Punjab State Board PSEB 9th Class Science Important Questions Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life Important Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
PSEB 9th Class Science Guide The Fundamental Unit of Life Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
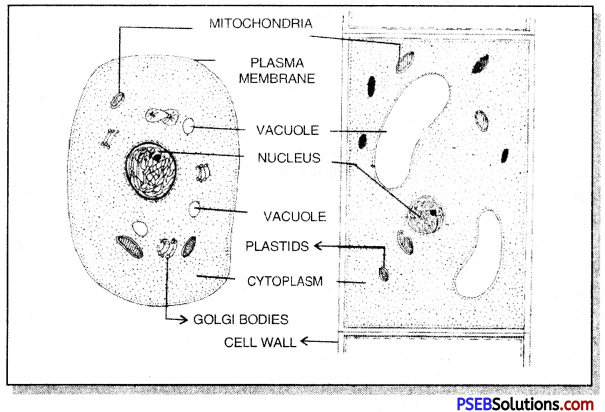
Make a comparison to write down ways in which plant cells are different from animal cell.
Answer:
| Features | Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
| 1. Cell wall | Cell wall is formed of cellulose. | Cell wall is absent. |
| 2. Centrosome | Absent. | Present. |
| 3. Vacuoles | Large-sized and many present, small-sized. | Generally absent but if only a few. |
| 4. Plastids | Present. | Absent. |
| 5. Reserve food | In the form of starch and paramylon. | In the form of glycogen |
| 6. Nucleus | Central. | Acentric away from centre. |
![]()
Question 2.
How is prokaryotic cell different from a eukaryotic cell?
Answer:
Differences between prokaryotic cell and eukaryotic cell
| Prokaryotic cell | Eukaryotic cell |
| 1. Found in Bacteria, blue-green algae and , Mycoplasma.
2. Primitive nucleus called nucleoid present. Chromosome is single, circular and double-stranded DNA but no proteins (so naked), No nuclear membrane. 3. Cell wall when present, it is formed of peptidoglycan. 4. Membrane-bound Cell-organelles like mitochondria, plastids, E.R., golgi bodies etc. is absent. 5. Ribosomes are of 70 S type. 6. Small-sized (1 – 10 um). 7. Cell division by fission or budding. |
2. A true nucleus present. Chromosomes are two to man, linear and formed of DNA and histones. Nuclear membrane present. 3. Cell wall when present in plant cells it is formed of cellulose. 4. Membrane-bound Cell-organelles like mitochondria, plastids, E.R., golgi bodies etc. is present. 5. Ribosomes are of 80 S type. 6. Large-sized (5 – 100 /un). 7. Cell division bv mitosis and meiosis. |
Question 3.
What would happen if a plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down?
Answer:
Plasma membrane maintains the shape and protects the organelles. If it gets ruptured the internal organisation will be lost and it will not be able to perform its function. Then cell wall die and contents of cell will get disintegrated.
Question 4.
What would happen to the life of a cell if there was no Golgi apparatus?
Answer:
1. The Golgi apparatus performs the function of storage, modification and packaging of materials synthesised in the cell. These materials will not be able to perform their function in its original form.
2. The formation of lysosomes will be affected.
Question 5.
Which organelle is known as the powerhouse of the cell? Why?
Answer:
Mitochondria are known as ‘power house’ of the cell. They are sites for synthesis, storage and transport of ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) commonly called energy currency.
![]()
Question 6.
Where do the lipids and proteins constituting the cell membrane get synthesised?
Answer:
- Proteins are synthesised bv ribosomes.
- SER is site for synthesis of lipid.
- These proteins and lipids are modified by golgi apparatus to form plasma membrane.
Question 7.
How does an Amoeba obtain its food?
Answer:
Plasma membrane is flexible and it enables the cell to engulf in food and other materials from the external environment. Such a process is termed endocytosis.
Question 8.
What is osmosis?
Answer:
Osmosis. It is a special case of diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane. It is a passage of water from a region of higher concentration through a semi- permeable membrane to a region of low water concentration.
Question 9.
Carry out the following osmosis experiment:
Take four peeled potato halves and hollow each one out to make potato cups. One of these potato cups should be made from a boiled potato. Put each potato cup in a trough containing water. Now,
(a) keep cup A empty
(b) put one teaspoon sugar in cup B
(c) put one teaspoon salt in cup C
(d) put one teaspoon sugar in the boiled potato cup D.
Keep this setup for two hours. Then observe the four potato cups and answer the following.
1. Explain why water gathers in the hollowed portion of B and C.
2. Why is potato A necessary for this experiment?
3. Explain why water does not gather in the hollowed out portions of A and D?
Answer:
1. The water gathers in hollowed portion of potato cups B and C due to osmosis.
2. Cup A acts as control experiment and indicates that cavity of potato will not induce any type of movement.
3. Cup A does not contain hypertonic solution hence water does not rise. In cup D, cells of potato cup being boiled cells are dead and no osmosis occurs.
Science Guide for Class 9 PSEB The Fundamental Unit of Life InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Who discovered cell and how?
Answer:
Robert Hooke (1665) discovered cell for the first time. He examined a thin slice of cork under the microscope. He observed that cork resembled the structure of a honey comb consisting of many hexagonal compartments and called these boxes ‘cells’.
Question 2.
Why is cell called the structural and functional unit of life?
Answer:
- Cells are arranged in proper and systematic order to form a body of living organism. Thus cells serve as basic building structural units for more complex organisms.
- Cell is also functional unit of life because all the metabolic activities of life take place at cell level.
- Respiration, digestion, excretion and reproduction occur at cell level.
- Cells contain genetic material which regulate cell functions and pass on all information to the next generation.
Question 3.
How do substances like C02 and water move in and out of the cell? Discuss.
Answer:
The substances like C02 and water move in and out of cell by the process of diffusion. There is spontaneous movement of substances from higher concentration to lower concentration. The movement of water across selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis.
![]()
Question 4.
Why is the plasma membrane called selectively permeable membrane?
Answer
Plasma membrane permits the entry and exit of selected materials in and out of the cell. It also prevents movement of some materials required within the cell. The membrane is called selectively permeable membrane.
Question 5.
Fill in the gaps in the following table illustrating differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
| Prokaryotic Cell | Eukaryotic Cell |
| 1. Size: generally small (1 – 10 µm) = 10-6m
2. Nuclear region ……………. and known as ……………….. 3. Chromosome single. 4. Membrane-bound cell organelles absent. |
1. Size: generally large 5 – 100 µm
2. Nuclear region well defined and surrounded by a nuclear membrane. 3. More than one. 4. ……………………………………………….. |
Answer:
2. Nuclear region undefined due to absence of nuclear membrane and known as Nucleoid.
4. Membrane-bound cell organelles such as mitochondria, Golgi bodies, chloroplast, etc. are present.
Question 6.
Can you name two organelles we have studied that contain their own genetic material?
Answer:
- Chloroplasts
- Mitochondria.
Question 7.
If the organization of the cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence, what will happen?
Answer:
Each cell has certain special cell organelles. Each performs a special function. If an organization is destroyed cell will stop performing basic functions and result in its death.
![]()
Question 8.
Why are lysosomes called ‘suicidal bags’?
Answer:
Lysosomes are membrane-bound sacs filled with enzymes and this enzyme may digest their own contents if burst. They carry out autolysis (auto = self; lysis = break down) hence called “suicidal bags.”
Question 9.
Where are proteins synthesized inside the cell?
Answer:
Proteins are synthesized on the ribosomes which are attached to the surface of RER or lie freely in the cytoplasm. Ribosomes are also called “protein factories” of cells.
