Punjab State Board PSEB 10th Class Science Important Questions Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Important Questions and Answers.
PSEB 10th Class Science Important Questions Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Give magnetic field due to solenoid. On what factors the strength of the field depends?
Or
What is solenoid? How does a solenoid behave like a bar magnet?
Answer:
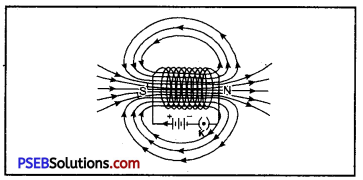
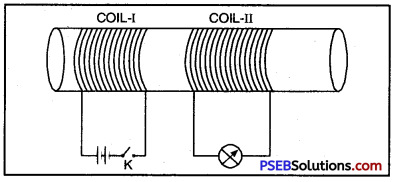
Solenoid. A solenoid is a long circular coil containing a large number of close turns of insulated copper wire.
Magnetic field due to solenoid. When an electric current is passed through the solenoid, it produces magnetic field around it as shown in Figure. Magnetic field produced by a current carrying solenoid is similar to the magnetic field produced by a bar magnet. The magnetic lines enter from one end of the solenoid and leave at the other end. If we look from left end, the current appears to be passing in the solenoid in clockwise direction and hence it acts as a south pole according to clock rule. If the solenoid is viewed from right side, the current appears to be in anticlockwise direction. Hence, right hand side face of the solenoid behaves as if this were a north pole.
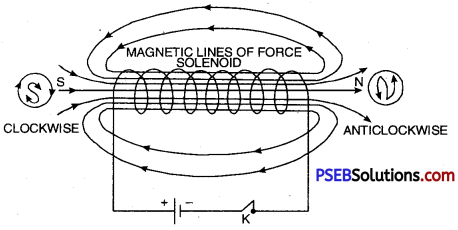
Magnetic field due to current carrying solenoid is similar to bar magner.
Since the current flows in the various turns of the solenoid in the same direction, the magnetic field produced by each turn of the solenoid adds up, giving a very strong resultant field inside the solenoid.
Hence, a solenoid may be used in making electromagnets.
The strength of the magnetic field produced depends upon the following three factors :
- Number of turns. The more the number of turns, the stronger will be the magnetic field produced.
- Strength of the current in the solenoid. Larger the current, stronger will be the magnetic field produced.
- Nature of core of solenoid. The strength of the field depends upon the core on which the coil is wound. For air core, field is very weak whereas for soft iron-core, the field is very strong. .
Question 2.
What is an electromagnet? Upon what factors its strength depends?
Answer:
Electromagnet: The combination of soft iron core and a current carrying insulated copper wire wound over it is called an electromagnet.
Very strong electromagnets can be produced by winding an insulated copper wire on a soft iron core.
When current is passed through a solenoid, a magnetic field is produced. Now if a soft iron core is placed inside the solenoid, the strength of the magnetic field becomes very large. The reason for increase in magnetic field is due to the fact that iron gets magnetised by induction.
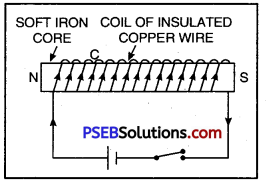
Electromagnet
A simple electromagnet is as shown in Figure. To make an electromagnet, a soft iron core is placed inside a solenoid having large turns of insulated copper wire. The two ends of the solenoid are connected to a battery and a key.
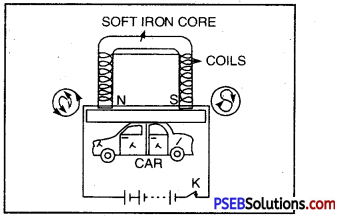
Electromagnet lifting a car.
Strength of electromagnet depends upon
- Number of turns. Strength of electromagnets is directly proportional to the number of turns.
- Current flowing. More the current flowing through the wire, stronger is the electromagnet.
- Length of the air gap. Lesser the length of air gap between poles, stronger is the electromagnet.
- Air gap between the poles of a U-shaped electromagnet is small, hence it is very strong
Question 3.
