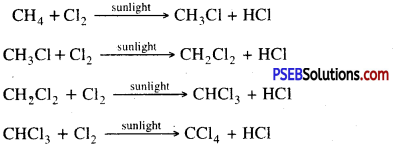
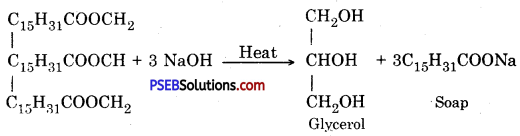
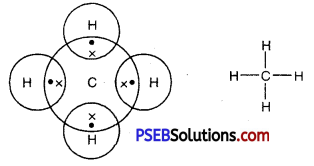
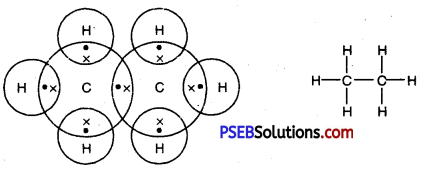
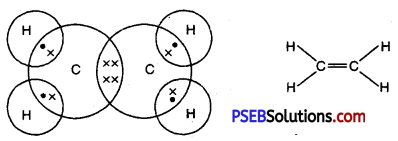
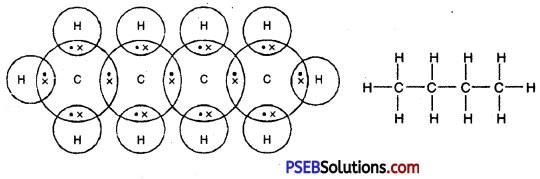
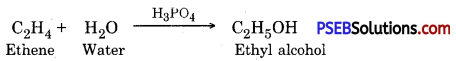
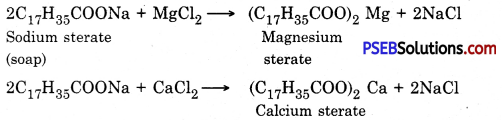
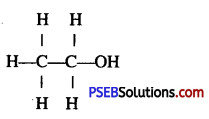
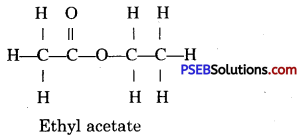
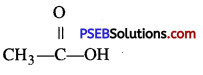
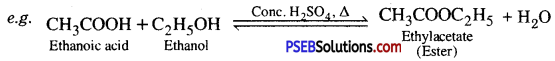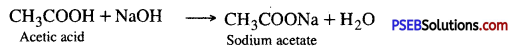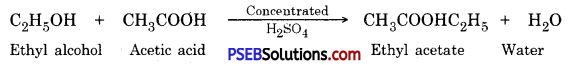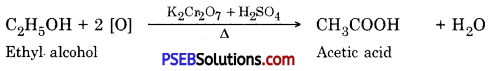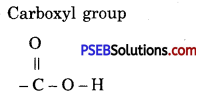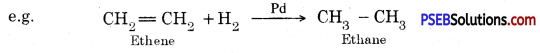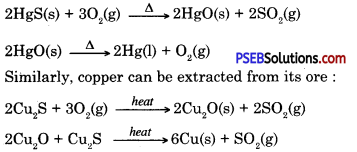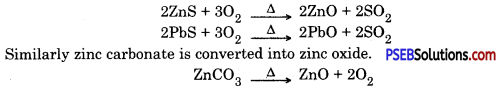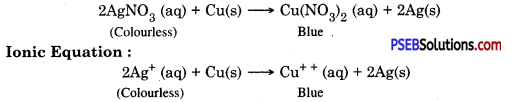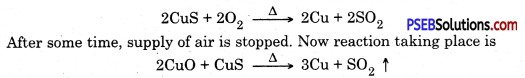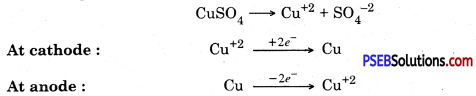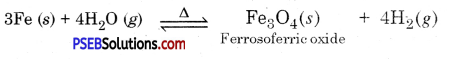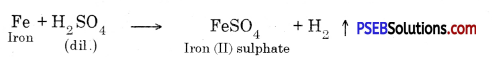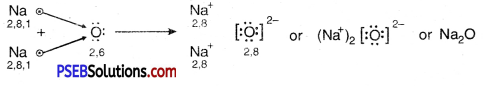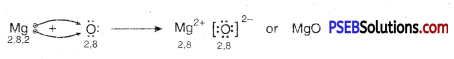Punjab State Board PSEB 10th Class Science Important Questions Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals Important Questions and Answers.
PSEB 10th Class Science Important Questions Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
Long Answer Typt Questions
Question 1.
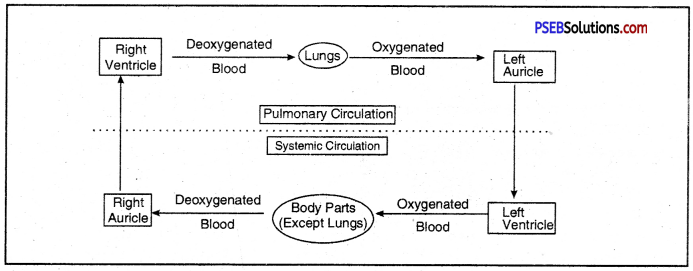
Show various steps involved in extraction of metal from an ore by a sketch.
Answer:
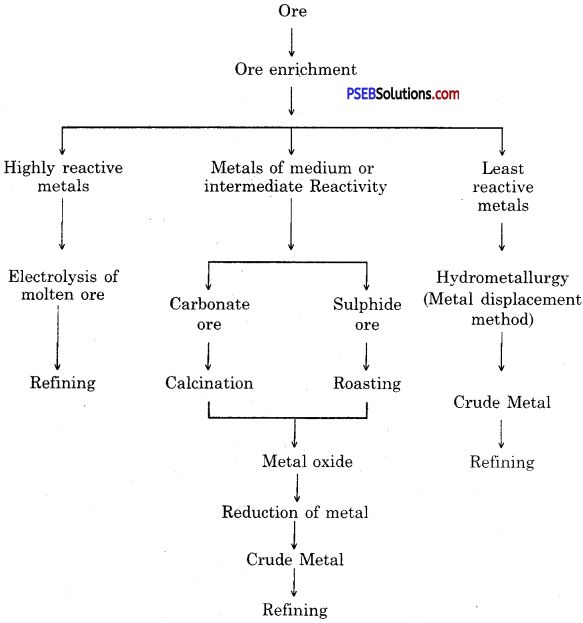
Steps involved in the extraction of metals from ores.
Question 2.
Give methods of enrichment of ores.
Answer:
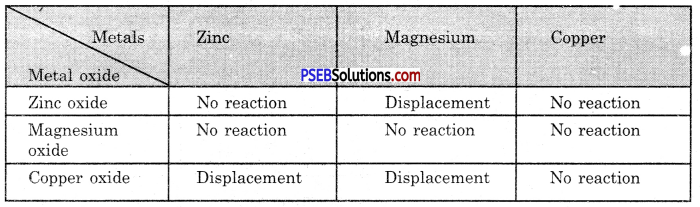
Methods of enrichment of ores. Ores or minerals are mined from earth these are usually contaminated with large amount of impurities which are called gangue. It is necessary to remove these impurities before extraction of metals. By removing gangue the ore is enriched and concentration of metal is increased. Therefore ore in enriched prior to other processes. Methods of removing gangue from ore depends on the difference of physical and chemical properties of both of them.
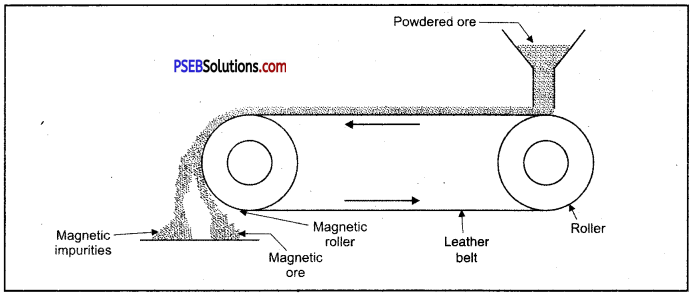
Enrichment of ore using magnetic method.
Physical methods of enrichment :
- Hydraulic Washing: In this method finely powdered ore is washed with jet of water. In this strong flow of water light gangue particles are washed away where as heavy ore particles settle down, Tin and lead ores are enriched by this method.
- Froth Floatation Method: In this method, mixture of powdered ore and water or some appropriate oil is taken in a tank. Ore particles are coated with oil and gangue particles are wet with water. A blast of compressed air is blown through the pipe of a rotating agitation to produce froth, due to this, mineral particles wetted with oil change into foam and float on the surface of water. Froth containing ore particles is easily transferred to another container sulphides of copper, lead and zinc are enriched by this method.
Chemical Methods: The chemical method used for the concentration of the ore is based on the difference in some chemical property of the metal and the impurities. An example of this method is the concentration of bauxite ore of aluminium.
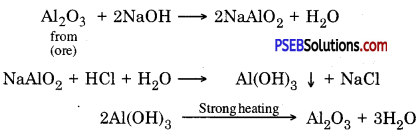
Concentration of aluminium ore by Bayer’s process: In this method, Bauxite is reduced by treating it with hot sodium hydroxide. It gives sodium meta aluminate (NaAlO2) which is soluble in water. The solution in filtered to remove the gangue present in the ore because it does not dissolve in sodium hydroxide. NaAlO2 is allowed to react with hydrochloric acid to obtain Aluminium hydroxide. On strong heating aluminium hydroxide pure aluminium oxide is obtained.
Following reactions take place
Question 3.
Explain General methods used in the extraction of metals.
Answer:
Steps involved in the extraction of metals :
- Enrichment (concentration) of ore.
- Converting concentrated ore into oxide.
- Reduction of metal oxide to obtain metal.
- Refining of impure metal.
1. Concentration :
(A) Hydraulic washing: This method is used for concentration of oxide ores Gangue particles are lighter as compared to ore particles. In this method powdered ore is washed with flowing water. Light gangue particles are washed away with water and heavy ore particles are left.
(B) Froth floatation method: In this method powdered ore is taken in a tank containing water pine oil is also added to it. Sulphide ore is wet with oil and gangue is wet with water.
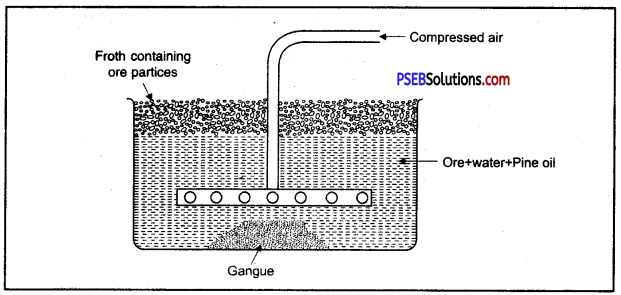
The water is agitated by blowing compressed air violently, a froth is formed on the surface of water. This froth carries the lighter ore particles along with it to the surface. Gangue particles are heavy and settle to the bottom.
(C) Magnetic separation.
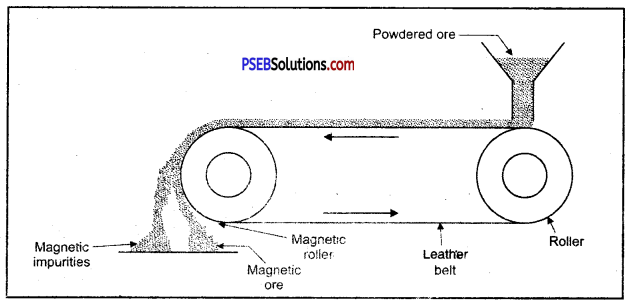
Enrichment of ore using magnetic method.
1. Magnetic method: This method is acceptable for magnetic impurities like iron, cobalt, Nickel etc. Minerals which are of magnetic nature got attracted towards magnetic field. Chromite and pyrolusite ores are enriched by this method. In this method ground ore is placed on a conveyer belt. This belt goes around two rollers one of which is magnetic. When ore comes near the magnetic roller then two heaps of magnetic and non magnetic materials are obtained. Iron ore magnetite is enriched by this method.
(D) Chemical separation: This process is based on the difference between chemical – properties of ores and gangue eg. Bauxite Al2O3.2H2O is impure form of aluminium oxide. It contains Iron (III) oxide (Fe2O3) and sand (SiO2) as main impurities. Due to iron (III) oxide its colour is red brown. Bayer’s process is used to obtain pure aluminium from / bauxite. In this methods powdered ore is mixed with heated sodium hydroxide.
Al2O3 (S) + 2NaOH (aq) → 2NaAlO2 (aq) + H2O (l)
NaAlO2 (aq) + 2H2O (l) → Al(OH)2 (s) + NaOH (aq)
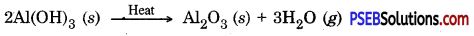
2. Converting concentrated ore into metal oxide
Roasting: In this process ore is heated in the presence of air to obtain metal oxide. Which can easily be reduced to obtain the metal.
Zinc blende contains zinc sulphide when concentrated zinc blende ore (zinc sulphide) is roasted in air then it gets oxidized to give zinc oxide.
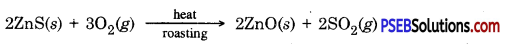
Calcination: In this process ore is heated in the absence of air to remove moisture and volatile impurities.
When carbonate ore is heated it dissociates to give metal oxide.
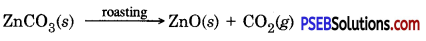
3. Extracting metals from metal oxide.
To obtain metal from metal oxide it is heated with some reducing agent. To obtain metals zinc, iron, tin etc. their oxides ore heated with carbon which acts as reducing agent.
ZnO(s) + C(s) → Zn(s) + CO(g)
Oxides of metals with medium activity can be reduced by using highly reactive metals like sodium, calcium and aluminium etc.
3MnO2(s) + 4Al(s) → 3Mn(l) + 2Al2O3(s) + heat
4. Electrolytic refining.
In this method impure metal is taken as anode and a thin strip of pure metal is taken in the form of cathode metal salt solution is taken as electrolyte. When electric current is passed through the electrolyte, pure metal from anode dissolves into solution and impurities settle down as anode mud.
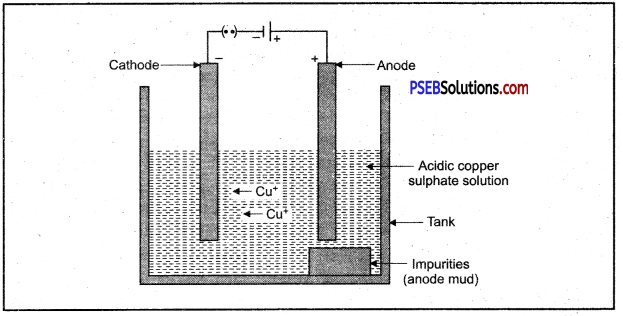
Electrolytic refining

