Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class Science Book Solutions Chapter 16 Light Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light
PSEB 8th Class Science Guide Light Textbook Questions and Answers
Exercises
Question 1.
Suppose you are in a dark room. Can you see objects in the room ? Can you see objects outside the room ? Explain.
Answer:
No, we cannot see anything in dark. As no light is falling on the objects in the room and they are not emitting any light on their own. So, nothing is visible inside the dark room.
Objects outside the room can be seen, if either there is light outside the room or objects are emitting their own light.
Question 2.
Differentiate between regular and diffused reflection. Does diffused reflection mean the failure of the laws of reflection ?
Answer:
Differences between regular reflection and diffused reflection:
| Regular reflection | Diffused reflection |
| 1. It occurs on a smooth, plane surface. | 1. It occurs on a rough, irregular surface. |
| 2. Reflected rays are parallel to one another. | 2. Reflected rays are unparallel to each other. |
Diffused reflection is not failure of laws of reflection. It is only due to irregularities on the reflecting surface.
![]()
Question 3.
Mention against each of the following whether regular or diffused reflection will take place when a beam of light strikes. Justify your answer in each case.
[a] Polished wooden table
[b] Chalk powder
[c] Cardboard surface
[d] Marble floor with water spread over it.
[e] Mirror
[f] Piece of paper.
Answer:
(a) Polished wooden table. Regular reflection, as wooden table has smooth polished surface.
(b) Chalk powder. Diffused reflection due to rough surface of chalk powder.
(c) Cardboard surface. Diffused reflection because cardboard has small irregularities on its surface.
(d) Marble floor with water spread over it. Regular reflection as water gives a smooth surface.
(e) Mirror. Regular reflection due to smooth surface.
(f) Piece of paper. Regular reflection if paper is fine and diffused reflection if paper is coarse.
Question 4.
State the laws of reflection.
Answer:
Laws of reflection.
- Angle of incidence (∠i) = Angle of reflection ( ∠r).
- Incident ray, reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
Question 5.
Describe an activity to show that the incident ray, the reflected ray, normal, the point of incidence lie in the same plane.
Experiment.
Take a white sheet, spread it on a table. Draw a line MM on it. Place a plane mirror vertically on this line. Now throw light on a comb in this ways that a parallel light rays fall on the mirror. Adjust it in such a way that a beautiful pattern of incident and reflected rays is formed. Now mark points A, B, C on incident ray and points D, E, F on its corresponding reflected ray. Switch off the torch and remove the mirror. Join the points and extend line to mirror. ABC will meet MM at O and DEF will all also be meeting at O. OA is incident ray and OF is reflected ray. Draw ON ⊥ MM .
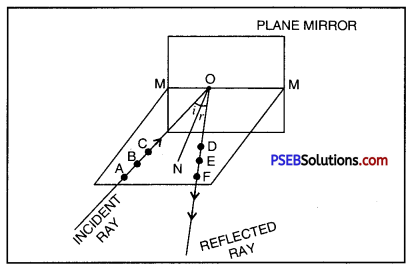
Measure the angle of incidence ∠AON and the angle of reflection ∠FON which would found to be equal. Incident ray, reflected ray and normal, all lie in one plane of paper.
Question 6.
Fill in the blanks in the following.
(a) A person 1 m in front of a mirror seems to be ……………….. m away from his image.
(b) If you touch your ………………….. ear with right hand in front of a plane mirror it will be seen that your right ear is touched with ……………… .
(c) The size of pupil becomes …………………. when you in dim light.
(d) Night birds have ………………. cones than rods in their eyes.
Answer:
(a) 2m
(b) Right, Left
(c) large
(d) more.
Choose the correct option in the Questions 7-8.
Question 7.
Angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection
(a) Always
(b) Sometimes
(c) Under special conditions
(d) Never.
Answer:
(a) Always.
![]()
Question 8.
Image formed by a plane mirror is
(a) virtual, behind the mirror and enlarged.
(b) virtual, behind the mirror and of same size as the object.
(c) real at the surface of mirror and enlarged.
