Punjab State Board PSEB 6th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 10 Practical Geometry Ex 10.1 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Practical Geometry Ex 10.1
1. What is the use of instrument ruler?
Solution:
We use instrument ruler to draw line segment and to measure their lengths.
![]()
2. What is the use of protractor?
Solution:
We use a protractor to draw and measure angle.
3. What is the use of compasses?
Solution:
We use compasses to mark equal lengths, draw arcs and circles.
4. Construct the following angles using set squares.
Question (i)
(i) 30°
(ii) 45°
(iii) 60°
(iv) 75°
(v) 90°.
Solution:
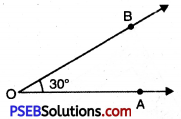
(i) Steps of Construction:
1. Draw a ray OA.
![]()
2. To construct an angle of 30° we use 30° set square. Place the set square in such a way that one of its edges containing the 30° angle coincides with the ray OA as shown in the figure.
3. Draw a ray OB starting from the vertex O along the 30° edge of the set square as shown in figure.
4. Remove the set square.
Thus, the required \(\angle \mathrm{AOB}\) = 30°.
![]()
(ii) Steps of Construction:
1. Draw a ray OA.
![]()
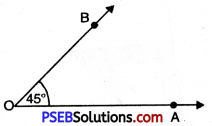
2. To construct an angle of 45° we use 45° set square.
Place a 45° set square along ray OA as shown in the figure.
3. Draw a ray OB starting from the vertex O along 45° the, edge of set square.
4. Remove the 45° set square. Thus, the required \(\angle \mathrm{AOB}\) = 45°
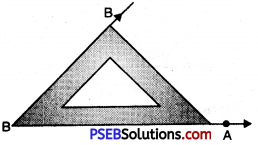
(iii) Steps of Construction.
1. Draw a ray OA.
![]()
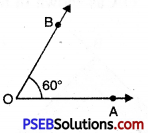
2. To construct an angle of 60°. We use 30° set square.
Place a 30° set square with 60° edge along ray OA as shown in the figure.
3. Draw a ray OB starting from the vertex O along 60° edge of the set square.
4. Remove the 30° set square. Thus the required \(\angle \mathrm{AOB}\) = 60°.
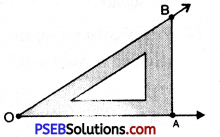
(iv) Steps of Construction
1. Draw a ray of OA.
![]()
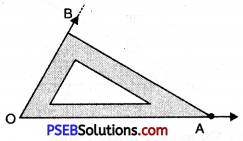
2. To draw angle of 75° we use both set squares in combination as 45° + 30° = 75°.
Place 45° set square with 45° edge along OA
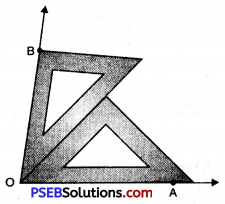
3. Place 30° set square adjacent to 45° set square as show. Draw a ray starting from the vertex O along the edge of 30° set square.
4. Remove both the set squares. Thus required \(\angle \mathrm{AOB}\) = 75°.
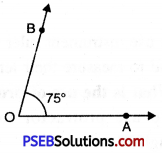
![]()
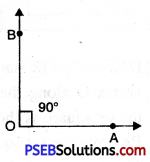
(v) Steps of Construction
1. Draw a ray OA.
![]()
2. To construct angle of 90° place any set square with 90° corner at O along OA.
3. Draw a ray OB starting from the vertex O along 90° edge of the set square.
4. Remove the set square. Thus, the required \(\angle \mathrm{AOB}\) = 90°.