Question 4.
(a). How do metals and non-metals react?
Answer:
Metals and non-metals react on the basis of electronic configuration in the valence shell.
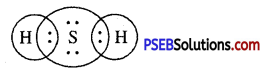
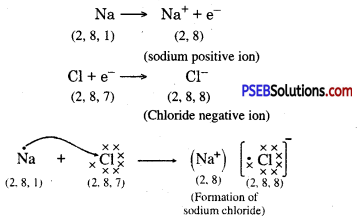
Sodium has only one electron in its outer most shell. If it lose its electrons of the M shell then L will become its outermost shell which have complete octet. Nucleus of this atom will have 11 protons but number of electrons is 10, therefore it is positively charged and gives Na+ sodium positive ions. On the other side, there are 7 electrons in the outer most shell of chlorine and it requires one electron to complete its octet. If there is reaction between chlorine and sodium then lost electron of sodium atom is gained by chlorine atom and chlorine atom becomes negatively charged by one unit. Because there are 17 protons in the nucleus of the chlorine atom and there are 18 electrons in K, L and M shells. Therefore, chloride negative ions Cl- is obtained.
Due to opposite charges sodium and chloride ions attract each other and they form strong bonds involving electrostatic forces and form sodium chloride.
Another ionic compound, magnesium chloride is shown in fig.
Formation of NaCl and MgCl2 by Electron transfer :
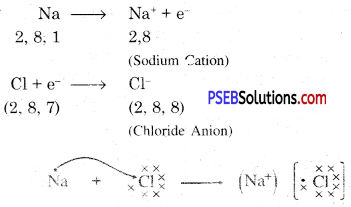
Formation of sodium chloride.
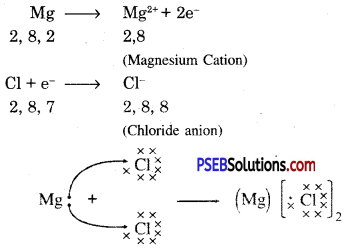
Formation of sodium chloride.
Compounds formed by metals and Non-Metals by the transfer of electrons between them are called ionic or electrovalent compounds.
(b) Write four main exceptions from normal properties of metals and Non-Metals.
Answer:
- All the metals are solid at room temperature except mercury. Melting point of metal is usually high but of Gallium and Cesium is low.
- Iodine is a non-metal but still shiny.
- Carbon is a non-metal which can have many forms. Diamond is allotrope of carbon. It is the hardest substance found in nature. Its melting and boiling point are very high. Another allotrope of carbon is graphite which is conductor of electricity.
- Alkali metal (lithium, sodium, Potassium) are so soft that these can be cut by knife. They have low density and low melting point.
Question 5.
How will you differentiate between metals and non-metals?
Answer:
Differences between metals and non-metals on the basis of physical properties :
| Metals |
Non-metals |
| 1. All metals are solid at room temperature. But mercury is liquid at room temperature. |
1. Non-metals exist in all the three states at room temperature. Phosphorous and sulphur are solid, H2, O2, N2 in gaseous state, and bromine in liquid state. |
| 2. Metals are ductile, malleable and tenacious. |
2. These are soft. |
| 3. Metals have lustre i.e. metal shine. |
3. They do not have lustre but diamond, graphite and iodine are exceptions. |
| 4. Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity but bismuth is exception. |
4.All non metals are non conductors except graphite and carbon gas. |
| 5. Metals have high melting and boiling points. |
5. Non metals have low melting and boiling points. |
| 6. Metals are hard but sodium and potassium can be cut by knife. |
6. These are not very hard but diamond is the hardest substance. |
| 7. Metals have very high relative densities but Na, K are exceptions. |
7. Non metals have very low relative densities. |
| 8. Metals are opaque. |
8. Gaseous non metals are transparent. |
Difference between metals and non-metals on the basis of chemical properties
| Metals |
Non-metals |
| 1. Metals form alkaline oxides some of them form bases. |
1. Non-metals form acidic or neutral oxides. |
| 2. Metals react with acids to displace hydrogen and form salts. |
2. Non-metals do not displaces hydrogen from acids. |
| 3. Metals are electropositive in nature. |
3. Non-metals are electronegative in nature. |
| 4. Metals combine with chlorine to form chlorides which are electrovalent compounds. |
4. Non-metals combine with chlorine to form chlorides which are covalent compounds. |
| 5. Some metals combine with hydrogen to form hydrides which are electrovalent. |
5. Non-metals combine with hydrogen to form hydrides which are covalent. |
| 6. Metals are reducing agents. |
6. Non-metals are oxidizing agents. |
| 7. Metals form positive ions in aqueous solution. |
7. Non-metals form negative ions in aqueous solution. |
Question 6.
Discuss about the extraction of metals
Answer:
Some metals are found in free state in nature. Some metals are found in the form of compounds. Metals at the bottom of reactivity series show very low reactivity. These are found in free state. Gold, silver, platinum and copper are found in free state.
Copper and silver are also found in the form of sulphide and oxide ores. Metals (K, Na, Ca, Mg and Al) which are at the top of reactivity series show very high reactivity that they are never found in free state. Metals at the middle of the reactivity series (Zn, Fe, Pb etc.) are moderately reactive. These are found in the form of oxide, sulphide or carbonate. Some metal ores are found in the form of oxides.
Metals are classified into three types:
(a) least reactive metals
(b) Moderately reactive metals
(c) highly reactive metals.
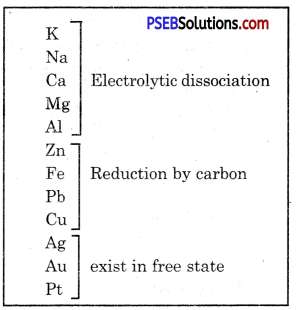
Reactivity series and metallurgy
Question 7.
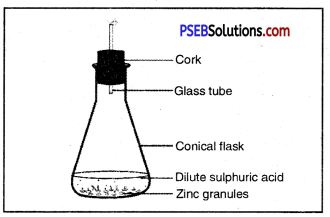
What is rust? What are the requirements necessary for its completion? Give ways to prevent rusting of iron?
Answer:
Surface of iron aquires a coating of a brown flaky substance called rust. It is a compound of Iron (III) Oxide and iron (III) hydroxide. It weakens the iron surface. Due to this, a great loss occurs to the iron articles.
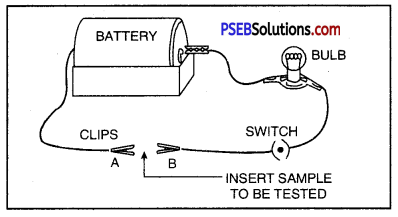
The presence of moisture and air is necessary for rusting of iron. This can be proved with an experiment. If we take new shining irons nails in three test tubes as shown, then we find that nails which are in contact with water and air, got rusted. If we completely immerse the nails in water and cover the water surface with oil so that there is no air available for the nails, then nails will not get rusted.
Similarly if we use CaCl, in the test tube absorbs all the moisture so that no moisture is available in this case also, nails will not get rusted.
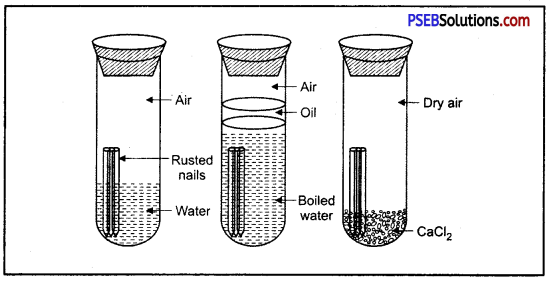
Ways to Prevent Rusting :
- Using oil or grease on the surface: If iron surface is covered with oil or grease it does not remain in contact with air and thus rusting is prevented. Machine parts are saved by this method.
- Using enamel: By painting iron surface, rusting can be prevented. Buses, cars, scooter, motor cycle, windows, trains etc. are saved by this method.
- Covering with plastic: Iron surface is covered with plastic. Iron furniture is saved by this method.
- Galvanization: A process of coating thin layer of zinc on iron is called galvanization. This method is used to prevent buckets, tubs, drums, iron sheets etc. from rusting.
- By electroplating: Iron can be electroplated by metals like Nickle, Chromium, aluminium etc. Rims, handles, bumpers etc. of vehicles are prevented from rusting by this method.
- By tin: Iron is coated with tin. Ghee canisters, boxes used for packing food are tinned.
- Converting to steel: Iron can be preverted from rusting by converting it into steel.