(d) real, behind the mirror and of same size as the object.
Answer:
(b) Virtual, behind the mirror and of same size as the object.
Question 9.
Describe the construction of a Kaleiodeoscope.
Answer:
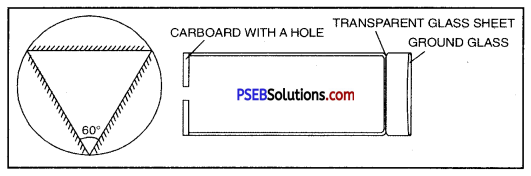
Construction of a Kaleiodeoscope. It is a toy to form many images by multiple reflections. A Kaleiodeoscope is made up of three strips of plane mirrors inclined at angles of 60° enclosed in a tube. One end of tube has a ground glass plate with a clear glass plate on its inner side. A metallic ring separates the two plates and the space is filled with coloured pieces of glass or broken bangles. A cardboard with a hole in the centre is fixed on the other end of the tube.
Question 10.
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye.
Answer:
Labelled diagram to show different parts of human eye.
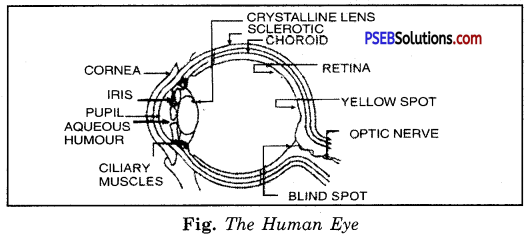
Question 11.
Gurmit wanted to perform activity 16.8 using a laser torch. Her teacher advised her not do so. Can you explain the basis of the teacher’s advice ?
Answer:
Laser torch has very sharp beams of light which can destroy the pupil or retina of the eye.
Question 12.
Explain how can you take care of your eyes.
Answer:
Care of eyes.
Eyes are the most precious gifts of nature. So we should take full care of our eyes by taking atleast following precautions.
- We should wash our eyes daily with clean water.
- We should not read or work in very bright or dim light.
- We should not read in a running vehicle.
- We should not rub our eyes.
- We should use sunglasses on hot summer day.
- We should not look directly at the sun. Also we should not look at the sun during solar eclipse.
- We should eat vitamin A rich food for healthy, clear eyes.
Question 13.
What is the angle of incidence of a ray if the reflected ray is at an angle of 90° to the incident ray ?
Solution:
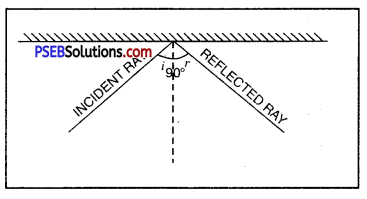
If ∠i = angle of incidence
∠r = angle of reflection
∠i + ∠r = 90 (given)
But ∠i = ∠r
(According to laws of reflection)
∴ ∠i + ∠i = 90°
2 ∠i = 90
∠r = ∠i – 45°
![]()
Question 14.
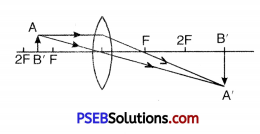
How many images of a candle will be formed if it placed between two parallel mirrors separated by 40 cm ?
Answer:
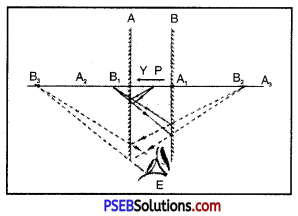
When mirrors are separated by 40 cm and are parallel to each other so that the angle between the mirrors is 0° which is not sulj-multiple of 360°. Then theoretically, the number of images formed would be infinite, but as a considerable amount of light is lost due to reflections so only a limited number of images are seen which is shown in figure.
Question 15.
Two mirrors meet at right angles. A ray of light is incident on one at an angle of 30° as shown is figure. Draw the reflected ray from the second mirror.
