Punjab State Board PSEB 6th Class Social Science Book Solutions Geography Chapter 6 Our India – In World Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Geography Chapter 6 Our India – In World
SST Guide for Class 6 PSEB Our India – In World Textbook Questions and Answers
I. Answer the following questions :
Question 1.
Which latitude divides India into two parts? Name the two parts.
Answer:
The Tropic of Cancer (23°30′ N) divides India into two parts. The northern part is called Sub-tropical India and the Southern part is known as Tropical India.
Question 2.
Name the neighbouring countries of India.
Answer:
India has seven countries as her neighbours. They are Pakistan, Afghanistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, Myanmar and Bangladesh.
Question 3.
Write down the. latitudinal and longitudinal location of India.
Answer:
The latitudinal location of India is 8°4′ N to 37°6′ N and the longitudinal location is 67°7′ E to 97°25′ E.
Question 4.
Why is India called a sub-continent?
Answer:
India is called a sub-continent because she has a great longitudinal and latitudinal length. She stands out’distinctly from the rest of the countries of the world.
![]()
Question 5.
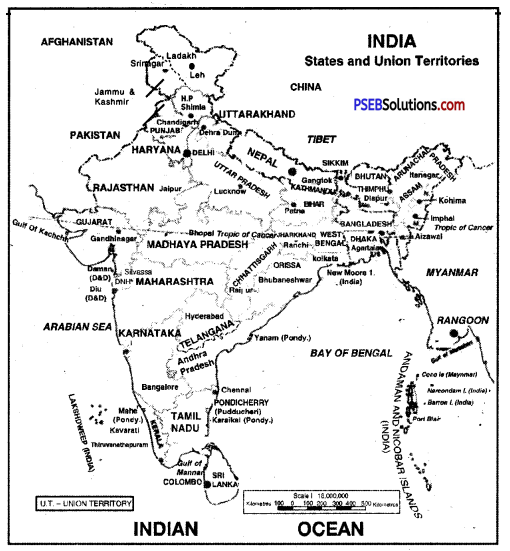
Into how many States and Union Territories India is divided from administrative point of view?
Answer:
From administrative point of view, India is divided info 28 States and 8 Union Territories.
Question 6.
Write down the names of the three seas or oceans that engulf the Indian Peninsula.
Answer:
The Indian Peninsula is engulfed by the Indian Ocean, the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal.
II. Fill in the blanks in the following :
Question 1.
_______ state is the lrgest state of India.
Answer:
Rajasthan
Question 2.
_______ is the smallest state of India.
Answer:
Goa
Question 3.
Indira Point is the _______ point of India.
Answer:
southernmost
Question 4.
From Kashmir to _______ India is one.
Answer:
Kanyakumari
![]()
Question 5.
Arunachal Pradesh is in _______ part of India.
Answer:
eastern.
III. Make proper pairs:
Question 1.
| A | B |
| (i) Andaman and Nicobar | (i) Our eastern neighbour |
| (ii) Maldives | (ii) Southern neighbour |
| (iii) Myanmar | (iii) Indian Island Group |
| (iv) Sri Lanka | (iv) Connected through oceanic boundary |
Answer:
| A | B |
| (i) Andaman and Nicobar | (iii) Indian Island Group |
| (ii) Maldives | (ii) Southern neighbour |
| (iii) Myanmar | (i) Our eastern neighbour |
| (iv) Sri Lanka | (iv) Connected through oceanic boundary |
Activity (Something To Do)
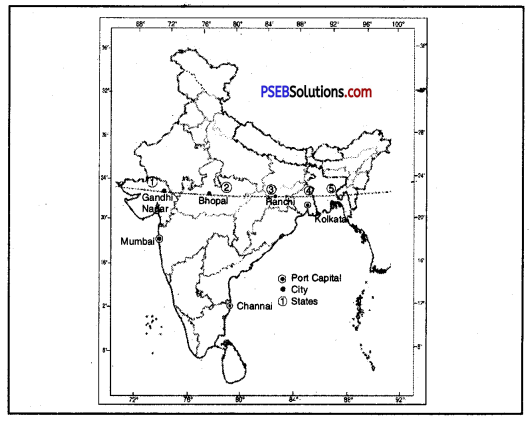
Question 1.
Name two main port cities which are also capital cities.
Answer:
Mumbai and Chennai.
![]()
Question 2.
Name three capital cities that are located fairly close to the tropic of cancer.
Answer:
- Gandhinagar
- Bhopal
- Ranchi.
