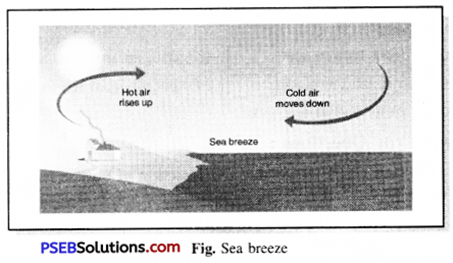
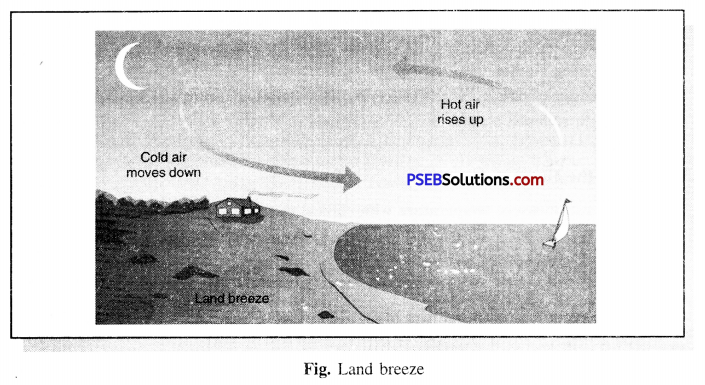
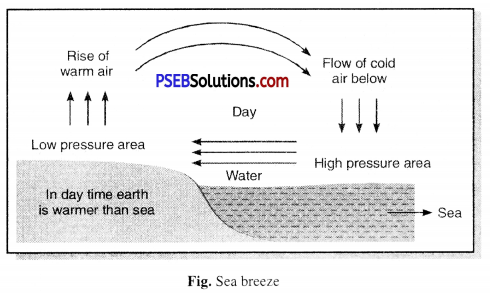
Punjab State Board PSEB 7th Class Science Book Solutions Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
PSEB 7th Class Science Guide Nutrition in Plants Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Fill in the Blanks:
(i) The process of obtaining and utilization of food by an organism is called ……………..
Answer:
nutrition
(ii) ………………. from the air is taken in through the tiny pores called stomata present on the surface of leaves.
Answer:
Carbon dioxide
(iii) ……………… is the initial product of photosynthesis.
Answer:
glucose (Carbohydrate)
![]()
(iv) The plants which depend on the food produced by other plants are called ………………..
Answer:
heterotrophs
2. State True or False:
(i) Carbohydrates is not an essential component of food.
Answer:
False
(ii) All green plants are autotrophs.
Answer:
True
(iii) Euglena is an organism that has both plant and animal like characters.
Answer:
True
(iv) Sunlight is not necessary for photosynthesis.
Answer:
False
3. Match the Column ‘A’ with Column ‘B’:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Agaricus | (a) Parasite |
| 2. Rhizobium | (b) Feaves |
| 3. Chlorophyll | (c) Feguminous plants |
| 4. Cuscuta | (d) Saprophyte |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Agaricus | (d) Saprophyte |
| 2. Rhizobium | (c) Leguminous plants |
| 3. Chlorophyll | (b) Leaves |
| 4. Cuscuta | (a) Parasite |
4. Choose the Correct Answer:
Question (i)
An Organism that fixes atmospheric nitrogen in the soil is :
(a) Amarbel
(b) Mushroom
(c) Rhizobium
(d) Chlorophyll
Answer:
(c) Rhizobium.
![]()
Question (ii)
The Organisms that cannot prepare their own food and depends on others for food are known as :
(a) Autotrophs
(b) Fleterotrophs
(c) Nutrients
(d) Minerals
Answer:
(b) Heterotrophs.
Question (iii)
Food factory of the plants is :
(a) Leaf
(b) Stem
(c) Root
(d) Flower
Answer:
(a) Leaf.
Question (iv)
Which of the following is a saprophyte ?
(a) Rhizobium
(b) Agaricus
(c) Cuscuta
(d) Protein
Answer:
(c) Cuscuta.
5. Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Question (i)
Define Nutrition.
