Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class Political Science Book Solutions Chapter 1 Political System Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 12 Political Science Chapter 1 Political System
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Define Political System. Write main characteristics of Political System.
Or
Describe the words Political and System separately and also write any three features of Political System.
Or
Define Political System and explain its four characteristics.
Answer:
Introduction:
Among the new concepts and trends of political analysis, the concept of political system occupies a pre-eminent place. It has revolutionised modern political science. The behavioural revolution in political science begins and ends with an over-emphasis on the concept of political system. It was Talcott Parsons, a sociologist who by writing his book ‘Social System’ popularised this concept in sociology. In political science this concept is associated with the names of David Easton, Gabriel Almond and several others of their camp. The concept has been borrowed from natural science in social sciences. Before understanding the concept of political system, it is essential to know the meaning of ‘Political’ and ‘System’.
What is Political:
The word ‘Political’ reflects power or authority. All these interactions involved in the struggle for power are ‘Political’. Any association becomes Political when its rule or decisions are obeyed by its members with the use or threat of physical force. According to Max Weber, “An association should be called political if and in so far as the enforcement of its order is carried out continually within a given territorial area by the application or threat of physical force.” Political includes all these which include power, influence, control or authority to a significant extent.
Meaning of the term ‘System’:
According to Oxford Dictionary, “A system is a complete whole, a set of connected things or parts, organised body of material or immaterial things.”
The word ‘system’ has been used and defined differently by different writers belonging to different disciplines. Ludivin van Bertallanfy describes system as a “set of elements standing in interaction.” Collin Cherry says that a system “is a whole which is compounded of many parts-an ensemble of attitudes.”
According to Gabriel A. Almond a system means a “particular set of properties in interaction A system has three characteristics:
1. comprehensiveness,
2. interdependence and
3. existence of boundaries.”
According to A. Hall and A. Fagen, “System is a set of objects together with relations between the objects and between their attitudes.”
Definitions of a Political System:
There are several definitions of the term ‘Political System.’ Max Weber says that a political system is a human community that successfully claims the monopoly of the legitimate use of physical force within a given territory. Kaplan and Lasswell consider the shaping and sharing of power as the main concern of political system with the help of threatened or actual use of severe deprivation for non-confirmity. Robert A. Dahl defines political system as “any persistent pattern of human relationships that involves to a significant extent power, rule or authority.”
Gabriel A. Almond expands “political system” to mean “that system of interaction to be found in all independent societies which performs the functions of interaction and adaptation (both internally and vis-a-vis other societies) by means of employment or threat of employment of more or less.” More briefly speaking, the political system is, “the legitimate order maintaining or transforming system within society”.
The use of the phrase “more or less’ by Almond, enables us to include totalitarian systems in which the legitimacy may be in doubt, revolutionary system in which the basics of legitimacy may be in process of change ; and non-western systems in which there may be more than one legitimate system. Physical compulsion distinguishes one political system from another. All inputs into the political system are in some way related to claim for the employment of legitimate compulsion. All the ‘outputs’ are related to the exercise of such legitimate compulsion.
Thus three things emerge out of Almond’s definition of political system:
- That a political system is a concrete whole influencing and in turn influenced by the environments,
- interactions take place not between individuals but between roles adopted by them, and
- the political system is an open system engaged in continuous communication with entities and systems beyond its own boundaries.
Thus all three characteristics of a system are found in Almond’s definition of political system:
- political system is comprehensive in the sense that it includes all the interactions-inputs as well as outputs;
- it is interdependent in the sense that various sub-sets of political systems are so closely associated with each other that a change in one sub-set produces a change in all the sub-sets; and
- there is a boundary or demarcation between one political system and another.
A political system not only includes formal governmental structures; like Executive, Legislative, Judiciary and other administrative agencies, but it includes traditional and informal structures; like kinship, caste, group, anomic groups e.g., demonstrations, violent incidents and murders, etc. So the scope of Political System is very large.
![]()
Question 2.
Describe the main characteristics of Political System.
Or
Write down the main components of Political System.
Answer:
According to Almond, a political system has three main properties of comprehensiveness, interdependence and boundaries and it has essential characteristics-Universality-of Political System, Universality of political structure, Universality of political functions, multifunctionality of political structure and culturally mixed character of the political system.
1. Comprehensiveness:
According to Almond, political system includes all the interactions-inputs as well as outputs,-that affect the use of political coercion. In other words, according to Almond, political system is not only concerned with the mere structures based on constitutional and legal foundations as parliaments, courts and bureaucracies or with informal organisations like political parties and pressure groups and means of communications, but it is concerned with all the structures in their political aspects, including undifferentiated structures like kinship and lineage, status and caste groups, religious and cultural bodies, as well as anomic phenomenon like violent riots and street demonstrations.
2. Interdependence:
According to Almond, political system also includes the political aspects of various sub-systems. Interdependence of various sub-systems is one of the most important elements of the political system. For example, the changes in the means of communications have transformed the electoral process, the characteristics of political parties, the legislature and the executive.
3. Existence of Boundaries:
It implies that there are points where the political system ends and other systems begin. The boudaries between society and polity differ from one political system to another. But the boundaries of a political system change from time to time. Besides the three properties of political system, Almond has also mentioned five characteristics of the political system:
(i) Universality of Political Systems:
According to Almond, all political systems whether primitive or modern or whether developing and developed, have political structures, i.e., they have a legitimate pattern of interaction by means of which internal and external order is maintained.
(ii) Universality of Political Structure:
According to Almond, all political systems have same structures that perform same functions though with varying degree of frequency. The articulative, aggregative and communicative functions may be performed diffusely within the society or intermittently through the kinship or lineage structure. An adequate analysis of a political system must locate and characterise all of these functions and not simply those performed by the specialised political structure.
(iii) Universality of Political Functions:
According to Almond, the approach of the student of comparative Politics should not be ‘structure-bound,’ rather it should be ‘function-bound’. According to Almond, every political system must perform the following functions:
(a) Input Functions.
Input category includes:
- Political Socialisation and- Recruitment,
- Interest articulation,
- Interest aggregation, and
- Political communication.
(b) Output Functions.Output category includes:
- Rule-making.