Question 8.
Explain General properties of ionic compounds.
Answer:
General properties of ionic compounds are given below:
- Physical nature: Due to strong force of attraction between positive ions and negative ions, ionic compounds are solid. They are brittle and break on pressing.
- Melting and boiling point: They have high melting and boiling points. Because a large amount of energy is required to break the strong inter ionic attraction.
- Solubility: Ionic compounds are normally soluble in water but are insoluble in Kerosene, Petrol etc.
- Electric Conductivity: In solid form ionic compounds do not conduct electricity because of strong and firm structure. Movement of ions is not possible. But ionic compounds can conduct electricity in molten state, because electrostatic force of attraction becomes very weak due to heat energy. Therefore ions can move freely and electric current can pass through it. Mobility of charged particles is necessary for conduction of electricity in a solution. Ions are present in aqueous solution of ionic compounds. When electric current is passed through the solution then ions start moving towards the opposite electrodes.
Question 9.
What is an alloy? Magnetic iron oxide explain the objective of their formation?
Answer:
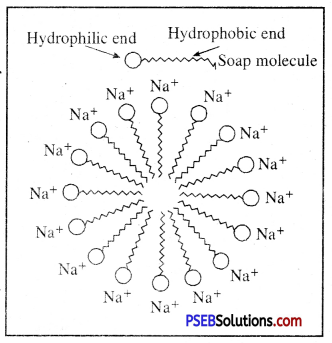
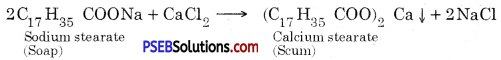
Alloy: An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of a metal with another metal or non-metal, e.g. solder is an alloy of lead and tin (Pb and Sn). Stainless steel, solder, brass, bronze, bell metal etc.
Uses of alloys :
- For increasing hardness: Iron is mixed with carbon to form stainless steel which is harder than iron. Copper is mixed with gold and lead is mixed with silver to make them hard. Duralium is an alloy made from aluminium and is very hard.
- Increasing strength: Steel, Duralium are hard as well as strong.
- Preventing Corrosion: By making stainless steel an alloy of iron, which do not get rusted.
- To produce sound: Bell metal is an alloy of copper and tin used to produce loud sound.
- To lower melting point: An alloy of Bismuth, tin and lead has low melting point.
- Moulding: Bronze and type metal.
- For change in colour: Aluminium bronze is an alloy of copper and aluminium is of golden colour.
- Domestic uses: Alloys are used in homes, factories, offices etc. e.g. utensils, almirahs, fans, refrigerators elements etc. are made up of alloys.
Question 10.
Explain the activity series of metals.
Answer:
All metals have different rates of activity. Some metals like sodium, potassium and calcium etc. are highly reactive. These metals combine with oxygen to form oxide and react with hydrogen to form hydrides. Some metals are compratively less reactive e.g. iron, zinc etc. Some metals are least reactive e.g. gold, silver. Reactivity of metals depends on their ability to lose electrons, Metals are arranged in a list in decreasing rate of their activity.
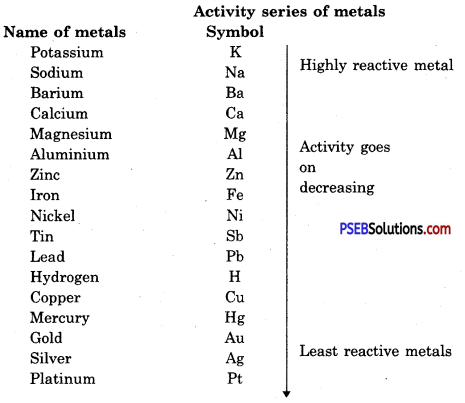
Metals which are above hydrogen are more reactive and those below hydrogen are lower in reactivity and are found in free state. In this series potassium is the most reactive metal in this series.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name two metals which are good conductors of heat and electricity. Name metals which are highly and least conducting with reference to heat.
Answer:
Copper and aluminium are good conductors of electricity and heat. Silver is very good conductor of heat whereas lead is not a good conductor of heat.
Question 2.
Define ductility with example.
Answer:
Property of drawing thin wires from a metal is called ductility. Gold is the highest ductile metal. We can draw 2 km long wire from 18 carat gold.
Question 3.
What is electrical conductivity? Name the metals which have the highest conductivity, less than this and the lowest conductivity.
Answer:
It is the ease with which electric current can flow through a metal. Those metals which offer very low resistance to the flow of current they have high conductivity. Silver, copper are very good conductors of current then comes gold, aluminium and tungsten. Lead and iron have least conductivity i.e., they offer very high resistance to the flow of current.
Question 4.
Which property of metals give them characteristic chemical properties?
Answer:
Metals form positive ions by loosing electrons. This property of formation of ions by the metals give them characteristics chemical properties, e.g., Mg form Mg ion by loosing two electrons :
Mg → Mg2+ + 2e–
Question 5.
Ionic compounds are found in which state? Comment on the melting and boiling point of ionic compounds.
Answer:
Compounds which are formed by the transfer of electrons from metals to Non¬Metals are called ionic or electrovalent compounds e.g., NaCl, LiCl, CaCl2, CaO, MgCl2. Ionic compounds have very high melting and boiling points because a large amount of energy is required to break the strong inter-ionic attractions.