Answer:
Nutrition. The act of obtaining and using food by the organism is called nutrition. Not all living things have the same food.
Question (ii)
What is photosynthesis ?
Answer:
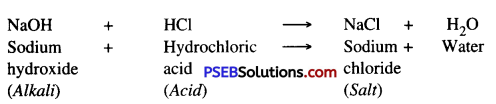
Photosynthesis. It is a process in which food (carbohydrates) is produced by the plants. During this process, carbon dioxide and water are synthesized into glucose (simple carbohydrates) in the presence of sunlight by plant’s green matter (chlorophyll pigment).
Through this action green plants convert light energy into chemical energy.
Chemical Equation :

Question (iii)
Name the raw materials required for photosynthesis.
Answer:
Ingredients for photosynthesis :
- Carbon dioxide
- Water
- Solar Energy
Question (iv)
What are insectivorous plants ?
Answer:
Insectivorous plants. Plants that have a system for catching and digesting organisms are called insectivorous plants, such as pitcher plant. The leaves of these plants are transformed into pot compositions to catch insects.
6. Short Answer Type Questions:
Question (i)
What do you mean by parasitic mode of nutrition ?
Answer:
Parasitic Nutrition. Nutrition in which the parasitic organism harms another organism and derives its food from it is called parasitic nutrition.
![]()
Question (ii)
Explain symbiotic relationship.
Answer:
Symbiotic relationship. Two different organisms co-exist with each other and depend on each other for their nourishment, then it is called symbiotic relationship. In this kind of relationship both the beings get benefit from each other. Like the fungus found on the roots of many plants. The fungus gets nourishment from the roots of the plant and in turn absorbs water and minerals from the soil. Fungus and moss are a good example of symbiotic relationship. Here the fungi absorb water from the earth and in turn the algae provide food through photosynthesis.
Question (iii)
How does the pitcher plant catch insects ?
Answer:

The pitcher plant transforms its leaves into pot-like structures to catch insects. This pot-like creation has curly hair on the face. When an insect sits on it, it slips down and cannpt climb up again and falls to the bottom of the pot. The enzymes present at the bottom digest the insect.
7. Long Answer Type Questions:
Question (i)
How are nutrients replenished in the soil ?
Answer:
Regain of nutrients by soil. Plants continue to absorb water, minerals and other nutrients from the soil which leads to lack of nutrients in the soil. Time to time nutrition should be provided to the soil so that the fertility of the soil is maintained. Farmers usually recreate these nutrient deficiencies by mixing manure in the soil and Fertilizers (which contain one or more preservatives) to fulfil nutrients.
In forest the forest waste, leaves and animal waste is decomposed by decomposers into nutrients to improve fertility of the soil.
Question (ii)
What do you mean by nutrients ? Explain various modes of nutrition in plants.
Answer:
Nutrients. Carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins and minerals are the main components of food. They help in the formation and function of the body and are called nutrients.
The main methods of nutrition in plants are :
(a) Autotrophic Nutrition. Those who prepare their own food from simple foods are called Autotrophs. This process of preparing food by such plants is called Autotrophic nutrition. All green plants are Autotrophic. In this method, chlorophyll, a green pigment present in plants, takes carbon dioxide and water from the air and makes food in the form of carbohydrates in the presence of solar energy. This action is called photosynthesis. Example-all green plants.
(b) Heterotrophic Nutrition. Some plants do not have green pigment (chlorophyll) and cannot make their own food, so they rely on food prepared by other plants for food. Such plants are called Heterotrophic plants and this method of obtaining food is called Heterotrophic nutrition. Example. Amar Bel.
PSEB Solutions for Class 7 Science Nutrition in Plants Important Questions and Answers
1. Fill in the Blanks:
(i) Green plants are called …………….. since they synthesise their own food.
Answer:
Autotrophs
(ii) The food synthesised by the plants is stored as ………………..
Answer:
Starch
![]()
(iii) In photosynthesis solar energy is captured by the pigment called …………….. .
Answer:
Chlorophyll
(iv) During photosynthesis plants take ……………… and produce …………….. .
