Punjab State Board PSEB 7th Class Social Science Book Solutions Geography Chapter 3 Atmosphere and Temperature Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Geography Chapter 3 Atmosphere and Temperature
SST Guide for Class 7 PSEB Atmosphere and Temperature Textbook Questions and Answers
I. Answer the following questions in about 1-15 words.
Question 1.
What do you understand by the atmosphere?
Answer:
There is a big protective balloon around the earth with a radius of almost 1600 kins. But the breatheable air (99%) is in the radius of 32 kms only.
Question 2.
Why we study atmosphere in Geography?
Answer:
Because atmosphere is the factor which mostly affects the life on earth.
Question 3.
Which is called Tropopause limit?
Answer:
The upper limit of stratosphere is known as tropopause limit.
Question 4.
What do you understand by Exosphere?
Answer:
The outer layer of atmosphere is called Exosphere. We don’t know much about this layer. Only this much is known that this layer contains very light gases like Hydrogen and Helium.
![]()
Question 5.
What are the elements other than the gases present in the atmosphere?
Answer:
Water vapours and dust particles besides gases which are present in atmosphere.
Question 6.
What is air pollution?
Answer:
Every year, thousand tons of pollutants accumulate in atmosphere. These pollutants are not natural. This man-made activity is called air pollution. It is of two types—Solid and Gas.
Question 7.
What is temperature and what are the units of measuring the temperature?
Answer:
In the air, the current heat element is called its temperature. Like the air temperature, the element of current heat inside something or organism is also called temperature. The temperature remains fluctuating.
Units of measureing temperature are :
- Celsius Scale
- Fahrenheit Scale.
Question 8.
Why is temperature very high on the Equator?
Answer:
On the equator, the’ sun rays are very -straight, so the temperature is more.
II. Give answers to the following questions in about 50-60 words.
Question 1.
What are the main factors that cause air pollution?
Answer:
1. Solid factors:
- Volcanoes pollute air through dust particles,
- In cities, many solid particles are emitted into air by man-made activities.
- After fuel combustion, the carbon particles accumulate in the air.
- The factories emit dust pollutants which contains Asbestos—a dangerous source of pollution.
2. Gaseous factors:
- The fumes emitted by motor vehicles is a dangerous source of air pollution.
- There is an extremely poisonous gas called carbon monoxide in the atmosphere where there is a maximum of transportation vehicles.
- Smog is another air pollutant that is a combination of smoke and fog.
- Another main reason for air pollution is the less ozone in the air.
Question 2.
What we call the lower layer of the atmosphere?
Answer:
The lower layer is called troposphere. This is the most dense layer of the atmosphere. It is actually an oval-shaped construction around the earth. Its average height is 12 kms. On the equator, it is almost 16-18 kms in height while at the poles, it is almost 6-8 kms. This layer always remains disturbed because all the activities like rainfall, clouds, thunder storms, etc. take place in this layer only. Most of the water vapours are also found in troposphere. 75% of air is found in the troposphere. When we move up the troposphere, the temperature decreases and the rate of decrease is 6.5 Celsius per km.
![]()
Question 3.
Write the ratio of main gases in the air.
Answer:
Air is actually a mixture of gases. Main gases are Nitrogen and Oxygen. Other important gases are argon, Carbon dioxide and Hydrogen. Nitrogen is almost 78.03%, Oxygen is 20.99%, Argon is 0.94%, Carbon dioxide is 0.03% and Hydrogen is almost 0.01%. In the whole atmosphere, more or less the quantity of gases almost remains stable. But as the height increases, the percentage of these gases decreases.
Question 4.
In which layer of the atmosphere the ozone gas exists? Why is it so important?
Answer:
In the atmosphere, ozone gas is found in stratosphere.
Importance It is a very important gas because it protects the live-world from the dangerous ultraviolet rays of the sun. It absorbs the heat from sun and the heat remains in the stratosphere. The upper layer of stratosphere remains heated as a consequence.
III. Fill in the Blanks :
Question 1.
As we go up to the hills, the temperature ___________
Answer:
decreases
Question 2.
The main sources of the temperature are ___________ and ___________
Answer:
sun, internal parts of earth
Question 3.
The ozone gas absorbs ___________ rays.
Answer:
ultraviolet
![]()
Question 4.
The electrically charged particles are found in ___________ layer.
Answer:
ionosphere
Question 5.
The wireless communication system works under ___________ waves.
Answer:
radio
Question 6.
___________ gas is found in maximum quantity in atmosphere.
Answer:
Nitrogen.
IV. Things to do:
Question 1.
What rules should be followed to avoid air pollution, prepare a chart and put it in your classroom.
Answer:
Do it yourself.
Question 2.
Draw a diagram of atmosphere showing different layers.
Answer:
Do it yourself.
