Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 7 Integrals Ex 7.5 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 7 Integrals Ex 7.5
Direction (1 – 21): Integrate the rational functions.
Question 1.
\(\frac{x}{(x+1)(x+2)}\)
Solution.
∫ \(\frac{x}{(x+1)(x+2)}\) dx
Let \(\frac{x}{(x+1)(x+2)}=\frac{A}{(x+1)}+\frac{B}{(x+2)}\)
⇒ \(\frac{x}{(x+1)(x+2)}=\frac{A(x+2)+B(x+1)}{(x+1)(x+2)}\)
⇒ x = A (x + 2) + B (x + 1)
Equating the coefficients of x and constant term, we get
A + B = 1 ……………(i)
2A + B = 0 ……………(ii)
On solving Eqs. (i) and (ii), we get
A = – 1 and B = 2
∴ \(\frac{x}{(x+1)(x+2)}=\frac{-1}{(x+1)}+\frac{2}{(x+2)}\)
⇒ \(\int \frac{x}{(x+1)(x+2)} d x=\int \frac{-1}{(x+1)}+\frac{2}{(x+2)} d x\)
= – log |x + 1| + 2 log |x + 2| + C
= log (x + 2)2 – log |x + 1| + C
= log \(\left|\frac{(x+2)^{2}}{(x+1)}\right|\) + C
![]()
Question 2.
\(\frac{1}{x^{2}-9}\)
Solution.
\(\int \frac{1}{x^{2}-9} d x=\int \frac{1}{x^{2}-3^{2}} d x\)
= \(\int \frac{1}{(x+3)(x-3)} d x\)
Let \(\frac{1}{(x+3)(x-3)}=\frac{A}{(x+3)}+\frac{B}{(x-3)}\)
1 = A (x – 3) + B (x + 3)
Equating the coefficients of x and constant term, we get
A + B = 0 and – 3A + 3B = 1
On solving, we get
A = – \(\frac{1}{6}\) and B = \(\frac{1}{6}\)
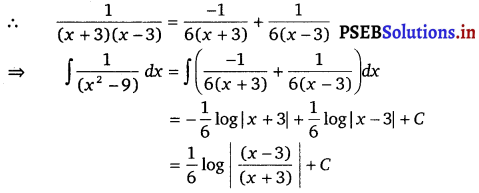
![]()
Question 3.
\(\frac{3 x-1}{(x-1)(x-2)(x-3)}\)
Solution.
∫ \(\frac{3 x-1}{(x-1)(x-2)(x-3)}\) dx
Let \(\frac{3 x-1}{(x-1)(x-2)(x-3)}=\frac{A}{(x-1)}+\frac{B}{(x-2)}+\frac{C}{(x-3)}\)
3x – 1 = A (x – 2) (x – 3) + B (x – 1) (x – 3) + C (x – 1) (x – 2) …………..(i)
Substituting x = 1, 2 and 3 respectively in equation (i), we get
A = 1, B = – 5 and C = 4
∴ \(\frac{3 x-1}{(x-1)(x-2)(x-3)}=\frac{1}{(x-1)}-\frac{5}{(x-2)}+\frac{4}{(x-3)}\)
⇒ \(\int \frac{3 x-1}{(x-1)(x-2)(x-3)} d x=\int\left\{\frac{1}{(x-1)}-\frac{5}{(x-2)}+\frac{4}{(x-3)}\right\} d x\)
= log |x – 1| – 5 log |x – 2| + 4 log |x – 3| + C
Question 4.
\(\frac{x}{(x-1)(x-2)(x-3)}\)
Solution.
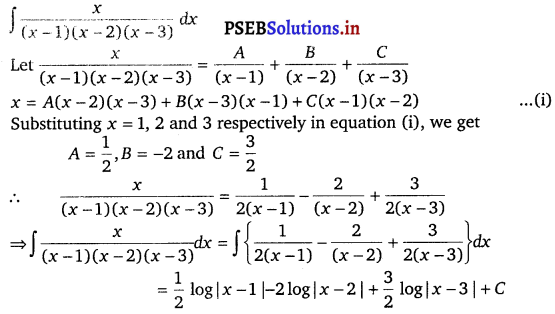
![]()
Question 5.