Answer:
Carbondioxide, Oxygen
2. State True or False:
(i) Carbondioxide is released during photosynthesis.
Answer:
False
(ii) Plants which synthesise their food themselves are called saprotrophs.
Answer:
False
(iii) The product of photosynthesis is not a protein.
Answer:
False
(iv) During photosynthesis solar energy is converted into chemical energy.
Answer:
True
3. Match the Column I with Column II :
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Chlorophyll | (a) Bacteria |
| (ii) Nitrogen | (b) Pitcher plant |
| (iii) Amarbel | (c) Leaf |
| (iv) Animals | (d) Parasite |
| (v) Insects | (e) Heterotrophs |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Chlorophyll | (c) Leaf |
| (ii) Nitrogen | (a) Bacteria |
| (iii) Amarbel | (d) Parasite |
| (iv) Animals | (e) Heterotrophs |
| (v) Insects | (b) Pitcher plant |
4. Choose the Correct Answer:
Question 1.
The organisms which depend upon other organisms for food are called ……………..
(a) Symbionts
(b) Parasites
(c) Autotrophs
(d) Saprophytes.
Answer:
(b) Parasites.
![]()
Question 2.
Which part of the plant usually contains stomata ?
(a) Roots
(b) Stem
(c) Leaves
(d) Flower.
Answer:
(c) Leaves.
Question 3.
Which gas is released during photosynthesis ?
(a) Oxygen
(b) Carbon dioxide
(c) Nitrogen
(d) Hydrogen.
Answer:
(a) Oxygen.
Question 4.
What is the unit of living beings
(a) Organ
(b) Organ system
(c) Cell
(d) Tissue.
Answer:
(c) Cell.
Question 5.
What is the ultimate source of energy in the living beings ?
(a) Moon
(b) Sun
(c) Stars
(d) Planet.
Answer:
(b) Sun.
Question 6.
Name one eatable fungus.
(a) Alga
(b) Bacteria
(c) Rhizopus
(d) Mushroom.
Answer:
(d) Mushroom.
Question 7.
Plants breathe through:
(a) Epidermis
(b) Buds
(c) Stomata
(d) Root hairs.
Answer:
(c) Stomata.
Question 8.
What are green coloured thread like structures over the pond water called ?
(a) Fungi
(b) Algae
(c) Amoeba
(d) Paramecium.
Answer:
(b) Algae.
![]()
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name the nutrients.
Answer:
Nutrients. Carbohydrates, vitamins, fats, proteins, minerals, roughage.
Question 2.
How do plants synthesise food ?
Answer:
Green plants synthesise their food material using carbondioxide, water and solar energy.
Question 3.
Name the various type of nutrition.
Answer:
Types of Nutrients. Autotrophic, Heterotrophic, Saprotrophic and Parasitic.
Question 4.
What are openings / pores in a leaf known as ?
Answer:
Stomata.
Question 5.
What is function of chlorophyll in a leaf ?
Answer:
Chlorophyll capture the energy of sunlight.
Question 6.
Which is ultimate source of energy for all living organisms ?
Answer:
Sun.
Question 7.
What are products of photosynthesis ?
Answer:
Carbohydrates and oxygen.
Question 8.
Name the various parts of plants which take part in photosynthesis.
Answer:
Green stems and green leaves.
![]()
Question 9.
Besides green leaves, which other coloured leaves are found in plants ?
Answer:
Deep red, violet or brown.
Question 10.
What is algae ?
Answer:
Algae It is a slimy, green patch found in pond or in stagnant water.
Question 11.
Do algae photosynthesis ? Why ?
Answer:
Yes, algae do photosynthesis as they contain chlorophyll.
Question 12.
From which elements are carbohydrates made up of ?
Answer:
Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
Question 13.
Name some four human parasites.
Answer:
- Mosquitoes
- lice
- bed bug
- leech.
Question 14.
Write one eatable fungus.
Answer:
Mushrooms.
Question 15.
Where does mould grow ?
Answer:
Moist and rainy areas.
![]()
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write the definite word for the following:
(i) Weak stem parasitic plant.