PSEB 7th Class Social Science Guide Atmosphere and Temperature Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions :
Question 1.
Trade winds are called :
(a) Seasonal winds
(b) Permanent Winds
(c) Local Winds
(d) Western Winds.
Answer:
(b) Permanent Winds.
![]()
Question 2.
The most important layer of the atmosphere is :
(a) Troposphere
(b) Tropospause
(c) Stratosphere
(d) Stratopause.
Answer:
(a) Troposphere.
Question 3.
How much percentage of atmosphere is made up of oxygen gas?
(a) 10.95%
(b) 20.95%
(c) 25.95%
(d) 30.55%.
Answer:
(6) 20.95%.
Question 4.
Which is the closest layer to the earth?
(a) Stratosphere
(b) Troposphere
(c) Mesosphere
(d) Excosphere.
Answer:
(b) Troposphere.
Question 5.
Which winds are seasonal winds?
(a) Trade
(b) Permanent
(c) Monsoons
(d) Westerlies.
Answer:
(c) Monsoons.
Fill in the Blanks :
Question 1.
Atmosphere is a mixture of different ___________
Answer:
Gases
![]()
Question 2.
Nitrogen and ___________ are the two main gases of atmosphere.
Answer:
Oxygen
Question 3.
___________ layer is the closest to the earth.
Answer:
Troposphere
Question 4.
The uppermost layer of stratosphere is called ___________
Answer:
Tropopause
Question 5.
___________ is the unit of measuring the temperature.
Answer:
Farenheit Scale.
True / False :
Question 1.
The big protective layer surrounding the earth is called lithosphere.
Answer:
False
Question 2.
On the equator temperature is very high.
Answer:
True
![]()
Question 3.
Troposphere is the upper most layer of the atmosphere.
Answer:
False
Question 4.
Weather is the day to day phenomena.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
During day time earth’s surface attracts sun rays.
Answer:
True
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write the elements of Atmosphere.
Answer:
Air, temperature, humidity, air pressure, etc.
Question 2.
What is temperature?
Answer:
In the air, the current heat element is called its temperature. Like the air temperature, the. element of current heat inside something or organism is also called temperature. The temperature remains fluctuating.
![]()
Question 3.
Write the importance of the following gases.
Answer:
- Nitrogen: It is found in the lower layer of the atmosphere. This gas helps the flora from dying.
- Oxygen: It protects the flora and fauna which cannot survive without oxygen.
- Carbon dioxide: Carbon dioxide protects the flora. It makes a blanket around the earth and does not let the heat escape from the atmosphere.
Question 4.
What is the importance of water vapours?
Answer:
The water vapours play a great role in changing the temperature.
Question 5.
What is condensation?
Answer:
When the air heats up it expands and becomes lighter and goes up in the air. The heavy air comes down and takes the base of displaced air. This process goes on and takes the form of a cycle. This cycle is known as condensation process.
Question 6.
As we move up the mountains, the temperature decreases. Why?
Answer:
The reason for less temperature at high places is that rays from the sun first heat up the surface and then heat up the atmosphere. So, the atmosphere near the earth’s surface becomes hot quickly and the upper part becomes less hot. This is the reason when we go up the mountains the temperature decreases.
Question 7.
(a) Write a note on ozone layer of the atmosphere.
Answer:
Ozone layer: A thick layer of ozone gas exists in upper atmosphere. This layer is useful as it absorbs ultraviolet rays of the sun.
(b) Why is it depleting? Where has been a hole in this layer found?
Answer:
ue to excessive use of chemicals and carbons (which react with ozone layer) the ozone layer is being depleted. This atoms explosions also deplete the ozone layer. In 1980, a hole in the ozone layer was noticed over Antarctica,
(c) What are its harmful effects?
Answer:
Through this hole, ultra-violet rays will reach the earth. These rays are harmful as these cause skin cancer. It may cause blindness.
![]()
Question 8.
“The atmosphere acts as a blanket or a glass-house.’ Discuss.
Answer:
Atmosphere acts like a blanket keeping the earth warm. It absorbs incoming solar radiation and does not allow radiation to escape. So equable temperatures are found.
Question 9.
Name the layers of atmosphere.
Answer:
- Troposphere
- Stratosphere
- Mesosphere
- Thermo-sphere.
Question 10.
Why there is difference in day time and night time temperature?
Answer:
During day time, earth’s surface attracts sun rays and at night, releases the heat absorbed. So at night, the temperature is low as compared to the day.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the Greenhouse effect of the atmosphere.
Answer:
The atmosphere is heated by the radiation from the earthy surface flow. This action is compared to that of a glass house on greenhouse in which vegetables and flowers are grown in polar areas. Glasshouse permits radiations to get in but does not allow radiation to escape out. Therefore glass house is warmer from inside than outside. The atmosphere also acts like a blanket keeping the earth warm. It is known as the greenhouse effect of atmosphere. This is due to presence of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide has the ability to absorb earth radiation. The carbon dioxide layer acts as a glass roof of the greenhouse. With the increase in carbon dioxide, the temperature of the earth is increasing. Due to this, the year 1955 was the hottest year in India during this century.
