Punjab State Board PSEB 6th Class Social Science Book Solutions Geography Chapter 3 Motions of the Earth Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Geography Chapter 3 Motions of the Earth
SST Guide for Class 6 PSEB Motions of the Earth Textbook Questions and Answers
I. Answer the following questions in brief :
Question 1.
What is rotation of Earth?
Answer:
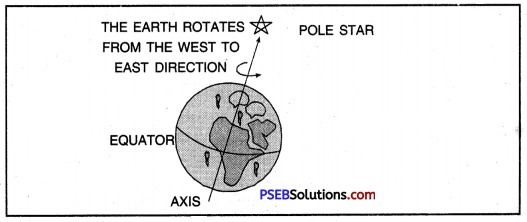
The earth rotates on its axis. It completes its round along its axis in twenty-four hours, from west to east. This is called Rotation of the Earth.
Question 2.
What is meant by “Inclination of the Earth’s axis”?
Answer:
The tilting of the Earth’s axis at an angle of 23%° from a perpendicular to the orbital plane is called “Inclination of the Earth’s axis”.
The Inclination of the Earth’s Axis
Question 3.
What causes the cycle of seasons?
Answer:
The cycle of seasons is caused mainly by the revolution of the earth around the sun and the inclination of the earth’s axis at an angle of 66 1/2° to the plane of its orbit which constantly points to the same direction.
Question 4.
Where do the vertical rays of the sun fall on June 21?
Answer:
The vertical rays of the sun fall on the Tropic of Cancer on June 21.
![]()
Question 5.
On September 23, which season is experienced in the Northern Hemisphere?
Answer:
On September 23, autumn season is experienced in the Northern Hemisphere.
Question 6.
When is winter solastice?
Answer:
In Southern Hemisphere in summer season when the sun shines vertically on the Tropic of Capricorn, it is winter solstice.
Question 7.
On September 23, which season is experienced in the Southern Hemisphere?
Answer:
On September 23, spring season is experienced in the Southern Hemisphere.
II. Distinguish between the following :
Question 1.
Summer Solstice and Winter Solstice.
Answer:
On 21st June, when the sun shines vertically on the Tropic of Cancer, it is called Summer Solstice. On the other hand, on 22nd December, when the sun shines vertically on the Tropic of Capricorn, it is known as Winter Solstice.
Question 2.
Spring Equinox and Autumn Equinox.
Answer:
On March 21 and September 23, days and nights are equal throughout the world. On March 21, spring season starts in the Northern Hemisphere. So this day is known as Spring Equinox.’On the other hand, on September 23, autumn season begins in the Northern Hemisphere. So this day is called Autumn Equinox.
![]()
Question 3.
Rotation and Revolution.
Answer:
The continuous spinning of the earth on its axis is called rotation. The earth takes twenty-four hours to complete one rotation on its axis. Days and nights are caused by the rotation of the earth.
Revolution, on the other hand, is the movement of the earth around the sun. The earth takes 36544 days to make a complete round of the sun, while rotating along its axis. Cycle of seasons is caused by the revolution of the earth.
III. Give reasons :
Question 1.
The sun rises in the east and sets in the west.
Answer:
The sun is stationary and the earth moves from west to east. Due to this movement of the earth, the sun appears to rise in the east and set in the west.
Question 2.
Days and nights are not always equal.
Answer:
On the equator, the rays of the sun fall vertically. So days and nights are equal there. But as we move away from the equator towards north or south, the rays of the sun fall slantingly. As a result, the length of days and nights increases or decreases. That is why days and nights are not equal.
Question 3.
On June 21, the South Pole is in continuous darkness.
Answer:
On June 21, the sun is away from the South Pole. So on this day, the South Pole is in continuous darkness.
Question 4.
Why do the sun, the moon and the stars appear moving round the earth, from east to west?
Answer:
The earth moves from west to east. It is because of this movement of the earth that the sun, the moon and the stars appear moving round the earth, from east to west.
IV. Fill in the blanks :
Question 1.
The earth rotates from __________ to __________
Answer:
west, east
![]()
Question 2.
The __________ is the line around which the earth turns.
Answer:
axis
Question 3.
The path along which earth travels around the sun is called the __________
Answer:
planetary path, (orbit)
Question 4.
The __________ areas experience six months long day and six months long night.
Answer:
polar.
PSEB 6th Class Social Science Guide Motions of the Earth Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions :
Question 1.