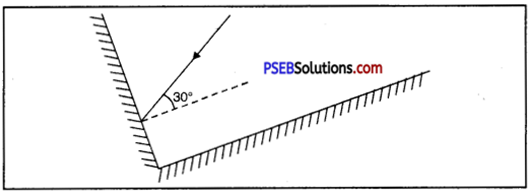
Solution:
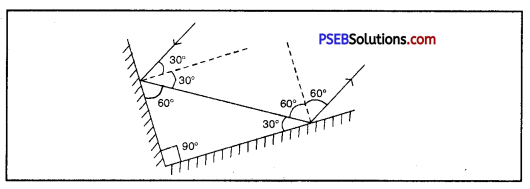
Question 16.
Bhoojo stands at A just on the side of a plane mirror as shown in figure. Can he see himself in the mirror ? Also can he see image of objects situated at P, Q and R ?

Solution:
Bhoojo cannot see his image in the mirror as he is standing outside the edge of mirror. He can see the images of P and Q easily but not the image of R.
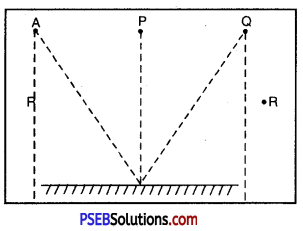
Question 17.
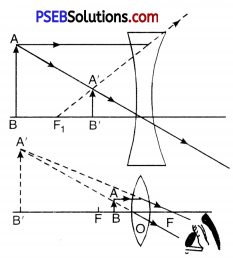
(a) Find out the position of image of an object situated at A in plane mirror.
(b) Can Paheli at B see this image ?
(c) Can Bhoojo at C see this image ?
(d) When Paheli moves from B to C where does the image of A move ?
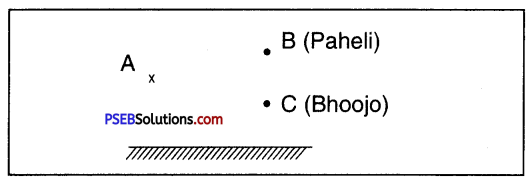
Answer:
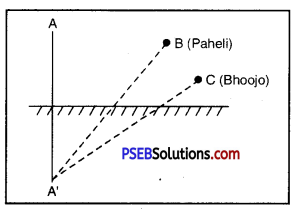
(a) The image of A in the mirror will be as far behind as the object in front of the mirror.
(b) Yes, Paheli can see the image.
(c) Yes, Bhoojo can see this image.
(d) When Paheli moved from B to C, the image of A will not move forward.
![]()
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Light Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The plane and polished surface that returns light falling on it in the same direction or any other direction is called:
(a) Lens
(b) Prisom
(c) Mirror
(d) Kaleidoscope.
Answer:
(c) Mirror.
Question 2.
How many colours are present in white sunlight ?
(a) 2
(b) 5
(c) 7
(d) 3.
Answer:
(c) 7.
Question 3.
What is the most convenient distance for reading by a normal eye ?
(a) 10 cm
(b) 25 cm
(c) 15 cm
(d) 20 cm.
Answer:
(b) 25 cm.
Question 4.
When you see in dim light the size of your pupil becomes:
(a) Small
(b) Large
(c) Neither small nor large
(b) Very small.
Answer:
(b) Large.
Question 5.
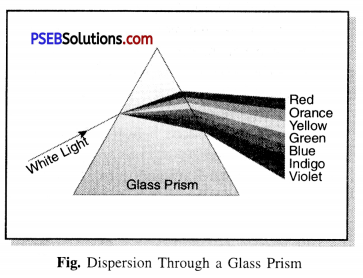
The Phenomena of splitting of light into its constituent colours is called:
(a) Reflection
(b) Refraction
(c) Dispersion
(b) Combination.
Answer:
(c) Dispersion.
Question 6.
The eye lenses focuses:
(a) On Cornea
(b) On Retina
(c) On Iris
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) On Retina.
![]()
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Can any one see in the dark ?
Answer:
No.
Question 2.
It is what that helps us to see objects ?
Answer:
Light.
Question 3.
Name any two Luminous bodies.
Answer:
- Sun
- Electric bulb.
Question 4.
Is moon a luminous or a non-luminous body ?
Answer:
Non-luminous.
Question 5.
Where is a reflection seen ?
