Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 4 Practical Geometry Ex 4.3 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 Practical Geometry Ex 4.3
1. Construct the following quadrilaterals:
Question (i).
Quadrilateral MORE
MO = 6 cm
OR = 4.5 cm
∠M = 60°
∠O = 105°
∠R = 105°
Solution:
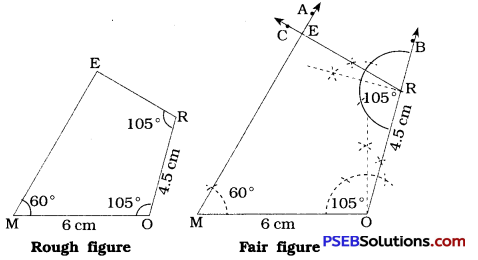
- Draw a line segment MO = 6 cm.
- At M, draw \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{MA}}\), such that ∠OMA = 60°
- At O, draw \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OB}}\) such that ∠MOB = 105°.
- With O as centre and radius = 4.5 cm, draw an arc intersecting \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OB}}\) at R.
- At R, draw \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{RC}}\) such that ∠ORC = 105°.
- Locate E at intersection of \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{RC}}\) and \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{MA}}\).
Thus, MORE is the required quadrilateral.
![]()
Question (ii).
Quadrilateral PLAN
PL = 4 cm
LA = 6.5 cm
∠P = 90°
∠A = 110°
∠N = 85°
Solution:
[Note : In □ PLAN, m∠P = 90°, m∠A = 110° and m∠N = 85°)
∴ m∠L = 360°- (m∠P + m∠A + m∠N)
= 360° – (90° + 110° + 85°)
= 360° – 285°
= 75°
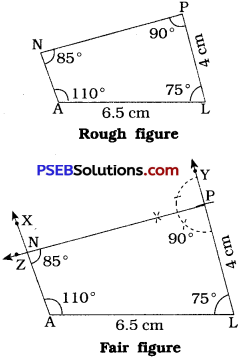
Steps of construction:
- Draw a line segment AL = 6.5 cm.
- At A, draw \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{AX}}\) such that ∠XAL = 110°. (Use protractor)
- At L, draw \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{LY}}\) such that ∠YLA = 75°. (Use protractor)
- With L as centre and radius = 4 cm, draw an arc intersecting \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{LY}}\) at P.
- At P, draw \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{PZ}}\) such that ∠ZPL = 90°. (∵ ∠ ZPY = 90°)
- Locate N at intersection of \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{AX}}\) and \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{PZ}}\).
Thus, PLAN is the required quadrilateral.
![]()
Question (iii).
Parallelogram HEAR
HE = 5 cm
EA = 6 cm
∠R = 85°
Solution:
[Note : □ HEAR is a parallelogram.
Opposite sides of parallelogram are of equal lengths.]
HE = 5 cm, ∴ AR = 5 cm, EA = 6 cm, ∴ HR = 6 cm
Adjacent angles of a parallelogram arc supplementary.
m∠R = 85° (given)
∴ m∠H = 180° – 85° = 95°
Opposite angles of a parallelogram are of equal measures,
m ∠ R = 85°
∴ m ∠ E = 85°
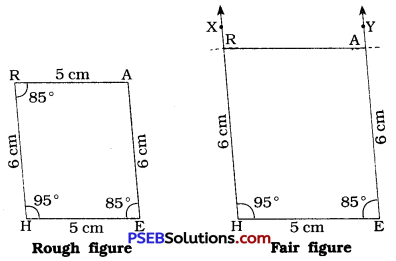
Steps of construction:
- Draw a line segment HE = 5 cm.
- At H, draw \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{HX}}\), such that ∠ XHE = 95°. (Use protractor)
- With H as centre and radius = 6 cm, draw an arc intersecting \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{HX}}\) at R.
- At E, draw \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{EY}}\) such that ∠ HEY = 85°. (Use protractor)
- With E as centre and radius = 6 cm, draw an arc intersecting \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{EY}}\) at A.
- Draw \(\overline{\mathrm{AR}}\).
Thus, HEAR is the required parallelogram.
![]()
Question (iv).
Rectangle OKAY
OK = 7 cm
KA = 5 cm
Solution:
[Note: Here, OKAY is a rectangle. Opposite sides of a rectangle are of equal lengths.]
OK = 7 cm, ∴ AY = 7 cm and KA = 5 cm, ∴ OY = 5 cm
Moreover, all angles of a rectangle are right angles.
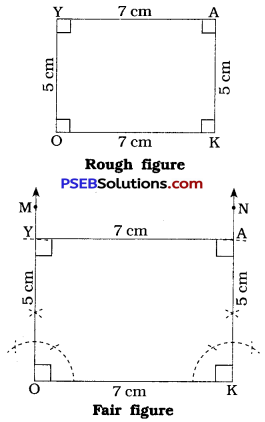
Steps of construction:
- Draw a line segment OK = 7 cm.
- At O, draw \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OM}}\) such that ∠ MOK = 90°.
- With O as centre and radius = 5 cm, draw an arc intersecting \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OM}}\) at Y.
- At K, draw \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{KN}}\) such that ∠ NKO = 90°.
- With K as centre and radius = 5 cm, draw an arc intersecting \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{KN}}\) at A.
- Draw \(\overline{\mathrm{AY}}\).
Thus, OKAY is the required rectangle.
