemy of the Hindus. He tortured and got Pir Buddhu Shah killed for he had helped Guru Gobind Singh Ji in the battle of Bhangani. In order to settle the score for this insult, Banda Singh Bahadur attacked Sadhaura and slaughtered a large number of Muslims. That is why, the place came to be known as Qatalgarhi.
5. Battle of Ropar: Banda Singh Bahadur was making preparations to attack Sirhind. Several Sikhs from Malwa and Majha joined under the banner of Banda Singh Bahadur. When Wazir Khan, the Faujdar of Sirhind, came to know about it, he ordered Sher Mohammad Khan and Nawab of Malerkotla to take steps against these Sikhs. A pitched battle took place at Ropar in which the Sikhs defeated the Mughals.
6. Conquest of Sirhind: Wazir Khan, the Faujdar of Sirhind had got the two younger sons, Zorawar Singh and Fateh Singh, of Guru Gobind Singh Ji killed by bricking them alive in the wall. So, Banda Singh Bahadur wanted to teach him such a lesson which should be remembered by the Muslims for a long time. On May 22, 1710 A.D., Banda Singh Bahadur attacked the army of Wazir Khan at Chappar Chiri. The Sikhs massacred the Muslims to such an extent that they shuddered at the very thought of it. Wazir Khan was killed and hanged on a tree upside down. Plundering and massacre stalked the whole Sirhind on May 24,1710 AD. This glorious conquest further boosted the morale of the Sikhs.
7. Conquest of Ganga Doab: Encouraged by the conquests of Banda Singh Bahadur, the Sikhs of most areas in Ganga Doab i.e. Saharanpur, Behat and Jalalabad etc. revolted against the tyranny of the Muslims. Banda Singh Bahadur availed himself of this opportunity and brought this region under his control.
8. Battle of Rahon: Shamas Khan, the Faujdar of Jalandhar Doab, was a cruel ruler. Fed up with his tyranny, the Sikhs revolted against him. Shamas Khan declared Jihad (religious war) against the Sikhs. In October ,1710, the the armies of Shamas Khan and Banda Singh Bahadur clashed at Rahon and a bloody battle ensued. The Sikhs came out victorious in this battle.
9. Attack of Mughals on Lohgarh: The increasing power of Banda Singh Bahadur was a challenge for Mughal emperor, Bahadur Shah. He sent a large army of 60,000 to Punjab under the command of Munim Khan to crush the power of Banda Singh Bahadur. This army suddenly besieged Banda Singh Bahadur in his capital, Lohgarh. Though the Mughal army took control of Lohgarh but it could not capture Banda Singh Bahadur.
10. Battle of Gurdas Nangal: In 1715 A.D. the newly appointed Governor of Punjab, Abdus Samad Khan made a surprise attack on the Sikhs at Gurdas Nangal. Banda Singh Bahadur was besieged along with some of his companions in the haveli of Duni Chand. Ultimately Banda Singh Bahadur had to give in.
![]()
Ranjit Singh’s Kingdom:
Question 3.
(a) On the given outline map of Punjab, show the places of five battles of Maharaja Ranjit Singh.
(b) Explain each battle place in about 20-25 words.
Or
(a) On the given outline map of Punjab, show the places of five important conquests of Maharaja Ranjit Singh.
(b) Write an explanatory note in about 20-25 words each on these conquests.
Or
Question 4.
(a) On the given outline map of Punjab, show the following places of battles of Maharaja Ranjit Singh.
- Lahore
- Amritsar
- Kashmir
- Multan
- Peshawar
(b) Write an explanatory note of about 25-25 words each on places shown in the map.
Or
(a) On the given outline map of Punjab, showing the rivers depict five places where Maharaja Ranjit Singh won the battles.
(b) Explain these five battles in about 20-25 words each.
Answer:
Undoubtedly Maharaja Ranjit Singh was the greatest ruler of Punjab. By his ability and efforts, he converted his small kingdom into a vast empire during his reign (1799-1839). His main conquests are mentioned below :
1. Conquest of Lahore, 1799 A.D.: The first and the most important conquest of Maharaja Ranjit Singh was the conquest of Lahore. The three Bhangi Sardars and Sahib Singh, Mohar Singh, and Chet Singh jointly ruled Lahore. People were very unhappy due to their tyrannical rule, so they invited Ranjit Singh to take over Lahore. Deeming it a golden chance, Ranjit Singh invaded Lahore and occupied it on July 7, 1799 A.D.
