Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class History Book Solutions Chapter 23 ਦੂਸਰਾ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ : ਕਾਰਨ, ਸਿੱਟੇ ਅਤੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਮਿਲਾਉਣਾ Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 12 History Chapter 23 ਦੂਸਰਾ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ : ਕਾਰਨ, ਸਿੱਟੇ ਅਤੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਮਿਲਾਉਣਾ
Long Answer Type Questions
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਛੇ ਕਾਰਨਾਂ ਦਾ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਵਰਣਨ ਕਰੋ । (Explain in brief the six causes of Second Anglo-Sikh War.)
ਜਾਂ
ਦੁਜੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਕੀ ਕਾਰਨ ਸਨ ? (What were the causes of Second Anglo-Sikh War ?)
ਜਾਂ
ਦੂਜੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਛੇ ਮੁੱਖ ਕਾਰਨ ਕੀ ਸਨ ? (What were the six main causes for Second Anglo-Sikh War ?) ਉੱਤਰ-
ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ – ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਮੁੱਖ ਕਾਰਨ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਸਨ-
1. ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦੀ ਆਪਣੀ ਹਾਰ ਦਾ ਬਦਲਾ ਲੈਣ ਦੀ ਇੱਛਾ – ਇਹ ਠੀਕ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਹੋਏ ਪਹਿਲੇ ਯੁੱਧ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦੀ ਹਾਰ ਹੋ ਗਈ ਸੀ, ਪਰ ਇਸ ਨਾਲ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਹੌਂਸਲੇ ਕਿਸੇ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਘੱਟ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੋਏ ਸਨ ।ਇਸ ਹਾਰ ਦਾ ਮੁੱਖ ਕਾਰਨ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦੇ ਨੇਤਾਵਾਂ ਵੱਲੋਂ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ ਗੱਦਾਰੀ ਸੀ । ਸਿੱਖ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਆਪਣੀ ਯੋਗਤਾ ‘ਤੇ ਪੂਰਾ ਵਿਸ਼ਵਾਸ ਸੀ । ਉਹ ਆਪਣੀ ਹਾਰ ਦਾ ਬਦਲਾ ਲੈਣਾ ਚਾਹੁੰਦੇ ਸਨ ।ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਇਹ ਇੱਛਾ ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦਾ ਇੱਕ ਮੁੱਖ ਕਾਰਨ ਬਣੀ ।
2. ਲਾਹੌਰ ਅਤੇ ਭੈਰੋਵਾਲ ਦੀਆਂ ਸੰਧੀਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਅਸੰਤੁਸ਼ਟ – ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਵਿਚਾਲੇ ਹੋਏ ਪਹਿਲੇ ਯੁੱਧ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦਰਬਾਰ ਨਾਲ ਲਾਹੌਰ ਅਤੇ ਭੈਰੋਵਾਲ ਨਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਸੰਧੀਆਂ ਕੀਤੀਆਂ। ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੇ ਲੋਕ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਅਣਥੱਕ ਯਤਨਾਂ ਸਦਕਾ ਬਣਾਏ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਸੰਧੀਆਂ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਖੇਰੂੰ-ਖੇਰੂੰ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਦੇਖ ਕੇ ਸਹਿਣ ਨਹੀਂ ਕਰ ਸਕਦੇ ਸਨ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਇੱਕ ਹੋਰ ਯੁੱਧ ਲੜਨਾ ਪੈਣਾ ਸੀ ।
3. ਸਿੱਖ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਅਸੰਤੋਸ਼ – ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦੀ ਸੰਧੀ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਖ਼ਾਲਸਾ ਫ਼ੌਜ ਦੀ ਗਿਣਤੀ 20,000 ਪੈਦਲ ਤੇ 12,000 ਘੋੜਸਵਾਰ ਨਿਸ਼ਚਿਤ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤੀ । ਇਸ ਕਾਰਨ ਹਜ਼ਾਰਾਂ ਦੀ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਿੱਖ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਨੌਕਰੀ ਤੋਂ ਜਵਾਬ ਦੇ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਦੇ ਮਨਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੀ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਰੋਸ ਪੈਦਾ ਹੋ ਗਿਆ ਅਤੇ ਉਹ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੀਆਂ ਤਿਆਰੀਆਂ ਕਰਨ ਲੱਗੇ ।
4. ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਸਖ਼ਤ ਸਲੂਕ – ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਵਿਧਵਾ ਅਤੇ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਮਾਂ ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਜੋ ਅਪਮਾਨਜਨਕ ਵਿਵਹਾਰ ਕੀਤਾ, ਉਸ ਨੇ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਫੈਲੇ ਰੋਸ ਨੂੰ ਹੋਰ ਭੜਕਾ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਉਹ ਇਸ ਅਪਮਾਨ ਦਾ ਬਦਲਾ ਲੈਣਾ ਚਾਹੁੰਦੇ ਸਨ ।
5. ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਦਾ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ – ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਕਰਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮਲਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਨੂੰ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ ਸਥਾਨ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਹੈ । ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਨੇ 20 ਅਪਰੈਲ, 1848 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਦੋ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਅਫ਼ਸਰਾਂ ਵੈਨਸ ਐਗਨਿਯੂ ਅਤੇ ਐਂਡਰਸਨ ਦੇ ਕਤਲਾਂ ਦੀ ਝੂਠੀ ਜ਼ਿੰਮੇਵਾਰੀ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਸਿਰ ਪਾਈ । ਇਸ ਕਾਰਨ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਦਾ ਖੂਨ ਖੌਲਣ ਲੱਗਾ ਅਤੇ ਉਸ ਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਦਾ ਝੰਡਾ ਬੁਲੰਦ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ।
6. ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਦੀ ਨੀਤੀ – 1848 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਨਵਾਂ ਗਵਰਨਰ-ਜਨਰਲ ਬਣਿਆ ਸੀ ।ਉਹ ਬਹੁਤ ਵੱਡਾ ਸਾਮਰਾਜਵਾਦੀ ਸੀ । ਉਹ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਆਪਣੇ ਅਧੀਨ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਕਿਸੇ ਸੁਨਹਿਰੀ ਮੌਕੇ ਦੀ ਭਾਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਸੀ । ਇਹ ਮੌਕਾ ਉਸ ਨੂੰ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ, ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਤੇ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਦਿੱਤਾ ।

ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ‘ਤੇ ਇੱਕ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਨੋਟ ਲਿਖੋ । (Write a short note on the revolt of Diwan Mool Raj.)
ਜਾਂ
ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਸੰਬੰਧੀ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਜਾਣਕਾਰੀ ਦਿਓ । (Give a brief account of the revolt of Diwan Mool Raj of Multan.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ 1844 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦਾ ਨਵਾਂ ਗਵਰਨਰ ਨਿਯੁਕਤ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ । ਉਹ ਲਗਭਗ 13\(\frac{1}{2}\) ਲੱਖ ਰੁਪਏ ਸਾਲਾਨਾ ਲਗਾਨ ਵਜੋਂ ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦਰਬਾਰ ਨੂੰ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਸੀ । ਬਾਅਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਇਹ ਰਕਮ ਵਧਾ ਕੇ ਲਗਭਗ 20 ਲੱਖ ਰੁਪਏ ਸਾਲਾਨਾ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਗਈ । ਪਰ ਇਸ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਹੀ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਰਾਜ ਦਾ ਤੀਜਾ ਹਿੱਸਾ ਉਸ ਕੋਲੋਂ ਲੈ ਲਿਆ ਗਿਆ । ਸਿੱਟੇ ਵਜੋਂ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਨੇ ਗਵਰਨਰੀ ਦੇ ਅਹੁਦੇ ਤੋਂ ਆਪਣਾ ਅਸਤੀਫ਼ਾ ਦੇ ਦਿੱਤਾ | ਮਾਰਚ, 1848 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਨਵੇਂ ਰੈਜ਼ੀਡੈਂਟ ਫਰੈਡਰਿਕ ਹਰੀ ਨੇ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਦਾ ਅਸਤੀਫ਼ਾ ਸਵੀਕਾਰ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ । ਉਸ ਨੇ ਕਾਹਨ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦਾ ਨਵਾਂ ਗਵਰਨਰ ਨਿਯੁਕਤ ਕਰਨ ਦਾ ਫੈਸਲਾ ਕੀਤਾ । ਉਸ ਦੀ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਲਈ ਦੋ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਅਫ਼ਸਰਾਂ ਐਗਨਿਯੂ ਅਤੇ ਐਂਡਰਸਨ ਨੂੰ ਭੇਜਿਆ ਗਿਆ ।
ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਨੇ ਬਿਨਾਂ ਕਿਸੇ ਵਿਰੋਧ ਦੇ 19 ਅਪਰੈਲ, 1848 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਕਿਲ੍ਹੇ ਦੀਆਂ ਚਾਬੀਆਂ ਕਾਹਨ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਹਵਾਲੇ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤੀਆਂ । ਪਰ 20 ਅਪਰੈਲ ਨੂੰ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਸਿਪਾਹੀਆਂ ਨੇ ਦੋਨੋਂ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਅਫ਼ਸਰਾਂ ਦਾ ਕਤਲ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਅਤੇ ਮਲਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਦੀ ਅਗਵਾਈ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਮਜਬੂਰ ਕੀਤਾ । ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਇਸ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਨੂੰ ਕੁਚਲਣ ਦੀ ਬਜਾਏ ਉਸ ਨੂੰ ਫੈਲਣ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਤਾਂ ਕਿ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦਰਬਾਰ ‘ਤੇ ਹਮਲਾ ਕਰਨ ਦਾ ਬਹਾਨਾ ਮਿਲ ਸਕੇ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਹਜ਼ਾਰਾ ਦੇ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਬਾਰੇ ਤੁਸੀਂ ਕੀ ਜਾਣਦੇ ਹੋ ? (What do you know about the revolt of Chattar Singh of Hazara ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਟਾਰੀਵਾਲਾ ਹਜ਼ਾਰਾ ਦਾ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ ਸੀ । ਉਸ ਦੀ ਲੜਕੀ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਨਾਲ ਮੰਗੀ ਹੋਈ ਸੀ | ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਇਸ ਰਿਸ਼ਤੇ ਦੇ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਸਨ ਕਿਉਂਕਿ ਇਸ ਨਾਲ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦੀ ਰਾਜਨੀਤਿਕ ਤਾਕਤ ਵੱਧ ਜਾਣੀ ਸੀ । ਇਹ ਤਾਕਤ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦੀ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਹੜੱਪਣ ਦੀ ਨੀਤੀ ਦੇ ਰਾਹ ਵਿੱਚ ਰੋੜਾ ਅਟਕਾ ਸਕਦੀ ਸੀ : ਕੈਪਟਨ ਐਬਟ ਜਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦਾ ਸਲਾਹਕਾਰ ਨਿਯੁਕਤ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ, ਸਿੱਖ ਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ ਤਬਾਹ ਕਰਨ ਦੀ ਯੋਜਨਾ ਤਿਆਰ ਕਰ ਰਿਹਾ ਸੀ । ਉਸ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਭੜਕਾਏ ਗਏ ਹਜ਼ਾਰਾਂ ਦੇ ਮੁਸਲਮਾਨਾਂ ਨੇ 6 ਅਗਸਤ, 1848 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਰਿਹਾਇਸ਼ਗਾਹ ‘ਤੇ ਹਮਲਾ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਇਹ ਵੇਖ ਕੇ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਕਰਨਲ ਕੈਨੋਰਾ ਨੂੰ ਵਿਦਰੋਹੀਆਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਕਾਰਵਾਈ ਕਰਨ ਦਾ ਹੁਕਮ ਦਿੱਤਾ ।
ਕਰਨਲ ਕੈਨੋਰਾ ਜੋ ਕੈਪਟਨ ਐਬਟ ਨਾਲ ਮਿਲਿਆ ਹੋਇਆ ਸੀ, ਨੇ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਹੁਕਮ ਨੂੰ ਮੰਨਣ ਤੋਂ ਇਨਕਾਰ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ। ਉਸ ਨੇ ਆਪਣੀ ਪਿਸਤੌਲ ਨਾਲ ਗੋਲੀਆਂ ਚਲਾ ਕੇ ਦੋ ਸਿੱਖ ਸਿਪਾਹੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਮਾਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਉਸ ਸਮੇਂ ਇੱਕ ਸਿੱਖ ਸਿਪਾਹੀ ਨੇ ਅੱਗੇ ਵੱਧ ਕੇ ਆਪਣੀ ਤਲਵਾਰ ਨਾਲ ਕੈਨੋਰਾ ਦਾ ਕੰਮ ਤਮਾਮ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਜਦੋਂ ਇਸ ਘਟਨਾ ਦੀ ਖ਼ਬਰ ਐਬਟ ਨੂੰ ਪਹੁੰਚੀ ਤਾਂ ਉਹ ਗੁੱਸੇ ਨਾਲ ਅੱਗ ਬਬੂਲਾ ਹੋ ਗਿਆ । ਉਸ ਨੇ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਅਹੁਦੇ ਤੋਂ ਹਟਾ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਅਤੇ ਉਸ ਦੀ ਜਾਗੀਰ ਜ਼ਬਤ ਕਰ ਲਈ । ਇਸ ਕਾਰਨ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦਾ ਖ਼ੂਨ ਉਬਲ ਗਿਆ ਤੇ ਉਸ ਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਬਗਾਵਤ ਕਰਨ ਦਾ ਐਲਾਨ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਚਿਲ੍ਹਿਆਂਵਾਲਾ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ‘ ਤੇ ਇੱਕ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਨੋਟ ਲਿਖੋ । (Write a note on the battle of Chillianwala.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਚਿਲ੍ਹਿਆਂਵਾਲਾ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੀਆਂ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਨ ਲੜਾਈਆਂ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਇੱਕ ਸੀ । ਲਾਰਡ ਹਿਊਗ ਗਫ਼ ਜੋ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਫ਼ੌਜਾਂ ਦਾ ਸੈਨਾਪਤੀ ਸੀ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਫ਼ੌਜ ਦਾ ਮੁਕਾਬਲਾ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਸੈਨਿਕ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਪਹੁੰਚਣ ਦੀ ਉਡੀਕ ਕਰ ਰਿਹਾ ਸੀ । ਇਸੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਗਫ਼ ਨੂੰ ਇਹ ਸੂਚਨਾ ਮਿਲੀ ਕਿ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਅਟਕ ਦੇ ਕਿਲ੍ਹੇ ਨੂੰ ਜਿੱਤ ਲਿਆ ਹੈ ਤੇ ਉਹ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਲਈ ਆ ਰਿਹਾ ਹੈ । ਅਜਿਹਾ ਹੋਣ ‘ਤੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਲਈ ਭਾਰੀ ਖ਼ਤਰਾ ਪੈਦਾ ਹੋ ਸਕਦਾ ਸੀ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਹਿਉਗ ਗਫ਼ ਨੇ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਪਹੁੰਚਣ ਤੋਂ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਹੀ 13 ਜਨਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਚਿਲ੍ਹਿਆਂਵਾਲਾ ਵਿਖੇ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀਆਂ ਫ਼ੌਜਾਂ ‘ਤੇ ਹਮਲਾ ਬੋਲ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਇਸ ਘਮਸਾਣ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦੇ ਚੰਗੇ ਛੱਕੇ ਛੁਡਵਾਏ । ਇਸ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦਾ ਇੰਨਾ ਭਾਰੀ ਨੁਕਸਾਨ ਹੋਇਆ ਕਿ ਇੰਗਲੈਂਡ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੀ ਹਾਹਾਕਾਰ ਮਚ ਗਈ ।ਇਸ ਅਪਮਾਨਜਨਕ ਹਾਰ ਕਾਰਨ ਸੈਨਾਪਤੀ ਲਾਰਡ ਹਿਊਗ ਗਫ਼ ਦੇ ਸਨਮਾਨ ਨੂੰ ਬਹੁਤ ਧੱਕਾ ਲੱਗਿਆ। ਉਸ ਦੀ ਜਗ੍ਹਾ ਚਾਰਲਸ ਨੇਪੀਅਰ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸੈਨਾ ਦਾ ਨਵਾਂ ਸੈਨਾਪਤੀ ਨਿਯੁਕਤ ਕਰਕੇ ਭਾਰਤ ਭੇਜਿਆ ਗਿਆ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 5.
ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਸਮੇਂ ਹੋਈ ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਦਾ ਕੀ ਮਹੱਤਵ ਸੀ ? (What is the importance of the battle of Gujarat in the Second Anglo-Sikh War ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੀ ਆਖਰੀ ਅਤੇ ਫੈਸਲਾਕੁੰਨ ਲੜਾਈ ਸੀ । ਇਹ ਲੜਾਈ 21 ਫ਼ਰਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਲੜੀ ਗਈ ਸੀ । ਇਸ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਿੱਖ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਦੀ ਗਿਣਤੀ 40,000 ਸੀ ਅਤੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਅਗਵਾਈ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ, ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਤੇ ਮਹਾਰਾਜ ਸਿੰਘ ਕਰ ਰਹੇ ਸਨ। ਦੂਜੇ ਪਾਸੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦੇ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਦੀ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਲਗਭਗ 68,000 ਸੀ ਅਤੇ ਲਾਰਡ ਹਿਊਗ ਗਫ਼ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਅਗਵਾਈ ਕਰ ਰਿਹਾ ਸੀ । ਕਿਉਂਕਿ ਇਸ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਦੋਹਾਂ ਪੱਖਾਂ ਵੱਲੋਂ ਤੋਪਾਂ ਦੀ ਬਹੁਤ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ ਸੀ ਇਸ ਲਈ ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਨੂੰ ਤੋਪਾਂ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਵੀ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦਾ ਬੜੀ ਬਹਾਦਰੀ ਨਾਲ ਮੁਕਾਬਲਾ ਕੀਤਾ । ਪਰ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦਾ ਗੋਲਾ-ਬਾਰੂਦ ਖ਼ਤਮ ਹੋ ਜਾਣ ਕਾਰਨ ਅੰਤ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਹਾਰ ਦਾ ਮੂੰਹ ਵੇਖਣਾ ਪਿਆ।
ਇਸ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦਾ ਭਾਰੀ ਨੁਕਸਾਨ ਹੋਇਆ ਅਤੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਗਦੜ ਮਚ ਗਈ । ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ, ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਤੇ ਮਹਾਰਾਜ ਸਿੰਘ ਰਾਵਲਪਿੰਡੀ ਵੱਲ ਦੌੜ ਗਏ । ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਨੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦਾ ਪਿੱਛਾ ਕੀਤਾ । ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ 10 ਮਾਰਚ ਨੂੰ ਆਪਣੇ ਹਥਿਆਰ ਸੁੱਟ ਦਿੱਤੇ । ਬਾਕੀ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਨੇ 14 ਮਾਰਚ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਅੱਗੇ ਆਪਣੇ ਹਥਿਆਰ ਸੁੱਟ ਦਿੱਤੇ । ਇਸ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਜਿੱਤ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ 29 ਮਾਰਚ, 1849 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ । ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਰਾਜ ਦਾ ਅੰਤ ਹੋ ਗਿਆ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 6.
ਦੁਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਕੀ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ ਪਏ ? (What were the results of the Second Anglo-Sikh War ?)
ਜਾਂ
ਸੰਖੇਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਦੂਸਰੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵਾਂ ਦਾ ਅਧਿਐਨ ਕਰੋ । (Study in brief the results of Second Anglo-Sikh War.)
ਜਾਂ
ਦੂਜੀ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਲੜਾਈ ਦੇ ਕੋਈ ਛੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ ਲਿਖੋ । (Explain the any six effects of Second Anglo-Sikh War.) ਉੱਤਰ-
ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਬੜੇ ਦੂਰ-ਦੁਰਾਡੇ ਸਿੱਟੇ ਨਿਕਲੇ । ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦਾ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਵਰਣਨ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਹੈ-
- ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਦਾ ਅੰਤ – ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਨ ਸਿੱਟਾ ਇਹ ਨਿਕਲਿਆ ਕਿ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਦਾ ਪੂਰੀ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਖਾਤਮਾ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਆਖਰੀ ਸਿੱਖ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਗੱਦੀ ਤੋਂ ਲਾਹ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ ।
- ਸਿੱਖ ਫ਼ੌਜ ਨੂੰ ਤੋੜ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ – ਦੂਜੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਮਗਰੋਂ ਇਸ ਸੈਨਾ ਨੂੰ ਵੀ ਨਿਸ਼ਸਤਰ ਕਰ ਕੇ ਤੋੜ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾਤਰ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਖੇਤੀਬਾੜੀ ਦੇ ਧੰਦੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਲਗਾਉਣ ਦੀ ਕੋਸ਼ਿਸ਼ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ । ਕੁਝ ਨੂੰ ਬ੍ਰਿਟਿਸ਼ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਸੈਨਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਰਤੀ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ ਗਿਆ ।
- ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਅਤੇ ਭਾਈ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਦੇਸ਼ ਨਿਕਾਲੇ ਦੀ ਸਜ਼ਾ – ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਮੌਤ ਦੀ ਸਜ਼ਾ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਗਈ ਸੀ । ਬਾਅਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਇਸ ਸਜ਼ਾ ਨੂੰ ਕਾਲੇਪਾਣੀ ਦੀ ਸਜ਼ਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਬਦਲ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਪਰ ਉਸ ਦੀ 11 ਅਗਸਤ, 1851 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਕਲਕੱਤੇ (ਕੋਲਕਾਤਾ) ਵਿਖੇ ਮੌਤ ਹੋ ਗਈ । ਭਾਈ ਮਹਾਰਾਜ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਸਿੰਘਾਪੁਰ ਜੇਲ੍ਹ ਵਿੱਚ ਭੇਜ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਇੱਥੇ ਉਸ ਦੀ 5 ਜੁਲਾਈ, 1856 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਮੌਤ ਹੋ ਗਈ ।
- ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਤੇ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਸਜ਼ਾ – ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਤੇ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਪੁੱਤਰ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਵੀ ਗ੍ਰਿਫ਼ਤਾਰ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ ਸੀ । ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਅਲਾਹਾਬਾਦ ਅਤੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਲਕੱਤੇ (ਕੋਲਕਾਤਾ) ਦੀਆਂ ਜੇਲ੍ਹਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਗਿਆ । 1854 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਨੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੋਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਰਿਹਾਅ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ।
- ਪੰਜਾਬ ਲਈ ਨਵਾਂ ਰਾਜ ਪ੍ਰਬੰਧ – ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਲਾ ਲੈਣ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਬੰਧ ਚਲਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਾਸਨਿਕ ਬੋਰਡ ਦੀ ਸਥਾਪਨਾ ਕੀਤੀ । ਇਹ 1849 ਈ. ਤੋਂ ਲੈ ਕੇ 1853 ਈ. ਤਕ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦਾ ਰਿਹਾ । ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਸੁਧਾਰਾਂ ਨੇ ਪੰਜਾਬੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਦਿਲਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਜਿੱਤ ਲਿਆ । ਸਿੱਟੇ ਵਜੋਂ ਉਹ 1857 ਈ. ਦੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਸਮੇਂ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਵਫ਼ਾਦਾਰ ਰਹੇ।
- ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੀਆਂ ਰਿਆਸਤਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਮਿੱਤਰਤਾ ਵਾਲਾ ਸਲੂਕ – ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਪਟਿਆਲਾ, ਨਾਭਾ, ਜੀਂਦ, ਮਲੇਰਕੋਟਲਾ, ਫ਼ਰੀਦਕੋਟ ਅਤੇ ਕਪੂਰਥਲਾ ਦੀਆਂ ਰਿਆਸਤਾਂ ਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਆਪਣਾ ਸਹਿਯੋਗ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਸੀ । ਇਸ ਕਾਰਨ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਆਪਣੀ ਮਿੱਤਰਤਾ ਬਣਾਈ ਰੱਖੀ ਅਤੇ ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਰਿਆਸਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਅਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਨਹੀਂ ਕੀਤਾ ।

ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 7.
ਕੀ ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਲਾਉਣਾ ਉੱਚਿਤ ਸੀ ? ਆਪਣੇ ਪੱਖ ਵਿੱਚ ਦਲੀਲਾਂ ਦਿਓ ? (Was it proper for Lord Dalhousie to annex Punjab to the British empire ? Give arguments in support of your answer.)
ਜਾਂ
ਕੀ ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਸੰਯੋਜਨ ਨਿਆਂਸੰਗਤ ਸੀ ? ਆਪਣੇ ਸ਼ਬਦਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਰਣਨ ਕਰੋ । (Was the annexation of Punjab by Lord Dalhousie justified ? Give reasons in your favour.)
ਜਾਂ
“ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਲਾਉਣਾ ਇੱਕ ਘੋਰ ਵਿਸ਼ਵਾਸਘਾਤ ਸੀ ।” ਵਿਆਖਿਆ ਕਰੋ । (“Annexation of Punjab was a violent breach of trust.” Explain.)
ਜਾਂ
ਕੀ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਸੰਯੋਜਨ ਨਿਆਂ ਸੰਗਤ ਸੀ ? ਇਸ ਪੱਖ ਵਿੱਚ ਛੇ ਦਲੀਲਾਂ ਦਿਉ । (Was the annexation of Punjab justified ? Give six reasons for it.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਲਾਉਣਾ ਨਿਆਂਸੰਗਤ ਨਹੀਂ ਸੀ ।
1. ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਬਗਾਵਤ ਲਈ ਭੜਕਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ – ਪਹਿਲੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਬਹੁਤ ਸਾਰੀਆਂ ਅਜਿਹੀਆਂ ਘਟਨਾਵਾਂ ਹੋਈਆਂ ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਬਗਾਵਤ ਲਈ ਭੜਕਾਇਆ। ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦੀ ਸੰਧੀ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੇ ਕਈ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਨ ਇਲਾਕੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਖੋਹ ਲਏ ਸਨ । ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਬਹੁਤ ਮਾੜਾ ਸਲੂਕ ਕੀਤਾ । ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਅਤੇ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਬਗ਼ਾਵਤ ਲਈ ਭੜਕਾਇਆ । ਸਿੱਟੇ ਵਜੋਂ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਬਗ਼ਾਵਤ ਲਈ ਮਜਬੂਰ ਹੋਣਾ ਪਿਆ ।
2. ਬਗ਼ਾਵਤ ਨੂੰ ਸਮੇਂ ਸਿਰ ਨਾ ਦਬਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ – ਜਦੋਂ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਵਿਚ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਦੀ ਅੱਗ ਭੜਕੀ ਤਾਂ ਉਸ ‘ਤੇ ਛੇਤੀ ਹੀ ਕਾਬੂ ਪਾਇਆ ਜਾ ਸਕਦਾ ਸੀ । ਅੱਠ ਮਹੀਨਿਆਂ ਤਕ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਨੂੰ ਫੈਲਣ ਦੇਣ ਪਿੱਛੇ ਇਕ ਡੂੰਘੀ ਰਾਜਸੀ ਚਾਲ ਸੀ । ਇਸ ਕਾਰਨ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੱਡੀ ਸੈਨਿਕ ਕਾਰਵਾਈ ਕਰਨ ਦਾ ਬਹਾਨਾ ਮਿਲ ਗਿਆ ਅਤੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਉੱਤੇ ਕਬਜ਼ਾ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ ।
3. ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਸੰਧੀ ਦੀਆਂ ਸ਼ਰਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪੂਰਾ ਨਹੀਂ ਕੀਤਾ – ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦਾ ਕਹਿਣਾ ਸੀ ਕਿ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਸੰਧੀ ਦੀਆਂ ਸ਼ਰਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪੂਰਾ ਕੀਤਾ ਹੈ । ਪਰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਸੰਧੀ ਦੀਆਂ ਕੇਵਲ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਸ਼ਰਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਹੀ ਪੂਰਾ ਕੀਤਾ, ਜਿਹੜੀਆਂ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਲਈ ਲਾਹੇਵੰਦ ਸਨ । ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦਾ ਇਹ ਕਹਿਣਾ ਕਿ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਸੰਧੀ ਦੀਆਂ ਸਾਰੀਆਂ ਸ਼ਰਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪੂਰਾ ਕੀਤਾ ਹੈ, ਨਿਰਾ ਝੂਠ ਹੀ ਹੈ ।
4. ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦਰਬਾਰ ਨੇ ਸੰਧੀ ਦੀਆਂ ਸ਼ਰਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪੂਰਾ ਕਰਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਪੂਰਨ ਸਹਿਯੋਗ ਦਿੱਤਾ – ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦਰਬਾਰ ਤਾਂ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਉੱਤੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦਾ ਕਬਜ਼ਾ ਹੋਣ ਤਕ ਸੰਧੀ ਦੀਆਂ ਸ਼ਰਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਵਫ਼ਾਦਾਰੀ ਨਾਲ ਨਿਭਾਉਂਦਾ ਰਿਹਾ | ਲਾਹੌਰ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਰੱਖੀ ਹੋਈ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸੈਨਾ ਦਾ ਪੂਰਾ ਖ਼ਰਚਾ ਦੇ ਰਹੀ ਸੀ । ਉਸ ਨੇ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੁਲਜ, ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਤੇ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਕੀਤੀਆਂ ਗਈਆਂ ਬਗ਼ਾਵਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਕੁਚਲਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਫ਼ੌਜਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪੂਰਾ ਸਹਿਯੋਗ ਵੀ ਦਿੱਤਾ
5. ਪੂਰੀ ਸਿੱਖ ਸੈਨਾ ਅਤੇ ਲੋਕਾਂ ਨੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਨਹੀਂ ਕੀਤਾ ਸੀ – ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਨੇ ਇਹ ਦੋਸ਼ ਲਗਾਇਆ ਸੀ ਕਿ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੀ ਪੂਰੀ ਸਿੱਖ ਸੈਨਾ ਅਤੇ ਲੋਕਾਂ ਨੇ ਮਿਲ ਕੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਸੀ । ਪਰ ਇਸ ਕਥਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਜ਼ਰਾ ਵੀ ਸੱਚਾਈ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੈ । ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੇ ਕੇਵਲ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਅਤੇ ਹਜ਼ਾਰਾ ਪ੍ਰਾਂਤਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਹੀ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਹੋਇਆ ਸੀ । ਬਹੁਤੀ ਸਿੱਖ ਫ਼ੌਜ ਅਤੇ ਲੋਕ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਵਫ਼ਾਦਾਰ ਰਹੇ।
6. ਪੰਜਾਬ ‘ਤੇ ਕਬਜ਼ਾ ਇੱਕ ਵਿਸ਼ਵਾਸਘਾਤ ਸੀ – ਪੰਜਾਬ ‘ਤੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦਾ ਕਬਜ਼ਾ ਇੱਕ ਘੋਰ ਵਿਸ਼ਵਾਸਘਾਤ ਸੀ । 1846 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਹੋਈ ਭੈਰੋਵਾਲ ਦੀ ਸੰਧੀ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਂਤੀ ਕਾਇਮ ਰੱਖਣ ਦੀ ਸਾਰੀ ਜ਼ਿੰਮੇਵਾਰੀ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦੀ ਸੀ । ਇਸ ਦੇ ਬਾਵਜੂਦ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਿਗੜ ਰਹੇ ਹਾਲਾਤਾਂ ਲਈ ਪੂਰੀ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਦੋਸ਼ੀ ਠਹਿਰਾਇਆ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 8.
ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਦੇ ਇਸ ਪੱਖ ਵਿੱਚ ਕੋਈ ਛੇ ਦਲੀਲਾਂ ਦਿਓ ਕਿ ਉਸ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਲਾਉਣਾ ਉੱਚਿਤ ਸੀ । (Give any six arguments in favour of Dalhousie’s annexation of the Punjab to the British empire.)
ਜਾਂ
ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਦੀ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਉੱਤੇ ਕਬਜ਼ੇ ਦੀ ਨੀਤੀ ਦੇ ਪੱਖ ਵਿੱਚ ਦਲੀਲਾਂ ਦਿਓ । (Give arguments in favour of Dalhousie’s policy of the annexation of Punjab.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
1. ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨੇ ਆਪਣੇ ਸ਼ਰਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਤੋੜਿਆ – ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਨੇ ਇਹ ਦੋਸ਼ ਲਗਾਇਆ ਕਿ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨੇ ਭੈਰੋਵਾਲ ਦੀ ਸੰਧੀ ਦੀਆਂ ਸ਼ਰਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਤੋੜਿਆ ਹੈ । ਸਿੱਖ ਸਰਦਾਰਾਂ ਨੇ ਇਹ ਵਚਨ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਸੀ ਕਿ ਉਹ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਰੈਜ਼ੀਡੈਂਟ ਨੂੰ ਪੂਰਾ ਸਹਿਯੋਗ ਦੇਣਗੇ । ਪਰ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਅਸ਼ਾਂਤੀ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਫੈਲਾਉਣ ਦਾ ਯਤਨ ਕੀਤਾ । ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਨੇ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਦੀ ਬਗ਼ਾਵਤ ਨੂੰ ਪੂਰੀ ਸਿੱਖ ਜਾਤੀ ਦੀ ਬਗਾਵਤ ਦੱਸਿਆ । ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਵਿਗੜ ਰਹੇ ਹਾਲਾਤ ‘ਤੇ ਕਾਬੂ ਪਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਲਾਉਣਾ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਸੀ ।
2. ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਚੰਗਾ ਮੱਧਵਰਤੀ ਰਾਜ ਨਾ ਰਹਿਣਾ – ਲਾਰਡ ਹਾਰਡਿੰਗ ਦਾ ਵਿਚਾਰ ਸੀ ਕਿ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਇਕ ਲਾਭਦਾਇਕ ਮੱਧਵਰਤੀ ਰਾਜ ਸਿੱਧ ਹੋਵੇਗਾ । ਇਸ ਕਾਰਨ ਬਿਟਿਸ਼ ਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ ਅਫ਼ਗਾਨਿਸਤਾਨ ਵੱਲੋਂ ਕਿਸੇ ਖ਼ਤਰੇ ਦਾ ਸਾਹਮਣਾ ਨਹੀਂ ਕਰਨਾ ਪਵੇਗਾ । ਪਰੰਤੂ ਉਸ ਦਾ ਇਹ ਵਿਚਾਰ ਗਲਤ ਸਿੱਧ ਹੋਇਆ ਕਿਉਂਕਿ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਅਫ਼ਗਾਨਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਦੋਸਤੀ ਹੋ ਗਈ ਸੀ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਨੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਆਪਣੇ ਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕਰਨਾ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਸਮਝਿਆ ।
3. ਕਰਜ਼ੇ ਦੀ ਅਦਾਇਗੀ ਨਾ ਕਰਨਾ – ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਨੇ ਇਹ ਦੋਸ਼ ਲਗਾਇਆ ਕਿ ਭੈਰੋਵਾਲ ਦੀ ਸੰਧੀ ਦੀਆਂ ਸ਼ਰਤਾਂ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦਰਬਾਰ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੂੰ 22 ਲੱਖ ਰੁਪਏ ਸਾਲਾਨਾ ਦੇਣਾ ਸੀ । ਪਰ ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦਰਬਾਰ ਨੇ ਇੱਕ ਪਾਈ ਵੀ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਨਾ ਦਿੱਤੀ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕਰਨਾ ਉੱਚਿਤ ਸੀ ।
4. ਪੰਜਾਬ ਉੱਤੇ ਕਬਜ਼ਾ ਕਰਨਾ ਲਾਭਦਾਇਕ ਸੀ – ਪਹਿਲੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਵਿੱਚ ਜਿੱਤ ਮਗਰੋਂ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦਾ ਵਿਚਾਰ ਸੀ ਕਿ ਆਰਥਿਕ ਪੱਖ ਤੋਂ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਕੋਈ ਲਾਭਦਾਇਕ ਪਾਂਤ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੈ । ਪਰ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਦੋ ਸਾਲ ਰਹਿਣ ਪਿੱਛੋਂ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪਤਾ ਲੱਗਿਆ ਕਿ ਇਹ ਰਾਜ ਕਈ ਪੱਖਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਲਈ ਲਾਭਦਾਇਕ ਸਿੱਧ ਹੋ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਕਾਰਨਾਂ ਕਰਕੇ ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਨੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਹੜੱਪਣ ਦਾ ਪੱਕਾ ਨਿਸ਼ਚਾ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ ।
5. ਪੰਜਾਬ ਉੱਤੇ ਕਬਜ਼ਾ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਸੀ – ਇਹ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਜੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਨਾ ਕੀਤਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਤਾਂ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਹਮੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਸਾਜ਼ਸ਼ਾਂ ਕਰਦੇ ਰਹਿਣਾ ਸੀ । ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਦੂਜੇ ਹਿੱਸਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਵੀ ਪੈ ਸਕਦਾ ਸੀ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਨੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕਰਨਾ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਸਮਝਿਆ ।
6. ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੇ ਲੋਕਾਂ ਲਈ ਚੰਗਾ – ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਦੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਉੱਤੇ ਕਬਜ਼ਾ ਕਰਨ ਦੇ ਪੱਖ ਵਿੱਚ ਇੱਕ ਦਲੀਲ ਇਹ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਅਜਿਹਾ ਕਰ ਕੇ ਉਸ ਨੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੇ ਲੋਕਾਂ ਲਈ ਇੱਕ ਚੰਗਾ ਕੰਮ ਕੀਤਾ । ਅਜਿਹਾ ਕਰਕੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਫ਼ੈਲੀ ਬਦਅਮਨੀ ਨੂੰ ਦੂਰ ਕੀਤਾ । ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਨ ਸੁਧਾਰਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਲਾਗੂ ਕੀਤਾ । ਇਸ ਕਾਰਨ ਲੋਕਾਂ ਨੇ ਸੁੱਖ ਦਾ ਸਾਹ ਲਿਆ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 9.
ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ‘ਤੇ ਇੱਕ ਨੋਟ ਲਿਖੋ । (Write a note on Maharaja Dalip Singh.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਛੋਟਾ ਪੁੱਤਰ ਸੀ । ਉਹ 15 ਸਤੰਬਰ, 1843 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਨਵਾਂ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਬਣਿਆ ਸੀ । ਉਸ ਸਮੇਂ ਉਸ ਦੀ ਉਮਰ ਕੇਵਲ 5 ਸਾਲ ਸੀ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਉਸ ਦਾ ਸਰਪ੍ਰਸਤ ਬਣਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ । ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਰਾਜ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਚਲਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਹੀਰਾ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਰਾਜ ਦਾ ਨਵਾਂ ਪ੍ਰਧਾਨ ਮੰਤਰੀ ਨਿਯੁਕਤ ਕੀਤਾ ਸੀ । ਭਾਵੇਂ ਉਹ ਬੜਾ ਸਿਆਣਾ ਸੀ ਪਰ ਉਸ ਨੇ ਪੰਡਤ ਜੱਲਾ ਨੂੰ ਮੁਸ਼ੀਰ-ਏ-ਖ਼ਾਸ ਦੇ ਅਹੁਦੇ ‘ਤੇ ਨਿਯੁਕਤ ਕਰਕੇ ਬਹੁਤ ਸਾਰੇ ਰਾਜ ਦਰਬਾਰੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਨਾਰਾਜ਼ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ ਸੀ ।
1844 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਹੀਰਾ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਕਤਲ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਜਵਾਹਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਰਾਜ ਦਾ ਨਵਾਂ ਪ੍ਰਧਾਨ ਮੰਤਰੀ ਬਣਿਆ ਪਰ ਉਹ ਬੜਾ ਹਠੀ ਅਤੇ ਅਯੋਗ ਸੀ । ਉਸ ਨੂੰ ਸਤੰਬਰ, 1845 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਕੰਵਰ ਪਿਸ਼ੌਰਾ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਕਤਲ ਕਾਰਨ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਨੇ ਮੌਤ ਦੀ ਸਜ਼ਾ ਦੇ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਸੀ । ਉਸ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਲਾਲ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਪ੍ਰਧਾਨ ਮੰਤਰੀ ਦੇ ਅਹੁਦੇ ‘ਤੇ ਨਿਯੁਕਤ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਉਹ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਹੀ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਮਿਲਿਆ ਹੋਇਆ ਸੀ । ਸਿੱਟੇ ਵਜੋਂ ਪਹਿਲੇ ਅਤੇ ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਹਾਰ ਦਾ ਮੂੰਹ ਦੇਖਣਾ ਪਿਆ | ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਗੱਦੀ ਤੋਂ ਲਾਹ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਅਤੇ 29 ਮਾਰਚ, 1849 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ ! 22 ਅਕਤੂਬਰ, 1893 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਪੈਰਿਸ ਵਿਖੇ ਮੌਤ ਹੋ ਗਈ ਸੀ ।

ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 10.
ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਜਾਂ ਜਿੰਦ ਕੌਰ ਤੇ ਇੱਕ ਨੋਟ ਲਿਖੋ । (Write a note on Maharani Jindan or Jind Kaur.)