Question 3.
Name five states from West to East.
Answer:
- Gujarat
- Madhya Pradesh
- Jharkhand
- West Bengal
- Tripura.
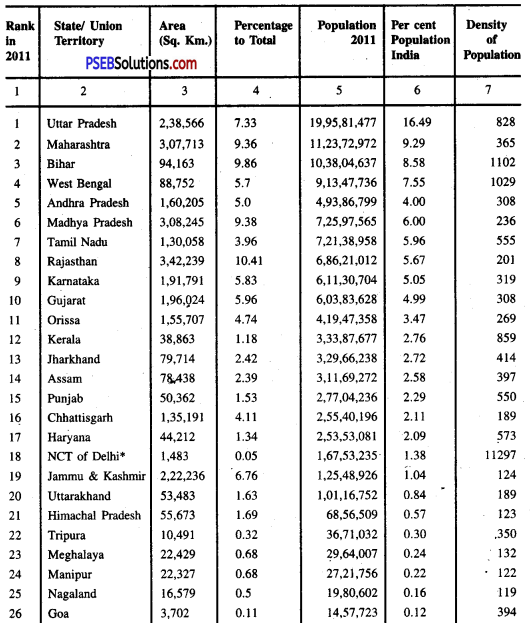
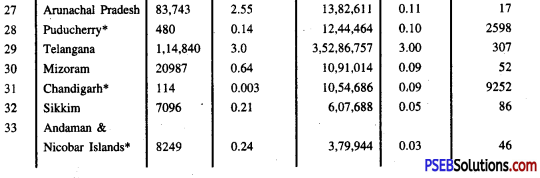
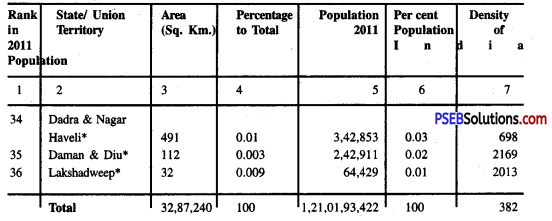
Area, Population And Density Of States And Union Territories (2011):
Based upon the Survey of India map, with the permission of the Surveyor General of India. The territorial waters of India extend into the sea to a distance of twelve nautical miles measured from the appropriate baseline. The boundary of Meghalaya shown on this map is as interpreted from the North-Eastern Areas (Reorganisation) Act. 1971, but has yet to be verified. Responsibility for the correctness of internal details shown on the map rests with the publisher.
PSEB 6th Class Social Science Guide Our India – In World Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions :
Question 1.
Which of the following is the exact north-south extent of India?
(A) 2933 km
(B) 3214 km
(Q 2930 km
(D) 3014 km
Answer:
(B) 3214 km.
![]()
Question 2.
Which of the following is the southernmost tip of the mainland?
(A) Kanyakumari
(B) Indira point
(Q J&K
(D) Malabar.
Answer:
(A) Kanyakumari.
Question 3.
How many islands lie in the Bay of Bengal?
(A) 250
(B) 204
(C) 205
(D) 206.
Answer:
(B) 204.
Question 4.
Which one of the following longitudes is the standard meridian for India?
(A) 69° 30’ E
(B) 82° 30’ E
(C) 75° 30’ E
(D) 90° 30’ E.
Answer:
(B) 82° 30’ E.
Question 5.
Which one of the following countries is larger in area than India?
(A) China
(B) Egypt
(C) France
(D) Iron.
Answer:
(A) China.
Fill in the Blanks :
Question 1.
_______ separates as India from Sri Lanka.
Answer:
Palk Strait
Question 2.
_______ is the smallest state of India.
Answer:
Goa
![]()
Question 3.
Lakshadweep is the _______ U.T.
Answer:
Smallest
Question 4.
_______ is the southernmost point of India.
Answer:
Indira point
Question 5.
_______ separates the Andaman Islands from the Nicobar Islands.
Answer:
Ten-degree channel.
True/False :
Question 1.
India has four physiographic units.
Answer:
False
Question 2.
Ahmedabad is located on Tropic of Cancer.
Answer:
True.
![]()
Question 3.
Fifteen states are coastal states of India.
Answer:
False
Question 4.
International boundaries of 7 countries touch India.
Answer:
True.
Question 5.
Lakshadweep is a group of coral islands.
Answer:
True.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name the Indian states having common frontiers with China.
Answer:
J&K, Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh.
Question 2.
Between which latitudes and longitudes the Indian sub-continent lies?