- Rule-application and
- Rule-adjudication.
4. Multifunctionality of Political Structure:
According to Almond, all political structure irrespective of the degree of specialisation in point of time or space, is multifunctional. Multi-functionality of Political Structure means that a political structure performs not one type of functions but many types of functions. For example, courts not only adjudicate, they also legislate. Similarly Legislatures not only legislate but they also perform administrative functions.
5. Culturally Mixed Character of Political Systems:
According to Almond, all political systems are mixed in the cultural sense. No political system is quite modern or western in the same sense as no individual is fully mature or emancipated from the ties and diffuse dependence.
Characteristics of Political System in Dahl’s View
Robert Dahl has mentioned in his book ‘Modern Political Analysis’ eight characteristics of Political system. But before discussing the characteristics Robert Dahl has said, “Remember these similarities are not a part of the definition of a political system. They are regularities-empirical regularities one might say- that one can expect to find in any large political system.”
1. Uneven Control of Political Resources:
According to a report of Dahl, “Control over political resources is distributed unevenly”. A political resource is a means by which one person can influence the behaviour of other persons. Political resources include money, information, food, the threat of force, job, friendship, social standing, the right to make laws, votes, and a great variety of other things. According to Dahl, there are four reasons why control over political resources is unevenly distributed in virtually all societies.
(i) Some specialization, of functions exists in every society:
Because of this specialization, everyone cannot have an equal control over resources. A foreign minister or a secretary of state knows better about the foreign affairs than ordinary citizens, because he (foreign minister) specializes in that sphere.
(ii) Because of inherited difference, people do not have control over resources.
(iii) Citizens differ in their objectives. Some have no interest in politics, others have too much of interest. Not everyone is equally motivated to go into politics, to become a leader, or to acquire the resources that help the leader gain influence over others.
(iv) Finally, some differences in incentives and goals are usually encouraged in societies in order to equip individuals for different specialities. If everyone wanted to be a full-time warrior, who would bear and rear the children? But differences in motivations are likely to lead to differences in resources-for example to greater military powers for warriors than others.
2. The Quest of Political Influence:
In almost every political system there are some members who seek to gain influence over the policies, rules and decisions enforced by the government-i.e. political influence. People seek political influence not necessarily for its own sake, but because control over the government helps them to achieve one or more of their goals. Control over the government is such an obvious and familiar way of furthering one’s goals or values that it is hard to imagine a political system in which no one sought power.
3. Unequal Distribution of Political Influence:
There is an unequal distribution of Political Influence among the adult members of a society. These with more political resources have large capacity to influence than others. The unequal distribution of Political influence is not modern in its origin ; it has always existed in our societies. Uneven control of political resources and the difference in purpose for which these resources are utilised, are a few factors responsible for this unequal distribution of Political Influence. Aristotle distinguished between master and slave, husband and wife.
Rousseau accepted property as the basis of inequality. Marx and Engels also accept almost similar basis. David Truman inl951 said, “Writers of the most diverse Political views and using the most widely variant methods of observation have called attention to the existence in almost all groups of an active minority identified by such condemnatory terms as ‘oligarchy’ and ‘old guard’ or such approving ones as public spirited citizens and civic leaders.” Thus these, with a larger amount of political influence, are known to be the leaders in a Political System.
4. Resolution of Conflicting aims:
The members of a Political System generally have conflicting aims. These aims are, of course, considered by the Govt, yet it does not mean that Government always interferes in these conflicting aims and activities of individual members. State interferes only when the use of power becomes imminent. A Government, for example, interferes in a dispute between the workers and owners of a mill or any other concern, when it endangers the National economy.
5. The Acquisition of Legitimacy:
While solving the conflicts in a Political System, rulers always take care of this thing that the means used for settlement should be based on moral principles and not on fear, violence or any other immoral consideration. Leaders in a Political System always try to establish legitimacy of their actions. This is particularly so in a democratic system.
6. Development of an Ideology:
The rulers in a political system essentially develop an ideology to prove the legitimacy of their acts. This ideology can be socialistic, democratic or any other, but it is not essential that every individual member of the system knows or understands that ideology.
7. Influence of other Political Systems:
Every Political System is influenced by other Political Systems. No Political system in modem age can develop in complete isolation. Each State has to regulate its system on the basis of international law, international treaties, agreements and international institutions.
8. The Inevitability of Change:
All political systems undergo change. From time immemorial political observers have pointed out the mutability of political systems. In the entire history of political institutions, no political system has been immutable. But it is important to note that characteristics of political systems, given by Dahl, are not the theoretical basis of political system. In other words from theory point of view it is not essential that characteristics must be available in every political system. But as far as the political form of political system is concerned almost all these characteristics are available in a political system.
![]()
Question 3.
Describe the meaning of ‘Political System’ and also explain its ‘input functions’.
Or
Write input and output functions of Political System.
Answer:
According to Shaw and Pierce, “The study of Politics needs some analytical tool which can help to describe and explain ‘Political’ activity. The term ‘system’ is a useful one for organizing one’s knowledge about many social objects. Employing the concept of system with its accompanying properties, is one way in which the characteristics and boundaries of the ‘Politician’ can be abstracted for study.” In this way after including the concept of ‘System’ in politics by modem political scholars, concept of political system has become a central point of study in political science.
The term ‘Political System’ reflects a new way of looking at political phenomena which was covered in old texts under such terms as ‘government’, ‘nation’ or ‘state’. Political system, however, denotes not only change of nomenclature but something much more. It includes not only new names for old things, but also some new terms to refer to activities and processes which were not formerly recognised as being parts or aspects of politics. The order of terms-state, government, nation-are limited by legal and institutional meanings. They referred to only the formal government institutions such as legislature, executive and judiciary.
But Political System includes not only governmental institutions such as legislature, court and administrative agencies, but all structures in their political aspects. Among these are traditional structures such as kinship ties and caste groupings, anomic phenomena such as assassinations, riots and demonstrations; as well as formal organisations like parties, interest groups and media of communication.”
Functions of Political Systems:
According to Almond, Political Systems perform two types of functions-Input functions and Output functions. Below, we discuss these briefly:
Input Functions:
Input functions are performed by non-governmental sub-systems society, and general environment. Almond has suggested four input functions of a Political System.