Movement of the earth on its axis is called :
(A) Revolution
(B) Rotation
(C) Resolution
(D) Cycle.
Answer:
(B) Rotation.
Question 2.
The axis of the earth which is an imaginary line makes an angle of with its orbital plane.
(A) 90°
(B) 60°
(C) 45°
(D) 66°
Answer:
(D) 66°.
Question 3.
The plane formed by the axis of earth and orbit is called __________
(A) Spherical plane
(B) Orbital plane
(C) Symmetric plane
(D) None of these.
Answer:
(B) Orbital plane.
![]()
Question 4.
Earth has __________ types of motions.
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 4
(D) 5.
Answer:
(A) 2.
Question 5.
When the earth is farthest from the sun, it is called :
(A) Aphelion
(B) Perihelion
(C) Solistices
(D) Equinoxes.
Answer:
(A) Aphelion.
Fill in the Blanks:
Question 1.
The earth mainly receives light from __________
Answer:
The sun
Question 2.
Period of rotation is called the __________
Answer:
Earthday
Question 3.
Australia lies in _____________ Hemisphere.
Answer:
Southern
Question 4.
Revolution of the earth causes change in_______________
Answer:
Seasons
![]()
Question 5.
Earth is in shape.
Answer:
Spherical.
True/False :
Question 1.
Earth takes 24 hrs to complete one rotation around its axis.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
On 23rd March rays of the sun fall on the equator.
Answer:
False
Question 3.
Seasons change due to the change in the position of the sun around the earth.
Answer:
False
Question 4.
Day and night on the earth occurs due to rotation of the earth.
Answer:
True
![]()
Question 5.
Every fourth year, month February is of 29 days.
Answer:
True
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How much time does the earth take to complete one rotation?
Answer:
The earth takes twenty-four hours to complete one rotation.
Question 2.
On what days do we have equal days and nights all over the world?
Answer:
We have equal days and nights all over the world on 21st March and 23rd September.
Question 3.
In which season is Christmas celebrated in Australia?
Answer:
Christmas in Australia is celebrated in summer season.
Question 4.
How much time does the earth take to complete one revolution?
Answer:
The earth takes 365 days and 6 hours to complete one revolution.
![]()
Question 5.
What causes days and nights?
Answer:
Rotation of the earth causes days and nights.
Question 6.
How much is the earth’s axis tilted from a perpendicular to the orbital plane?
Answer:
The earth’s axis is tilted at an angle of 23Vi° from a perpendicular to the orbital plane.
Question 7.
When the Northern Hemisphere is inclined towards the sun, which hemisphere will have the longer days and shorter nights?
Answer:
The Northern Hemisphere will have the longer days and shorter nights.
Question 8.
Which place on the earth has. days and nights of equal length throughout the year?
Answer:
The equator has days and nights of equal length throughout the year.
Question 9.
What is the position of the earth on 21st June?
Answer:
The North Pole remains inclined towards the sun, while the South Pole is away from it.
Question 10.
When is the autumn season in the Southern Hemisphere?
Answer:
The autumn season in the Southern Hemisphere is on 21st March.
Question 11.
On what days do we have days and nights equal in the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn?
Answer:
On 21st March and 23rd September.
![]()
Question 12.
Why does the sun at noon give more heat?
Answer:
The sun at noon gives more heat because its rays on the earth’s surface are vertical.
Question 13.
“The earth is not a perfect sphere.” Explain.
Answer:
The earth is a spheroid. It is flattened at the Poles. It has a bulge in the middle. Its shape is that of a Geoid. It is due to the centrifugal force acting on earth.
Question 14.
‘The real earth has no needle.’ Explain.
Answer:
If a needle is fixed through the globe in a tilted manner, it is called axis. The points of the needle on the globe are north pole and south pole. The globe can be moved around the needle. But the real earth has no such needle because the axis is an imaginary line.
Question 15.
The sun never sets or rises. Discuss.
Answer:
The sun seems to be rising or setting due to Rotation. Actually it is the earth that movps. The sun is stationary. It does not set or rise.
Question 16.
What is a planetary path?
Answer:
All the planets move along an elliptical path called orbit. It is also called planetary path.
![]()
Question 17.
What is Ferral’s law?
Answer:
All the winds and ocean currents move towards the right in the northern hemisphere and towards left in the southern hemisphere. It is called Ferral’s law.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Distinguish between Morning and Evening.