Question 6.
What is difference between minerals and ores?
Answer:
| Sr. No. Minerals |
Ores |
| 1. Those natural occuring substances, which contain metals in the form of compounds. |
1. These are the minerals from which metals can be extracted easily and cheaply. |
| 2. In many of the minerals percent age amount of metals is large and in some it is less. |
2. In all the ores, percentage amount of metals is enough. |
| 3. In some minerals there are so many impurities which create difficulty in the extraction of metals. |
3. Ores do not have such problematic impurities. |
| 4. All the minerals can not be used for extracting metals. All the minerals are not ores. |
4. All the ores can be used to extract metals. |
Question 7.
How are the metals extracted, which are at the top of reactivity series?
Answer:
Metals which are towards the top of reactivity series are sodium, calcium, magnesium, aluminium. There are very reactive. These metals can not be obtained by heating them with carbon. These have more affinity towards oxygen, therefore these are extracted by electrolytic reduction. Sodium, magnesium and calcium are obtained by the electrolysis of their molten chlorides. Metals got deposited at cathode and chorine is liberated at anode.
At cathode : Na+ + e– → Na
At anode : 2Cl– → Cl2 + 2e–
Aluminium is obtained by the electrolytic reduction of aluminium oxide.
At cathode ; Al3+ + 3e– → Al