1. Political Socialization and Recruitment
2. Interest Articulation
3. Interest Aggregation
4. Political Communication.
1. Political Socialization and Recruitment:
In one’s childhood, one has no interest in politics. A child is generally ignorant about politics, but gradually when he grows up, he starts understanding the political conceptions and then finally he starts playing a role also in the political system. This is the process of socialization.
According to Almond and Powell, ‘Political Socialization is the process through which political cultures are maintained or changed.” So the process of political socialization can be utilised for both bringing a change as well as for maintaining status-quo. It is a continuous process. Political Parties and Pressure Groups, which are the main agencies of political socialization, are involved in making the people conscious about their values and in attracting their attention towards their values. The process of socialization has its special importance in a democratic system.
The process of socialization, in a system, is supplemented by Recruitment. Roles and actors in a system keep on changing. Rulers, officials, leaders all change in a system. New ones replace the older ones. Defining Recruitment, Almond and Powell write, “We use the term Political to refer to the functions by means of which the roles of political systems are filled. ” There can be both generalized or specialized recruitment.
2. Interest Articulation:
In simple words, Interest Articulation is the presentation of Demands in a system. According to Almond and Powell, “The process by which individuals and groups make demands upon the political decision makers, we call, interest articulation. ” Different individuals and groups present their demands or articulate their interests before those who have the right to make decisions.
It is an important process in the political system, because unless the groups or individuals present their demands before the rulers, no policy can be formulated and their demands cannot be met. If the groups or individuals in a system are not allowed to present their demands or interests, it may lead to violent activities. Interests, in a political system, can be articulated by way of petitions, suggestions, addresses, statements, demonstrations or even violent means. Students and labour groups adopt the techinque of strikes etc. The democratic system provides proper means for interest articulation to the people.
3. Interest Aggregation:
In no political system different laws of the interests of different groups can be created. A common policy is formulated for the interests of almost all the groups. The process of combining the interests of various groups is known as Interest Aggregation. According to Almond and Powell. “The functions of converting demands into general policy alternatives is called interest aggregation. ” There are two ways to perform this function.
First by co-ordinating the interests of various nature and second by the recruitment of those who have faith in one national policy. An individual wants a particular thing to be done on the basis of his interests. Interest groups aggregate the interests of various sub-groups and make a demand. Political Parties on the basis of various demands made by different groups, prepare a policy. This is a continuous process in a political system.
4. Political Communication:
Political Communication is the most important function of a Political System. It is through this process that other functions are performed. Everybody, whether a citizen or an official, has to depend upon information, because all activities in a system are to be regulated on the basis of information. That is why in a democratic system there is too much of emphasis on the freedom of press, speech and expression, whereas it is crushed or controlled in a totalitarian system. Means of communication have a definite impact on a Political System. Without communication, Interest articulation is not possible.
The freedom and autonomy of the communication system has been recognized in modern developed societies. On the basis of the structure of the communication system, we can compare the political systems with each other. According to Almond and Powell, “The analysis and comparison of the performance of political communication is one of the most interesting and useful means of examining different political systems. ” In a comparative study we look at communication from four angles, namely,
- Homogeneity
- Mobility
- Volume
- Direction.
Output Functions:
The output functions of a Political System are similar to those of the administrative activities of a State. Almond himself has accepted that they are similar to the traditional government functions. But still they should be described not as government functions, but as output functions of a political system. Almond has suggested three main output functions:
1. Rule Making,
2. Rule Application,
3. Rule Adjudication.
Let us know about these briefly.
1. Rule Making:
There must be certain rules in the society to regulate the relationships between the individuals. In a political system the rule-making function is performed by the Legislature and its allied agencies. The use of the term ‘rule-making’ in place of ‘law-making’ has been justified by Almond on the ground that the term ‘law-making’ reflects a particular structure and a definite process, whereas rule-making is a much more diffused process in which all political systems are involved. Almond and Powell believe that constitutionalism demands that, “rules must be made in certain ways and by specific institutions and with certain kinds of limitations.”
2. Rule Application:
The function of the political system is not only to make rules, but also to apply them. If rules are not properly implemented the whole purpose of rule-making is lost and the desired results then cannot be expected. In a political system ‘Rule application’ is the responsibility of bureaucracy. Even the judicial decisions are implemented by the civil servants. Sometime this function is performed by the rule-making department also.
But in a developed political system the two functions are performed by separate departments. According to Almond, “The presence of differentiated and well developed structures for rule application greatly expand the capability of a political system to manipulate its environment. ”
3. Rule Adjudication:
Whenever a rule is created, the fear of its violation is always present. Now, he who violates these rules, must be punished. That is why almost every rule contains in itself the punishment for those, who violate it. But before such a punishment is given to any individual it must be established that he had actually violated the rule of the land. This is the function of courts or the judiciary or in modem terminology, the Rule Adjudication department.
This department peforms another function and that is the interpretation of laws. In an ideal political system this department is kept independent of all controls so that judges work impartially, independently and fearlessly. An analysis of all these functions of a political system presents models, Almond and Coleman have described five such models:
- The Model democracy-Japan, India and Israel.
- The Tutelary democracy-Ghana, Nigeria. In their model Legislature and Judiciary are comparatively weaker than Executive.
- The Modernizing Oligarchy-Myanmar (Burma), Turkey and Sudan. In such a model the democratic constitution remains suspended. Authority is vested in either Bureaucracy or in Armed Forces.
- The Totalitarian Oligarchy-Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. This is called Guardian-Bureaucracy.
- The Traditional Oligarchy-Kuwait, Saudi Arab. Recruitment in this model is on the basis of kinship.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain David Easton’s Concept of Political System.
Or
Discuss the functions of Political System with reference to the views of David Easton.
Answer:
General System’s theory is concerned with all types of systems whereas the System’s theory covers only the political system. Oran Young is of the opinion that System Theory is a product of General System Theory. But Spiro believes that System Theory was present before the General Systems Theory came into existence.
System Analysis:
David Easton was the first Political Scientist to adopt the system analysis in Politics, in 1965, in his books, ‘A Framework of Political Analysis’ and ‘A System Analysis of Political Life.’ He gave a new interpretation, which is of great importance for us today.