Answer:
| Morning | Evening |
| 1. It is the time of sunrise. | 1. It is the time of sunset. |
| 2. The rays of the sun appear on the horizon in the east. | 2. The rays of the sun appear to be descending to the horizon in the west. |
| 3. It is the time between the day break and noon. | 3. It is the time between the noon and sunset. |
Question 2.
Distinguish between Rotation and Revolution.
Answer:
The distinction between rotation and revolution is as under :
| Rotation | Revolution |
| 1. The spinning of the Earth on its axis is called rotation. | 1. Annual motion of the Earth round the Sun is called revolution. |
| 2. The time of rotation is about 24 hours. | 2. The time of revolution is 365 days 6 hours. |
| 3. Days and nights follow each other in regular succession in all parts of the Earth due to rotation. | 3. The change of season takes place because of the revolution of the Earth. |
Question 3.
Why do people experience more heat during noon than in the morning or evening?
Answer:
The rays of the sun are vertical at noon and slanting in the morning and evening. The great amount of heat is received by the earth when the sun’s rays fall vertical over it. Hence, people experience more heat during noon. Since the sun’s rays fall slanting in the morning and evening, they scatter over the greater area and hence they are comparatively cool.
Question 4.
Why do we have longer days and shorter nights in the Northern Hemisphere during summers?
Answer:
The earth’s axis is inclined by 23 1/2° to one side. Due to .this inclination, the Northern Hemisphere remains inclined towards the sun during one half of the year. Hence, the days are fonger and nights are shorter. In contrast, the Southern Hemisphere is always away from the sun during this half of the year.
Question 5.
What is a leap year? Why does a leap year have an extra day than an ordinary year?
Answer:
A leap year is one which has 366 days. It comes after a cycle of four years.
The earth moves around the sun and takes 365 days and 6 hours to make a complete round of it. We take 365 days in a year and ignore six hours. But these six hours make a day in four years. Hence, one day is added to every fourth year. Thus, every fourth year is called a leap year because it has 366 days. The extra day is added to the month of February. In an ordinary year, February has 28 days while in a leap year, it has 29 days.
![]()
Question 6.
How are days and nights caused?
Answer:
Days and nights are caused due to rotation. The earth rotates on its axis from West to East. When it rotates, one half of the earth turns towards light and has therefore day. The other half turns away
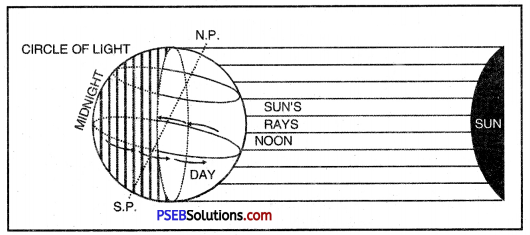
Day and Night
from the sun and remains in darkness and has night. During 24 hours, every part of the earth comes in turn before the sun and then goes into darkness. Therefore, the position of day and night keeps on changing. When it is day in one hemisphere, it is night in the other. The circle that divides the day from night on the globe is called circle of illumination (circle of light). This circle does not coincide with the inclined axis of the earth.
Question 7.
Make Difference between Summer and Winter Solstice.
Answer:
| Summer Solstice | Winter Solstice |
| 1. Summer solstice occurs on 22nd June in Northern hemisphere. | 1. Winter solstice occurs on 22nd December in the Northern hemisphere. |
| 2. The whole Northern hemisphere experiences more heat and light. | 2. Northern hemisphere exper¬iences less heat and light. |
| 3. It is summer in the Northern hemisphere. | 3. It is winter in the Northern hemisphere. |
| 4. Days are longer, nights are shorter. | 4. Days are shorter, nights are longer. |
| 5. Reverse conditions prevail in the Southern hemisphere. | 5. Reverse conditions prevail in the Southern hemisphere. |
Question 8.
What would happen if the Earth did not rotate?
Answer:
If the earth did not rotate :
- The portion before the sun would have remained the same and continued to experience day regularly.
- On the other hand the portion of the Earth away from the sun would have experienced night continuously.
- Life would have not been possible on the Earth in such a situation.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
(a) Define Rotation.
Answer:
Rotation: The spinning of the earth on its axis from West to East is called rotation.
(b) What is the period of rotation?