Answer:
Between 8° N To 37° N latitude and 68°E to 97° E longitudes.
Question 3.
Name the major rivers of India which constitute the North Indian Plain.
Answer:
The major rivers of India constituting the North Indian Plain are the Sutlej, Ganga and Brahmaputra.
![]()
Question 4.
Name five major hill ranges constituting the Purvanchal.
Answer:
Five major hill ranges constituting the Purvanchal are Patkoi Bum, Garo, Khasi, Jaintia and Lushai.
Question 5.
Why are the Himalayas called young mountains?
Answer:
The Himalayas are called young mountains because they have been formed recently in world history.
Question 6.
Which is the largest delta in the world?
Answer:
The Ganga-Brahmaputra Delta is the largest delta in the world.
Question 7.
Which strait separates India from Sri Lanka?
Answer:
Palk Strait separates India from Sri Lanka.
Question 8.
Name the largest and the smallest Union Territories in area.
Answer:
Andaman and Nicobar is the largest and Lakshadweep is the smallest in terms of area.
Question 9.
What is the length and breadth of the Himalayas?
Answer:
The length of the Himalayas is 3600 km and breadth is 150 to 400 km.
Question 10.
Name three ranges of the Himalayas.
Answer:
Three ranges of the Himalayas are the Shiwaliks, Himachal (Lesser Himalayas) and the Himadris (Greater Himalayas).
![]()
Question 11.
What are dunes? Give one example.
Answer:
The longitudinal valleys between the Shiwaliks and Lesser Himalayas are called dunes. For example, Dehradun.
Question 12.
Name some famous hill stations found in Himachal ranges.
Answer:
Dalhousie, Shimla, Mussoorie, Nainital and Darjeeling are some famous hill stations found in Himachal ranges.
Question 13.
Name the highest mountain peak of the world.
Answer:
Mt. Everest is the highest mountain peak of the world. Its height is 8848 metres.
Question 14.
Name the highest mountain peak of the Himalayas in India.
Answer:
The highest mountain peak of the Himalayas in India is Kanchanjunga (Sikkim).
Question 15.
Name the plateaus in Central Highlands.
Answer:
Malwa, Bundelkhand, Baghelkhand and Chhotanagpur.
![]()
Question 16.
Name the main ranges of Western Ghats.
Answer:
Sahyadri, Nilgiris, Annamalai and Cardamom hills.
Question 17.
Name a group of coral islands.
Answer:
The Lakshadweep Islands.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name the island groups in Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal.
Answer:
The Arabian Sea has Lakshadweep Group of Islands and the Bay of Bengal has Andaman Group of Islands and Nicobar Group of Islands. India has almost a total of 250 islands, out of which 204 lie in the Bay of Bengal.
Question 2.
What is a sub-continent?
Answer:
A sub-continent is a part of continent, an independent geographical unit, distinctly separated from the main continent.
Question 3.
Write a short note on the Himalayas.
Answer:
The Himalayas are young fold mountains. They have been formed due to folding by different earth movements. Parallel mountain ranges are formed in these mountains. These mountains are the loftiest mountain system of the world. The highest mountain peak Mt. Everest (8848 mt.) lies in the Himalayas. These mountains extend in an arc. Here, deep gorges anc U-shaped valleys are formed.
![]()
Question 4.
Distinguish Shiwaliks from Greater Himalayas.
Answer:
| Shivalik | Greater Himalayas |
| 1. Shiwaliks are called Outer Himalayas. | 1. Greater Himalayas are called Himadris. |
| 2. These mountains have an average height of about 1200 metres. | 2. These mountains have an average height of about 6000 metres. |
| 3. These consist of loose unconsolidated sediments. | 3. These consist of the highest peaks like Mt. Everest. |
Question 5.
Describe the boundaries of India.
Answer:
Boundaries of India.
- India is a country of vast geographical expanse.
- It is bounded by the mighty Himalayas in the north.
- Arabian sea bounds it in the west.
- Bay of Bengal forms its boundary in the east.
- Indian ocean bounds it in the south.
Question 6.
How is India a country of vast geographical expanse?
Answer:
- India has an area of about 32.8 crore hectares.
- Its north-south extent from Kashmir to Kanyakumari is about 3200 kms.
- It extends east-west from Arunachal Pradesh to Kutchh over 2900 kms.
- The lofty mountains, the Thar desert, the Northern plains, Peninsular Plateau, east and west coasts and islands present a diversity of land forms.
![]()
Question 7.