2. Conquest of Amritsar, 1805 A.D.: The city of Amritsar was very important for the Sikhs from a religious point of view. It was considered the Mecca of the
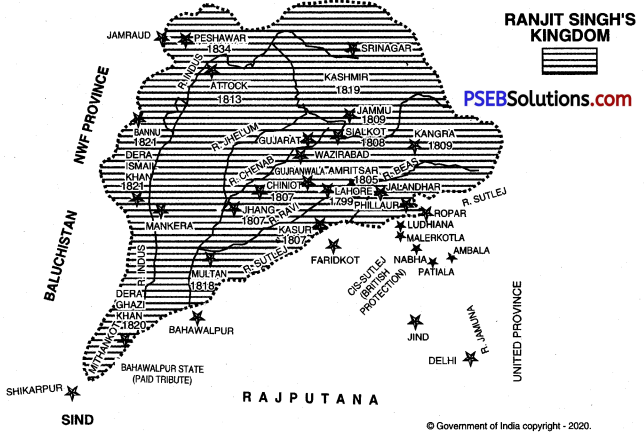
Sikhs. It was also the most famous trade centre. In order to be an emperor of the Punjab, the control over Amritsar was essential. In 1805 A.D. Ranjit Singh invaded Amritsar and defeated Mai Sukhan, the widow of Gulab Singh. In this way, Amritsar was conquered.
3. Conquest of Kasur 1807 A.D.: Nizam-ud-Din, the ruler of Kasur had accepted the subordination of Ranjit Singh. After his death in 1807 A.D. his successor Qutub-ud-Din refused to accept the suzerainty of Ranjit Singh. Consequently, Ranjit Singh invaded Kasur, defeated Qutab-ud-Din and occupied Kasur. After this, Ranjit Singh defeated Ahmad Khan the ruler of Jhang and annexed it to his kingdom.
4. Conquest of Sialkot, 1808 A.D.: Jiwan Singh was the ruler of Sialkot. Maharaja Ranjit Singh asked him to hand over the fort in exchange for a Jagir. When, Jiwan Singh refused to oblige, Maharaja Ranjit Singh invaded Sialkot in 1808 A.D. and beseized Sialkot.
5. Conquest of Kangra, 1809 A.D.: In 1809 A.D. the Gurkhas of Nepal surrounded the fort of Kangra. Sansar Chand, the ruler of Kangra sought assistance from Maharaja Ranjit Singh against the Gurkhas. He promised to hand over the fort of Kangra to Maharaja Ranjit Singh for this help. The army of Ranjit Singh made the Gurkhas flee from Kangra. But, now, Sansar Chand dilly-dallied in handing over the fort to Maharaja Ranjit Singh. At this, Ranjit Singh imprisoned Anurodh, the son of Sansar Chand. Being helpless, he handed over the fort of Kangra to Ranjit Singh.
6. Conquest of Gujarat, 1809 A.D.: Sahib Singh Bhangi was the ruler of Gujarat. He kept hatching conspiracies against Ranjit Singh. Therefore, Maharaja Ranjit Singh deputed Faqir Aziz-ud-Din to invade Gujarat. He defeated Sahib Singh and conquered Gujarat.
7. Conquest of Jammu, 1809 A.D.: Jai Singh ruled over Jammu. When he died in 1809 A.D., Maharaja Ranjit Singh sent an army under the command of Diwan Bhawani Das to conquer Jammu. He easily took the control of Jammu.
8. Conquest of Attock in 1813 A.D.: Maharaja Ranjit Singh had secured the famous fort of Attock from Jahandad Khan in exchange for a Jagir. This fort was very important from the geographical point of view.
9. Conquest of Multan, 1818 A.D.: Multan was very important from trade and geographical point of view. Sind could be easily conquered by having a control over Multan. The Maharaja had to attack seven times to conquer Multan. Every time, Muzaffar Khan the ruler of Multan evaded Maharaja Ranjit Singh by offering him a heavy ransom. In 1818 A.D. Maharaja Ranjit Singh resolved to make a conquest of Multan. He sent a vast army under the command of Misar Diwan Chand. After a pitched battle the army of Maharaja Ranjit Singh conquered Multan. It was indeed one of the important conquests of Maharaja Ranjit Singh.
10. Conquest of Kashmir, 1819 A.D.: The valley of Kashmir was famous for its scenic beauty and trade. Ranjit Singh tried to conquer it in 1813 and 1814 A.D. but did not succeed. The conquest of Multan greatly encouraged Maharaja Ranjit Singh. He sent a huge army under the command of Misar Diwan Chand to conquer Kashmir. This army defeated Jabbar Khan, the ruler of Kashmir and occupied Kashmir in 1819 A.D.
11. Conquest of Dera Ghazi Khan, 1820 A.D.: Maharaja Ranjit Singh sent a military expedition under the command of Jamadar Khushal Singh to conquer Dera Ghazi Khan. This army defeated Zaman Khan the ruler of Dera Ghazi Khan and took control of this state.