\(\frac{2 x}{x^{2}+3 x+2}\)
Solution.
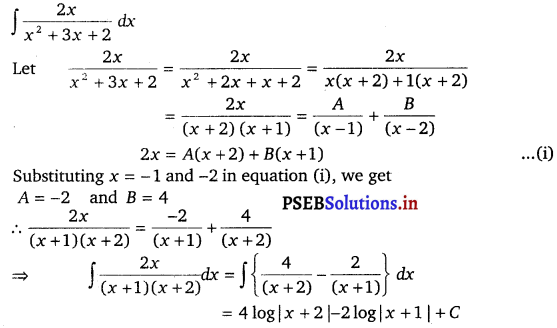
Question 6.
\(\frac{1-x^{2}}{x(1-2 x)}\)
Solution.
It can be seen that the given integrand is not a proper fraction.
Therefore, on dividing (1 – x2) by x (1 – 2x), we get
\(\frac{1-x^{2}}{x(1-2 x)}=\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{2-x}{x(1-2 x)}\right)\)
Let \(\frac{2-x}{x(1-2 x)}=\frac{A}{x}+\frac{B}{(1-2 x)}\)
⇒ (2 – x) = A (1 – 2x) + Bx ……….(i)
Substituting x = 0 and \(\frac{1}{2}\) in equation (i) we get
A = 2 and B = 3
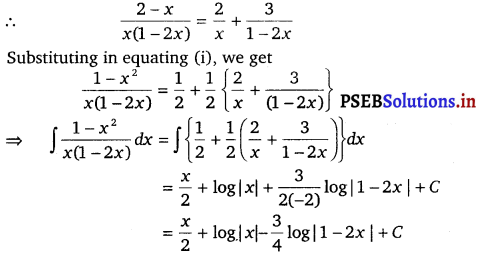
![]()
Question 7.
\(\left(x^{2}+1\right)(x-1)\)
Solution.
∫ \(\left(x^{2}+1\right)(x-1)\) dx
Let \(\frac{x}{\left(x^{2}+1\right)(x-1)}=\frac{A x+B}{\left(x^{2}+1\right)}+\frac{C}{(x-1)}\)
x = (Ax + B) (x – 1) + C (x2 + 1)
⇒ x = Ax2 – Ax + Bx – B + C
Equating the coefficients of x2, x and constant term, we get
A + C = O;
– A + B = 1;
– B + C = 0
On solving, we get
A = – \(\frac{1}{2}\), B = \(\frac{1}{2}\) and C = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
From equation (1), we get
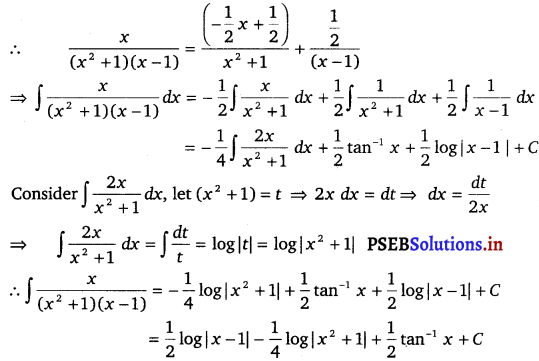
Question 8.
\(\frac{x}{(x-1)^{2}(x+2)}\)
Solution.
∫ \(\frac{x}{(x-1)^{2}(x+2)}\) dx
Let \(\frac{x}{(x-1)^{2}(x+2)}=\frac{A}{(x-1)}+\frac{B}{(x-1)^{2}}+\frac{C}{(x+2)}\)
x = A (x – 1) (x + 2) + B (x + 2) + C (x – 1)2
Substituting x = 1, we get
B = \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Equating the coefficients of x2 and constant term, we get
A + C = 0;
– 2A + 2B + C = 0
On solving, we get
A = \(\frac{2}{9}\) and C = – \(\frac{2}{9}\)
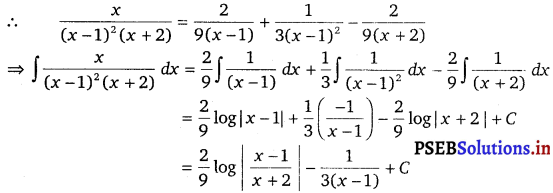
![]()
Question 9.