Meaning of Political System according to Easton:
Political system differs from General Systems. It is ominpresent and is found everywhere, may be that it exists in different forms.
Defining Political System, Easton has said that “Political System is that system of interaction in any society through which binding and authoritative allocations of value are made and implemented.” He has further said that, “the idea of Political System proves to be an appropriate and indeed unavoidable starting point in research. Although, there is often uncertainty about the unity of Political Science as a discipline, most students of Political Science do feel quite instinctively that research into political aspects of life does differ from enquire into any other, sufficiently, so to constitute a separate intellect enterprise.”
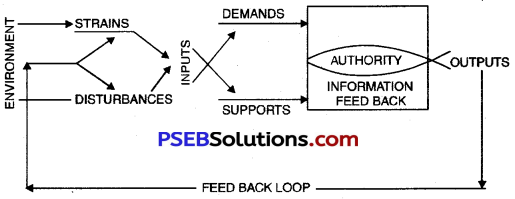
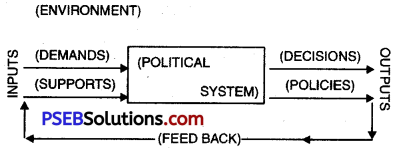
Easton’s analysis of Political System is without any boundaries. For him, the scope of Political System is very large. It includes all types of formal and informal actions and interactions, structures and values. Political System is a sub-system of social system and it can, therefore be analysed. It is affected by all other systems and sub-systems. It adopts inputs and produces output.
Inputs and Outputs in a Political System:
Easton has described two types of inputs in a political system:
1. Demand and 2. Support.
Demand:
Easton has explained demand by saying “A demand is an expression of opinion that an authoritative allocation with regard to a particular subject-matter should or should not be made by those responsible for doing so.”
Demand can be of many types, for example, demand for fixed working hours, demand for public security, demand for franchise, demand for information or for sending messages etc. Support can also be of many types, for example, materialistic support like, paying taxes, joining armed forces, financial help during emergency. Similarly, another support can be to obey the laws and help in their execution. Yet, another support can be to use right to vote and to participate in the political activities.
Input Support:
According to Easton, no demand can be satisfied without support, but the related problems are-how much support, and from where and which members of political system? One will get support if others are satisfied by his actions or activities or interests. Every political system will have to get the support of environments, if it is to survive. The support can be in the form of actions which are supportive or it can be to a specific political object.
lt can also be an over all support to the political community, to a particular structure or political authorities, holding power at a given time. He was also of the view that the support could be for all things or for any one of them. But at the same time, it cannot be taken for granted that support once obtained will continue for ever. The support can also increase or decline, according to certain developments. But such a situation will arise only when a political system has failed to deliver the goods.
Easton believed that input in a Political System is like the raw material which when supplemented by support takes the form of outputs.
Outputs of Political System:
Demands and supports are inputs of a political system, but along with inputs, there are also some outputs. A political system might be having excellent public support, it might also have lofty ideals to achieve and the society on the whole might even extend co-operation to it, but it will survive only when it gives its output, namely how far the system has proved to society useful or what has it given to the society. According to Easton, “Outputs not only help to influence events in the broader sense of which the system is a part, but also in doing so they help to determine each succeeding round of inputs that finds its way into the political system.” Outputs are of three types according to Easton, viz.
1. Tax or personal service,
2. Regulated behaviour and
3. Distribution of general services or opportunities
Easton also tried to establish a relationship between the Political System and the Environment. Environment creates demands and the conversion process converts them into decisions or policies. Support originates out of the satisfaction about the decisions taken or policies made. This process continues in a political system till the system bears the strains and stresses in forms of demands. When this situation reaches a critical stage and the strains and stresses become unbearable for a political system, the system collapses.
Following are the main premises of input-output process, as described by David Easton:
1. System,
2. Environment,
3. Response and
4. Feedback.
1. System: System has, already, been defined in the beginning of this part of the chapter.
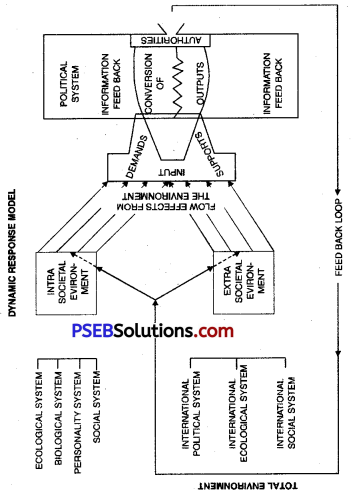
2. Environment:
Political System is a set of interactions. It converts inputs into outputs. Just as every conversion has the impact of a particular type of
environment, similarly, the conversion of inputs into outputs depends upon political environment. According to Eatson, Political Environment is of two types,
(i) Extra Societal
(ii) Intra Societal.
The Extra Societal environment means international environment which includes groups, cultural and economic systems. The Intra Societal environment includes structural, social and other circumstances which are influential in the society.
3. Response:
Political System allocates values in the society. Environment influences the Political System in this regard and puts all types of strains and stresses on the Political System. The success or failure of a Political System depends upon the reaction of the system about their strains and stresses. These stresses constitute the inputs and only few of these are converted into outputs. How far an environment system faces these inputs, is the response of the Political System. For this purpose, Political System articulates four types of rules:
- Communicative Rules, which regulate the conversion process.
- Cultural Rules, through which political system determines cultural values.
- Communicatory Instruments, through which the political system increases the possibility of its control over output.
They include Press, Radio and T.V. etc.
4. Reductionist Reactions or Aggregation, through which the possibility of demands is reduced as is done by unification etc.
Apart from Demands, the other input in the environment is the political support. Support can be of three types:
- Overt or Covert
- Positive or Negative
- General and Widespread or Particular or special.
Levels of Support:
There are three levels of support; namely:
- Political community
- Regime
- Authorities.