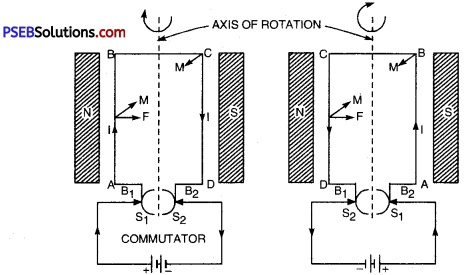
Explain principal, construction and working of D.C. generator.
Answer:
Electric Generator. It is a device that converts mechanical energy into electric energy. It only converts the form of energy into another form. In generator, mechanical energy is the input while electric energy is obtained as output.
Principle: Generator is based on the principal that “when a conductor cuts magnetic lines of force, then according to the Faraday’s, electromagnetic law, electromagnetic force (emf) is induced in it which makes induced current to flow in the circuit when the circuit is closed”.
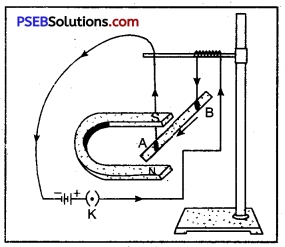
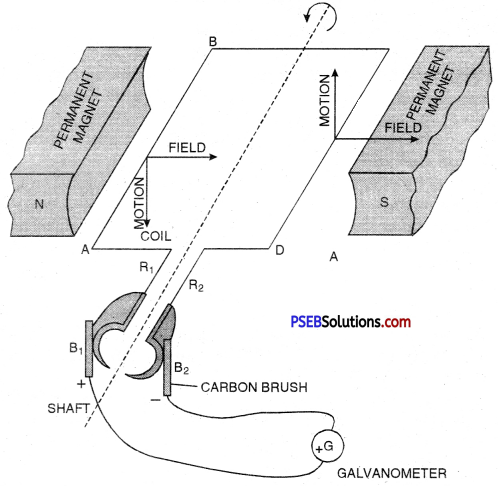
Construction: A D.C generator has the following main parts :
- Armature: It consists of a coil ABCD in which an insulated copper wire is wound into number of turns around a soft iron core, called armature. It is fixed on an axis and is capable to rotate with steam or running water.
- Field Magnet: There are two strong pole pieces (electro magnet)-in which the coil is placed forms a field magnet. In small generators, permanent magnets while in big generators electromagnets are used.
- Slip Rings: At the ends of the coil two slip rings R1, and R2 are attached. These two work as commutators.
- Carbon Brush Split: Rings R1 and R2 soft touch against the carbon brushes B1 and B2. When the coil rotates the slip rings R1 and R2 in turn touch B1 and B2.
- From carbon brushes B1 and B2 electric current is taken to the load (output). In the diagram galvanometer is shown in place of load.
Working. When the coil rotated about its axis, then emf is induced in arms AB and CD of the coil. The direction of induced electromagnetic force can be determined by Fleming’s right hand rule.
Suppose in the beginning the coil is in vertical position with its arm AB in the lower position and CD in the upper position. When the coil is rotated about its axis then during the first half rotations the arm AB moves in the upward direction and CD in the downward direction. According to Fleming’s right hand rule the direction of induced current in arm AB will be from A to B and in CD it is from C to D.
The arm AB on reaching the upper most position begins to move downward while the arm CD would begin to move in the upward direction. Therefore, the direction of induced current in the arms AB and CD gets reversed but to keep the direction of current in the load (output) same, the split rings are used. In the second half of the rotation the end of the coil comes in contact with the split ring R2 and the end D touches the split ring Rx so that the direction of current remain same in the load.
Question 4.
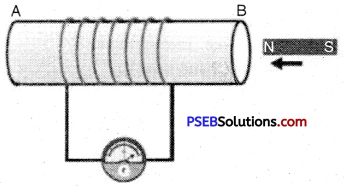
Arrange an activity to show that current is produced due to change in magnetic field.