12. Conquest of Peshawar, 1834 A.D : Peshawar was an important region from the geographical point of view. In his first expedition in 1818 A.D. Maharaja Ranjit Singh had defeated Yar Mohammad Khan and Dost Mohammad Khan but he resolved not to include Peshawar in his empire. In 1823 A.D., Azim Khan, a minister of Afghanistan took over the control of Peshawar. Maharaja Ranjit Singh defeated him in a pitched battle of Naushehra and again got control over Peshawar. He annexed Peshawar to his empire in 1834 A.D.
Extent of the Empire:
The empire of Maharaja Ranjit Singh extended from Ladakh in the North to Shikarpur in the South and from the Sutlej in the East to Peshawar in the West.
![]()
The First Anglo-Sikh War:
Question 5.
(a) On the given outline map of the Punjab, show five places of the battles of the First Anglo-Sikh War.
(b) Write an explanatory note in about 20-25 words each on the battles of the First Anglo-Sikh War.
Or
(a) On the given outline map of the Punjab, show the location of the battles of the First Anglo-Sikh War.
(b) Write an explanatory note in about 20-25 words each on the places as shown in the map.
Or
(a) On the given outline map of the Punjab, Show five battle places of the First Anglo-Sikh War.
(b) Explain five battle places in 20-25 words.
Or
(a) On the given outline map of the Punjab, showing rivers depict five places of the First Anglo-Sikh War on the map of Punjab.
(b) Write in about 20-25 words each about the spots shown in the map.
Answer:
The First Anglo-Sikh War was fought during the period of Lord Hardinge in 1845-46 A.D. During this War the Sikhs fought valiantly, but they had to face defeat due to the treachery of their leaders. This War was fought at the following main places :
1. Battle of Mudki: First battle between the English and the Sikhs was fought at Mudki, about 20 miles away from Ferozepur, on December 18, 1845 A.D. Lai Singh commanded the Sikh army. On the other side, Lord Hugh Gough was commanding the British troops. It was a bloody and fierce battle. Due to the treachery of Lai Singh, the Sikhs had to face defeat. Although the British became victorious in this battle, they realised that facing the Sikhs was not a child’s play.
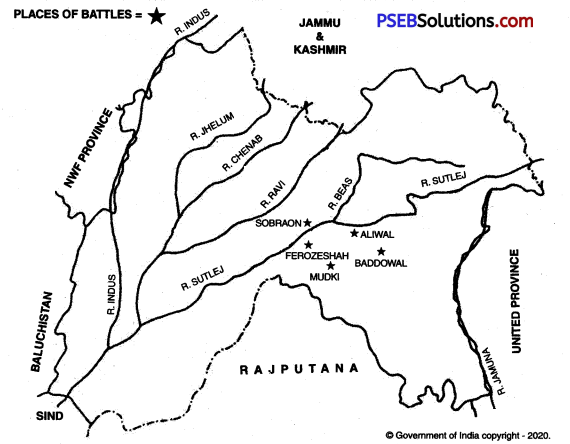
2. Battle of Ferozeshah: The second important battle between the British and the Sikhs was fought on December 21, 1845 A.D. The Sikh army was commanded by Lai Singh and Teja Singh in this battle. On the other hand, the British army was led by the experienced generals like Hugh Gough, John Littler and Lord Hardinge. In the beginning of this battle, the Sikh soldiers launched a stunning attack on the English army. It was getting ready to surrender before the Sikh army. But here again due to the treachery of Lai Singh and Teja Singh the Sikhs were defeated.
3. Battle of Baddowal: The third battle between the British and the Sikhs was fought at Baddowal, 18 miles away from Ludhiana on January 21, 1846AD. Sardar Ranjodh Singh Majithia was leading the Sikh army in this battle and Harry Smith commanded the British army. In this battle the Sikhs routed the British and they fled to Ludhiana.
4. Battle of Aliwal: Harry Smith wanted to take revenge of his defeat at Baddowal. Brigadier Wheeler, along with several soldiers joined Harry Smith which boosted the latter’s morale. He attacked the Sikh army under the command of Ranjodh Singh at Aliwal on January 28,1846 A.D. It was a terrible battle. Due to the treachery of Ranjodh Singh the British won this battle. The Sikh army suffered a heavy loss of life (3500) in this battle.
5. Battle of Sobraon: The last and the most decisive battle of the First Anglo- Sikh War was fought at Sobraon. It was fought on February 10, 1846 A.D. The Sikh troops were commanded by Lai Singh and Tefa Singh. On the other hand the British troops were commanded by experienced generals like Huge Gough and Lord Hardinge. The fierce attack launched by the Sikhs on the British caused consternation in their camp. At this juncture Lai Singh and Teja Singh, who were secretly in league with the British took to their heels leaving the Sikh army in the lurch. Sham Singh Attariwala came forward and commanded the Sikh-army. He showed rare feats of bravery but was ultimately killed. In this battle, the Sikhs suffered a humiliating defeat.