Support, according to Easton, can be towards three types of special things:
1. Towards political community which is based on labour division,
2. Towards the basic values of Political System and
3. Towards Political Authorities.
4. Feedback:
Feedback means to take back to the system in shape of inputs, the impact and result of the outputs. This brings continuity in the System. According to Easton, the Feedback is the process of combining the results of outputs with inputs and establishing a cyclic relationship between inputs and outputs. Feedback can be of two types:
- The Negative Feedback: This is related to the information relating to the system and defective rule making.
- Objective Alerting Feedback is related to the purpose and direction of political system.
Flow Model:
Easton found certain defects in the Equilibrium analysis of Almond and presented his input and output analysis as Flow Model. He tried to prove that the Political Analysis depends upon the capacity of the system.
![]()
Question 5.
Write main differences between state and political system.
Answer:
Modern political concepts vastly differ from traditional Political concepts. The writers of traditional Political Science considered State, its main subject whereas the modern writers regard Political System in place of State, its primary subject.
State, in ancient time, was regarded the main subject of Political Science. So Prof. Garner opined, “Political System begins and ends with the State.” Like Garner, writers like Bluntschli, Gettell, Garies, Gilchrist, Lord Acton etc. considered State the central point of Political Science. But the modern writers don’t agree with this traditional viewpoint. For them, Political System instead of State, is the main subject of Political Science.
They are of the view that to confine the scope of Political Science to State only, is to destroy its practical utility. These main writers are Almond and Powell, Charles Merriam, Harold Lasswell, David Easton, Stephen, L. Wasby. According to Almond and Powell, a vast structure is needed to make Political Science more effective and system analysis can provide this structure. State and Political System differ from each other, but it is essential to explain the meaning of ‘State’ and ‘Political System’ before pointing out main distinction between the two.
Meaning of State:
In the words of Prof. Gilchrist, “The State exists where a number of people brought on a definite territory are unified under a Government which in internal matter is the organ for expressing their sovereignty and in external matter is independent of other Governments.” This definition clearly points out that population, definite territory, Government and Sovereignty are the four main elements without which a State cannot be established. If any of these four elements is missing, State can’t be founded.
Meaning of Political System:
According to Almond and Powell, “When we speak of Political System, we include all the interactions which affect the use of threat or use of Legitimate Physical force. The Political System includes not only Governmental institutions such as legislatures, courts and administrative agencies, but all structures in their political aspects. Among these are traditional structures such as kinship ties and caste grouping; and anomic phenomena such as assassinations, riots and demonstrations; as well as formal organisations like parties, interest groups and media of communications.
In this way, Political System includes all the formal and informal institutions, groups and organisations which affect political life in one way or the other, besides Governmental organisations. The Political System is not only concerned with the formulation of laws and their implementation but also to get them obeyed forcibly.
Differences between State and Political System:
Following are the main differences between State and Political System
1. State has four essential elements whereas Political System has many:
The main difference between the State and Political System is that the State has four essential elements whereas Political System has many. Population, definite territory, Government and sovereignty are the four essential elements of the State. The existence of State can’t be even imagined in the absence of a single element.
But Political System has numerous elements instead of certain elements, such as, exploration of Political effects, attainment of legitimacy, influence of other subjects and Political Systems and the study of reactions. It is difficult to determine the elements of Political System since it is not a combination of particular elements but of the mutual interactions of different roles.
2. State deals with legal and institutional structure but Political System deals with the processes:
State is concerned with legal and institutional structure whereas the Political system deals with processes. Many writers presented models related to these processes which deal with Political System.
3. Scope of Political System is wider than that of State:
The scope of Political System is wider than that of State. State is mainly concerned with formal institutions whereas Political System includes processes, whether formal or informal. The boundaries of Political System are the widest ones as they are practical and based on scientific policies. According to Almond and Powell, “The Political System includes not only governmental institutions, such as legislature, courts and. administrative agencies, but all structures in these Political aspects.” The concept of Political System is wider than the concept of State.
4. Sovereignty is the main feature of State while legitimate physical coercive force is the main feature of Political System:
Internal and external sovereignty is the most important feature of State. State is omnipotent and all the citizens and institutions have to obey its orders. But the concept of sovereignty holds no importance in Political System. Modern political writers don’t believe that any Political System is free from internal and external influences. They accept the view that Political System is certainly affected by intra-societal and extra-societal environment.
Along with it, the importance of external sovereignty has lessened in the modern international age. The Political System of every country is affected by the Political Systems of other countries. Modern Political Scientists use the expression ‘Legitimate physical coercive force’ in place of Internal sovereignty. In fact, according to their view point, Political System has power to legitimate coercive force.
5. State is a traditional concept while Political System is a modern one:
State is a traditional concept and generally the concepts like State, nation, Government, Constitution, laws, sovereignty have been used in traditional Politics. But the use of the word ‘State’ and other concepts connected with it have lessened nowadays. If a writer, in modern age, uses the word ‘State’ in place of Political System, he is called traditional.
6. Political System implies the existence of interdependent parts, while the concept of State is devoid of such character:
According to Almond and Powell, “A system implies the interdependence of parts and a boundary between it and environment. By interdependence, we mean that when the characteristics of one part in a system change, all other parts and the system as a whole are affected.”
The Governmental institutions i.e. legislature, judiciary and executive , political parties, welfare groups etc. are considered parts of a Political System. When any part of it undergoes a significant change, the whole system is affected. No such characteristic is present in the concept of State.
7. Boundaries of State fixed whereas it is not possible to restrict the boundaries of the Political System:
The State has fixed boundaries. So it is possible to estimate the beginning and end of the boundaries. But Political Systems can’t be restricted in boundaries. The boundaries of Political System are the boundaries of its processes. These boundaries are liable to change.
8. States are the same everywhere, but Political Systems are different. States are the same at every place:
Whether the States are big or small, their four elements-Population, definite territory, Government and sovereignty are essential. The four elements are found in the States of India, England, Japan, China, Sri Lanka, Myanmar (Burma) and Russia. But the forms of Political System are different in various States.
9. State is Permanent while political system is dynamic:
State is permanent whereas the Political System is dynamic. State comes to an end when it is deprived of sovereignty. But the state is re-established by regaining sovereignty. Political System is dynamic and it goes on changing according to time and circumstances.