\(\frac{3 x+5}{x^{3}-x^{2}-x+1}\)
Solution.
∫ \(\frac{3 x+5}{x^{3}-x^{2}-x+1}\) dx = \(\int \frac{3 x+5}{\left(x^{2}-1\right)(x-1)} d x=\int \frac{3 x+5}{(x-1)(x+1)(x-1)} d x\)
= \(\int \frac{3 x+5}{(x-1)^{2}(x+1)}\) dx
Let \(\frac{3 x+5}{(x-1)^{2}(x+1)}=\frac{A}{(x-1)}+\frac{B}{(x-1)^{2}}+\frac{C}{(x+1)}\)
3x + 5 = A (x – 1) (x + 1) + B (x + 1) + C (x – 1)2
3x + 5 = A (x2 – 1) + B (x + 1) + C (x + 1 – 2x) …………….(i)
Substituting x = 1 in equation (i), we get
B = 4
Equating the coefficients of x2 and x, we get
A + C = 0;
B – 2C = 3
On solving, we get
A = – \(\frac{1}{2}\) and C = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
∴ \(\frac{3 x+5}{(x-1)^{2}(x+1)}=\frac{-1}{2(x-1)}+\frac{4}{(x-1)^{2}}+\frac{1}{2(x+1)}\)
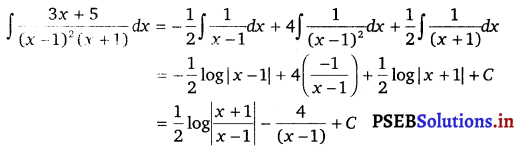
Question 10.
\(\frac{2 x-3}{\left(x^{2}-1\right)(2 x+3)}\)
Solution.
∫ \(\frac{2 x-3}{\left(x^{2}-1\right)(2 x+3)}\) dx = ∫ \(\frac{2 x-3}{(x+1)(x-1)(2 x+3)}\) dx
Let \(\frac{2 x-3}{(x+1)(x-1)(2 x+3)}=\frac{A}{(x+1)}+\frac{B}{(x-1)}+\frac{C}{(2 x+3)}\)
⇒ (2x – 3) = A (x – 1) (2x + 3) + B (x + 1)(2x + 3) + C (x + 1) (x – 1)
⇒ (2x – 3) = A (2x2 + x – 3) + B (2x2 + 5x + 3) + C (x2 – 1)
⇒ (2x – 3) = (2A + 2B + C) x2 + (A + 5B) x + (- 3A + 3B – C)
Equating the coefficients of x2 and x, we get
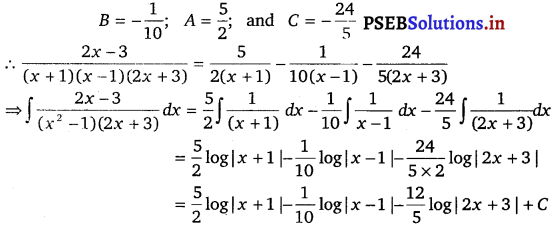
![]()
Question 11.
\(\frac{5 x}{(x+1)\left(x^{2}-4\right)}\)
Solution.
∫ \(\frac{5 x}{(x+1)\left(x^{2}-4\right)}\) dx = ∫ \(\frac{5 x}{(x+1)(x+2)(x-2)}\) dx
Let \(\frac{5 x}{(x+1)(x+2)(x-2)}=\frac{A}{(x+1)}+\frac{B}{(x+2)}+\frac{C}{(x-2)}\)
5x = A (x + 2) (x – 2) + B (x + 1) (x – 2) + C (x + 1) (x + 2)
Substituting x = – 1, – 2, and 2 respectively in equation (i), we get
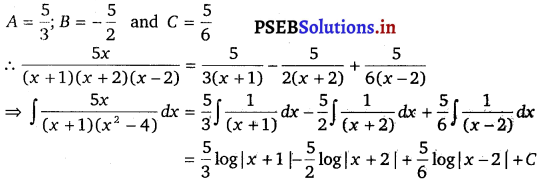
Question 12.