Answer:
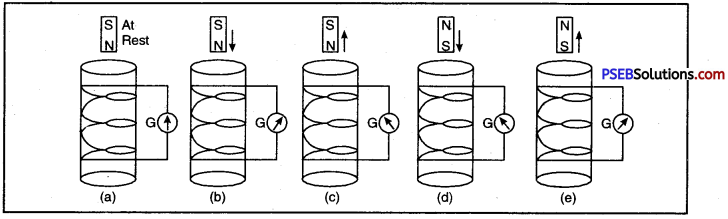
Make a coil XY having large number of terms of insulated copper wire wound area as shown in the figure. Connect the ends of the coil to a sensitive galvanometer.
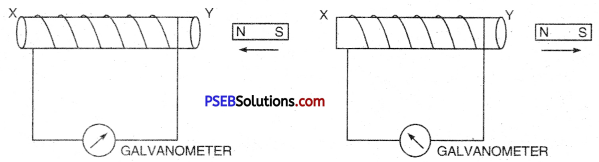
Now quickly bring N-pole of a bar magnet but see that it does not touch the coil. You will see deflection in the galvanometer which proves that current is flowing in the galvanometer. Note the direction of deflection in the galvanometer.
Now take away the magnet as shown in fig 13.20. Again you will notice deflection in the galvanometer but diis time the direction of deflection is opposite to the first. If we do not move the magnet and keep it stationary near the coil then there is no deflection in galvanometer. This experiment shows that when there is a relative motion between the coil and the magnet then current is induced in the circuit.
![]()
Question 5.
What are essential precautions to be used while using electricity?
Answer:
The following precautions should be observed while using electricity :
- Turn off all switches including main switch whenever sparking or fire is noticed.
- All connections must be tight. Wires must be covered with proper insulation of proper thickness. All joints must be covered with insulating tape of a good quality. Defective / switches should be immediately replaced.
- Fuses should always be connected to live wire. The earth wire must be connected to the body of electric appliance.
- Fuse must be of proper rating and should always be connected to live wire.
- Whenever repairs are needed, switch off main switch. If however , repairs need a direct handling of live wire, rubber gloves, rubber shoes and a plier with insulated handle should be used.
- If inspite of all the precautions, a person gets a shock due to accidental touching a live wire, one should try to provide such a person with support of some non-conducting material like wood, plastic or rubber. Never try to pull away person by your hand.
- Always put on dry rubber shoes while repairing the circuit.
Question 6.
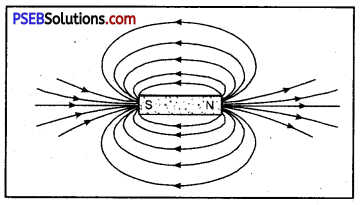
What are magnetic field lines? How can the magnetic lines of force due to a bar magnetic be shown?
Answer:
Magnetic Field. The area of field around the magnet in which the force of attraction or repulsion due to magnet is experienced, is called Magnetic field.
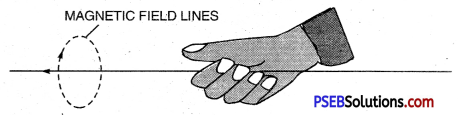
Magnetic field lines: It is the path in the magnetic field, along which the unit N-pole would move when it is free to move.
magnet can be shown by the following two methods :
1. Place a magnet on a cardboard sheet. Now spread iron filings on the Cardboard and tap it gently will when the iron filings will arranged itself in the pattern of magnetic lines of force.
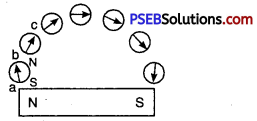
2. Drawing magnetic lines of a bar magnet Activity. Place a bar magnet on a white sheet and mark its boundary with pencil. Place a magnetic compass needle near the North-pole of the magnet. Now mark the position of poles of the magnetic needle with a sharp pencil. Now move the magnetic compass needle in such a position so that its S-pole is in the position of previous position of North-pole, Again mark position of N-pole with pencil. Repeat this process so that you reach south- pole of the bar magnet. Now join these marked points making a free hand curve.

This curve represents a magnetic line of force. In the same way by taking another point near the north pole of the bar magnet get different line of force. By taking various points and drawing different curve for each of the points you will get a pattern of magnetic lines of force due to a bar magnet.