Answer:
In mirror.
Question 6.
Which surface can act as a mirror ?
Answer:
Any polished and smooth surface.
![]()
Question 7.
If you are standing in front of a mirror and observing your own image what is the relation between the distance of the object and the image from the mirror ?
Answer:
Distance of object from the mirror = Distance of image from the mirror.
Question 8.
What is the angle of reflection, when a ray of light is incident normally on a plane mirror ?
Answer:
Zero.
Question 9.
Name two objects which split white light into many colours.
Answer:
Water bubbles, surface of CD, prism.
Question 10.
Name the seven colours of light.
Answer:
Red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet.
Question 11.
Give one example of dispersion of light in nature.
Answer:
A rainbow.
Question 12.
Is focal length of eye lens fixed ? If not, why ?
Answer:
No. Eye lens has variable focal length. Focal length of Eye lens varies due to action of ciliary muscles.
![]()
Question 13.
What is the function of sclerotic in human eye ?
Answer:
Sclerotic provides a solid shape to the eye and protects it from external injuries.
Question 14.
What is the function of ciliary muscles in human eye ?
Answer:
Eye lens is held in its position by ciliary muscles. Ciliary muscles help the eye lens to change its focal length by adjusting its curvature.
Question 15.
What is the function of rods on the retina ?
Answer:
Rods are sensitive to intensity of light. The more the intensity of light, more are they excited.
Question 16.
What are cones ?
Answer:
Cones on retina are sensitive to different colours. If cones are absent or insufficient, the person is colour blind.
Question 17.
What is basic cause of colour blindness ?
Answer:
It is due to absence or insufficient number of cones on the retina. Seeing sun or towards it during solar eclipse may cause colour blindness.
Question 18.
Why cats and bats are able to see at night ?
Answer:
They have very large number of rods on retina. Hence, they are able to see even a small quantity of light.
Question 19.
At what rate the images pass one after the other on a cinema screen ?
Answer:
25 or more per second.
![]()
Question 20.
What type of photosensitive cells are present on the retina of the eye ?
Answer:
Cones and rods.
Question 21.
Name one device that can be used by short statured person to see over the head of a crowd.
Answer:
Periscope.
Question 22.
Find out the letters of English alphabet or any another language known to you in which the image formed in a plane mirror appears exactly like the letter itself.
Answer:

Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are luminous and non-luminous bodies ? Give examples.
Answer:
Luminous Bodies.
Those objects which emit their own light, are called luminous bodies e.g. sun, stars, burning fire, radium etc.
Non-luminous Bodies.
Those objects which do not emit light of their own but shine due to other luminous bodies, are called Non-Luminous bodies. They are visible only, when light falls on them.
e.g. Moon, earth and other planets, things in a room.
Question 2.
How do we see objects ?
Answer:
When light from a light source falls on any object, it is scattered by it. The scattered light enters our eyes to form the image of the object and the object is, thus, seen.
Question 3.
Give the conditions necessary for seeing an object.
Answer:
Conditions for Seeing Objects. To see an object, the following three conditions are required to be satisfied:
- Source of light to make object visible
- The object
- Eye sight.
Question 4.
What is a virtual image ? Give one situation where a virtual image is formed.
Answer:
Virtual image.
An image, which cannot be obtained on a screen, is called a virtual image. Virtual image is formed when reflected rays do not actually meet at a point.
Image formed in a plane mirror is always virtual.
![]()
Question 5.
What do you understand by lateral inversion ?
Answer:
Lateral Inversion.
In a plane mirror, the right side of the object becomes left side of the image and the left side of the object becomes right side of the image. That is the image is sideways inverted. This phenomenon, is called lateral inversion.
Question 6.
State the laws of reflection of light.
Answer:
Laws of reflection.
The reflection at the smooth surface is found to obey the following two laws, called the laws of reflection.
- The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
i.e., ∠i – ∠r. - The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence lie in the same plane.
Question 7.
What is diffused reflection and regular reflection ?
Answer:
Diffused Reflection.