Question 8.
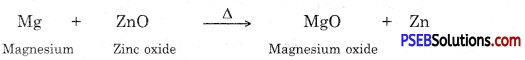
How the metals, which are in the middle of the activity series extracted?
Answer:
Metals which are in the middle of the activity series are iron, zinc, lead, copper etc. These are found in the form of sulphides or carbonates. It is easy to obtain metals from their oxides compared to sulphides or carbonates. Therefore before extraction metal sulphide or carbonates are converted into their oxide. Sulphide ores are converted into metal oxides by heating in the presence of air. This is known as roasting. Carbonate ores are heated in limited supply of air to convert them into oxides. This is known as calcination. Following reactions take place during roasting and calcination of zinc.
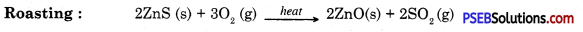
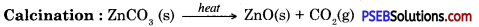
Then by using carbon as reducing agent, metal is extracted from metal oxide, e.g. when Zinc oxide is heated with carbon it gets reduced to give zinc.
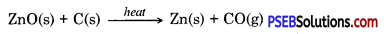
In addition to using carbon for reduction, displacement reaction can be used to extract metals. More reactive metals like sodium, calcium, aluminium etc. can be used as reducing agents because these can displace atoms which are below them in the reactivity series. For example, when mangnese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder then following reaction takes place.
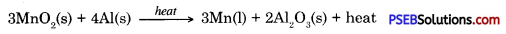
Question 9.
How will you extract metals which are low in the activity series?
Answer:Metals low in the activity series are less reactive and can be obtained from metal oxides simply by heating. Cinnabar (Hgs) an ore of mercury (Hg) when heated change to mercuric oxide (HgO), on heating it further it is reduced to mercury.
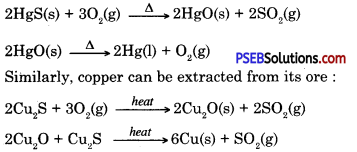
Question 10.
Explain the reactions of metals with water.
Answer:
On reacting with water, metals form metal oxide and produce hydrogen. These dissolve in water to form metal hydroxide. But all metals do not react with water.
Metals like sodium and Potassium react with cold water, vigorously. The reaction of sodium and Potassium is very vigorous and exothermic that hydrogen produced starts burning simultaneously.
2K (s) + 2H2O (l) → 2KOH (aq) + H2(g) + heat
2Na (s) + 2H2O (l) → 2NaOH (aq) + H2(g) + heat
Reaction of calcium with water is slow. Heat produced in this reaction is not enough to burn the hydrogen produced in the reaction.
Ca (s) + 2H2O(l) → Ca (OH)2 + H2(g)
Metals like iron, aluminium, zinc etc. do not react with cold water and not even with hot water. But they react with steam to form metal oxide and produce, hydrogen.
2Al(s) + 3H2O(g) → Al2O3(S) + 3H2(g)
3Fe(s) + 4H2O(g) → Fe3O4(s) + 4H2(g)
Metals like lead, copper, silver and gold etc. do not react with water.
Question 11.
How do metals react with :
1. Oxygen
2. Dilute acids
3. Chlorine
4. Hydrogen.
Answer:
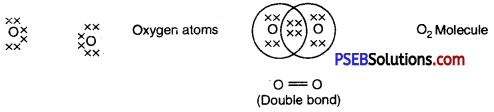
I. Reaction of metals with oxygen: Metals combine with oxygen to form metal oxides. Metal atoms lose their loosely bound electrons to form positive ions where as oxygen atoms gain electrons to form negative oxide ions. These metal oxide are basic in nature. Since all metals have different level of reactivity therefore they combine with oxygen at different temperatures.
1. Na and K Combine with oxygen at normal temperature to form oxides which dissolve in water to form hydroxide.
4 Na (s) + O2(g) → 2Na2S(s)
Na2O(s) + H2O → 2NaOH (or)
2. If magnesium is burned in air it forms magnesium oxide.
Mg → Mg2+ + 2e-
O + 2e– → O2-
Mg2+ + O2- → MgO
3. Copper and iron combine with oxygen at high temperature in dry air.

II. Reaction of metals with dilute acids. Metals reacts with dilute acids to produce hydrogen gas. Rate of reactivity is different.
1. Na, K, Zn, Mg, Fe etc. are reactive in decreasing order.
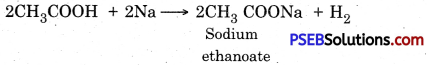
2Na + HCl → 2NaCl + H2 ↑
Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2↑
Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2↑
2. Dilute nitric acid reacts with metals like Cu, Ag, Pb, Hg to form NO (nitrogen oxide).
Cu + 8HNO3 → 3Cu (NO3)2 + 2NO + 4H2O
3Ag + 4HNO3 → 3AgNO3 + NO + 2H2O
3. Dilute nitric acid reacts with Mg and Mn to produce hydrogen gas.
Mg + 2HNO3 → Mg (NO3)2 + H2 ↑
4. Gold and platinum do not react with dilute acids.
III. Reaction of metals with chlorine. Metals combines with chlorine to form electrovalent chlorides.
Ca + Cl2 → CaCl2
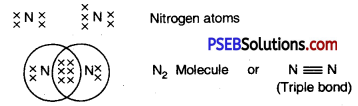
IV. Reaction of metals with hydrogen. Reactive metals like Na, K, Ca etc. react with hydrogen to form hydrid.
2Na + H2 → 2NaH
Ca + H2 → CaH2
V. Reaction of metals with water:
1. Water at normal temperature react with Na, K and Ca to liberate hydrogen gas.
2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2 ↑
Ca + 2H2O → Ca (OH)2 + H2 ↑
2. Mg, Zn and Fe react with boiling water to form oxide.
Mg + H2O → MgO + H2 ↑
3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2 ↑