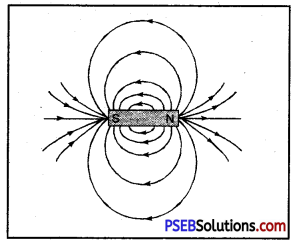
Magnetic lines o force around a bar magnet.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How will you prove that current flowing through a copper wire produces magnetic effect?
Answer:
- On passing current through a thick copper wire with a magnetic needle placed in its neighbourhood will be deflected.
- This shows that current flowing through a copper wire produces magnetic field all round it.
Question 2.
What do you understand by magnetic effect of current? To understand this effect give Oersted experiment.
Answer:
Magnetic Effect of Electric Current. When electric current flows through a conducting wire, then magnetic field is produced all round it. This effect of electric current is known as magnetic effect.
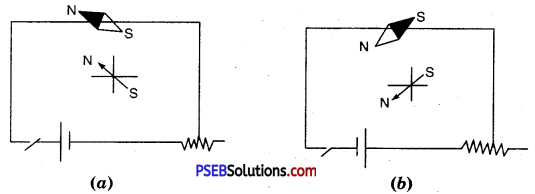
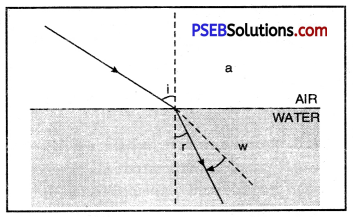
Oersted Experiment. Oersted took a conducting wire XY and placed a magnetic needle under this wire, then pressed the key and passed current through the wire in the direction from X to Y as shown in figure (a). He observed that the N-pole of the magnetic needle gets displaced towards west. Similarly, he repeated the experiment by reversing the direction of flow of current in the wire by changing the terminals of battery connected to the ends of the wire. This time the direction of deflection of the needle was opposite i.e. from Y to X as shown in figure (b).
The direction of deflection of magnetic needle can be remembered by ‘SNOW’ rule. This rule states that “If current in the wire XY flows from south pole to north pole when the current carrying conductor is placed above the conductor then the N-pole of the conductor gets displaced towards the west direction.”
Question 3.
Define magnetic field and write important properties of magnetic lines of force.
Answer:
Magnetic Field. It is the field or region around a magnetic in which the effect of magnet (force of attraction or repulsion) can be experienced.
Magnetic Lines of Force. The path on which a unit N-pole moves when it is free to move, is called magnetic line of force.
Important properties of magnetic lines of Force.
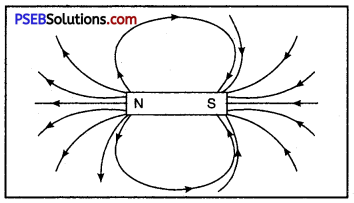
- Outside the magnet, magnetic lines of force start from north pole (N-pole) of the magnet and end at its south pole (S-pole).
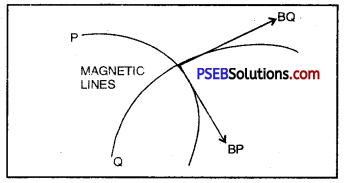
- No two magnetic lines of force intersect each other and if they do so then it would mean that the point of intersection there are two directions of magnetic lines of force which is impossible.
- At any point or the magnetic field the direction of the field lines is along the tangent at that point.
Question 4.
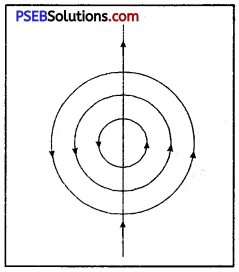
How will you represent diagrammatically uniform and non-uniform magnetic field?
Answer:
The uniform magnetic field represented by equally spaced parallel lines while non-uniform magnetic field is represented either by non-parallel lines or by unequally spaced lines. These are shown in the diagrams below :
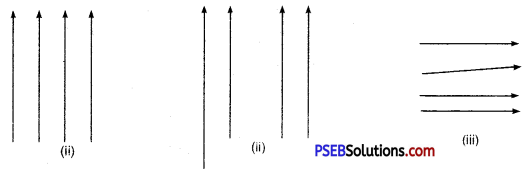
(i) Uniform magnetic field, (ii) and (iii) Non-uniform magnetic field.
![]()
Question 5.