It takes place when the surface is not smooth or polished e.g., wall, paper. The rays reflected from an uneven surface are not parallel but scattered in all directions and such reflection is called diffused reflection.
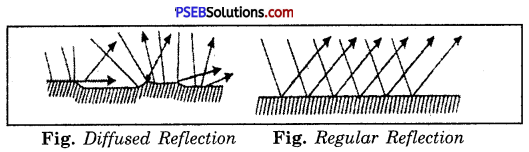
Regular Reflection.
It takes place when a beam of light falls on a smooth and polished surface, e.g., a mirror. The reflected rays from an even surface form a clear image.
Question 8.
What do you understand by reflection of light ?
Answer:
Reflection of light.
When a ray of light falls on a mirror, or polished surface, it is sent back in a particular direction obeying certain laws of reflection. This phenomenon is known as reflection of light.
Question 9.
Define the following:
1. Reflected Ray
2. Angle of reflection.
Answer:
1. Reflected Ray. A streak of light, starting from the mirror, is called reflected ray.
2. Angle of reflection. The angle made by the reflected ray with the normal at the point of incidence is called angle of reflection. It is represented by r.
Question 10.
If incident ray strikes the mirror at 90°, what will be the angle of reflection ?
Answer:
If incident ray strikes the mirror normally, then after reflection, the ray will come back along the same path. As the angle of incidence is zero, so angle of reflection will also be zero.
![]()
Question 11.
Define the term ‘Dispersion of light.’
Answer:
Dispersion of Light.
When a beam of light passes through a prism, the white light splits into seven colours. This phenomenon of splitting of white light into its constituent colours by a prism is known as dispersion of light.
Question 12.
While passing through a prism, why does the white light split into seven colours.
Answer:
The rays of different colours pass smoothly through air but when passing through a prism they have to change the speed according to the angle of prism. Different colours have different wave lengths and thus, they choose different paths. So, the spectrum is seen.
Question 13.
What is myopia ?
Answer:
Myopia.
The focal length of the eyes of some people is very small. Therefore, the image of distant object is not formed on their retina but it is formed at a point in front of the retina. In other words, they cannot see distant objects. This defect of vision is called Myopia or short sightedness.
Question 14.
What is hypermetropia ?
Answer:
Hypermetropia.
When people grow old, the muscles of the eyes lose their strength to control the curvature of the lens. As a result, the image of nearby objects is not formed at the retina, but it is formed behind the retina. So these people cannot see nearby objects clearly. This defect of vision is called Hypermetropia or Farsightedness.
Question 15.
Explain in short perception of colour.
Answer:
Perception of colour.
Human eye contains large number of rods and cones which are sensitive to light. Rods respond to the intensity of light and cones respond to the colour of the light. If cone cells are absent in the eye then such a person is colour blind. With the help of cones cells one can perceive colour. This is called perception of colour.
Question 16.
The following picture shows the reflection of light:
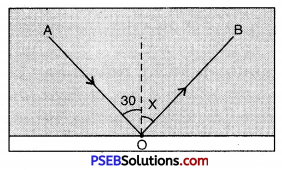
(A) Name the ray AO
(B) Name the ray OB
(C) Find the value of angle x
Answer:
(A) Name of ray AO = Incident7 ray
(B) Name the ray OB = Reflected ray
(C) Value of angle x = 30° because angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Differentiate between a real image and a virtual image.
Answer:
Differences between a real image and a virtual image.
| Real Image | Virtual Image |
| 1. The real image is formed when the rays of light actually meet after reflection. | 1. The image formed is virtual when the rays of light don’t meet after reflection. |
| 2. Real image can be obtained on the screen. | 2. Virtual images cannot be obtained on the screen. |
| 3. Real image is always inverted. | 3. Virtual image is always erect. |
Question 2.
State the characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror.
Answer:
Characteristics of the image formed in a plane mirror.
- The image is as far behind the plane mirror, as the object is in front of it.
- The image is laterally (sideways) inverted.
- The image is of the same size as that of the object.
- The image formed in a plane mirror is virtual, erect and of the same size as the object.
- The image formed in a plane mirror cannot be obtained on the screen.