This PSEB 9th Class Science Notes Chapter 6 Tissues will help you in revision during exams.
PSEB 9th Class Science Notes Chapter 6 Tissues
→ A cell is the structural and functional unit of life, while the group of cells coordinating to perform a specific function is called tissue.
→ The scientific study of tissues is called histology.
→ A cluster of cells called a tissue is arranged and designed so as to give the highest possible efficiency as tissues have provided division of labor in multicellular organisms.
→ A Group of tissues is called an organ.
→ A Group of organs constitute an organ system.
![]()
→ Due to improved organisation, higher efficiency, multicellular organisms have higher survival value.
→ Plant Tissues:
- Most of the plant cells are dead which provides mechanical strength and needs less maintenance.
- In plants, there is some tissue that continue dividing.
- On the basis of the power of division of cells, plant tissues are of two types: Meristematic tissues and permanent tissues.
- Meristematic tissue has the power of division throughout life, so helps in the growth of the plant but in some specific regions.
- Meristematic tissue is of three types: apical, lateral, and intercalary.
- Meristem is of two types depending upon the power of division: primary meristem and secondary meristem.
- Simple Permanent tissue has lost the division power and is of three types: Parenchyma, Collenchyma, and Sclerenchyma.
- Tissue may be simple or complex.
- Xylem and phloem are complex tissues.
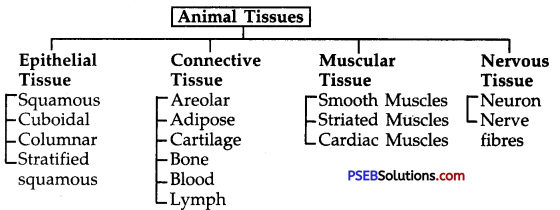
→ Animal Tissues:
- On the basis of their functions, animal tissues are of four types: Epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissue.
- The muscles of the heart show rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout life.
- The functional combination of nerve and muscle tissue is fundamental to most animals.
- This combination enables the animals to move rapidly in response to stimuli.
→ Tissue: A group of similar or dissimilar cells alongwith intercellular substances coordinating to perform a specific function. Blood, phloem, and muscles are examples of tissues.
→ Meristematic tissue: The immature cells which are in a state of division and growth with no intercellular spaces.
→ Meristem: A group of cells capable of dividing to form new cells.
→ Companion cells: These are narrow, elongated, and nucleated cells that are connected to sieve tube cells.
![]()
→ Phloem Parenchyma: Parenchyma tissue associated with phloem.
→ Tendon: A band of white fibres surrounded by connective tissue sheath which joins muscles to bone.
→ Sarcolemma: Surface covering of striated muscle fibres.
→ Sarcoplasm: Cytoplasm of a muscle fibre.
→ Sarcomere: A structural and functional unit of muscle fibre.
→ Chlorenchyma: The type of parenchyma cells having chloroplast and carrying out photosynthesis.
→ Actin: It is a type of protein present in muscle fibres.
→ Bone marrow: A hemopoietic tissue inside the marrow cavity of the bones.
→ Cartilage: An elastic skeletal tissue that acts as a shock absorber.
→ Neurilemma: It is a covering around nerve fibres formed of Schwann cells.
→ Ligament: A band of yellow fibres surrounded by connective tissue sheath which joins bone to bone.
→ Osteoblasts and Osteocytes: They are bone-forming and bone cells respectively.
→ Schwann Cells: Cells around nerve fibres that form neurilemma.
→ Blood platelets: Blood corpuscles that help in blood clotting at an injury.
![]()
→ Axon: An efferent nerve process of a neuron.
→ I-band: It is a thin band of multiple fibres formed of actin protein.
→ Epithelial tissue: An animal covering and protective tissue.
→ Histology: Microscopic study of tissues.
→ Xylem: A compound tissue formed of tracheids, vessels, parenchyma, and fibres, and helps in the conduction of water and minerals in the plants.
→ Phloem: A compound tissue formed of sieve tube cells, companion cells, parenchyma, and fibres, and helps in the conduction of food in the plants.
→ Tracheids: These are elongated dead cells with large cavities and possess highly lignified cell walls.
→ Sieve tubes: These are tubular cells with perforated walls.
→ Vessels: These are composed of many cells joined end to end with their perforated walls to give a tube-like appearance.