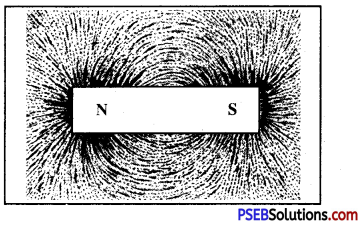
In the given figure what are the lines shown around the magnet called? Also give any two properties of these lines.
Answer:
In the figure the lines shown around the magnet are called magnetic field lines.
Properties of magnetic field lines,
- Outside magnetic: the magnetic field lines start from the N-pole of the magnet and end at the S-Pole while inside the magnet the direction of magnetic lines are from S-Pole to the N-Pole.
- The direction of magnetic field at any point of the magnetic line of force is represented by the tangent drawn to the curve at that point.
Question 6.
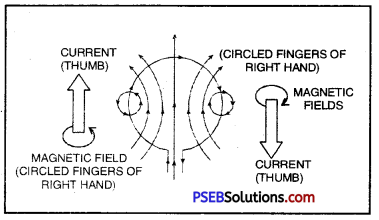
What is Maxwell’s Right hand thumb Rule? For what purpose this rule is used?
Answer:
Maxwell’s Right Hand Thumb Rule According to this rule “To find the direction of magnetic field around a straight carrying conductor if the straight conductor is held in right hand in such a way that your thumb points in the direction of current then the curling fingers would determine. The direction of magnetic field lines.”
The rule is used to determine the direction of magnetic field lines produced around a straight conductor carrying current.
Question 7.
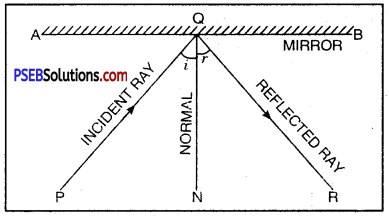
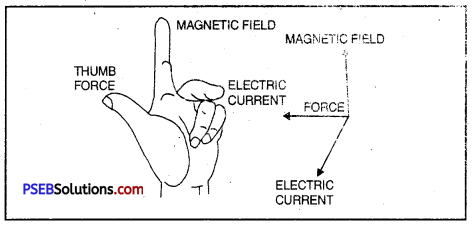
Which rule is shown in the figure? Define the rule. In which device this rule is used?
Answer:
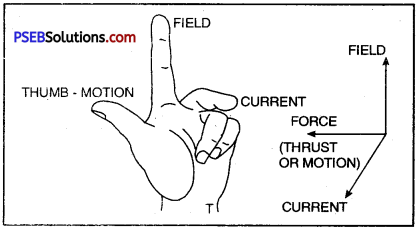
Fleming’s Left Hand Rule is shown in the figure.
Fleming’s Left Hand Rule. According to this rule, stretch your left hand in such a way that the thumb, forefinger and central finger are mutually at right angle to each other. If the fore finger points in the direction of the magnetic and the central finger points in the direction of current, the thumb gives the direction of the force acting on the conductor.
This rule is used in the working of an electric motor.
Question 8.
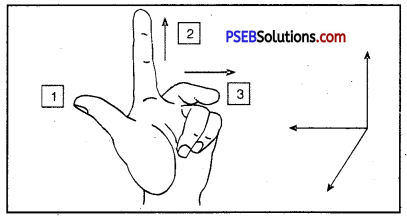
Fleming’s left hand rule, Label the diagram.
Answer:
Fleming’s Left Hand Rule. According to this rule, stretch your left hand in such a way that the thumb, forefinger and central finger are mutually at right angle to each other. If the fore finger points in the direction of the magnetic and the central finger points in the direction of current, the thumb gives the direction of the force acting on the conductor.
This rule is used in the working of an electric motor.
- Force acting on the conductor OR direction of motion
- Direction of magnetic field
- Direction of current
Question 9.
Name the law shown in the figure. Label 1 and 2 law.