The First Anglo-Sikh War came to an end on March 9,1846 A.D. with the Treaty of Lahore. On December 16,1846 A.D. a new Treaty of Bhairowal was imposed on the Punjab. Although Punjab was not annexed to the British Empire, these treaties reduced the sovereignty of Punjab to a great extent.
![]()
The Second Anglo-Sikh War:
Question 6.
(a) On the given outline map of Punjab, show the location of battles fought during the Second Anglo-Sikh War.
(b) Write an explanatory note in about 20-25 words each Punjab on the battles of the Second Anglo-Sikh War as shown in the map.
Or
(a) On the given outline map of Punjab, show the places of battles of the Second Anglo-Sikh War.
(b) Explain these battle places in about 20-25 words.
Or
(a) On the given outline map of Punjab, showing the rivers depict battle places of the Second Anglo-Sikh War on the map of Punjab.
(b) Write in about 20-25 words each about the spots shown in the map.
Or
(a) On the given outline map of Punjab, show the following places of the Second Anglo-Sikh War.
- Ram Nagar
- Chillianwala
- Multan
- Gujarat.
(b) Write in about 70-75 words about the spots shown in the map.
Answer:
The Second Anglo-Sikh War was fought during the period of Lord Dalhousie in 1848-49 A.D. The Sikhs had to face defeat at the end of this war. Consequently, the rule of the Sikhs in Punjab came to an end and the rule of the British began.
1. Battle of Ram Nagar: The first battle of the Second Anglo-Sikh War was fought at Ram Nagar on November 22, 1848 A.D. Lord Hugh Gough commanded the British troops, while the Sikh troops were commanded by Sher Singh. In this battle two famous British generals, Havelock and Cureton were killed. Though Ram Nagar was not a battle of great consequence, yet the Sikh victory in it gave them the much-needed boost to their morale.
2. Battle of Chillianwala: The battle of Chillianwala was one of the most important battles of the Second Anglo-Sikh War. It was fought on January 13, 1849 A.D. Lord Hugh Gough commanded the British troops, while the command
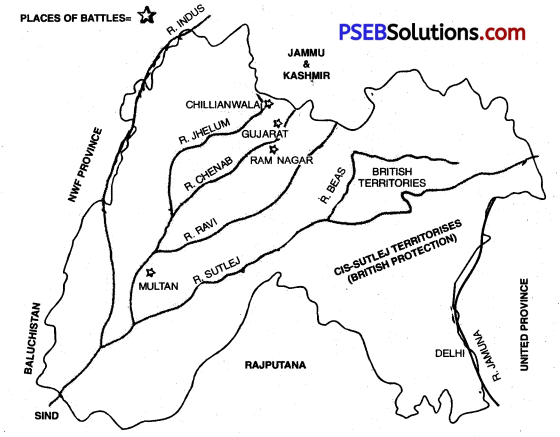
troops had to taste such a humiliating disaster at the hands of the Sikhs, that its echoes were heard in England. The British casualties included 132 officers and other ranks. Lord Gough was held responsible for their worst defeat and it was decided to send Sir. Charles Napier from England to replace him.
3. Battle of Multan: In Multan, Diwan Moolraj raised the banner of revolt against the British. In order to capture the fort of Multan, the British army under the command of General Whish laid siege to it. Sher Singh too joined hands with Diwan Moolraj. As the victory was not in sight, General Whish played a trick. He created a rift between Sher Singh and Moolraj by throwing forged letters in their camps. As a result, Sher Singh left Diwan Moolraj in the lurch. Consequently, Mootraj could not face the onslaught of the British army single-handed. On January 22, 1849 A.D. Diwan Moolraj surrendered unconditionally. This victory of Multan boosted the morale of British soldiers.
4. Battle of Gujarat: The battle of Gujarat was the last and decisive battle of the Second Anglo-Sikh War. In this battle, the Sikh army was commanded by Sher Singh, Chattar Singh, and Bhai Maharaj Singh. On the other hand, the British army was led by Lord Hugh Gough. This battle was fought on February 21, 1849 A.D. Since heavy artillery was used in this battle from both sides, this battle is also known as the Battle of Guns. The Sikh army soon ran short of ammunition. As a consequence, their guns were rendered useless. Seeing this golden opportunity, the British forces launched a fierce attack on the Sikh army. It created confusion and chaos among the Sikh soldiers. They lost 3000 to 5000 soldiers in this battle. On March 10, 1849 A.D. Chattar Singh and Sher Singh surrendered before General Gilbert. On March 14, the remaining Sikh soldiers also surrendered.
On March 29, 1849, A.D. Punjab was annexed to the British empire. Thus, the Sikh empire established by Maharaja Ranjit Singh through indefatigable efforts came to an end.