10. The concept of Political System involves the process of conversion of inputs into outputs while the concept of State deals with some specific functions:
The process of conversion of inputs into outputs is the important characteristic of Political System. David Easton is of the view that Political System is another name of the process of conversion of outputs into inputs which is related to political decisions. This process always continues in a political system. To fulfill the aim, Political System has to perform rule-making functions, rule-application functions and rule- adjudication functions. But the State has to perform particular functions. Political writers have divided the functions of the State into two categories:
(i) Compulsory functions and
(ii) Optional functions.
Some aspects of cultural, religious, moral and social life are considered beyond the jurisdiction of State. But no aspect of life, if its any part is related to politics, can be segregated from Political System.
11. Concept of Political System is more analytical than State:
State is a descriptive view-it can be explained but not analysed. But contrary to it Political system is an analytical concept. The existence of State is only in the minds of individuals and can’t be found in real life.
12. Political System is a better means of bringing integration and adaptation than the State:
Another difference between the State and political system is that Political System is a better means of bringing integration and adaptation to the state. According to Almond and Powell, “The Political System is that System of interactions to be found in all dependent societies while performing the functions of integration and adaptations.”
13. Political Socialisation and Political Culture have special importance in Political System, not for the State.
Conclusion:
In the end, we can say that State is a traditional concept whereas Political System is a modern concept. The scope of Political System is wider than that of State.
![]()
Short Answer type Questions
Question 1.
Write down the meaning of Political System. Or Which system is called Political System?
Answer:
The term political system consists of 1. Political 2. System. The word ‘Political’ reflects power or authority. The word ‘System’ is used for a set of clear interactions which have definite boundaries. According to Oxford Dictionary, ‘A system is a complete whole, a set of connected things or parts, organised body of material or immaterial things.’ Political System includes not only formal governmental structure but it also includes traditional and informal structures like kinship, caste, group, etc. Political System is related to the proper use of power. A political system is actually that which includes all legal, formal, informal, social and political elements in a society.
Question 2.
Define Political System.
Answer:
- According to Max Weber, “A political system is a human community that successfully claims the monopoly of the legitimate use of physical force within a given territory.”
- Robert A. Dahl defines political system as, “Any persistent pattern of human relationship that involves to a significant extent power, rule or authority.”
- According to Almond and Powell, “When we speak of political system, we include all interactions which affect the use of threat of legitimate coercion.”
![]()
Question 3.
Describe the functions of Political System.
Answer:
According to Almond, Political System performs two types of functions-Input functions and Output functions.
1. Input functions:
Input functions are performed by non-governmental sub-systems, society and general environment. Almond suggested four input functions of a Political System:
- Political Socialization and Recruitment.
- Interest Articulation.
- Interest Aggregation.
- Political Communication.
2. Output functions. Almond has suggested three main output functions:
- Rule Making.
- Rule Application.
- Rule Adjudication.
Question 4.
Write any four differences between State and Political System Or Distinguish between State and Political System.
Answer:
Following are the main differences between State and Political System:
1. State has four essential elements whereas Political System has many. Population, definite Territory, Government and Sovereignty are the four essential elements of the state. But Political System has numerous elements.
2. Sovereignty is the main feature of State while legitimate physical coercive force is the main feature of Political System.
3. State is permanent while Political System is dynamic.
4. States are the same everywhere, but Political Systems are different. States are the same at every place whether the States are big or small. Their four elements Population, definite territory, Government and sovereignty are essentials. But the forms of Political System are different in various States.
![]()
Question 5.
What are boundaries of a Political System?
Answer:
Each political system has boundaries which separate it from economic, social and cultural systems. Almond defines boundaries as ‘points where one political system ends and the other political system begins’. The boundaries between society and polity differ from one political system to another. The boundaries of the political system are not territorial boundaries ; these boundaries relate to human relationships and their activities. But the boundaries of a political system change from time to time.
Question 6.
Describe input functions of Political System. Or Write down the input functions of Political System.
Answer:
Almond has suggested four input functions of a Political System:
1. Political Socialization and Recruitment:
According to Almond and Powell, “Political socialization is the process through which political cultures are maintained or changed.” So the process of political socialization can be utilised for both bringing a change as well as for maintaining status-quo. The process of socialization in a system is supplemented by Recruitment.
2. Interest Articulation: In simple words, Interest Articulation is the presentation of Demands in a System.
3. Interest Aggregation:
In no political system different laws for the interests of different groups can be created. A common policy is formulated for the interests of almost all the groups.
4. Political Communication: Political communication is the most important function of a Political System.
![]()
Question 7.
Write three output functions of Political System.
Answer:
Almond has suggested three main output functions:
1. Rule Making:
There must be certain rules in the society to regulate the relationships between the individuals. In a political system the rule making function is performed by the legislature and its allied agencies.
2. Rule Application: The function of the political system is not only making rules, but also to apply them.
3. Rule Adjudication:
Whenever a rule is created, the fear of its violation is always present. Now, he who violates these rules, must be punished. This is the function of courts or the judiciary or in modern terminology, the Rule Adjudication department.
Question 8.
What is the meaning of the word ‘Political’?
Answer:
The word ‘Political’ reflects power or authority. All the interactions involved in the struggle for power are ‘Political’. Any association becomes ‘Political’ when its rules or decisions are obeyed by its members with the use of threat or physical force. According to Max Weber, “An association should be called political if and in so far as the enforcement of its order is carried out continually within a given territorial area by the application of threat or physical force.” Political includes power, influence, control or authority to a significant extent.
Question 9.
What do you mean by the term System?
Answer:
According to Oxford Dictionary, “A system is a complete whole, a set of connected things or parts, organised body of material or immaterial things.” The word system has been used and defined differently by different writers belonging to different disciplines. Ludwin Van Bertall Anfy describes system as a “Set of elements standing in interaction.”
Collin Cherry says that a system, “is a whole which is compound of many parts-an ensemble of attitudes.” According to Gabriel A. Almond ,“A system implies the interdependence of parts and a boundary between it and environment.” By environment, we mean that when the characteristics of one part in a system change, all other parts and the system as a whole are affected. The main characteristics of a system are:
- Comprehensiveness
- Interdependence
- Existence of boundaries
- Existence of sub-system
- Wholeness etc.