ਜਾਂ
ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਬਾਰੇ ਤੁਸੀਂ ਕੀ ਜਾਣਦੇ ਹੋ ? (What do you know about Maharani Jindan ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ, ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਮਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਰਾਣੀ ਸੀ । ਜਦੋਂ 15 ਸਤੰਬਰ, 1843 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਨਵਾਂ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਬਣਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ਤਾਂ ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਉਸ ਦਾ ਸਰਪਸਤ ਨਿਯੁਕਤ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਕਿਉਂਕਿ ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ ਆਜ਼ਾਦ ਕਾਇਮ ਰੱਖਣਾ ਚਾਹੁੰਦੀ ਸੀ ਇਸ ਲਈ ਉਹ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਅੱਖਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਬਹੁਤ ਰੜਕਦੀ ਸੀ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਦਸੰਬਰ, 1846 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦਰਬਾਰ ਨਾਲ ਹੋਈ ਭੈਰੋਵਾਲ ਦੀ ਸੰਧੀ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਸਾਰੀਆਂ ਸ਼ਕਤੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਖੋਹ ਲਿਆ ਸੀ ਅਤੇ ਉਸ ਦੀ ਡੇਢ ਲੱਖ ਰੁਪਿਆ ਸਾਲਾਨਾ ਪੈਨਸ਼ਨ ਨਿਯਤ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਗਈ । ਅਗਸਤ, 1847 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਰਾਣੀ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ੇਖੂਪੁਰਾ ਦੇ ਕਿਲ੍ਹੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਨਜ਼ਰਬੰਦ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ।
ਮਈ, 1848 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਨੂੰ ਦੇਸ਼ ਨਿਕਾਲਾ ਦੇ ਕੇ ਬਨਾਰਸ ਭੇਜ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਜੇਲ੍ਹ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਬਹੁਤ ਮਾੜਾ ਸਲੂਕ ਕੀਤਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਸੀ । ਅਪਰੈਲ, 1849 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਭੇਸ ਬਦਲ ਕੇ ਨੇਪਾਲ ਪਹੁੰਚਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਫਲ ਹੋ ਗਈ । 1861 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਜਦੋਂ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਇੰਗਲੈਂਡ ਤੋਂ ਭਾਰਤ ਆਇਆ ਤਾਂ ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਉਸ ਨੂੰ ਮਿਲਣ ਲਈ ਨੇਪਾਲ ਤੋਂ ਆਈ । ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਆਪਣੀ ਮਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਆਪਣੇ ਨਾਲ ਹੀ ਇੰਗਲੈਂਡ ਲੈ ਗਿਆ ।ਇੱਥੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਦੋਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਇਕੱਠੇ ਨਾ ਰਹਿਣ ਦਿੱਤਾ | ਅੰਤ 1 ਅਗਸਤ, 1863 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਉਹ ਇਸ ਸੰਸਾਰ ਤੋਂ ਚਲ ਵਸੀ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 11.
ਭਾਈ ਮਹਾਰਾਜ ਸਿੰਘ ‘ਤੇ ਇੱਕ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਨੋਟ ਲਿਖੋ । (Write a brief note on Bhai Maharaj Singh.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਭਾਈ ਮਹਾਰਾਜ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੌਰੰਗਾਬਾਦ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਸੰਤ ਭਾਈ ਬੀਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਚੇਲੇ ਸਨ । 1845 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਉਹ ਭਾਈ ਬੀਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਮੌਤ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਗੱਦੀ ‘ਤੇ ਬੈਠੇ । ਉਹ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੀ ਸੁਤੰਤਰਤਾ ਨੂੰ ਬਣਾਈ ਰੱਖਣ ਦੇ ਹੱਕ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਨ । ਇਸ ਉਦੇਸ਼ ਨਾਲ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਪਿੰਡ-ਪਿੰਡ ਵਿੱਚ ਜਾ ਕੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਦੇ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਪ੍ਰਚਾਰ ਕਰਨਾ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਕੀਤਾ । ਸਿੱਟੇ ਵਜੋਂ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਨੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਸੰਪੱਤੀ ਜ਼ਬਤ ਕਰ ਲਈ ਅਤੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਗ੍ਰਿਫ਼ਤਾਰ ਕਰਾਉਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਨੂੰ 10,000 ਰੁਪਏ ਇਨਾਮ ਦੇਣ ਦੀ ਘੋਸ਼ਣਾ ਕੀਤੀ । ਇਸ ਦੇ ਬਾਵਜੂਦ ਭਾਈ ਮਹਾਰਾਜ ਸਿੰਘ ਨਿਡਰ ਹੋ ਕੇ ਆਪਣਾ ਪ੍ਰਚਾਰ ਕਰਦੇ ਰਹੇ ।ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ, ਹਜ਼ਾਰਾ ਦੇ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਟਾਰੀਵਾਲਾ ਅਤੇ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਪੁੱਤਰ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਦਾ ਝੰਡਾ ਬੁਲੰਦ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਪ੍ਰੇਰਿਤ ਕੀਤਾ। ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਦੂਜੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੀਆਂ ਸਾਰੀਆਂ ਲੜਾਈਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਹਿੱਸਾ ਲਿਆ ।
ਉਹ ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਸਿੱਖ ਫ਼ੌਜਾਂ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਅੱਗੇ ਹਥਿਆਰ ਸੁੱਟਣ ਦੇ ਹੱਕ ਵਿੱਚ ਨਹੀਂ ਸਨ । ਅਜਿਹਾ ਹੋਣ ‘ਤੇ ਉਹ ਜੰਮੂ ਚਲੇ ਗਏ ।ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਕਾਬਲ ਦੇ ਸ਼ਾਸਕ ਨਾਲ ਮਿਲ ਕੇ 3 ਜਨਵਰੀ, 1850 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਕਰਨ ਦੀ ਇੱਕ ਯੋਜਨਾ ਬਣਾਈ । ਇਸ ਯੋਜਨਾ ਬਾਰੇ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਨੂੰ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਹੀ ਪਤਾ ਚਲ ਗਿਆਂ । ਸਿੱਟੇ ਵਜੋਂ ਉਸ ਨੇ ਭਾਈ ਮਹਾਰਾਜ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ 28 ਦਸੰਬਰ, 1849 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਗ੍ਰਿਫ਼ਤਾਰ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ । ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਕਲਕੱਤਾ ਅਤੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਿੰਘਾਪੁਰ ਜੇਲ੍ਹ ਵਿੱਚ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਗਿਆ । ਇੱਥੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ 5 ਜੁਲਾਈ, 1856 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਮੌਤ ਹੋ ਗਈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸਤਾਵ ਰੂਪੀ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ (Essay Type Questions)
ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਕਰਨ (Causes of the Second Anglo-Sikh War)
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਪਰਿਸਥਿਤੀਆਂ ਦਾ ਵਰਣਨ ਕਰੋ ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਕਰਕੇ ਦੂਜਾ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਹੋਇਆ । ਇਸ ਯੁੱਧ ਲਈ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਕਿੱਥੋਂ ਤਕ ਜ਼ਿੰਮੇਵਾਰ ਸਨ ? (Discuss the circumstances leading to the Second Anglo-Sikh War. How far were the British responsible for it ?)
ਜਾਂ
ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਮੁੱਖ ਕਾਰਨ ਕੀ ਸਨ ? (What were the main causes of the Second Anglo-Sikh War ?)
ਜਾਂ
ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਨ ਕਾਰਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਵਿਆਖਿਆ ਕਰੋ । (Explain important causes of the Second Anglo-Sikh War.)
ਜਾਂ
ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਲਿਖੋ । (Write the reasons of Second Anglo-Sikh War.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਪਹਿਲੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦੀ ਜਿੱਤ ਹੋਈ ਅਤੇ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਹਾਰ ਦਾ ਮੂੰਹ ਵੇਖਣਾ ਪਿਆ | ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਅਪਮਾਨਜਨਕ ਵਿਹਾਰ ਅਤੇ ਥੋਪੀਆਂ ਗਈਆਂ ਸੰਧੀਆਂ ਨਾਲ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਗੁੱਸਾ ਹੋਰ ਭੜਕ ਉੱਠਿਆ । ਇਸ ਦਾ ਨਤੀਜਾ ਦੁਜੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਾਹਮਣੇ ਆਇਆ । ਇਸ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਮੁੱਖ ਕਾਰਨ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਸਨ-
1. ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦੀ ਆਪਣੀ ਹਾਰ ਦਾ ਬਦਲਾ ਲੈਣ ਦੀ ਇੱਛਾ (Sikh desir to avenge their defeat in the First Anglo-Sikh War) – ਇਹ ਠੀਕ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਹੋਏ ਪਹਿਲੇ ਯੁੱਧ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦੀ ਹਾਰ ਹੋ ਗਈ ਸੀ, ਪਰ ਇਸ ਨਾਲ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਹੌਸਲੇ ਕਿਸੇ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਘੱਟ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੋਏ ਸਨ । ਇਸ ਹਾਰ ਦਾ ਮੁੱਖ ਕਾਰਨ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦੇ ਨੇਤਾਵਾਂ ਲਾਲ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਤੇ ਤੇਜਾ ਸਿੰਘ ਵੱਲੋਂ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ ਗੱਦਾਰੀ ਸੀ । ਸਿੱਖ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਆਪਣੀ ਯੋਗਤਾ ‘ਤੇ ਪੂਰਾ ਵਿਸ਼ਵਾਸ ਸੀ । ਉਹ ਆਪਣੀ ਹਾਰ ਦਾ ਬਦਲਾ ਲੈਣਾ ਚਾਹੁੰਦੇ ਸਨ । ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਇਹ ਤੀਵਰ ਇੱਛਾ ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦਾ ਇੱਕ ਮੁੱਖ ਕਾਰਨ ਬਣੀ ।
2. ਲਾਹੌਰ ਅਤੇ ਭੈਰੋਵਾਲ ਦੀਆਂ ਸੰਧੀਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਅਸੰਤੁਸ਼ਟ (Punjabis were dissatisfied with the Treaties of Lahore and Bhairowal) – ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਵਿਚਾਲੇ ਹੋਏ ਪਹਿਲੇ ਯੁੱਧ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦਰਬਾਰ ਨਾਲ ਲਾਹੌਰ ਅਤੇ ਭੈਰੋਵਾਲ ਨਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਸੰਧੀਆਂ ਕੀਤੀਆਂ । ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਸੰਧੀਆਂ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਜਲੰਧਰ ਦੁਆਬ ਵਰਗੇ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਉਪਜਾਉ ਦੇਸ਼ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਆਪਣੇ ਅਧੀਨ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ ਸੀ | ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ ਦਾ ਇਲਾਕਾ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਆਪਣੇ ਮਿੱਤਰ ਗੁਲਾਬ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਹਵਾਲੇ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਸੀ । ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੇ ਲੋਕ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਅਣਥੱਕ ਯਤਨਾਂ ਸਦਕਾ ਬਣਾਏ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ ਖੇਰੂੰ-ਖੇਰੂੰ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਦੇਖ ਕੇ ਸਹਿਣ ਨਹੀਂ ਕਰ ਸਕਦੇ ਸਨ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਇੱਕ ਹੋਰ ਯੁੱਧ ਲੜਨਾ ਪੈਣਾ ਸੀ ।
3. ਸਿੱਖ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਰੋਸ (Resentment among the Sikh Soldiers) – ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦੀ ਸੰਧੀ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਖ਼ਾਲਸਾ ਫ਼ੌਜ ਦੀ ਗਿਣਤੀ 20,000 ਪੈਦਲ ਤੇ 12,000 ਘੋੜਸਵਾਰ ਨਿਸ਼ਚਿਤ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤੀ । ਇਸ ਕਾਰਨ ਹਜ਼ਾਰਾਂ ਦੀ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਿੱਖ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਨੌਕਰੀ ਤੋਂ ਜਵਾਬ ਦੇ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਦੇ ਮਨਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੀ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਰੋਸ ਪੈਦਾ ਹੋ ਗਿਆ ਅਤੇ ਉਹ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੀਆਂ ਤਿਆਰੀਆਂ ਕਰਨ ਲੱਗੇ ।
4. ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਸਖ਼ਤ ਸਲੂਕ (Harsh Treatment with. Maharani Jindan) – ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਵਿਧਵਾ ਅਤੇ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਮਾਂ ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਜੋ ਅਪਮਾਨਜਨਕ ਵਿਵਹਾਰ ਕੀਤਾ ਉਸ ਨੇ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਫੈਲੇ ਰੋਸ ਨੂੰ ਹੋਰ ਭੜਕਾ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦੀ ਸੰਧੀ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਨਾਬਾਲਗ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਸਰਪ੍ਰਸਤ ਮੰਨਿਆ ਸੀ । ਪਰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਭੈਰੋਵਾਲ ਦੀ ਸੰਧੀ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਦੀਆਂ ਸਾਰੀਆਂ ਸ਼ਕਤੀਆਂ ਖੋਹ ਲਈਆਂ । 1847 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ੇਖੂਪੁਰਾ ਦੇ ਕਿਲ੍ਹੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਨਜ਼ਰਬੰਦ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ । 1848 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਨੂੰ ਦੇਸ਼ ਨਿਕਾਲਾ ਦੇ ਕੇ ਬਨਾਰਸ ਭੇਜ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ ਬਦਸਲੂਕੀ ਕਾਰਨ ਸਾਰੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਗੁੱਸੇ ਦੀ ਲਹਿਰ ਦੌੜ ਗਈ ।
5. ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਦਾ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ (Revolt of Diwan Moolraj) – ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਕਰਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਨੂੰ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ ਸਥਾਨ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਹੈ । 1844 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦਾ ਨਵਾਂ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ ਬਣਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ | ਪਰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਗ਼ਲਤ ਨੀਤੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਦਸੰਬਰ 1847 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਨੇ ਆਪਣਾ ਅਸਤੀਫ਼ਾ ਦੇ ਦਿੱਤਾ । 1848 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਕਾਹਨ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦਾ ਨਵਾਂ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ ਨਿਯੁਕਤ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ | ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਤੋਂ ਚਾਰਜ ਲੈਣ ਲਈ ਕਾਹਨ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਭੇਜੇ ਗਏ ਦੋ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਅਫ਼ਸਰਾਂ ਵੈਨਸ ਐਗਨਿਯੁ ਅਤੇ ਐਂਡਰਸਨ ‘ਤੇ ਕੁਝ ਸਿਪਾਹੀਆਂ ਨੇ ਹਮਲਾ ਕਰਕੇ 20 ਅਪਰੈਲ, 1848 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਕਤਲ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਅਤੇ ਕਾਹਨ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਗ੍ਰਿਫ਼ਤਾਰ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ | ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਨੇ ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਕਤਲ ਦੀ ਸਾਰੀ ਜ਼ਿੰਮੇਵਾਰੀ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਸਿਰ ਪਾਈ । ਇਸ ਕਾਰਨ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਦਾ ਖੂਨ ਖੌਲਣ ਲੱਗਾ ਅਤੇ ਉਸ ਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਦਾ ਝੰਡਾ ਬੁਲੰਦ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ | ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਗਵਰਨਰ-ਜਨਰਲ ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਅਜਿਹੇ ਹੀ ਮੌਕੇ ਦੀ ਤਲਾਸ਼

ਵਿੱਚ ਸੀ । ਉਹ ਚਾਹੁੰਦਾ ਸੀ ਕਿ ਇਹ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾ ਭੜਕ ਜਾਏ ਅਤੇ ਉਸ ਨੂੰ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਉੱਤੇ ਕਬਜ਼ਾ ਕਰਨ ਦਾ ਮੌਕਾ ਮਿਲ ਜਾਏ । ਡਾਕਟਰ ਕ੍ਰਿਪਾਲ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ,
‘‘ਉਹ ਚੰਗਿਆੜੀ ਜਿਸ ਨੇ ਭਾਂਬੜ ਬਾਲਿਆ ਅਤੇ ਜਿਸ ਵਿੱਚ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਸੁਤੰਤਰ ਰਾਜ ਸੜ ਕੇ ਸੁਆਹ ਹੋ ਗਿਆ, ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਤੋਂ ਉੱਠੀ ਸੀ ।’’ 1
6. ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦਾ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ (Revolt of Chattar Singh) – ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਟਾਰੀਵਾਲਾ ਹਜ਼ਾਰਾ ਦਾ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ ਸੀ । ਉਸ ਦੇ ਇੱਕ ਸਿਪਾਹੀ ਨੇ ਇੱਕ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਕੈਨੋਰਾ ਦਾ ਕਤਲ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਇਸ ’ਤੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਅਹੁਦੇ ਤੋਂ ਹਟਾ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਅਤੇ ਉਸ ਦੀ ਜਾਗੀਰ ਜ਼ਬਤ ਕਰ ਲਈ । ਇਸ ਕਾਰਨ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਬਗਾਵਤ ਕਰਨ ਦਾ ਐਲਾਨ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਸਿੱਟੇ ਵਜੋਂ ਚਾਰ-ਚੁਫ਼ੇਰੇ ਬਗਾਵਤ ਦੀ ਅੱਗ ਫੈਲ ਗਈ ।
7. ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦਾ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ (Revolt of Sher Singh) – ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦਾ ਪੁੱਤਰ ਸੀ । ਜਦੋਂ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਆਪਣੇ ਪਿਤਾ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦੀ ਬਦਸਲੂਕੀ ਬਾਰੇ ਪਤਾ ਲੱਗਿਆ ਤਾਂ ਉਸ ਨੇ ਵੀ 14 ਸਤੰਬਰ, 1848 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਕਰਨ ਦਾ ਐਲਾਨ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਉਸ ਦੀ ਅਪੀਲ ‘ਤੇ ਕਈ ਸਿੱਖ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਝੰਡੇ ਅਧੀਨ ਇਕੱਠੇ ਹੋ ਗਏ ।
8. ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਦੀ ਨੀਤੀ (Policy of Lord Dalhousie) – ਜਨਵਰੀ, 1848 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਗਵਰਨਰ-ਜਨਰਲ ਬਣਿਆ ਸੀ । ਉਸ ਨੇ ਲੈਪਸ ਦੀ ਨੀਤੀ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀਆਂ ਬਹੁਤ ਸਾਰੀਆਂ ਰਿਆਸਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕੀਤਾ | ਕੇਵਲ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਹੀ ਇੱਕ ਅਜਿਹਾ ਰਾਜ ਸੀ ਜਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਹਾਲੇ ਤਕ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਨਹੀਂ ਕੀਤਾ ਜਾ ਸਕਿਆ ਸੀ । ਉਹ ਕਿਸੇ ਸੁਨਹਿਰੀ ਮੌਕੇ ਦੀ ਤਲਾਸ਼ ਵਿੱਚ ਸੀ । ਇਹ ਮੌਕਾ ਉਸ ਨੂੰ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ, ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਤੇ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਕੀਤੇ ਗਏ ਵਿਦਰੋਹਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਮਿਲਿਆ ।
ਜਦੋਂ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਦੀ ਅੱਗ ਭੜਕਦੀ ਨਜ਼ਰ ਆਈ ਤਾਂ ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਨੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹੀਆਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਕਾਰਵਾਈ ਕਰਨ ਦਾ ਆਦੇਸ਼ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਕਮਾਂਡਰ-ਇਨ-ਚੀਫ਼ ਲਾਰਡ ਹਿਊਗ ਗਫ਼ 16 ਨਵੰਬਰ ਨੂੰ ਫ਼ੌਜ ਲੈ ਕੇ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦਾ ਮੁਕਾਬਲਾ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਦਰਿਆ ਚਨਾਬ ਵੱਲ ਚਲ ਪਿਆ ।

ਯੁੱਧ ਦੀਆਂ ਘਟਨਾਵਾਂ (Events of the War)
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਵਿਚਾਲੇ ਹੋਏ ਦੂਜੇ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੀਆਂ ਘਟਨਾਵਾਂ ਦਾ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਵਰਣਨ ਕਰੋ । (Discuss in brief the events of the Second Anglo-Sikh War.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਚਲਾਕ ਨੀਤੀਆਂ ਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼-ਸਿੱਖ ਸੰਬੰਧਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਇੱਕ ਹੋਰ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਨੇੜੇ ਲਿਆ ਖੜਾ ਕੀਤਾ | ਮਲਰਾਜ, ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਤੇ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਨੂੰ ਦੇਖਦੇ ਹੋਏ ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਨੇ ਲਾਰਡ ਹਿਊਗ ਗਫ਼ ਨੂੰ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਕੁਚਲਣ ਲਈ ਭੇਜਿਆ । ਸਿੱਟੇ ਵਜੋਂ ਦੂਜਾ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਹੋ ਗਿਆ । ਇਸ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੀਆਂ ਮੁੱਖ ਘਟਨਾਵਾਂ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੀਆਂ ਸਨ-
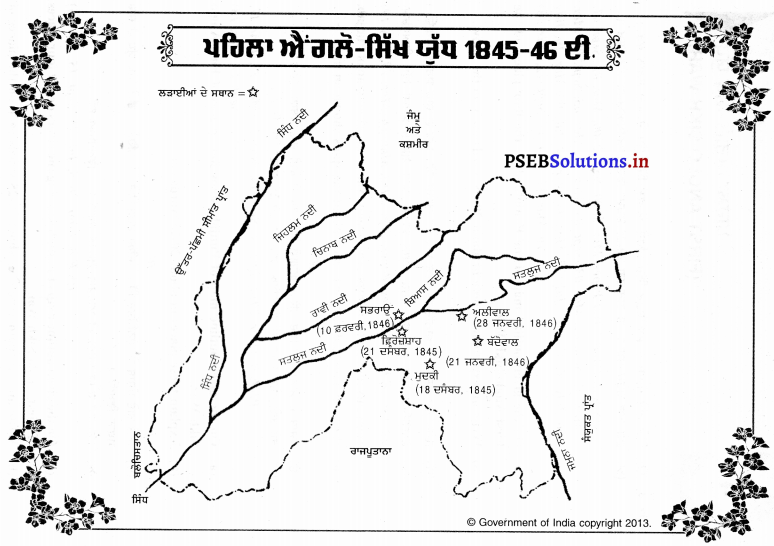
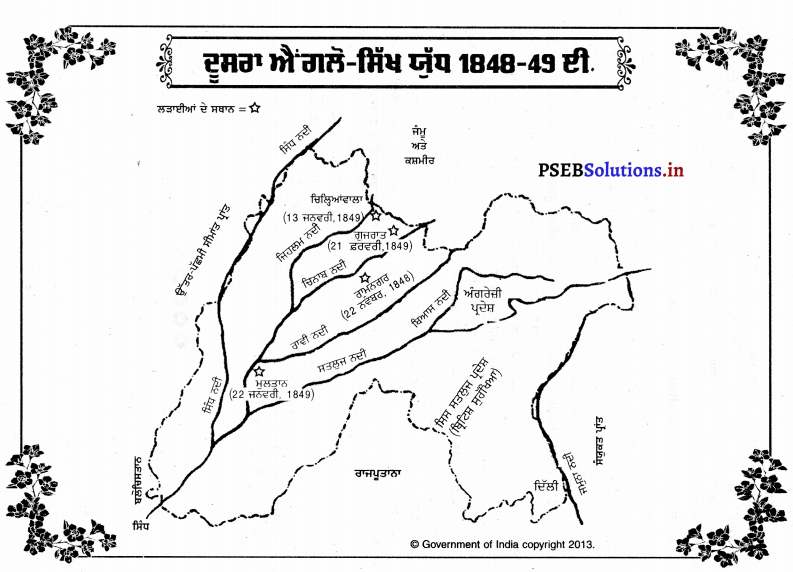
1. ਰਾਮਨਗਰ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ (Battle of Ramnagar) – ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੀ ਪਹਿਲੀ ਲੜਾਈ 22 ਨਵੰਬਰ, 1848 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਰਾਮਨਗਰ ਦੇ ਸਥਾਨ ‘ਤੇ ਹੋਈ | ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸੈਨਾ ਦੀ ਅਗਵਾਈ ਲਾਰਡ ਹਿਊਗ ਗਫ਼ ਕਰ ਰਿਹਾ ਸੀ । ਉਸ ਅਧੀਨ 20,000 ਸੈਨਿਕ ਸਨ । ਸਿੱਖ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਦੀ ਅਗਵਾਈ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਕਰ ਰਿਹਾ ਸੀ ਅਤੇ ਉਸ ਅਧੀਨ 15,000 ਸੈਨਿਕ ਸਨ । ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦੇ ਹਮਲੇ ਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦੇ ਛੱਕੇ ਛੁਡਾ ਦਿੱਤੇ । ਇਸ ਲੜਾਈ ਤੋਂ ਹਿਊਗ ਗਫ਼ ਨੂੰ ਪਤਾ ਲੱਗ ਗਿਆ ਕਿ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦਾ ਮੁਕਾਬਲਾ ਕਰਨਾ ਆਸਾਨ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੈ ।
2. ਚਿਲਿਆਂਵਾਲਾ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ (Battle of Chillianwala) – ਚਿਲ੍ਹਿਆਂਵਾਲਾ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਦੁਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੀਆਂ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਨ ਲੜਾਈਆਂ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਇੱਕ ਸੀ । ਇਹ 13 ਜਨਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਲੜੀ ਗਈ ਸੀ । ਜਦੋਂ ਗਫ਼ ਨੂੰ ਇਹ ਖ਼ਬਰ ਮਿਲੀ ਕਿ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਆਪਣੇ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਸਮੇਤ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਲਈ ਪਹੁੰਚ ਰਿਹਾ ਹੈ ਤਾਂ ਉਸ ਨੇ 13 ਜਨਵਰੀ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ‘ਤੇ ਹਮਲਾ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਇਹ ਲੜਾਈ ਬਹੁਤ ਭਿਆਨਕ ਸੀ । ਇਸ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸੈਨਾ ਦੇ 695 ਸੈਨਿਕ ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ 132 ਅਫ਼ਸਰ ਵੀ ਮਾਰੇ ਗਏ । ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ 4 ਤੋਪਾਂ ਵੀ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦੇ ਹੱਥ ਆ ਗਈਆਂ । ਸੀਤਾ ਰਾਮ ਕੋਹਲੀ ਦੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ,
‘‘ਜਦੋਂ ਦਾ ਭਾਰਤ ਉੱਤੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਕਬਜ਼ਾ ਕੀਤਾ ਸੀ ਚਿਲਿਆਂਵਾਲਾ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਇਹ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਭੈੜੀ ਹਾਰ ਸੀ ।’’ 1
ਚਿਲ੍ਹਿਆਂਵਾਲਾ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦੇ ਹੋਏ ਭਾਰੀ ਵਿਨਾਸ਼ ਕਾਰਨ ਇੰਗਲੈਂਡ ਦੇ ਲੋਕਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਹਾਹਾਕਾਰ ਮਚ ਗਈ । ਇਸ ਕਾਰਨ ਲਾਰਡ ਹਿਊਗ ਗਫ਼ ਨੂੰ ਬਦਲ ਕੇ ਸਰ ਚਾਰਲਸ ਨੇਪੀਅਰ ਨੂੰ ਮੁੱਖ ਸੈਨਾਪਤੀ ਨਿਯੁਕਤ ਕਰਨ ਦਾ ਫੈਸਲਾ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ।
3. ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ (Battle of Multan) – ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਵਿਖੇ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਕਰਨ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਉਸ ਨਾਲ ਆ ਰਲਿਆ ਸੀ । ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਇੱਕ ਚਾਲ ਚੱਲੀ । ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਜਾਅਲੀ ਚਿੱਠੀਆਂ ਲਿਖ ਕੇ ਮਲਰਾਜ ਅਤੇ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਵਿਚਕਾਰ ਗ਼ਲਤ-ਫਹਿਮੀ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤੀ । ਸਿੱਟੇ ਵਜੋਂ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਦਾ ਸਾਥ ਛੱਡ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਦਸੰਬਰ, 1848 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਜਰਨਲ ਵਿਸ਼ ਨੇ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਕਿਲ੍ਹੇ ਨੂੰ ਘੇਰਾ ਪਾ ਲਿਆ | ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਵੱਲੋਂ ਸੁੱਟਿਆ ਇੱਕ ਗੋਲਾ ਅੰਦਰ ਪਏ ਬਾਰੂਦ ’ਤੇ ਆਣ ਡਿੱਗਾ । ਇਸ ਕਾਰਨ ਬਹੁਤ ਸਾਰਾ ਬਾਰੂਦ ਨਸ਼ਟ ਹੋ ਗਿਆ ਅਤੇ ਮਲਰਾਜ ਦੇ 500 ਸੈਨਿਕ ਵੀ ਮਾਰੇ ਗਏ । ਇਸ ਭਾਰੀ ਨੁਕਸਾਨ ਕਾਰਨ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਲਈ ਮੁਕਾਬਲੇ ਨੂੰ ਜਾਰੀ ਰੱਖਣਾ ਬੜਾ ਔਖਾ ਹੋ ਗਿਆ ! ਅੰਤ ਮਜਬੂਰ ਹੋ ਕੇ 22 ਜਨਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਅੱਗੇ ਹਥਿਆਰ ਸੁੱਟ ਦਿੱਤੇ । ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦੀ ਇਸ ਜਿੱਤ ਨਾਲ ਚਿਲਿਆਂਵਾਲਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦੀ ਜੋ ਹੱਤਕ ਹੋਈ ਸੀ, ਉਸ ਦੀ ਕਾਫ਼ੀ ਹੱਦ ਤਕ ਪੂਰਤੀ ਹੋ ਗਈ ।
4. ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ (Battle of Gujarat) – ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਦੁਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੀ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਨ ਅਤੇ ਨਿਰਣਾਇਕ ਲੜਾਈ ਸੀ । ਇਸ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਤੇ ਭਾਈ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਸਿੰਘ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਲਈ ਆ ਗਏ । ਅਫ਼ਗਾਨਿਸਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਬਾਦਸ਼ਾਹ ਦੋਸਤ ਮੁਹੰਮਦ ਖ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਵੀ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦੀ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਲਈ, 3,000 ਘੋੜਸਵਾਰ ਸੈਨਾ ਭੇਜੀ ਸੀ । ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦੀ ਕੁਲ ਫ਼ੌਜ 40,000 ਸੀ । ਦੂਜੇ ਪਾਸੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸੈਨਾ ਦੀ ਅਗਵਾਈ ਲਾਰਡ ਹਿਊਗ ਗਫ਼ ਹੀ ਕਰ ਰਿਹਾ ਸੀ | ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਕੋਲ 68,000 ਸੈਨਿਕ ਸਨ । ਇਸ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਦੋਹਾਂ ਪਾਸਿਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਤੋਪਾਂ ਦੀ ਕਾਫ਼ੀ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ ਸੀ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਇਹ ਲੜਾਈ ਇਤਿਹਾਸ ਵਿੱਚ ‘ਤੋਪਾਂ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਹੈ ।
ਇਹ ਲੜਾਈ 21 ਫ਼ਰਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਹੋਈ । ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਤੋਪਾਂ ਦਾ ਬਾਰੂਦ ਛੇਤੀ ਮੁੱਕ ਗਿਆ । ਸਿੱਟੇ ਵਜੋਂ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਆਪਣੀਆਂ ਤੋਪਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਸਿੱਖ ਸੈਨਾ ‘ਤੇ ਜ਼ਬਰਦਸਤ ਹਮਲਾ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਇਸ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਿੱਖ ਸੈਨਾ ਦਾ ਭਾਰੀ ਨੁਕਸਾਨ ਹੋਇਆ । ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ 3,000 ਤੋਂ 5,000 ਤਕ ਸੈਨਿਕ ਇਸ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਾਰੇ ਗਏ । ਇਸ ਲੜਾਈ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਸਿੱਖ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਗਦੜ ਮੱਚ ਗਈ । 10 ਮਾਰਚ, 1849 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਤੇ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਰਾਵਲਪਿੰਡੀ ਦੇ ਨੇੜੇ ਜਨਰਲ ਗਿਲਬਰਟ ਅੱਗੇ ਆਪਣੇ ਹਥਿਆਰ ਸੁੱਟ ਦਿੱਤੇ ।
ਇੱਕ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਇਤਿਹਾਸਕਾਰ ਪਤਵੰਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ,
‘‘ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੂਜੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦਾ ਅੰਤ ਹੋਇਆ ਅਤੇ ਇਸ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਹੀ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਗੌਰਵਮਈ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ `ਤੇ ਪਰਦਾ ਪੈ ਗਿਆ ।’’ 2
ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਸਿੱਟੇ (Consequences of the War)
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਮੁੱਖ ਸਿੱਟਿਆਂ ਦਾ ਵਰਣਨ ਕਰੋ । (Discuss the main results of the Second Anglo-Sikh War.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਬੜੇ ਦੂਰ-ਦੁਰਾਡੇ ਸਿੱਟੇ ਨਿਕਲੇ । ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦਾ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਵਰਣਨ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਹੈ-
1. ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਦਾ ਅੰਤ (End of the Empire of Maharaja Ranjit Singh) – ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਨ ਸਿੱਟਾ ਇਹ ਨਿਕਲਿਆ ਕਿ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਦਾ ਪੂਰੀ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਖ਼ਾਤਮਾ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਆਖਰੀ ਸਿੱਖ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਗੱਦੀ ਤੋਂ ਲਾਹ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਉਸ ਨੂੰ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਛੱਡ ਕੇ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਕਿਸੇ ਵੀ ਹਿੱਸੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਰਹਿਣ ਦੀ ਇਜਾਜ਼ਤ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਗਈ । ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦਰਬਾਰ ਦੀ ਸਾਰੀ ਜਾਇਦਾਦ ’ਤੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦਾ ਕਬਜ਼ਾ ਹੋ ਗਿਆ | ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਕੋਹਿਨੂਰ ਹੀਰਾ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਤੋਂ ਲੈ ਕੇ ਰਾਣੀ ਵਿਕਟੋਰੀਆ ਨੂੰ ਭੇਂਟ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਕੁਝ ਸਮੇਂ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਇੰਗਲੈਂਡ ਭੇਜ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ । 1893 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਪੈਰਿਸ ਵਿਖੇ ਮੌਤ ਹੋ ਗਈ ।
2. ਸਿੱਖ ਫ਼ੌਜ ਨੂੰ ਤੋੜ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ (Sikh Army was Disbanded) – ਦੂਜੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਮਗਰੋਂ ਇਸ ਸੈਨਾ ਨੂੰ ਵੀ ਨਿਸ਼ਸਤਰ ਕਰ ਕੇ ਤੋੜ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾਤਰ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਖੇਤੀਬਾੜੀ ਦੇ ਧੰਦੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਲਗਾਉਣ ਦੀ ਕੋਸ਼ਿਸ਼ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ । ਕੁਝ ਨੂੰ ਬ੍ਰਿਟਿਸ਼ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਸੈਨਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਰਤੀ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ ਗਿਆ ।
3. ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਅਤੇ ਭਾਈ ਮਹਾਰਾਜ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਦੇਸ਼ ਨਿਕਾਲੇ ਦੀ ਸਜ਼ਾ (Banishment of Diwan Moolraj and Bhai Maharaj Singh) – ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਮੌਤ ਦੀ ਸਜ਼ਾ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਗਈ ਸੀ । ਬਾਅਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਇਸ ਸਜ਼ਾ ਨੂੰ ਕਾਲੇਪਾਣੀ ਦੀ ਸਜ਼ਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਬਦਲ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਪਰ ਉਸ ਦੀ 11 ਅਗਸਤ, 1851 ਨੂੰ ਕਲਕੱਤੇ ਕੋਲਕਾਤਾ) ਵਿਖੇ ਮੌਤ ਹੋ ਗਈ | ਮਹਾਰਾਜ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਇਲਾਹਾਬਾਦ ਅਤੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਲਕੱਤੇ ਕੋਲਕਾਤਾ) ਦੀ ਜੇਲ੍ਹ ਵਿੱਚ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਗਿਆ । ਇਸ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਉਸ ਨੂੰ ਸਿੰਘਾਪੁਰ ਜੇਲ੍ਹ ਵਿੱਚ ਭੇਜ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਇੱਥੇ ਉਸ ਦੀ 5 ਜੁਲਾਈ, 1856 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਮੌਤ ਹੋ ਗਈ ।
4. ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਤੇ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਸਜ਼ਾ (Punishment to Chattar Singh and Sher Singh) – ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਤੇ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਪੁੱਤਰ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਵੀ ਗ੍ਰਿਫ਼ਤਾਰ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ ਸੀ । ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਇਲਾਹਾਬਾਦ ਅਤੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਲਕੱਤੇ ਕੋਲਕਾਤਾ) ਦੀਆਂ ਜੇਲ੍ਹਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਗਿਆ । 1854 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਨੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੋਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਰਿਹਾਅ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ।
5. ਪੰਜਾਬ ਲਈ ਨਵਾਂ ਰਾਜ ਪ੍ਰਬੰਧ (New Administration for the Punjab) – ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਲਾ ਲੈਣ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਬੰਧ ਚਲਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਾਸਨਿਕ ਬੋਰਡ ਦੀ ਸਥਾਪਨਾ ਕੀਤੀ । ਇਹ 1849 ਈ. ਤੋਂ ਲੈ ਕੇ 1853 ਈ. ਤਕ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦਾ ਰਿਹਾ । ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਾਸਨਿਕ ਢਾਂਚੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਈ ਤਬਦੀਲੀਆਂ ਕੀਤੀਆਂ । ਉੱਤਰ-ਪੱਛਮੀ ਸੀਮਾ ਨੂੰ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਸੁਰੱਖਿਅਤ ਬਣਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ । ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦਾ ਨਿਸ਼ਸਤਰੀਕਰਨ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਨਿਆਂ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਨੂੰ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਸਸਤਾ ਅਤੇ ਛੇਤੀ ਨਿਆਂ ਦੇਣ ਵਾਲੀ ਬਣਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ । ਪੰਜਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਸੜਕਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਨਹਿਰਾਂ ਦਾ ਜਾਲ ਵਿਛਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ । ਖੇਤੀਬਾੜੀ ਨੂੰ ਉਤਸ਼ਾਹਿਤ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਜਾਗੀਰਦਾਰੀ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਨੂੰ ਸਮਾਪਤ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਵਪਾਰ ਨੂੰ ਉਤਸ਼ਾਹਿਤ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਯਤਨ ਕੀਤੇ ਗਏ । ਪੰਜਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਪੱਛਮੀ ਢੰਗ ਦੀ ਸਿੱਖਿਆ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ । ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਸੁਧਾਰਾਂ ਨੇ ਪੰਜਾਬੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਦਿਲਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਜਿੱਤ ਲਿਆ । ਸਿੱਟੇ ਵਜੋਂ ਉਹ 1857 ਈ. ਦੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਸਮੇਂ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਵਫ਼ਾਦਾਰ ਰਹੇ ।
6. ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੀਆਂ ਰਿਆਸਤਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਮਿੱਤਰਤਾ ਵਾਲਾ ਸਲੂਕ (Friendly attitude towards Princely States of the Punjab) – ਦੁਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਪਟਿਆਲਾ, ਨਾਭਾ, ਜੀਂਦ, ਮਲੇਰਕੋਟਲਾ, ਫ਼ਰੀਦਕੋਟ ਅਤੇ ਕਪੂਰਥਲਾ ਦੀਆਂ ਰਿਆਸਤਾਂ ਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਆਪਣਾ ਸਹਿਯੋਗ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਸੀ । ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਆਪਣੀ ਮਿੱਤਰਤਾ ਬਣਾਈ ਰੱਖੀ ਅਤੇ ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਰਿਆਸਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਨਹੀਂ ਕੀਤਾ ।

ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਵਿਚਕਾਰ ਹੋਏ ਦੁਸਰੇ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਅਤੇ ਸਿੱਟੇ ਬਿਆਨ ਕਰੋ । (Discuss the causes and results of Second Anglo-Sikh War.)