Question 2.
What is global warming? What are its causes? State its effects.
Answer:
Global warming. The burning of fossil fuels (coal, gas, petroleum), the cultivation of soil, large scale industrialisation, rapid means of transport and deforestation has caused an imbalance in the atmosphere. These activities are increasing the amount of carbon dioxide. Thus greenhouse effect has raised the average, the temperature of the earth by 0.5° C. By the year 2050, the earth’s average temperature will go up by 2°C. This is called global warming. Global warming is causing a rise in sea levels due to melting of glaciers. It is threatening to submerge many coastal areas.
![]()
Question 3.
Write a note on Environmental pollution.
Answer:
Environmental pollution has become a serious problem for mankind. It is threatening the existence of mankind. The composition of air is being altered by undesirable chemical, physical and biological elements. It is known as air-pollution.
Pollutants: The common pollutants found in air are as follows :
- Deposited matter like soot, smoke, sand-dust.
- Gases like sulphur, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxide, Ammonia, Flourine, etc.
- Chemical Compounds like arines, phosgenes, detergents.
- Metals like lead, iron, zinc, mercury.
- Sewage.
- Radio-active substances.
- Noise and heat.
A. Atmospheric Pollution: Atmosphere is of fundamental importance for our existence. Due to industrial revolution, the atmospheric pollution is increasing gradually. It has harmed the ultra-violet shielding ozone layer. The addition of heat-trapping greenhouse gases will cause a disaster.
The volcanic eruptions, forest fires, natural decay of organic and inorganic matter is causing visibility. Smoke is injurious to health. Acid rain has changed the composition of air and water.
Fossil Fules: The buring of fuels and chemicals is increasing the amount of carbon dioxide in atmosphere. It has increased by 25%. With the result, the average temperature of the earth is increasing. It has increased 0.3°C to 0.7°C during the last century. Deforestation has also led to increase in carbon-dioxide. The increasing use of fuels in vehicles has increased the amount of sulphur dioxide, carbon monoxide and has created many respiratory diseases.
B. Water Pollution: Water is another indispensable source of our life. Pollution of water has caused far-reaching implications. It is a serious problem in metropolitans like Delhi, Kolkata and Mumbai. It not only affects the water of rivers, tanks and lakes; but also ocean water.
The following factors affect water pollution
- Domestic sewage .
- Industrial wastes
- Agricultural activities
- Thermal pollution
- Marine pollution.
C. Land Pollution: Land is one of the most important components of life support system. Land is degrading due to overuse from centuries depletion of land is caused by :
- Soil erosion
- Pollutant.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain in detail the layers of atmosphere.
Answer:
It is estimated that the atmosphere is spread up to a radius of 1600 kms. It can be divided into four main layers described as follows :
1. Troposphere: This is the lowermost layer of atmosphere and is closest to the earth. Its average height is 12 km. Most of the clouds, water vapours and dust particles are found in this layer. This is the weather-making layer and favours human life. The temperature decreases in this layer at the rate of 1°C for every 165 metres.
2. Stratosphere: This layer lies next to the troposphere. Its height ranges from 12 to 80 km. The temperatures are very low and fairly constant. It is free from clouds, dust particles and convection currents.
3. Ozonosphere: This is a zone of ozone gas. It absorbs ultraviolet rays of the sun. It has high temperature. It is known as thermosphere also.
4. Ionosphere: This layer extends upto a height of 800 kms. Ozone gas, lone gas electrons and atoms are found in this layer. This layer absorbs ultraviolet rays of the sun and reflects radio waves.
5. Exosphere: This is the uppermost layer of the atmosphere. Its upper height is unknown due to inaccessibility. It is a highly rarefied layer. It is known only to aerospace-ships.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the composition of atmosphere.
Answer:
Composition of the Atmosphere. The atmosphere mainly consists of a mixture of gases in a fairly constant composition.
The atmosphere is composed of the following three elements :
1. Gases: Nitrogen and Oxygen are the two major gases found in the atmosphere. In pure dry air, Nitrogen occupies 78% and Oxygen occupies 21% by volume. The remaining 1% is composed of a number of gases like Hydrogen, Argon, Ozone, Helium, Carbon dioxide. The proportions of the gases remain constant.
Active gases: Oxygen, Nitrogen, Hydrogen, Carbon dioxide, Ozone are active gases. Oxygen is the most vital gas for sustaining life. Nitrogen and Carbon dioxide are essential for plant life and help in the process of Photosynthesis.
Inert Gases: Argon, Neon, Helium, Krypton are inert gases which are not so effective.