![]()
Question 10.
What is Interest Aggregation? Who performs this function?
Answer:
In no political system different laws for the interests of different groups can be created. A common policy is formulated for the interests of almost all the groups. The process of combining the interests of various groups is known as Interest Aggregation. According to Almond and Powell, “The functions of converting demands into general policy alternative is called interest aggregation.”
There are two ways to perform this function First by coordinating the interests of various natures and second by the recruitment of those who have faith in the one national policy. An individual wants a particular thing to be done on the basis of his interests. Interest groups aggregate the interests of various groups to make a demand.
Question 11.
What is Feedback-Loop Mechanism? Or Describe the Process of ‘Feedback-Loop’ of David Easton. Or What do you mean by Feedback Loop mechanism?
Answer:
The concept of Feedback-Loop Mechanism in Political System is given by David Easton. He says that political system is a process to convert inputs into outputs and there is a close relationship between inputs and outputs. The decisions which are made by political system in a form of outputs once again take form of raw material for inputs. This process of providing raw material to a system again and again continues. David Easton called this process Feedback-Loop Mechanism.
![]()
Question 12.
Write four main characteristics of Political System.
Answer:
The main characteristics of political system are as follows:
1. Comprehensiveness:
The political system does not include only the governmental structures, but also those formal and informal organizations which take part in one way or other in political process and influence the political authority.
2. Interdependence:
According to Almond, political system also includes the political aspects of various sub-systems. Any change in any sub-system is bound to affect functioning of other sub-systems.
3. Existence of Boundaries:
It implies that there are points where political system ends and other system begins. Each political system has boundaries which separate it from economic, social and cultural system.
4. Universality of Political System
According to Almond, all political systems whether primitive or modern or whether developing or developed, have political structure.
Question 13.
What is Interest Articulation? Or Explain the Interest Articulation function of Political System.
Answer:
In simple words, Interest Articulation is the presentation of Demands in a system. According to Almond and Powell, “The process by which individuals and groups make demands upon the political decision makers, we call, interest articulation.” Different individuals and groups present their demands or articulate their interests before those who have the right to make decisions. It is an importai?t process in the political system, because unless the groups or individuals do not present their demands before the rulers, no policy can be formulated and their demands cannot be met.
If the groups or individuals in a system are not allowed to present their demands or interests, it may lead to violent activities. Interests, in a political system, can be articulated by way of petitions, suggestions, addresses, statements, demonstrations or even violent means. Students and labour groups adopt the technique of strikes etc. The democratic system provides proper means for interest articulation to the people.
![]()
Question 14.
What do you mean by universality of Political Structures?
Answer:
According to Almond, all political systems have same structures that perform same functions though with varying degree of frequency. The articulative, aggregative and communicative functions may be performed diffusely within the society or intermittently through the kinship or lineage structure. An adequate analysis of a political system must locate and characterise all of these functions and not simply those performed by the specialised political structure.
Question 15.
Describe the multifunctionality of Political Structure.
Answer:
According to Almond, all political structures irrespective of the degree of specialization in point of time or space, are multifunctional. Multifunctionality of political structure means that a political structure performs not one type of functions but many types of functions. For example, courts not only adjudicate, they also legislate. Similarly, Legislatures not only legislate but they also perform administrative functions.
![]()
Question 16.
What do you mean by Inputs?
Answer:
According to David Easton, input in a political system is like the raw material which when supplemented by support takes the form of outputs. Easton has described two types of inputs in a political system: Demand and Support.
Very Short Answer type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the meaning of Political System.
Answer:
The term political system consists of 1. Political 2. System.
The word ‘Political’ reflects power or authority. The word ‘System’ is used for a set of clear interactions which have definite boundaries. Political System is related to the proper use of power. A political system is actually that which includes all legal, formal, informal, social and political elements in a society.
Question 2.
Give two definitions of a Political System.
Answer:
- According to Max Weber, “A political system is a human community that successfully claims the monopoly of the legitimate use of physical force within a given territory.”
- Robert A. Dahl defines political system as, “Any persistent pattern of human relationship that involves to a significant extent power, role or authority.”
![]()
Question 3.
Mention the functions of Political System.
Answer:
According to Almond, Political System performs two types of functions-Input functions and Output functions.
1. Input functions:
Input functions are performed by non-governmental sub-systems, society and general environment. Almond suggested four input functions of a Political System.
2. Output functions:
Almond has suggested three main output functions:
- Rule Making
- Rule Application
- Rule Adjudication.
Question 4.
Write down two differences between State and Political System.
Answer:
Following are the main differences between State and Political System:
- State has four essential elements whereas Political System has many. Population, definite Territory, Government and Sovereignty are the four essential elements of the state. But Political System has numerous elements.
- Sovereignty is the main feature of State while legitimate physical coercive force is the main feature of Political System.
Question 5.
Write down any two general characteristics of a political system as given by Prof. Robert A Dahl.
Answer:
- Uneven Control of Political Resources. According to Robert A. Dahl, “Control over political resources is distributed unevenly.”
- The Quest for Political Influence. In almost every political system there are some members who seek to gain influence over the policies, rules and decisions enforced by the government i.e. political influence.
![]()
Question 6.
Write two input functions of a Political System.
Answer:
Almond has suggested four input functions of a Political System:
1. Political Socialization and Recruitment:
According to Almond and Powell, “Political socialization is the process through which political cultures are maintained or changed.” So the process of political socialization can be utilized for both bringing a change as well as for maintaining status-quo. The process of socialization in a system is supplemented by Recruitment.
2. Interest Articulation. In simple words, Interest Articulation is the presentation of Demands in a System.
Question 7.
Write down any two output functions of a Political System.
Answer:
Almond has suggested three main output functions:
1. Rule Making:
There must be certain rules in the society to regulate the relationships between the individuals. In a political system the rule making function is performed by the legislature and its allied agencies.
2. Rule Application: The function of the political system is not only making rules, but also to apply them.
Question 8.
What do you mean by Interest Aggregation?
Answer:
The process of combining the interests of various groups is known as Interest Aggregation. According to Almond and Powell, “The functions of converting demands into general policy alternative is called interest aggregation.”