How does unity in diversity exist in India?
Answer:
(a) There is a great variety in climate, vegetation, wildlife as well as language and culture in India.
(b) In this diversity there is unity. It is reflected in traditions that bind us as one nation.
(c) India has a population of 1.22 billion crore according to the Census of 2011.
(d) It is the second-most populous country of the world after China.
Question 8.
Write any four features of the Ganga Basin.
Answer:
The Ganga basin is a part of northern plains. It lies at the foot of the Himalayas. It is an alluvium plain formed by the deposition of sediments brought from the Himalayas by rivers. It is a flat lowland. It has fertile alluvial soils, namely Khadar and Bangar. These soils have led to the development of agriculture. The basin has been divided into many Doabs.
Question 9.
Name the major rivers of Peninsular India.
Answer:
Some rivers of Peninsular India flow eastward into the Bay of Bengal. These are Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna and Kaveri. Some rivers flow westward into the Arabian Sea. These rivers include Narmada and Tapti.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe the Northern Plains of India.
Answer:
The Northern Plains of India are a region of a vast alluvial plain. This region extends from Punjab-Haryana Plains to Assam Valley. It is 3200 km long and 150 to 300 km wide. Its average height is 150 metres. It covers an area of 7.5 lakh sqvkm.
It can be divided into the following parts :
1. The Punjab-Haryana Plains. These plains owe their origin to the depositional work of the Sutlej, the Beas and the Ravi rivers. This is a uniform and flat plain and is formed by the Indus and its five tributaries. Due to creation of international border between India and Pakistan in 1947, greater part of it went to Pakistan. To the other side, due to the rise of surface near Delhi, the Yamuna has started flowing towards east. Delhi and its surrounding area work as a water divide between the Ganga and Indus River Drainage System.
The interfluves formed on the basis of river boundaries can be divided into four sub-divisions :
- Bari Doab or Majha: Area between the Ravi and the Beas is known as Bari Doab or the Majha plain in Punjab.
- Bist Doab: Area between the Beas and the Sutlej is called Bist Doab or the Doaba plain in Punjab.
- Malwa: Plain area spreading from the Satluj to the Ghaggar is called Malwa Plain in Punjab.
- Plain of Haryana: Area from the Ghaggar to the Yamuna is known as Plain of Haryana.
2. The Thar Desert Plain. The drier and the flat area extending from the southern parts of Punjab and Haryana to the Rann of Kuchchh of Gujarat is known as the Thar Desert. The Aravali mountain ranges form its eastern boundary. Due to the scarcity of rain, whole of the region has become sand-duned. In the Barmer District sand-dunes are 50 to 100 metres high. In whole of this dry region the action of wind is very fast. Westward along the Aravalis, there are fertile plains, called Rohi. There are many salt lakes like Samber lake.
3. The Ganga Plain. This plain is spread over the states of Uttar Pradesh and Bihar, extending from the Yamuna in the west to the international boundary of Bangladesh in east and the Shiwaliks in the north. This vast and fertile plain is important from the historic, agricultural and dense population point of view. The main rivers of this plain are the Ganga, the Yamuna, the Ramganga, the Chambal, the Betwa, the Kali and the Pandu.
4. The Brahmputra Plain. These plains are also called the Assam plains. The Brahmputra, Sesari, Dibang and Lohit are the rivers of this plain.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the Indian islands.
Answer:
India has almost a total of 250 islands. On the basis of their location, these islands are divided into two main sub-divisions :
- Offshore Islands
- Onshore Islands.
1. Offshore Islands.: These islands are further divided into two :
(a) The Island Group of the Arabian Sea. Formed with the deposit of coral reefs in the South-eastern Arabian Sea these islands are known as Lakshadweep. They are 25 in number. The whole group has three major parts. The northern part is named as Amindive, the middle as Laccadive and the southern as Minicoy.
(b) The Island Group of the Bay of Bengal. Some of these islands are made up by volcanic eruption and some are the raised parts of the peaks of sub-merged hills.
These islands also have three main parts :
- Andaman Island Group,
- Nicobar,
- Other Adjoining Islands.
There are about 120 islands in the Andaman Group of Islands. Indira Point island of Nicobar is the southernmost point of India.
2. Onshore Islands. In these islands near the delta of Ganges, small islands such as Wheeler, New Moor, etc. are found. Some islands are found near the coast of Tamil Nadu. Big islands like Diu are situated near the coast of Gujarat.
In Khambat and Rann of Kutchchh, islands of various sizes are found.