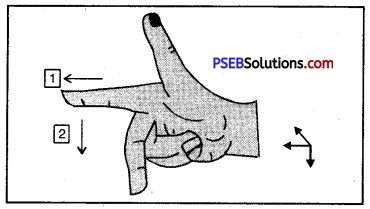
Answer:
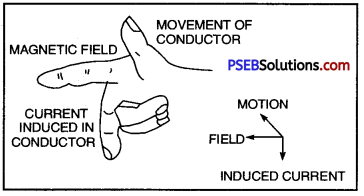
The figure represents Fleming’s Right Hand Thumb Rule
- Magnetic Field
- Current induced in the conductor.
![]()
Question 10.
In the alongside figure a straight conductor B is carrying current in the vertical downward direction.
(a) What will be the direction of magnetic field lines around the conductor?
(b) Name the law which you have used for your answer.
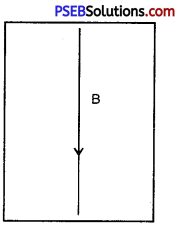
Answer:
(a) Clockwise.
(b) Maxwell’s Righthand Thumb Rule.
Question 11.
What is Electro-magnetic Induction?
Answer:
Electro-magnetic Induction. The process of producing e.m.f by changing the magnetic lines of force linked with the circuit, is called electromagnetic induction. The electromagnetic force (e.m.f) so produced is called induced electromotive force.
Question 12.
List some such electric appliances in which electric motor is used.
Answer:
With the help of electric motor all such appliance work in which it is required to produce rotatory in motion e.g. Electric fan, tape recorder, mixer etc.
Question 13.
What is Electric Fuse? What is its importance?
Answer:
Electric Fuse. It is a device used in electric circuits which prevents the other electric appliances connected in the circuit from being damaged by high current. It has low meeting point.
Importance (use) of Electric Fuse. If for some reason heavy current begins to flow in the circuit then fuse wire melts and breaks the circuit and accident is prevented.
Question 14.
Why the fuse wire should have high resistance and low melting point?
Answer:
The fuse wire should have high resistance and low melting point because when it is connected in series then heavy current will not flow through fuse wire due to its high resistance and the heat produced will melt it due to its low melting point. Thus the electric appliances connected in the circuit would be saved from damage.
Question 15.
What is meant by over-loading?
Answer:
Over-loading. Overloading means to draw large current from the mains. This happens when many appliances are connected with single socket simultaneously. The supply wires as well the wires used in household wiring has a specific rating. The rating of 15 A means that if a current upto 15A is passed through the circuit, there is no likely damage feared to the circuit. But if a current more than maximum allowed limit is passed, there may be excessive heating of the wires and it may damage the wiring.
Question 16.
When does an electric short-circuit occur?
Answer:
Short-circuiting. An electric circuit is said to be short-circuited if a live wire touches neutral wire or earth wire, a large current flows through the circuit due to almost zero resistance of the circuit. This results in increase of temperature and hence heating of wires which may cause fire or damaging the appliance.
To save the circuit from damage due to over-loading or short-circuiting, a fuse of proper rating is put in each circuit.
Question 17.
What are hazards of electricity?
Answer:
Hazards of Electricity. Electricity is the most important source of energy. A proper use of electricity is a boon while improper use is very dangerous and may prove to be fatal. There are number of hazards.
- If by accident a person touches a live wire, he gets a very severe shock which may prove fatal.
- Loose connections, defective switches and sockets can cause sparking which may lead to fire.
- Short circuiting due to damaged wires or overloading of circuits can cause fires.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is a dynamo?
Answer:
Dynamo. It is a device which converts mechanical energy into electric energy.
![]()
Question 2.
On what principle is an a.c. motor based?
Answer:
It is based upon Fleming’s left hand rule.
Question 3.
What is an electric motor?
Answer:
Electric motor. It is a device which converts electric energy into mechanical energy.
Question 4.
List three sources of magnetic field?
Answer:
Electromagnet, load stone, solenoid, bar magnet.
Question 5.
Name the physical quantity whose S.I. unit is weber/m2.
Answer:
Magnetic field.
Question 6.
In which part of a bar magnet, the magnetic field lines are more denser?
Answer:
At the poles of a magnet.
Question 7.
How does the strength of the magnetic field at the centre of a circular coil of a wire depend on : (a) radius of the coil (b) number of turns of the coil.