Question 12.
What is roasting? When do you use it?
Answer:
Roasting. After enrichment of ore, it is heated in the presence of dir, this process is called roasting sulphides or carbonates of some metals are converted into oxides, because extraction of metal is easy from oxides. Carbonates and sulphides of zinc and lead are converted into oxides by roasting.
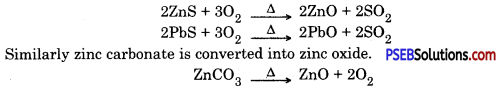
Question 13.
If a copper plate remains immersed in silver nitrate solution for some time then what happens? Write the ionic equation for the reaction.
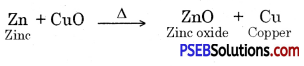
Answer:
Copper is more reactive than silver. Copper will displace silver from the solution and silver gets deposited on copper. Colour of the solution becomes blue.
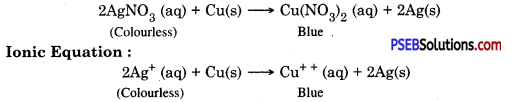
Question 14.
Copper sulphate solution is stored in an iron container. After some days holes were seen in the container. Write the reaction. Explain the reaction on the basis of activity series.
Answer:
Iron is more reactive than copper and is placed before copper in the activity series. Therefore iron can displace copper from copper sulphate solution, due to this reaction holes were seen in the container.
CuSO4 + Fe → FeSO4 + Cu
Cu2+ (aq) + Fe(s) → Fe2+ (aq) + Cu(s)
Thus iron displaced copper.
Question 15.
Why copper becomes green if left open in air. Why?
Answer:
Copper reacts with moist carbon dioxide which is present in air. This makes its surface dull and a green layer is seen on the surface of copper. This green substance is copper carbonate.
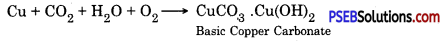
Question 16.
What is 24 carat gold?
Answer:
Pure gold is called 24 carat gold. It is very soft. It can be used to make ornaments. Small amount of silver or copper is mixed with it to make it harder. In our country usually 22 carat gold is used to make ornaments. This means 22 pure gold is mixed with 2 parts of copper or silver.
Question 17.
Which process is used for the enrichment of sulphide ore. Explain in brief two steps involved in the extraction of metal from enriched sulphide ore.
Answer:
Sulphide ore is finely grounded to get powder. This is then enriched by using ‘Froth floation process’.
Steps involved in the extraction of metal from enriched sulphide ore :
1. Roasting: Enriched ore is heated in the presence of air to get oxides. This process is called roasting.
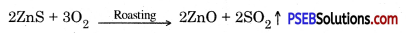
2. Reduction. Oxide of the enriched ore is heated with reducing agent to extract the metal.
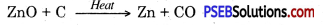
Question 18.
Give differences :
(i) Hydraulic washing and liquation.
Answer:
| Hydraulic Washing |
Liquation |
| 1. This process is used for concentration of an ore. |
1. The process is used for refining of metals. |
| 2. Ore is washed with washing. |
2. This is used for refining metal having low melting points. |
(ii) Electrolytic reduction and reduction by carbon.
Answer:
| Electrolytic reduction |
Reduction by carbon |
| 1. Here cathode acts as reducing agent. It converts metal ions into metals by providing electrons. |
- Carbon is used as reducing agent.
|
| 2. This method is used to reduce the salts of highly reactive metals. |
2. This method is used to reduce the oxides of metals which are in the middle of activity series. |
Question 19.
An alloy of yellow’ colour is made up of two metals A and B. When this alloy was dipped in dilute sulphuric acid, a layer dissolved in acid and formed colourless solution. B did not dissolve in it and the surface of alloy attained red brown colour. What is A and B?
Answer:
Yellow coloured alloy is brass which is mixture of zinc and copper. In this A is zinc and B is copper.
Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2
Question 20.
Sulphur dioxide (SO2) gas is produced when a certain ore is heated. Write the method involved in the extraction of metal from this ore.
Answer:
SO2 gas is produced when copper pyrites an ore of copper is heated.
Following steps are involved in the extraction of metal from this ore :
1. Ore is ground to get powder. It is mixed with water and pine oil. Compressed air is blown to separate impurities. This way ore gets enriched, this method is called froth floatation method.
2. Now the enriched ore is roasted. A part of CuS converts to CuO
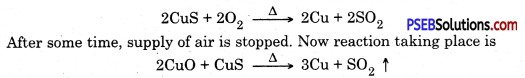
Copper is in liquid state and is purified by electric refining.
3. Electrical refining. In this process impure copper rod is taken as anode and pure copper plate is taken as cathode. Electric current is passed through copper sulphate solution in the presence of acid
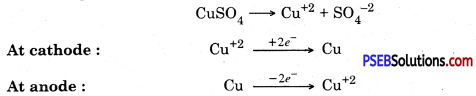

Question 21.
What is Thermite process? Write its uses.
Answer:
Some displacement reactions are highly exothermic. The quantity of heat produced is so high that metals obtained are in molten state. When Iron (III) oxide (Fe2O3) reacts with aluminium then a large amount of heat is produced.
Fe2O3(s) + 2Al(s) → 2Fe(l) + Al2O3(s) + heat
This is known as thermite process. This process is used to weld the rails and to join the cracks in machines.
Question 22.
Give five uses of non-metals.
Answer:
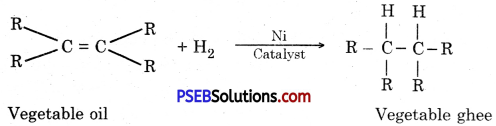
- Hydrogen is used in the preparation of vegetable oil.
- Carbon is an important non-metal which is main constituent of vitamins, proteins, carbohydrates, enzymes etc. Graphite is used as an electrode in various cells.
- Nitrogen is used in ammonia, Nitric acid and fertilizers. Its presence in air controls the rate of combustion.
- Presence of oxygen is the base of our life. Combustion is also possible in the presence of oxygen.
- Sulphur is used in many medicines and is also used to make explosives.
Question 23.
Differentiate Roasting and Calcination.
Answer:
| Roasting |
Calcination |
| 1. Roasting is used for sulphide ores. |
1. Calcination is used for carbonate and hydrated ores. |
| 2. Ore is heated in the presence of air. |
2. Ore is heated in the absence of air. |
| 3. SO2 gas is produced. |
3. CO2 gas is produced. |
Question 24.
How is ionic compound sodium chloride, forms from sodium and chlorine?
Answer:
Sodium and chloride ions are oppositely charged and thus attract each other
They are bound together by strong electrostatic force of attraction and exist in the form of sodium chloride (NaCl). Sodium chloride does not exist as a molecule but as a set of ions :
Question 25.
Ionic compounds are insulators when in solid state whereas when in aqueous solution they become conductors. Why?
Answer:
There exist a strong force of attraction between positive and negative ions of the ionic compounds, due to which these compounds are solid and hard. Due to their firm and rigid structure ions cannot move. But in molten state or in aqueous solution the force between opposite ions become weak and the ions can move freely. Therefore electricity can pass through ionic compounds when in liquid form.
Question 26.
What is aqua regia? Explain.
Answer:
Aqua regia is a mixutre of concentrated hydrochloric acid and concentrated nitric acid in the ratio of 3 : 1. It can dissolve gold where no single acid can do this. Aqua regia (Latin word for Royal water) is highly corrosive and fuming liquid. It can also dissolve platinum.
Question 27.
Give two main ores of aluminium. Also give two alloys of aluminium.
Answer:
Two ores of aluminium are :
- Bauxite, Al2O3. 2H2O
- Cryolite, Na3 (AlF6).
Two alloys of aluminium are :
- Duralium
- Magnalium.
Question 28.
Give uses of pure metals.
Answer:
- Copper and aluminium wires are used in the transmission of power (electricity).
- Utensils, Machines etc. are made up of iron, aluminium and copper.
- Gold and silver are used to make ornaments, these are also used in sweets in the form of silver foil.
- Metals like cadmium, titanium, zinconium etc. are used in nuclear energy and space science projects.
- Aluminium foil is used to wrap eatables.
- Titanium and its alloys are used in airplane, airplane structure and engine, chemical reactor.
- Metals are used in broken bones and body parts.
Question 29.
Which gas is produced, when reactive metals come in contact with dilute hydrochloric acid? Write the chemical reaction between iron and dil. H2SO4.
Answer:
When reactive metals come in contact with dil. hydrochloric acid then (H2) hydrogen gas is produced.
Hydrogen gas is produced when iron reacts with dil. H2SO4.
Fe + H2SO4 → FeSO4 + H2 ↑