\(\)
Solution.
It can be seen that the given integrand is not a proper fraction.
Therefore, on dividing (x3 + x + 1) by x2 – 1, we get
Let \(\frac{2 x+1}{x^{2}-1}=\frac{A}{(x+1)}+\frac{B}{(x-1)}\)
⇒ 2x + 1 = A (x – 1) + B (x + 1) ………………(i)
Substituting x = 1 and – 1 in equation (i), we get
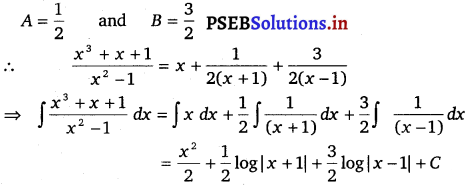
![]()
Question 13.
\(\frac{2}{(1-x)\left(1+x^{2}\right)}\)
Solution.
∫ \(\frac{2}{(1-x)\left(1+x^{2}\right)}\) dx
Let \(\frac{2}{(1-x)\left(1+x^{2}\right)}=\frac{A}{(1-x)}+\frac{B x+C}{\left(1+x^{2}\right)}\)
2 = A (1 + x2) + (Bx + C) (1 – x)
⇒ 2 = A + Ax2 + Bx – Bx2 + C – Cx
Equating the coefficient of x2, x, and constant term, we get
A – B = 0;
B – C = 0;
A + C = 2
On solving, we get
A = 1; B = 1 and C = 1
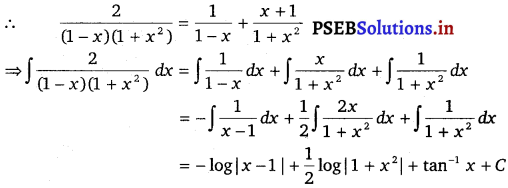
Question 14.
\(\frac{3 x-1}{(x+2)^{2}}\)
Solution.
∫ \(\frac{3 x-1}{(x+2)^{2}}\) dx
Let \(\frac{3 x-1}{(x+2)^{2}}=\frac{A}{(x+2)}+\frac{B}{(x+2)^{2}}\)
⇒ 3x – 1 = A (x + 2) + B
Equating the coefficient of x and constant term, we get
A = 3; 2A + B = – 1
⇒ B = – 7
∴ \(\frac{3 x-1}{(x+2)^{2}}=\frac{3}{(x+2)}-\frac{7}{(x+2)^{2}}\)
∫ \(\frac{3 x-1}{(x+2)^{2}}\) dx = \(3 \int \frac{1}{(x+2)} d x-7 \int \frac{x}{(x+2)^{2}} d x\)
= 3 log |x + 2| – 7 \(\left(\frac{-1}{(x+2)}\right)\) + C
= 3 log |x + 2| + \(\frac{7}{(x+2)}\) + C
![]()
Question 15.
\(\frac{1}{x^{4}-1}\)
Solution.
∫ \(\frac{1}{x^{4}-1}\) dx = \(\int \frac{1}{\left(x^{2}-1\right)\left(x^{2}+1\right)} d x=\int \frac{1}{(x+1)(x-1)\left(1+x^{2}\right)} d x\)
Let \(\frac{1}{(x+1)(x-1)(1+x)^{2}}=\frac{A}{(x+1)}+\frac{B}{(x-1)}+\frac{C x+D}{\left(x^{2}+1\right)}\)
1 = A (x – 1) (x2 + 1) + B (x + 1) (x2 + 1) + (Cx + D) (x – 1)
1 = A (x3 + x – x2 – 1) + B (x3 + x + x2 + 1) + Cx3 + Dx2 – Cx – D
1 = (A + B + C) x3 + (- A + B + D) x2 + (A + B – C) x + (- A + B – D)
Equating the coefficient of x3, x2, x and constant term, we get
A + B + C = 0;
– A + B + D = 0;
A + B – C = 0;
– A + B – D = 1
On solving, we get
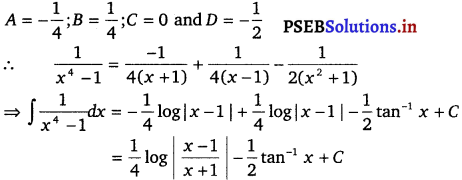
![]()
Question 16.