Question 9.
Explain the Feedback-Loop System.
Answer:
The concept of Feedback-Loop Mechanism in Political System is given by David Easton. He says that political system is a process to convert inputs into outputs and there is a close relationship between inputs and outputs. The decisions which are made by political system in a form of outputs once again take form of raw material for inputs. This process of providing raw material to a system again and again continues. David Easton called this process Feedback-Loop Mechanism.
![]()
Question 10.
Write two main characteristics of Political System.
Answer:
1. Comprehensiveness:
The political system does not include only the governmental structures, but also those formal and informal organizations which take part in one way or other in political process and influence the political authority.
2. Interdependence:
According to Almond, political system also includes the political aspects of various sub-systems. Any change in any sub-system is bound to affect functioning of other sub-systems.
Question 11.
Explain Interest Articulation.
Answer:
In simple words, Interest Articulation is the presentation of Demands in a system. According to Almond and Powell, “The process by which individuals and groups make demands upon the political decision makers, we call, interest articulation.”
Question 12.
Who wrote the book “The Political System’ and when?
Answer:
The book ‘The Political System’ was written by David Easton in 1953.
Question 13.
What do you mean by Political Communication?
Answer:
Political Communication is the most important function of a Political System. It is through this process that other functions are performed. Everybody, whether a citizen or an official, has to depend upon information, because all activities in a system are to be regulated on the basis of information. That is why in a democratic system there is too much of emphasis on the freedom of press, speech and expression, whereas it is crushed or controlled in a totalitarian system.
![]()
Question 14.
Who is the author of The Process of Government’?
Answer:
Arthur Bentley is the author of ‘The Process of Government’.
One Line Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the meaning of the word ‘Political’ in Political System.
Or
What is meaning of word ‘Politics’ in the Political System?
Answer:
A community or an association is called political if its orders are enforced by the administrative staff through coercion or physical force.
Question 2.
Give the meaning of system.
Answer:
The word ‘System’ is used to indicate a group of interactions.
Question 3.
Write the meaning of Political System.
Answer:
A political system means that persistent pattern of relationships whose conduct involves authority or power.
Question 4.
Write any one definition of Political System.
Answer:
David Easton has said, “Political system is a set of interactions abstracted from the totality of social behaviour, through which authoritative values are allocated for a society.”
![]()
Question 5.
Write one feature of Political System.
Answer:
Political system is found in every society.
Question 6.
Write down one output function of the Political System.
Answer:
Rule making is an important output function of a Political System.
Question 7.
Write any one input function performed by a Political System.
Answer:
Political Socialisation and Recruitment.
Question 8.
Mention any one difference between State and Political System.
Answer:
A political system has interdependence of parts but a state does not have any such feature.
Question 9.
What do you mean by Feedback Loop Mechanism? Explain.
Answer:
Feedback means to reprocess the results of the outputs as inputs in the system.
![]()
Question 10.
Write the definition of Political System given by Almond and Powell.
Answer:
Almond and Powell has stated, “When we speak of political system, we include all interactions which affect the use or threat of legitimate coercion.”
Question 11.
Who is the writer of famous book ‘The Political System’?
Answer:
David Easton.
Question 12.
Which political thinker used the term “The Political System’ first time?
Answer:
David Easton.
Question 13.
Write any one difference between State and Political System.
Answer:
There are four elements of State, but elements of political system are not fixed.
Question 14.
What is Interest Articulation?
Answer:
In simple words, Interest Articulation is the presentation of Demands in a system. According to Almond and Powell, “The process by which individuals and groups make demands upon the political decision makers, we call interest articulation. ”
![]()
Question 15.
What is Interest Aggregation?
Answer:
The process of combining the interests of various groups is known as Interest Aggregation.
Question 16.
What do you mean by ‘Rule Making Function’?
Answer:
There must be certain rules in the society to regulate the relationships between the individuals. In a political system the rule-making function is performed by the Legislature and its allied agencies.
Question 17.
What is ‘Rule Adjudication Function’?
Answer:
Almost every rule contains in itself the punishment for those, who violate it. But before such a punishment is given to any individual it must be established that he had actually violated the rule of the land. This is the function of courts or the judiciary or in modern terminology, the Rule Adjudication department.
Question 18.
What is ‘Rule Application Function’?
Answer:
In a political system ‘Rule application’ is the responsibility of bureaucracy. Even the judicial decisions are implemented by the civil servants. Sometime this function is performed by the rule-making department also. But in a developed political system the two functions are performed by separate departments.
![]()
Question 19.
Write two input demands.
Answer:
1. Demand for the allocation of goods and services.
2. Demand for regulation of behavior.
Fill In The Blanks
1. The concept of Feedback Loop Mechanism is given by ………………… .
Answer:
David Easton
2. ‘The Political System’ of David Easton was published in ………………… .
Answer:
1953
3. Political System is found in every ………………… .
Answer:
society
4. Rule making is an important ……………… function of a Political System.
Answer:
output
5. Political Socialisation and Recruitment is an ……………… function performed by Political System.
Answer:
input.
![]()
True Or False Statement
1. Almond Powell is the writer of famous book ‘The Political System’.
Answer:
False
2. David Easton is the writer of famous book The Political System’.
Answer:
True
3. The concept of Political System originated in the 20th century.
Answer:
True
4. There are four elements of Political System.
Answer:
False
![]()
Choose The Correct Answer
Question 1.
Who is the writer of famous hook The Political System’?
(a) David Easton
(b) Almond
(c) Max Weber
(d) Lasswell.
Answer:
(a) David Easton
Question 2.
The concept of Political System originated in the:
(a) 19th Century
(b) 18th Century
(c) 20th Century
(d) 17th Century.
Answer:
(c) 20th Century
Question 3.
Who gave the concept of Feedback Loop Mechanism?
(a) Almond
(b) David Easton
(c) Lasswell
(d) Max Weber.
Answer:
(b) David Easton
![]()
Question 4.
Which of the following is not a feature of Political System?
(a) Political System is found in developed countries.
(b) Political System is found in every society.
(c) Political System has interdependence of parts.
(d) Universality of Political System.
Answer:
(a) Political System is found in developed countries.