Answer:
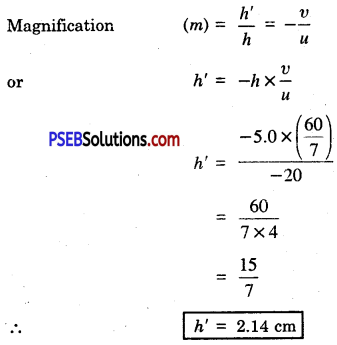
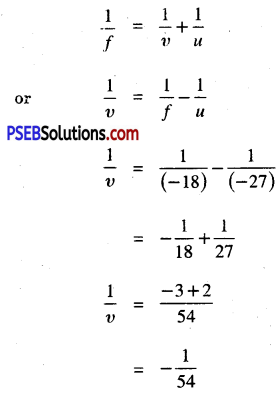
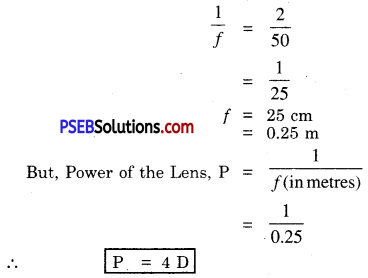
(a) Strength of magnetic field (B) ∝ \(\frac{1}{\text { radius of the coil }(r)}\)
(b) Strength of magnetic field (B) ∝ Number of turns of the coil (N).
Question 8.
Name any two devices which uses electric motor as an essential component in their working.
Answer:
- Water pump
- Electric fan.
Question 9.
Define an electromagnet.
Answer:
Electromagnet. The combination of an soft iron core and current carrying insulated wire wound over it, is called an elctromagnet.
Question 10.
Define magnetic pole.
Answer:
Magnetic poles are points near the ends of a magnet where magnetic field is maximum,
Question 11.
Give a property of a Magnet.
Answer:
Directive Property (stays always in N-S directions, when suspended freely).
Question 12.
Name two electric devices which act on magnetic effect of electric current.
Answer:
- Electric bell
- Loud-speaker.
Question 13.
What is electric fuse?
Answer:
Fuse is a safety device which saves electric circuit from damage due to over loading a short circuit.
Question 14.
Which electrical phenomenon is responsible for deflection of galvanometer needle in the given figure?
Answer:
Electric Induction.
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
The direction of magnetic field produced on passing electric current in a conductor is determined by
(A) MaxweI1s Left hand rule
(B) Fleming’s right hand rult
(C) Fleming’s left hand rule
(D) Faraday’s law.
Answer:
(A) MaxweJi Left hand rule
![]()
Question 2.
The direction of the force produced in a current carrying coil placed in a strong magnetic field is determined by
(A) Maxwell’s right hand rule
(B) Fleming’s right hand rule
(C) Fleming’s left hand rule
(D) Faraday’s law.
Answer:
(C) Fleming’s left hand rule
Question 3.
What is the colour of neutral wire in a domestic electric circuit?
(A) Black
(B) Red
(C) Green
(D) No specific colour.
Answer:
(A) Black
Question 4.
When a current carrying wire and neutral wire come in contact so that heavy current begins to flow, this arrangement is called:
(A) Overloading
(B) Short circuit
(C) Earthing
(D) All the above.
Answer:
(B) Short circuit
Question 5.
Connecting metallic frame of high power electrical appliances with the earth wire of domestic circuit is called
(A) Overloading
(B) Short circuit
(C) Earthing
(D) Ail of these
Answer:
(C) Earthing
Question 6.
Which of the following is source of direct current?
(A) Dry cell
(B) Button cell
(C) Lead battery
(D) All these.
Answer:
(D) All these.
Question 7.
The device used for producing electric current is called a :
(A) Generator
(B) Galvanorneter
(C) Ammeter
(D) Motor.
Answer:
(A) Generator
Question 8.
Similar magnetic poles
(A) Attract
(B) Repel
(C) Both attract and repel
(D) None of these.
Answer:
(B) Repel.
Question 9.
Magnetic field lines are.
(A) Straight lines
(B) Curved
(C) Closed curves
(D) Triangular.
Answer:
(C) Closed curves