Answer:
The earth takes about 24 hours (23 hours 56 minutes 4 seconds) to complete one rotation. It is also known as daily motion of the earth.
(c) What are its effects?
Answer:
Effects:
- Rotation causes days and nights.
- All bodies like sun, moon, planets appear to move from East to West.
- Tides occur regularly twice a day.
- Winds and ocean currents change their directions.
- The four main directions (North, South, East, West) can.be determined with the help of rotation.
- We get a measure of time. A day consists of 24 hours-one complete rotation.
- The different times of a day like sunrise, noon, sunset, midnight can be determined due to rotation.
![]()
Question 2.
(a) What is a revolution?
Answer:
Revolution: The spinning of the earth around the sun, along an elliptical orbit from West to East is known as revolution.
(b) What is period of revolution?
Answer:
It takes a year or 36514 days to complete one revolution. Hence it is also known as annual motion of the earth. The earth’s axis is always inclined at a fixed angle of 66/4° to the plane of the ecliptic,
(c) What are aphelion and perihelion?
Answer:
When the earth is farthest from the sun (152 million kms) it is aphelion. When the earth is nearest the sun (147 million km) it is perihelion,
(d) What are its effects?
Answer:
Effects:
- Due to revolution, the lengths of days and nights vary at a place at different times of the year.
- Revolution causes a change of seasons.
- It helps in the location of Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn due to the fact that the sun’s rays fall vertical here.
- Altitude of the mid-day sun changes.
- It gives us a measure of time for one year.
- Poles have days and nights of 6 months duration.
- It determines the distribution of solar energy on the earth.
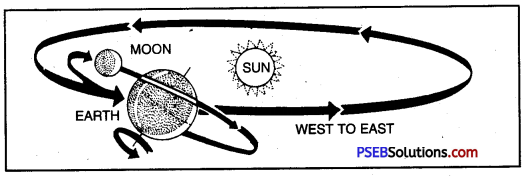
Rotation and Revolution
Question 3.
(a) How many seasons are there in a year?
Answer:
Normally, four seasons are experienced during a year- spring, summer, autumn, and winter.
(b) What are the causes of seasons?
Answer:
The change of seasons is due to the following reasons :
- Rotations of the earth.
- The inclination of the earth’s axis at 66 1/2° to the plane of the orbit.
- The axis remains always in the same direction.
- Revolution of the earth.
(c) Describe the conditions in each position.
Answer:
Due to the four seasons, the earth keeps on changing its position at different times of the year or during one revolution. These are seasonal positions. Each position of the earth with relation to the sun changes and explains different seasons.
Seasonal Positions :
1. Position on 21 June:
- North pole is inclined towards the sun and the South pole is tilted away from the sun.
- The larger part of the northern hemisphere is in daylight, while the larger part of the southern hemisphere is in darkness.
- Days are longer than nights in northern hemisphere while nights are longer in the southern hemisphere.
- The Sun shines vertical on the Tropic of Cancer (2314°N), but the southern hemisphere has slanting rays.
Hence the Northern hemisphere, with vertical rays and longer days has summer season. The southern hemisphere with slanting rays and shorter days has winter season. This position is also called the Summer Solstice. 21st June is the longest day and the shortest night in the northern hemisphere.
2. Position on 22 December: This position of the earth comes six months after the first position.
- The South pole is inclined towards the sun and the north pole turns away from the soil.
- The major part of the southern hemisphere is in light, while the major part of the northern hemisphere is in darkness.
- Days are shorter than nights in the northern hemisphere while days are longer in the southern hemisphere.
- The sun shines vertically on the Tropic of Capricorn (2314 °S) and the northern hemisphere gets slanting rays.
Hence the southern hemisphere with perpendicular rays and longer days has the summer season. This is the season of the southern summer and of the northern winter. It is also called the Winter Solstice. December 22 is the longest day and shortest night in the southern hemisphere.
3. Positions of 21st March, 23rd September:
- In these positions, the sun shines vertically on the equator.
- The circle of light passage through the poles dividing the globe into equal parts.
- Neither of the poles is inclined towards the sun.
- Every parallel has one half in darkness and the other half in light, with the result, the days and nights are equal all over the world.
- Both the hemispheres have similar seasons. It is autumn on 23rd September in the northern hemisphere and spring in the southern hemisphere.
- It is spring on 21st March in the northern hemisphere and autumn in the southern hemisphere. These positions are called Equinoxes (meaning equal nights).