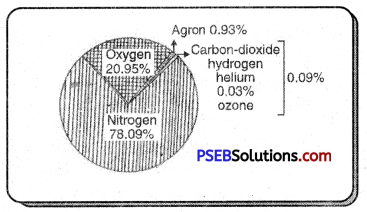
Atmosphere: Composition
| Gas | % of total Atmosphere | Height in km. |
| Nitrogen | 78.03% | 125 |
| Oxygen | 20.95% | 95 |
| Argon | 0.93% | – |
| Carbon dioxide | 0.03% | 30 |
| Hydrogen | 0.01% | 200 |
| Other gases | 0.05% | – |
| Total | 100.00% | – |
It shows that Nitrogen (N2) alone occupies about four-fifths of air by volume and oxygen (02) one-fifth. In addition to the above, other gases like Neon, Methane, Krypton and Radon are also present in the atmosphere. The atmoshpere is odourless, colourless and tasteless. It is mobile, elastic, both compressible and expandable. It is invisible but, it has weight and pressure.
2. Water Vapour: Water vapour represents 2% of the air by volume. It is mostly found in the lower layers of the troposphere. About half the water vapour in the air lies below an altitude of 2000 metres. It is of primary importance to man. It absorbs insolation. It is the source of all condensation and precipitation on the earth. Water vapour, an unstable element is obtained from oceans, lakes, rivers and other water bodies.
3. Dust Particles: The atmosphere holds in suspension many dust particles whose sizes vary. The major source of dust particles are deserts, lake beds, beaches and dry river beds. These are found in the lower layer of the atmosphere. These affect sun rays by scattering and absorbing insolation. These are responsible for the formation of clouds, fog and smog. Solid particles like carbon, salt, pollen grains, etc. are also found in the lower layers of the atmosphere.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain in detail the factors affecting the temperature of a place.
Answer:
Temperature is never stable. It goes on changing with time and place. Many factors affect the temperature which are as follows :
1. Distance from the Equator: On the equator the sun rays are straight. So, the heat is more and as a result the temperature is more. As we move towards polar regions the sun rays become .slant and as a result these regions are cold and the temperature is very less.
2. Height from Sea Level: The place which is higher than the sea level has less temperature. The reason is that when we near the sea coast the air is dense but as we move up the air becomes thin. So, the high places have low temperature, e.g. Shimla is at a more height than Chandigarh. So, the temperature of Shimla is less than the temperature of Chandigarh.
3. Distance from Sea: In comparison to land, the water beats up early. So, the places which are near the sea the temperature is neither more nor less. But the places which are away from the sea, there the temperature is less in winter and more in summer, e.g. Mumbai has stable temperature because of its closeness to sea. Whereas, Amritsar is very far away from sea and as a result there is much difference in summer and winter temperature.
4. Sea Waves: The sea waves are of two types hot and cold. Where the hot waves flow the temperature there increases and where the cold waves flow the temperature there decreases.
5. Winds: The winds that come from sea are full of water vapours and produce rainfall. As a result the temperature becomes less. On the other hand the winds coming from dry areas increase the temperature of places which come in their contact.
6. Direction of Mountains: The mountains which are horizontal to the direction of winds they cannot stop the watery winds and as a result no rainfall happens there. But the areas with vertical mountains to the wind direction can stop the winds and cause rainfall.
7. Slope of Mountains: The mountain’s slope facing the sun had more temperature. While the other side of the mountains has no temperature.
8. Types of Soil: The sandy soil heats up quicker than the clay. So, in the arid areas the temperature in the daytime, is more. But in the nighttime, it is less.
9. Clouds and Rains: The places where there are more clouds and rains have less temperature because clouds stop the sunlight from reaching the earth directly. As a result, the temperature is less. Similarly, the rains also decrease the temperature.
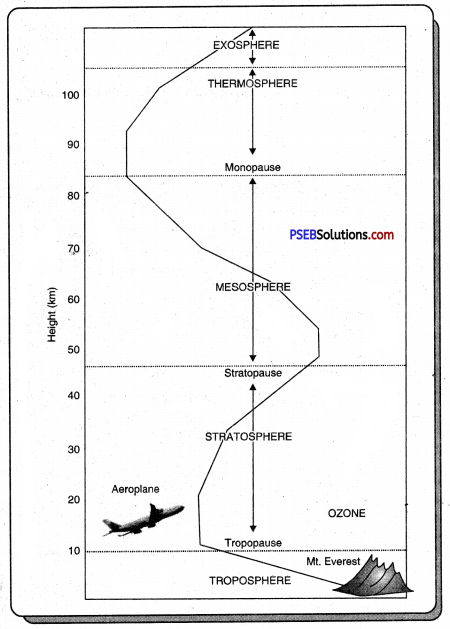
Layers of Atmosphere