Question 30.
What is the function of cryolite in the electrolytic reduction of alumina?
Answer:
Cryolite has two functions in the extraction of aluminium :
- To reduce the melting point of alumina.
- Alumina is bad conductor of electricity on mixing cryolite (Na2AlF3), Al2+ ions are produced from alumina.
Question 31.
How do iron and aluminium react with water?
Answer:
Aluminium and iron do not react with cold or hot water. But react with steam to form metal oxide and hydrogen.
2Al(s) + 3H2O(g) → Al2O3(s) + 3H2(g)
3Fe(s) + 3H2O(g) → Fe3O4(s) + 3H2(g)
Question 32.
What happen when :
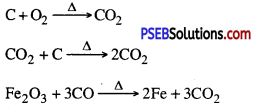
(i) Iron oxide is heated with coke?
Answer:
Iron oxide is readuced to iron.
(ii) Magnesium is treated with dilute sulphuric acid?
Answer:
Hydrogen is produced
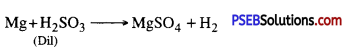
(iii) Zinc is added to blue vitriol solution?
Answer:
Blue colour of solution gradually faders away
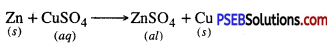
Question 33.
What is rust? Explain it with the help of a chemical reaction.
Answer:
If iron is left open in moist air, a brown layer is produced on its surface. This brown coloured layer is of Ferric oxide and ferric hydroxide. This is called rust. This makes iron weak.
4Fe + 3O2 + 3H2O → Fe2O3 + 2Fe(OH)3
Question 34.
Write names of main alloys and their constituents?
Answer:
| Alloys |
Constituents |
Uses |
| 1. Steel |
Iron, carbon |
used in airplanes, buildings vehicles etc. |
| 2. Stainless steel |
Iron, Carbon, Chromium |
utensils, machine parts, knife, blade, food and milk industry, nuts, bolts, taps etc. |
| 3. Brass |
Copper, Zinc |
utensils, idols, airplanes, medals, steam driven train parts etc. |
| 4. Bronze |
Copper, tin |
utensils and other apparatus. |
| 5. Solder |
Lead, tin |
For joining/welding electric wires. |
| 6. German Silver |
Copper, Nickel, zinc |
Airplane wings, utensils used in kitchen of airplanes and other materials. |
| 7. Bell metal |
Copper,tin |
For making bells. |
| 8. Duralium |
Aluminium, copper magnesium and mangnese in very small amount. |
In airplane |
| 9. Magnoleum |
Aluminium, magnesium |
Light weight tools and cheap utensils. |
| 10. Gun metal |
Copper, tin, zinc |
For making gears of vehicles and machines. |
Question 35.
Write the names of metals found in Bronze and Duralium, give uses of these alloys.
Answer:
Bronze. It is 90% copper and 10% tin. It is used in idols, medals, coins and vessels used for cooking food.
Duralium. It consists of 95% aluminium, 4% copper, 0.5% magnesium and 0.5% manganese. It is used in aeroplanes, space crafts, kitchen vessels.
Question 36.
What is rust? What is its chemical formula?
Answer:
When iron is left open in air, then a layer of iron oxide is formed on the surface of iron. This brown matter is rust. It corrodes the metal. Its chemical formula is Fe2O3. xH2O.

Question 37.
What are metals?
Answer:
The elements which are on the left and in the middle of the periodic table and have metallic lustre are called metals. These are usually ductile, malleable, good conductor of electricity and heat, hard and have high density. They form basic oxides. Examples of metals are gold, iron, silver, copper, platinum etc.
Question 38.
What is ihe reason of catching fire by potassium and sodium on their own?
Answer:
Potassium and sodium reacts with water vigorously and violently. The reaction is very violent and highly exothermic that hydrogen produced in the reaction catches fire on its own.
Question 39.
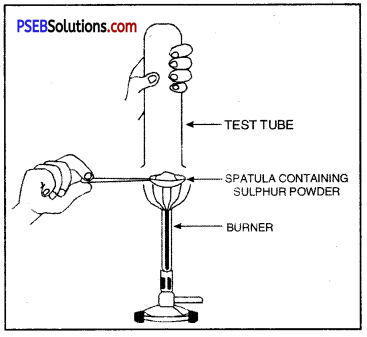
Observe the figure given below and name the gas produced. Also give the chemical equation.
Answer:
Hydrogen gas is produced
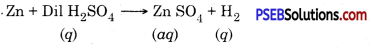
Question 40.
What is indicated by the following figure?
Or
With the help of a labelled diagram prove that both oxygen/air and water are necessary for rusting of iron.
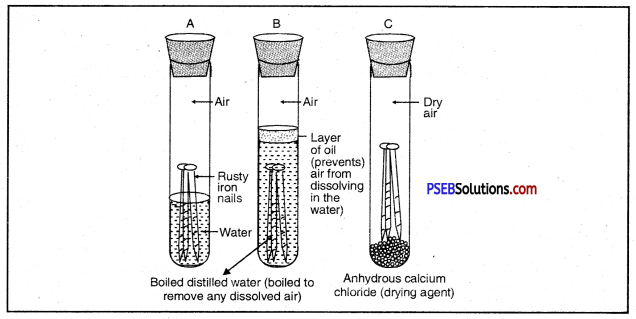
Answer:
Both air and moisture are required for rusting of iron.
Question 41.
Why the substance obtained by mixing small amount of carbon in iron is used largely for various purposes?
Answer:
When small amount of carbon is mixed with iron it changes to steel. This is stronger than iron. It can be used in ships, vehicles, dams.
Question 42.
Write a chemical equation for the reaction taking place in the test tube. How does the colour of solution change? What is change in colour of iron nails?
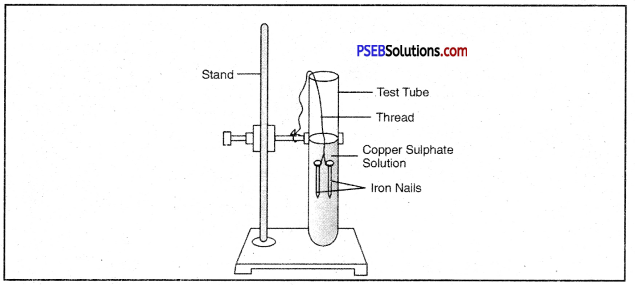
Answer:
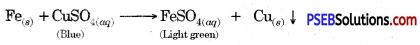
The colour of the solution changes from blue to light green. The colour of Iron nails changes from grey to brown.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Give one example of metal which is liquid at room temperature.
Answer:
Mercury.
Question 2.
Name one metal and one non-metal which is liquid at room temperature.
Answer:
Metal-Mercury.
Non-Metal—Bromine
Question 3.
Name one non-metal which has bright lustre.
Answer:
Iodine.
Question 4.
Name one non-metal which does not have bright.
Answer:
Phosphorus.
Question 5.
Which of the following metal are liquid at body temperature (37° C): Gallium, Magnesium, Caesium, Aluminium.
Answer:
Gallium and Caesium.
Question 6.
Name one non-metal which is a good conductor of electricity?
Answer:
Graphite (Carbon).