(ii) A plant in which both Autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition are found,
(iii) The holes through which gases are exchanged in the leaves.
Answer:
(i) Amar bel (Cuscuta)
(ii) Pitcher plant
(iii) Stomata
Question 2.
Differentiate autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition.
Answer:
Differences between autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition.
| Autotrophic nutrition | Heterotrophic nutrition |
| (1) Organisms prepare their own food by obtaining energy from sun. | (1) Organisms obtain ready-made food from other plants or animals. |
| (2) It occurs in green plants and blue green algae. | (2) It occurs in parasitic plants, fungi, most of bacteria and animals. |
Question 3.
Why do coloured leaves photosynthesise when they are not green in colour ?
Answer:
Coloured leaves (red, brown etc.) do contain chlorophyll but large amount of red, brown pigment mask the green colour. So, they can photosynthesise.
Question 4.
How do fungus grow on the things ?
Answer:
Spores of fungi are present in air. When they land on wet and warm things, they germinate.
Question 5.
How do lichens show symbiotic relationship ?
Answer:
Lichens, a chlorophyll partner algae and non-green fungus live together. The fungus provides shelter, water and minerals to algae while algae provides food which is synthesised by it. So they both show symbiotic relationship.
![]()
Question 6.
Explain the parasitic relationship between Rhizobium and plants.
Answer:
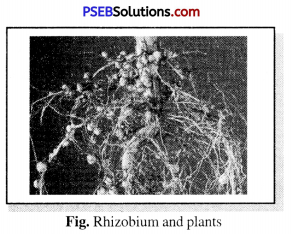
Rhizobium is a bacterium that lives in nodules on the roots of legumes. It converts the nitrogen in the air into a usable form which is used by the plant and in return provides shelter and food to bacteria.
Question 7.
What do you understand by a parasites, saprophytes and symbiosis ? Give one example for each.
Answer:
- Parasites. Those plants or animals which obtain their food from a host and also get shelter from it, are known as parasites, e.g. Cuscuta and Viscum etc.
- Symbiosis. It is a type of relationship which is mutually beneficial for both the parents (host and parasite), e.g. Lichens are combination of algae and fungi. The fungus holds the algal cells in its mat of web-like hyphae and in return supplies water and dissolved minerals.
- Saprophytes. Those organisms which grow on dead and decaying organic matter and obtain their food from decomposed bodies are known as saprophytes, e.g. Bacteria, mushrooms etc.
Question 8.
Distinguish between a parasite and a saprotroph.
Answer:
Differences between a parasite and saprotroph.
| Parasite | Saprotroph |
| (1) These organisms depend upon other living organisms for its food. Example : Cuscuta, tape- worms, roundworms. |
(1) These organisms obtain their food from dead organic matter. Example : Fungi, bacteria. |
| (2) They produce special type of organs like suckers, hooks to obtain their food. | (2) They secrete some enzymes to decompose complex molecules into simple form. |
Question 9.
What are the conditions required for Autotrophic nutrition and its basic and by-products ?
Answer:
Photosynthesis is essential for Autotrophic nutrition which requires the following conditions : (1) sunlight (2) chlorophyll (green pigment), (3) carbon dioxide and (4) water.
The by-products of this process are: The basic products of photosynthesis are oxygen gas and glucose. Afterwards glucose is stored in the form of starch.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Symbiosis is beneficial for both the partners, justify.
Answer:
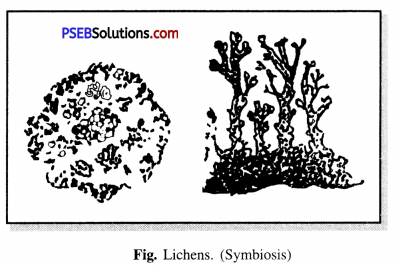
Symbiosis. The type of association in which both the partner’s benefit is called symbiosis.
In plants like lichens, there is an association between green algae and non-green fungus. The fungus forms a mat of web-like hyphae to hold the algal cells. The fungal hyphae supply water and minerals to the algae. The algae can synthesize food for themselves as well as for the fungus.