\(\frac{1}{x\left(x^{n}+1\right)}\)
Solution.
[Hint : Multiply numerator and denominator by xn – 1 and put xn = t]
Solution.
\(\frac{1}{x\left(x^{n}+1\right)}\)
Multiplying numerator and denominator by xn – 1, we get
Let xn = t
⇒ xn – 1 dx = dt

Question 17.
\(\frac{\cos x}{(1-\sin x)(2-\sin x)}\) [Hint: Put sin x = t]
Solution.
∫ \(\frac{\cos x}{(1-\sin x)(2-\sin x)}\) dx
Let sin x = t
⇒ cos x dx = dt
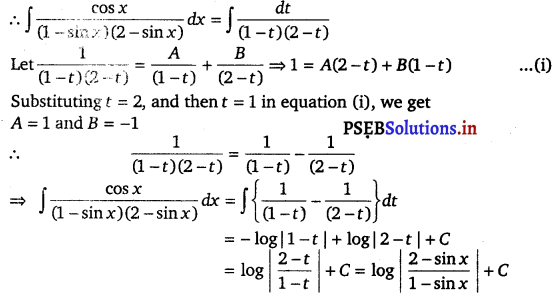
![]()
Question 18.
\(\frac{\left(x^{2}+1\right)\left(x^{2}+2\right)}{\left(x^{2}+3\right)\left(x^{2}+4\right)}\)
Solution.
\(\frac{\left(x^{2}+1\right)\left(x^{2}+2\right)}{\left(x^{2}+3\right)\left(x^{2}+4\right)}\) = 1 – \(\frac{\left(4 x^{2}+10\right)}{\left(x^{2}+3\right)\left(x^{2}+4\right)}\)
Let \(\frac{4 x^{2}+10}{\left(x^{2}+3\right)\left(x^{2}+4\right)}=\frac{A x+B}{\left(x^{2}+3\right)}+\frac{C x+D}{\left(x^{2}+4\right)}\)
4x2 + 10 = (Ax + B) (x2 + 4) + (Cx + D) (x2 + 3)
4x2 + 10 = Ax3 + 4Ax + Bx2 + 4B + Cx3 + 3Cx + Dx2 + 3D
4x2 + 10 = (A + C) x3 +(B + D)x2 + (4A + 3C) x + (4B + 3D)
Equating the coefficients of x3, x2, x and constánt term, we get
A + C = 0;
B + D = 4;
4A + 3C = 0;
4B + 3D = 10
On solving, we get
A = 0, B = – 2, C = 0 and D = 6
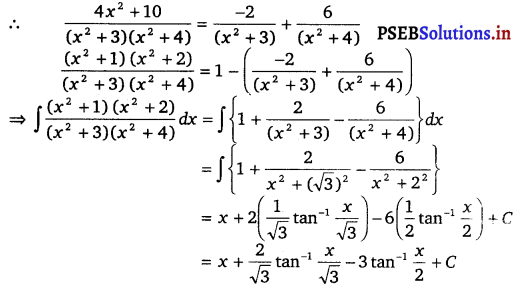
![]()
Question 19.
\(\frac{2 x}{\left(x^{2}+1\right)\left(x^{2}+3\right)}\)
Solution.
∫ \(\frac{2 x}{\left(x^{2}+1\right)\left(x^{2}+3\right)}\) dx
Let x2 = t
⇒ 2x dx = dt
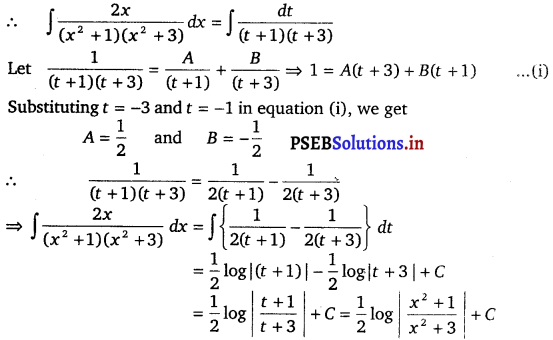
Question 20.