Question 7.
Arrange the following metals in the decreasing order of reactivity,
Fe, Zn, Cu, Na, Ag.
Answer:
Na > Zn > Fe > Cu > Ag.
Question 8.
Out of Sodium, Calcium, Aluminium, Copper and Magnesium name the metal which reacts with
(i) Boiling water
Answer:
Magnesium
(ii) Steam.
Answer:
Copper.
Question 9.
Sodium metal is kept under kerosene oil, why?
Answer:
This is because sodium reacts with moist air as well as water.
Question 10.
A non-metal X, exists in two forms Y and Z. Y is the hardest substance and Z is a poor conductor of electricity. What are X, Y and Z?
Answer:
Y = Diamond Z = Graphite X = Carbon
Y and Z are allotropic forms of carbon.
Question 11.
An element, A form two oxides AO and AOa. AO is neutral and AO2 is acidic : Indicate whether A is metal or non-metal.
Answer:
A is non-metal.
Question 12.
Name the reaction to convert metal into its oxide .
Answer:
Oxidation.
Question 13.
Ionic solids have high melting points, why?
Answer:
In ionic solids, there are strong electrostatic forces of attraction between the oppositely charged ions and a large amount of energy required to overcome these forces.
Question 14.
An element X reacts with oxide to form oxide, X2O which dissolves in water and turns red litmus solution blue. Give the nature of oxide and indicate X is metal or non-metal.
Answer:
X2O is basic. X is metal.
Question 15.
What is the nature of metal oxides?
Answer:
Basic.
Question 16.
Name two noble metals.
Answer:
Gold and platinum.
Question 17.
Name an ore of mercury.
Answer:
Mercury sulphide (Hgs).
Question 18.
Name two metalloids.
Answer:
Arsenic, antimony.
Question 19.
Metals lose lustre when placed in air, why?
Answer:
This is because their surfaces are covered with oxides, carbonates or sulphide layer’s .
Question 20.
Name two metals which can be cut with a knife.
Answer:
Sodium and potassium.
Question 21.
Why do metals aquire different shapes?
Answer:
This is due to malleability and ductility of metals.

Question 22.
Name the metal which is poor conductor of heat.
Answer:
Lead.
Question 23.
Name the metal which offers resistance to the flow of electricity.
Answer:
Mercury.
Question 24.
Which of the following metals can be drawn into wires?
Answer:
Cu, Al, Fe, Pb.
Question 25.
Name four non-metals which are solid at room temperature.
Answer:
Carbon, Sulphur, Phosphorous, and iodine.
Question 26.
Name the elements which are present in abundance in earth’s crust.
Answer:
Oxygen and silicon.
Question 27.
What are alkalies? Give one example.
Answer:
Alkali. It is a metal hydroxide soluble in water Example : Sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
Question 28.
Name two amphoteric oxide.
Answer:
- Aluminium oxide (Al2O3)
- Zinc Oxide (ZnO)
Question 29.
What happens when magnesium is heated to ignition temperature?
Answer:
Magnesium burns with white light producing magnesium oxide.
Question 30.
Name the metal which does not react with dil. HCl.
Answer:
Copper.
Question 31.
Name two metals which react with hydrogen.
Answer:
Sodium and potasium.
Question 32.
Give the reaction when a piece of Calcium reacts with water.
Answer:
Ca + 2H2O → Ca (OH)2 + 4H2.
Question 33.
Give the reactions when red hot iron reacts with steam.
Answer:
Ca + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + H2.
Question 34.
Why is zinc oxide called amphoteric oxide?
Answer:
This is because zinc oxide reacts with both acid as well as base.
Question 35.
The metals Na, K and Ca react with hydrogen to form hydroxide but other metals don’t, why?
Answer:
This is because Na, K and Ca are highly reactive metals.
Question 36.
Give the reactions which occur when zinc plate is added to copper sulphate solution.
Answer:
Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu.
Question 37.
Out of the metals, Na, Cu, Au, which is
(i) Most reactive and
Answer:
Most reactive metal-Sodium (Na)
(ii) Least reactive?
Answer:
Least reactive metal-Gold (Au).
Question 38.
Arrange the following metals in the decreasing order of reactivity, Zinc, Mercury and Aluminium.
Answer:
Al < Zn < Hg.

Question 39.
Name two metals which occur in free state in nature.
Answer:
Gold and Platinum.
Question 40.
Define corrosion of metals.
Answer:
It is the interaction of surface of metal with air and moisture forming a layer of oxide, halide or carbonate layer on its surface.
Question 41.
Name a metal which undergoes corrosion in air.
Answer:
Iron.
Question 42.
Name two metals which are not corroded easily.
Answer:
Gold and silver.
Question 43.
Why does copper utensils turn green on exposure to air?
Answer:
Copper reacts with oxygen, carbon dioxide and moisture to form a green coloured compound (basic copper carlxmate):
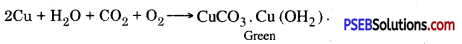
Question 44.
Name two metals which are both malleable and ductile.
Answer:
- Copper
- Aluminium.
Question 45.
Name the most abundant metal in the earth’s crust.
Answer:
Aluminium.
Question 46.
Name the metal that gives a green coating when exposed to moisture.
Answer:
Copper.
Question 47.
Which is the most lightest metal known to us?
Answer:
Lithium.
Question 48.
Name two metals which occur in free state in nature.
Answer:
- Gold
- Platinum.
Question 49.
Name one of the most common ore of aluminium.
Answer:
Bauxite (Al2O3. 2H2O).
Question 50.
What is an amalgam?
Answer:
An amalgam is an alloy of mercury with some other metals.
Question 51.
Name two metals which :
(a) readily burn in air an
Answer:
Metals which readily burn in air are :
- sodium
- magnesium.
(b) do not burn.
Answer:
metals which do not burn readily in air are :
- Copper
- iron.
Question 52.
Name the metal which is best conductor of electricity.
Answer:
Silver.

Question 53.
Name one metal which reacts with cold water.
Answer:
Sodium.
Question 54.
Name one metal
(i) more reactive than hydrogen and
Answer:
Sodium
(ii) less reactive than hydrogen.
Answer:
Silver.
Question 55.
Write the chemical name of any one compound ore of sulphur.
Answer:
Zinc sulphide (ZnS).
Question 56.
Name the metal used in galvanisation of iron.
Answer:
Zinc.
Question 57.
The metal which is found in nature in the free state is
Answer:
Gold and Platinum.
Question 58.
What chemical process is used for obtaining a metal from its oxide?
Answer:
Reduction process.
Question 59.
Which metals do not corrode easily?
Answer:
The metals which are not attacked by air and moisture don’t corrode easily.
Multiple Choice Questions :
Question 1.
The non-metal which is liquid at room temperature is:
(A) Chlorine
(B) Bromine
(C) Fluorine
(D) Iodine.
Answer:
(B) Bromine
Question 2.
Most reactive metal is:
(A) Na
(B) Mg
(C) Au
(D) K
Answer:
(D) K
Question 3.
The property due to which metals can be beaten into sheets is :
(A) Malleability
(B) Ductility
(C) Metallic lustre
(D) Hardness.
Answer:
(A) Malleability
Question 4.
The axnphoteric oxide is:
(A) ZnO
(B) BaO
(C) K2O
(D) Na2O.
Answer:
(A) ZnO

Question 5.
Copper gets covered with green layer when exposed to air due to the formation of:
(A) CuSO4
(B) CuCO3. Cu(OH)2
(C) Cu (NO3)2
(D) CuO.
Answer:
(B) CuCO3. Cu(OH)2
Question 6.
During galvanisation, the metal whose layer is deposited is:
(A) Gallium
(B) Aluminium
(C) Zinc
(D) Silver.
Answer:
(C) Zinc
Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
Brass is an alloy of copper and ____________
Answer:
Zinc.
Question 2.
____________ is the best conductor of electricity.
Answer:
Silver.
Question 3.
All the ores are ____________
Answer:
Minerals.
Question 4.
Copper can be refined by ____________
Answer:
Electrorefining.

![]()