\(\frac{1}{x\left(x^{4}-1\right)}\)
Solution.
\(\frac{1}{x\left(x^{4}-1\right)}\)
Multiplying numerator and denominator by x3, we get
\(\frac{1}{x\left(x^{4}-1\right)}=\frac{x^{3}}{x^{4}\left(x^{4}-1\right)}\)
![]()
Question 21.
\(\frac{1}{\left(e^{x}-1\right)}\) [Hint: Put ex = t]
Solution.
∫ \(\frac{1}{\left(e^{x}-1\right)}\) dx
Let ex = t
⇒ ex dx = dt
⇒ \(\int \frac{1}{e^{x}-1} d x=\int \frac{1}{t-1} \times \frac{d t}{t}=\int \frac{1}{t(t-1)} d t\)
Let \(\frac{1}{t(t-1)}=\frac{A}{t}+\frac{B}{t-1}\)
⇒ 1 = A (t – 1) + t …………..(i)
Substituting t = 1 and t = 0 in equation (i), we get
A = – 1 and B = 1
∴ \(\frac{1}{t(t-1)}=\frac{-1}{t}+\frac{1}{t-1}\)
⇒ ∫ \(\frac{1}{t(t-1)}\) dt = log \(\left|\frac{t-1}{t}\right|\) + C
= log \(\left|\frac{e^{x}-1}{e^{x}}\right|\) + C
![]()
Direction (22 – 23) Choose the correct answer:
Question 22.
∫ \(\frac{x d x}{(x-1)(x-2)}\) equals
(A) log \(\left|\frac{(x-1)^{2}}{x-2}\right|\) + C
(B) log \(\left|\frac{(x-2)^{2}}{x-1}\right|\) + C
(C) log \(\left|\left(\frac{x-1}{x-2}\right)^{2}\right|\) + C
(D) log |(x – 1) (x – 2)| + C
Solution.
Let \(\frac{x}{(x-1)(x-2)}=\frac{A}{(x-1)}+\frac{B}{(x-2)}\)
⇒ x = A (x – 2) + B (x – 1) …………….(i)
Substituting x = 1 and 2 in equation (i), we get
A = – 1 and B = 2
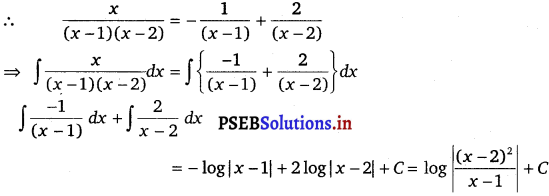
Hence, the correct answer is (B).
![]()
Question 23.
∫ \(\frac{d x}{x\left(x^{2}+1\right)}\) equals
(A) log |x| – \(\frac{1}{2}\) log (x2 + 1) + C
(B) log |x| + \(\frac{1}{2}\) log (x2 + 1) + C
(C) – log |x| + \(\frac{1}{2}\) log (x2 + 1) + C
(D) \(\frac{1}{2}\) log |x| + log (x2 + 1) + C
Solution.
Let \(\frac{1}{x\left(x^{2}+1\right)}=\frac{A}{x}+\frac{B x+C}{x^{2}+1}\)
⇒ 1 = A(x2 + 1) + (Bx + C) x
Equating the coefficients of x2, x and constant term, we get
A + B = 0;
C = 0; A = 1
On solving, we get
A = 1; B = – 1 and C = 0
∴ \(\frac{1}{x\left(x^{2}+1\right)}=\frac{1}{x}+\frac{-x}{x^{2}+1}\)
⇒ \(\int \frac{1}{x\left(x^{2}+1\right)} d x=\int\left\{\frac{1}{x}-\frac{x}{x^{2}+1}\right\} d x\)
= log |x| – \(\frac{1}{2}\) log (x2 + 1) + C
Hence, the correct answer is (A).