ਜਾਂ
ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ-ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਪਰਿਣਾਮਾਂ ਦਾ ਵਰਣਨ ਕਰੋ । (What were the causes and results of the 2nd Anglo-Sikh War ? Explain.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਪਹਿਲੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦੀ ਜਿੱਤ ਹੋਈ ਅਤੇ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਹਾਰ ਦਾ ਮੂੰਹ ਵੇਖਣਾ ਪਿਆ | ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਅਪਮਾਨਜਨਕ ਵਿਹਾਰ ਅਤੇ ਥੋਪੀਆਂ ਗਈਆਂ ਸੰਧੀਆਂ ਨਾਲ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਗੁੱਸਾ ਹੋਰ ਭੜਕ ਉੱਠਿਆ । ਇਸ ਦਾ ਨਤੀਜਾ ਦੁਜੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਾਹਮਣੇ ਆਇਆ । ਇਸ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਮੁੱਖ ਕਾਰਨ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਸਨ-
1. ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦੀ ਆਪਣੀ ਹਾਰ ਦਾ ਬਦਲਾ ਲੈਣ ਦੀ ਇੱਛਾ (Sikh desir to avenge their defeat in the First Anglo-Sikh War) – ਇਹ ਠੀਕ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਹੋਏ ਪਹਿਲੇ ਯੁੱਧ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦੀ ਹਾਰ ਹੋ ਗਈ ਸੀ, ਪਰ ਇਸ ਨਾਲ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਹੌਸਲੇ ਕਿਸੇ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਘੱਟ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੋਏ ਸਨ । ਇਸ ਹਾਰ ਦਾ ਮੁੱਖ ਕਾਰਨ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦੇ ਨੇਤਾਵਾਂ ਲਾਲ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਤੇ ਤੇਜਾ ਸਿੰਘ ਵੱਲੋਂ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ ਗੱਦਾਰੀ ਸੀ । ਸਿੱਖ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਆਪਣੀ ਯੋਗਤਾ ‘ਤੇ ਪੂਰਾ ਵਿਸ਼ਵਾਸ ਸੀ । ਉਹ ਆਪਣੀ ਹਾਰ ਦਾ ਬਦਲਾ ਲੈਣਾ ਚਾਹੁੰਦੇ ਸਨ । ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਇਹ ਤੀਵਰ ਇੱਛਾ ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦਾ ਇੱਕ ਮੁੱਖ ਕਾਰਨ ਬਣੀ ।
2. ਲਾਹੌਰ ਅਤੇ ਭੈਰੋਵਾਲ ਦੀਆਂ ਸੰਧੀਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਅਸੰਤੁਸ਼ਟ (Punjabis were dissatisfied with the Treaties of Lahore and Bhairowal) – ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਵਿਚਾਲੇ ਹੋਏ ਪਹਿਲੇ ਯੁੱਧ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦਰਬਾਰ ਨਾਲ ਲਾਹੌਰ ਅਤੇ ਭੈਰੋਵਾਲ ਨਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਸੰਧੀਆਂ ਕੀਤੀਆਂ । ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਸੰਧੀਆਂ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਜਲੰਧਰ ਦੁਆਬ ਵਰਗੇ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਉਪਜਾਉ ਦੇਸ਼ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਆਪਣੇ ਅਧੀਨ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ ਸੀ | ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ ਦਾ ਇਲਾਕਾ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਆਪਣੇ ਮਿੱਤਰ ਗੁਲਾਬ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਹਵਾਲੇ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਸੀ । ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੇ ਲੋਕ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਅਣਥੱਕ ਯਤਨਾਂ ਸਦਕਾ ਬਣਾਏ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ ਖੇਰੂੰ-ਖੇਰੂੰ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਦੇਖ ਕੇ ਸਹਿਣ ਨਹੀਂ ਕਰ ਸਕਦੇ ਸਨ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਇੱਕ ਹੋਰ ਯੁੱਧ ਲੜਨਾ ਪੈਣਾ ਸੀ ।
3. ਸਿੱਖ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਰੋਸ (Resentment among the Sikh Soldiers) – ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦੀ ਸੰਧੀ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਖ਼ਾਲਸਾ ਫ਼ੌਜ ਦੀ ਗਿਣਤੀ 20,000 ਪੈਦਲ ਤੇ 12,000 ਘੋੜਸਵਾਰ ਨਿਸ਼ਚਿਤ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤੀ । ਇਸ ਕਾਰਨ ਹਜ਼ਾਰਾਂ ਦੀ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਿੱਖ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਨੌਕਰੀ ਤੋਂ ਜਵਾਬ ਦੇ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਦੇ ਮਨਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੀ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਰੋਸ ਪੈਦਾ ਹੋ ਗਿਆ ਅਤੇ ਉਹ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੀਆਂ ਤਿਆਰੀਆਂ ਕਰਨ ਲੱਗੇ ।
4. ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਸਖ਼ਤ ਸਲੂਕ (Harsh Treatment with. Maharani Jindan) – ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਵਿਧਵਾ ਅਤੇ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਮਾਂ ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਜੋ ਅਪਮਾਨਜਨਕ ਵਿਵਹਾਰ ਕੀਤਾ ਉਸ ਨੇ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਫੈਲੇ ਰੋਸ ਨੂੰ ਹੋਰ ਭੜਕਾ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦੀ ਸੰਧੀ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਨਾਬਾਲਗ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਸਰਪ੍ਰਸਤ ਮੰਨਿਆ ਸੀ । ਪਰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਭੈਰੋਵਾਲ ਦੀ ਸੰਧੀ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਦੀਆਂ ਸਾਰੀਆਂ ਸ਼ਕਤੀਆਂ ਖੋਹ ਲਈਆਂ । 1847 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ੇਖੂਪੁਰਾ ਦੇ ਕਿਲ੍ਹੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਨਜ਼ਰਬੰਦ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ । 1848 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਨੂੰ ਦੇਸ਼ ਨਿਕਾਲਾ ਦੇ ਕੇ ਬਨਾਰਸ ਭੇਜ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ ਬਦਸਲੂਕੀ ਕਾਰਨ ਸਾਰੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਗੁੱਸੇ ਦੀ ਲਹਿਰ ਦੌੜ ਗਈ ।
5. ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਦਾ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ (Revolt of Diwan Moolraj) – ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਕਰਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਨੂੰ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ ਸਥਾਨ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਹੈ । 1844 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦਾ ਨਵਾਂ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ ਬਣਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ | ਪਰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਗ਼ਲਤ ਨੀਤੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਦਸੰਬਰ 1847 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਨੇ ਆਪਣਾ ਅਸਤੀਫ਼ਾ ਦੇ ਦਿੱਤਾ । 1848 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਕਾਹਨ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦਾ ਨਵਾਂ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ ਨਿਯੁਕਤ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ | ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਤੋਂ ਚਾਰਜ ਲੈਣ ਲਈ ਕਾਹਨ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਭੇਜੇ ਗਏ ਦੋ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਅਫ਼ਸਰਾਂ ਵੈਨਸ ਐਗਨਿਯੁ ਅਤੇ ਐਂਡਰਸਨ ‘ਤੇ ਕੁਝ ਸਿਪਾਹੀਆਂ ਨੇ ਹਮਲਾ ਕਰਕੇ 20 ਅਪਰੈਲ, 1848 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਕਤਲ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਅਤੇ ਕਾਹਨ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਗ੍ਰਿਫ਼ਤਾਰ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ | ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਨੇ ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਕਤਲ ਦੀ ਸਾਰੀ ਜ਼ਿੰਮੇਵਾਰੀ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਸਿਰ ਪਾਈ । ਇਸ ਕਾਰਨ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਦਾ ਖੂਨ ਖੌਲਣ ਲੱਗਾ ਅਤੇ ਉਸ ਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਦਾ ਝੰਡਾ ਬੁਲੰਦ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ | ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਗਵਰਨਰ-ਜਨਰਲ ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਅਜਿਹੇ ਹੀ ਮੌਕੇ ਦੀ ਤਲਾਸ਼

ਵਿੱਚ ਸੀ । ਉਹ ਚਾਹੁੰਦਾ ਸੀ ਕਿ ਇਹ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾ ਭੜਕ ਜਾਏ ਅਤੇ ਉਸ ਨੂੰ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਉੱਤੇ ਕਬਜ਼ਾ ਕਰਨ ਦਾ ਮੌਕਾ ਮਿਲ ਜਾਏ । ਡਾਕਟਰ ਕ੍ਰਿਪਾਲ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ,
‘‘ਉਹ ਚੰਗਿਆੜੀ ਜਿਸ ਨੇ ਭਾਂਬੜ ਬਾਲਿਆ ਅਤੇ ਜਿਸ ਵਿੱਚ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਸੁਤੰਤਰ ਰਾਜ ਸੜ ਕੇ ਸੁਆਹ ਹੋ ਗਿਆ, ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਤੋਂ ਉੱਠੀ ਸੀ ।’’ 1
6. ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦਾ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ (Revolt of Chattar Singh) – ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਟਾਰੀਵਾਲਾ ਹਜ਼ਾਰਾ ਦਾ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ ਸੀ । ਉਸ ਦੇ ਇੱਕ ਸਿਪਾਹੀ ਨੇ ਇੱਕ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਕੈਨੋਰਾ ਦਾ ਕਤਲ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਇਸ ’ਤੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਅਹੁਦੇ ਤੋਂ ਹਟਾ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਅਤੇ ਉਸ ਦੀ ਜਾਗੀਰ ਜ਼ਬਤ ਕਰ ਲਈ । ਇਸ ਕਾਰਨ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਬਗਾਵਤ ਕਰਨ ਦਾ ਐਲਾਨ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਸਿੱਟੇ ਵਜੋਂ ਚਾਰ-ਚੁਫ਼ੇਰੇ ਬਗਾਵਤ ਦੀ ਅੱਗ ਫੈਲ ਗਈ ।
7. ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦਾ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ (Revolt of Sher Singh) – ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦਾ ਪੁੱਤਰ ਸੀ । ਜਦੋਂ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਆਪਣੇ ਪਿਤਾ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦੀ ਬਦਸਲੂਕੀ ਬਾਰੇ ਪਤਾ ਲੱਗਿਆ ਤਾਂ ਉਸ ਨੇ ਵੀ 14 ਸਤੰਬਰ, 1848 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਕਰਨ ਦਾ ਐਲਾਨ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਉਸ ਦੀ ਅਪੀਲ ‘ਤੇ ਕਈ ਸਿੱਖ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਝੰਡੇ ਅਧੀਨ ਇਕੱਠੇ ਹੋ ਗਏ ।
8. ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਦੀ ਨੀਤੀ (Policy of Lord Dalhousie) – ਜਨਵਰੀ, 1848 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਗਵਰਨਰ-ਜਨਰਲ ਬਣਿਆ ਸੀ । ਉਸ ਨੇ ਲੈਪਸ ਦੀ ਨੀਤੀ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀਆਂ ਬਹੁਤ ਸਾਰੀਆਂ ਰਿਆਸਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕੀਤਾ | ਕੇਵਲ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਹੀ ਇੱਕ ਅਜਿਹਾ ਰਾਜ ਸੀ ਜਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਹਾਲੇ ਤਕ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਨਹੀਂ ਕੀਤਾ ਜਾ ਸਕਿਆ ਸੀ । ਉਹ ਕਿਸੇ ਸੁਨਹਿਰੀ ਮੌਕੇ ਦੀ ਤਲਾਸ਼ ਵਿੱਚ ਸੀ । ਇਹ ਮੌਕਾ ਉਸ ਨੂੰ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ, ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਤੇ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਕੀਤੇ ਗਏ ਵਿਦਰੋਹਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਮਿਲਿਆ ।
ਜਦੋਂ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਦੀ ਅੱਗ ਭੜਕਦੀ ਨਜ਼ਰ ਆਈ ਤਾਂ ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਨੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹੀਆਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਕਾਰਵਾਈ ਕਰਨ ਦਾ ਆਦੇਸ਼ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਕਮਾਂਡਰ-ਇਨ-ਚੀਫ਼ ਲਾਰਡ ਹਿਊਗ ਗਫ਼ 16 ਨਵੰਬਰ ਨੂੰ ਫ਼ੌਜ ਲੈ ਕੇ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦਾ ਮੁਕਾਬਲਾ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਦਰਿਆ ਚਨਾਬ ਵੱਲ ਚਲ ਪਿਆ ।
ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਬੜੇ ਦੂਰ-ਦੁਰਾਡੇ ਸਿੱਟੇ ਨਿਕਲੇ । ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦਾ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਵਰਣਨ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਹੈ-
1. ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਦਾ ਅੰਤ (End of the Empire of Maharaja Ranjit Singh) – ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਨ ਸਿੱਟਾ ਇਹ ਨਿਕਲਿਆ ਕਿ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਦਾ ਪੂਰੀ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਖ਼ਾਤਮਾ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਆਖਰੀ ਸਿੱਖ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਗੱਦੀ ਤੋਂ ਲਾਹ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਉਸ ਨੂੰ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਛੱਡ ਕੇ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਕਿਸੇ ਵੀ ਹਿੱਸੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਰਹਿਣ ਦੀ ਇਜਾਜ਼ਤ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਗਈ । ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦਰਬਾਰ ਦੀ ਸਾਰੀ ਜਾਇਦਾਦ ’ਤੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦਾ ਕਬਜ਼ਾ ਹੋ ਗਿਆ | ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਕੋਹਿਨੂਰ ਹੀਰਾ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਤੋਂ ਲੈ ਕੇ ਰਾਣੀ ਵਿਕਟੋਰੀਆ ਨੂੰ ਭੇਂਟ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਕੁਝ ਸਮੇਂ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਇੰਗਲੈਂਡ ਭੇਜ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ । 1893 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਪੈਰਿਸ ਵਿਖੇ ਮੌਤ ਹੋ ਗਈ ।
2. ਸਿੱਖ ਫ਼ੌਜ ਨੂੰ ਤੋੜ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ (Sikh Army was Disbanded) – ਦੂਜੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਮਗਰੋਂ ਇਸ ਸੈਨਾ ਨੂੰ ਵੀ ਨਿਸ਼ਸਤਰ ਕਰ ਕੇ ਤੋੜ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾਤਰ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਖੇਤੀਬਾੜੀ ਦੇ ਧੰਦੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਲਗਾਉਣ ਦੀ ਕੋਸ਼ਿਸ਼ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ । ਕੁਝ ਨੂੰ ਬ੍ਰਿਟਿਸ਼ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਸੈਨਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਰਤੀ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ ਗਿਆ ।
3. ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਅਤੇ ਭਾਈ ਮਹਾਰਾਜ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਦੇਸ਼ ਨਿਕਾਲੇ ਦੀ ਸਜ਼ਾ (Banishment of Diwan Moolraj and Bhai Maharaj Singh) – ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਮੌਤ ਦੀ ਸਜ਼ਾ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਗਈ ਸੀ । ਬਾਅਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਇਸ ਸਜ਼ਾ ਨੂੰ ਕਾਲੇਪਾਣੀ ਦੀ ਸਜ਼ਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਬਦਲ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਪਰ ਉਸ ਦੀ 11 ਅਗਸਤ, 1851 ਨੂੰ ਕਲਕੱਤੇ ਕੋਲਕਾਤਾ) ਵਿਖੇ ਮੌਤ ਹੋ ਗਈ | ਮਹਾਰਾਜ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਇਲਾਹਾਬਾਦ ਅਤੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਲਕੱਤੇ ਕੋਲਕਾਤਾ) ਦੀ ਜੇਲ੍ਹ ਵਿੱਚ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਗਿਆ । ਇਸ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਉਸ ਨੂੰ ਸਿੰਘਾਪੁਰ ਜੇਲ੍ਹ ਵਿੱਚ ਭੇਜ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਇੱਥੇ ਉਸ ਦੀ 5 ਜੁਲਾਈ, 1856 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਮੌਤ ਹੋ ਗਈ ।
4. ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਤੇ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਸਜ਼ਾ (Punishment to Chattar Singh and Sher Singh) – ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਤੇ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਪੁੱਤਰ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਵੀ ਗ੍ਰਿਫ਼ਤਾਰ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ ਸੀ । ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਇਲਾਹਾਬਾਦ ਅਤੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਲਕੱਤੇ ਕੋਲਕਾਤਾ) ਦੀਆਂ ਜੇਲ੍ਹਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਗਿਆ । 1854 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਨੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੋਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਰਿਹਾਅ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ।
5. ਪੰਜਾਬ ਲਈ ਨਵਾਂ ਰਾਜ ਪ੍ਰਬੰਧ (New Administration for the Punjab) – ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਲਾ ਲੈਣ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਬੰਧ ਚਲਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਾਸਨਿਕ ਬੋਰਡ ਦੀ ਸਥਾਪਨਾ ਕੀਤੀ । ਇਹ 1849 ਈ. ਤੋਂ ਲੈ ਕੇ 1853 ਈ. ਤਕ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦਾ ਰਿਹਾ । ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਾਸਨਿਕ ਢਾਂਚੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਈ ਤਬਦੀਲੀਆਂ ਕੀਤੀਆਂ । ਉੱਤਰ-ਪੱਛਮੀ ਸੀਮਾ ਨੂੰ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਸੁਰੱਖਿਅਤ ਬਣਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ । ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦਾ ਨਿਸ਼ਸਤਰੀਕਰਨ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਨਿਆਂ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਨੂੰ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਸਸਤਾ ਅਤੇ ਛੇਤੀ ਨਿਆਂ ਦੇਣ ਵਾਲੀ ਬਣਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ । ਪੰਜਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਸੜਕਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਨਹਿਰਾਂ ਦਾ ਜਾਲ ਵਿਛਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ । ਖੇਤੀਬਾੜੀ ਨੂੰ ਉਤਸ਼ਾਹਿਤ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਜਾਗੀਰਦਾਰੀ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਨੂੰ ਸਮਾਪਤ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਵਪਾਰ ਨੂੰ ਉਤਸ਼ਾਹਿਤ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਯਤਨ ਕੀਤੇ ਗਏ । ਪੰਜਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਪੱਛਮੀ ਢੰਗ ਦੀ ਸਿੱਖਿਆ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ । ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਸੁਧਾਰਾਂ ਨੇ ਪੰਜਾਬੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਦਿਲਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਜਿੱਤ ਲਿਆ । ਸਿੱਟੇ ਵਜੋਂ ਉਹ 1857 ਈ. ਦੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਸਮੇਂ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਵਫ਼ਾਦਾਰ ਰਹੇ ।
6. ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੀਆਂ ਰਿਆਸਤਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਮਿੱਤਰਤਾ ਵਾਲਾ ਸਲੂਕ (Friendly attitude towards Princely States of the Punjab) – ਦੁਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਪਟਿਆਲਾ, ਨਾਭਾ, ਜੀਂਦ, ਮਲੇਰਕੋਟਲਾ, ਫ਼ਰੀਦਕੋਟ ਅਤੇ ਕਪੂਰਥਲਾ ਦੀਆਂ ਰਿਆਸਤਾਂ ਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਆਪਣਾ ਸਹਿਯੋਗ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਸੀ । ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਆਪਣੀ ਮਿੱਤਰਤਾ ਬਣਾਈ ਰੱਖੀ ਅਤੇ ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਰਿਆਸਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਨਹੀਂ ਕੀਤਾ ।

ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਮਿਲਾਉਣਾ (Annexation of the Punjab)
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 5.
“ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਮਿਲਾਉਣਾ ਇੱਕ ਬਹੁਤ ਵੱਡਾ ਵਿਸ਼ਵਾਸਘਾਤ ਸੀਂ” । ਚਰਚਾ ਕਰੋ । (“Annexation of Punjab was a violent breach of trust.” Discuss.)
ਜਾਂ
ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਿਲਯ ਦਾ ਆਲੋਚਨਾਤਮਕ ਵਰਣਨ ਕਰੋ । (Examine critically Lord Dalhousie’s annexation of Punjab.)
ਜਾਂ
‘‘ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਲਾਉਣਾ ਸਿਧਾਂਤਹੀਨ ਅਤੇ ਅਣਉੱਚਿਤ ਸੀ ।” ਕੀ ਤੁਸੀਂ ਇਸ ਕਥਨ ਨਾਲ ਸਹਿਮਤ ਹੋ ? ਆਪਣੇ ਪੱਖ ਵਿੱਚ ਦਲੀਲਾਂ ਦਿਓ । (“The annexation of Punjab by Lord Dalhousie to the British Empire was unprincipled and unjustified.” Do you agree to this view ? Give arguments in your favour.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ 1848 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਗਵਰਨਰ-ਜਨਰਲ ਬਣ ਕੇ ਆਇਆ ਸੀ । ਉਹ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਸਾਰੇ ਗਵਰਨਰ-ਜਨਰਲਾਂ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡਾ ਸਾਮਰਾਜਵਾਦੀ ਸੀ । ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਵੀ ਉਸ ਦੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜਵਾਦੀ ਨੀਤੀ ਦਾ ਸ਼ਿਕਾਰ ਹੋਣਾ ਪਿਆ । 29 ਮਾਰਚ, 1849 ਈ. ਲਾਹੌਰ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕਰਨ ਦੀ ਘੋਸ਼ਣਾ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ । ਇਸ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਲਾਹੌਰ ਕਿਲ੍ਹੇ ਤੋਂ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦੇ ਝੰਡੇ ਨੂੰ ਉਤਾਰਿਆ ਗਿਆ ਅਤੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦੇ ਝੰਡੇ ਨੂੰ ਲਹਿਰਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ । ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੇ ਸਿੱਖ ਰਾਜ ਦਾ ਖ਼ਾਤਮਾ ਹੋ ਗਿਆ ।
I. ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਦੀ ਮਿਲਾਉਣ ਦੀ ਨੀਤੀ ਦੇ ਪੱਖ ਵਿੱਚ ਦਲੀਲਾਂ (Arguments in favour of Dalhousie’s Policy of Annexation)
ਡਬਲਿਊ. ਡਬਲਿਉ. ਹੰਟਰ, ਮਾਰਸ਼ਮੈਨ ਅਤੇ ਐੱਮ. ਐੱਸ. ਲਤੀਫ ਆਦਿ ਇਤਿਹਾਸਕਾਰਾਂ ਨੇ ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਲਾਉਣ ਦੇ ਪੱਖ ਵਿੱਚ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੀਆਂ ਦਲੀਲਾਂ ਦਿੱਤੀਆਂ ਹਨ-
1. ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨੇ ਆਪਣੇ ਸ਼ਰਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਤੋੜਿਆ (Sikhs had broken their Promises) – ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਨੇ ਇਹ ਦੋਸ਼ ਲਗਾਇਆ ਕਿ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨੇ ਭੈਰੋਵਾਲ ਦੀ ਸੰਧੀ ਦੀਆਂ ਸ਼ਰਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਤੋੜਿਆ ਹੈ । ਸਿੱਖ ਸਰਦਾਰਾਂ ਨੇ ਇਹ ਵਚਨ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਸੀ ਕਿ ਉਹ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਰੈਜ਼ੀਡੈਂਟ ਨੂੰ ਪੂਰਾ ਸਹਿਯੋਗ ਦੇਣਗੇ | ਪਰ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਅਸ਼ਾਂਤੀ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਫੈਲਾਉਣ ਦਾ ਯਤਨ ਕੀਤਾ । ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਨੇ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਦੀ ਬਗ਼ਾਵਤ ਨੂੰ ਪੂਰੀ ਸਿੱਖ ਜਾਤੀ ਦੀ ਬਗਾਵਤ ਦੱਸਿਆ । ਉਸ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਇਹ ਬਗਾਵਤ ਦੁਬਾਰਾ ਸਿੱਖ ਰਾਜ ਦੀ ਸਥਾਪਨਾ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ ਸੀ । ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਤੇ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਪੁੱਤਰ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਕਰ ਕੇ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਦਾ ਸਾਥ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਵਿਗੜ ਰਹੇ ਹਾਲਾਤ ‘ਤੇ ਕਾਬੂ ਪਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਲਾਉਣਾ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਸੀ । ਇਸੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਦਾ ਕਹਿਣਾ ਸੀ,
“ਨਿਰਸੰਦੇਹ ਮੈਨੂੰ ਇਹ ਪੱਕਾ ਵਿਸ਼ਵਾਸ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਮੇਰੀ ਕਾਰਵਾਈ ਸਮੇਂ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ, ਨਿਆਂਪੂਰਨ ਅਤੇ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਸੀ ।’’ 1
2. ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਚੰਗਾ ਮੱਧਵਰਤੀ ਰਾਜ ਨਾ ਰਹਿਣਾ (Punjab remained no more a useful Buffer State) – ਲਾਰਡ ਹਾਰਡਿੰਗ ਦਾ ਵਿਚਾਰ ਸੀ ਕਿ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਇੱਕ ਲਾਭਦਾਇਕ ਮੱਧਵਰਤੀ ਰਾਜ ਸਿੱਧ ਹੋਵੇਗਾ । ਇਸ ਕਾਰਨ ਬ੍ਰਿਟਿਸ਼ ਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ ਅਫ਼ਗਾਨਿਸਤਾਨ ਵੱਲੋਂ ਕਿਸੇ ਖ਼ਤਰੇ ਦਾ ਸਾਹਮਣਾ ਨਹੀਂ ਕਰਨਾ ਪਵੇਗਾ | ਪਰੰਤੂ ਉਸ ਦਾ ਇਹ ਵਿਚਾਰ ਗ਼ਲਤ ਸਿੱਧ ਹੋਇਆ ਕਿਉਂਕਿ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਅਫ਼ਗਾਨਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਦੋਸਤੀ ਹੋ ਗਈ ਸੀ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਨੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਆਪਣੇ ਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕਰਨਾ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਸਮਝਿਆ ।
3. ਕਰਜ਼ੇ ਦੀ ਅਦਾਇਗੀ ਨਾ ਕਰਨਾ (Non-payment of the Loans) – ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਨੇ ਇਹ ਦੋਸ਼ ਲਗਾਇਆ ਕਿ ਭੈਰੋਵਾਲ ਦੀ ਸੰਧੀ ਦੀਆਂ ਸ਼ਰਤਾਂ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦਰਬਾਰ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੂੰ 22 ਲੱਖ ਰੁਪਏ ਸਾਲਾਨਾ ਦੇਣਾ ਸੀ । ਪਰ ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦਰਬਾਰ ਨੇ ਇੱਕ ਪਾਈ ਵੀ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਨਾ ਦਿੱਤੀ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕਰਨਾ ਉੱਚਿਤ ਸੀ ।
4. ਪੰਜਾਬ ਉੱਤੇ ਕਬਜ਼ਾ ਕਰਨਾ ਲਾਭਦਾਇਕ ਸੀ (It was advantageous to annex Punjab) – ਪਹਿਲੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਵਿੱਚ ਜਿੱਤ ਮਗਰੋਂ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦਾ ਵਿਚਾਰ ਸੀ ਕਿ ਆਰਥਿਕ ਪੱਖ ਤੋਂ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਕੋਈ ਲਾਭਦਾਇਕ ਪ੍ਰਾਂਤ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੈ । ਪਰ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਦੋ ਸਾਲ ਰਹਿਣ ਪਿੱਛੋਂ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪਤਾ ਲੱਗਿਆ ਕਿ ਇਹ ਰਾਜ ਕਈ ਪੱਖਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਲਈ ਲਾਭਦਾਇਕ ਸਿੱਧ ਹੋ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਕਾਰਨਾਂ ਕਰਕੇ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਨੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਹੜੱਪਣ ਦਾ ਪੱਕਾ ਨਿਸ਼ਚਾ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ ।
5. ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੇ ਲੋਕਾਂ ਲਈ ਲਾਭਦਾਇਕ (Advantageous for the people of Punjab) – ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਦਾ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਉੱਤੇ ਕਬਜ਼ਾ ਕਰਨਾ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੇ ਲੋਕਾਂ ਲਈ ਵਰਦਾਨ ਸਿੱਧ ਹੋਇਆ । ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਮੌਤ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦਰਬਾਰ ਸਾਜ਼ਸ਼ਾਂ ਦਾ ਇੱਕ ਅੱਡਾ ਬਣ ਚੁੱਕਿਆ ਸੀ । ਅਜਿਹੀ ਸਥਿਤੀ ਦਾ ਫਾਇਦਾ ਉਠਾ ਕੇ ਚੋਰਾਂ, ਡਾਕੂਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਠੱਗਾਂ ਨੇ ਆਪਣਾ ਧੰਦਾ ਜ਼ੋਰਾਂ ‘ਤੇ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਸੀ । ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਆਪਣੇ ਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕਰਕੇ ਇੱਥੇ ਸ਼ਾਂਤੀ ਦੀ ਮੁੜ ਸਥਾਪਨਾ ਕੀਤੀ । ਪੁਲਿਸ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਅਤੇ ਨਿਆਂ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਨੂੰ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਕੁਸ਼ਲ ਬਣਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ । ਖੇਤੀਬਾੜੀ ਅਤੇ ਵਪਾਰ ਨੂੰ ਉਤਸ਼ਾਹਿਤ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਪੰਜਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਸੜਕਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਨਹਿਰਾਂ ਦਾ ਜਾਲ ਵਿਛਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ । ਲੋਕਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪੱਛਮੀ ਸਿੱਖਿਆ ਦੇਣ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਬੰਧ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ।
6. ਪੰਜਾਬ ਉੱਤੇ ਕਬਜ਼ਾ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਸੀ (Annexation of the Punjab was Inevitable)-ਇਹ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਜੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਨਾ ਕੀਤਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਤਾਂ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਹਮੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਸਾਜ਼ਸ਼ਾਂ ਕਰਦੇ ਰਹਿਣਾ ਸੀ । ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਦੂਜੇ ਹਿੱਸਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੀ ਪੈ ਸਕਦਾ ਸੀ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਨੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕਰਨਾ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਸਮਝਿਆ ।
II. ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਦੀ ਮਿਲਾਉਣ ਦੀ ਨੀਤੀ ਦੇ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਦਲੀਲਾਂ (Arguments against Dalhousie’s Policy of Annexation)
ਈਵਾਨਜ਼ ਬੈਂਲ, ਜਗਮੋਹਨ ਮਹਾਜਨ, ਗੰਡਾ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਤੇ ਖੁਸ਼ਵੰਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਆਦਿ ਇਤਿਹਾਸਕਾਰਾਂ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਲਾਏ ਜਾਣ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਅੱਗੇ ਲਿਖੀਆਂ ਦਲੀਲਾਂ ਦਿੱਤੀਆਂ ਗਈਆਂ ਹਨ-
1. ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਬਗਾਵਤ ਲਈ ਭੜਕਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ (Sikhs were provoked to Revolt) – ਪਹਿਲੇ ਐਂਗਲੋਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਬਹੁਤ ਸਾਰੀਆਂ ਅਜਿਹੀਆਂ ਘਟਨਾਵਾਂ ਹੋਈਆਂ ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਬਗਾਵਤ ਲਈ ਭੜਕਾਇਆ । ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦੀ ਸੰਧੀ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੇ ਕਈ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਨ ਇਲਾਕੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਖੋਹ ਲਏ ਸਨ । ਸਿੱਟੇ ਵਜੋਂ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਖ਼ਜ਼ਾਨੇ ‘ਤੇ ਮਾੜਾ ਅਸਰ ਪਿਆ। ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦਰਬਾਰ ਦੀ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਫ਼ੌਜ ਨੂੰ ਤੋੜ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ | ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਬਹੁਤ ਮਾੜਾ ਸਲੂਕ ਕੀਤਾ । ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਅਤੇ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਬਗਾਵਤ ਲਈ ਭੜਕਾਇਆ । ਸਿੱਟੇ ਵਜੋਂ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਬਗਾਵਤ ਲਈ ਮਜਬੂਰ ਹੋਣਾ ਪਿਆ ।
2. ਬਗਾਵਤ ਨੂੰ ਸਮੇਂ ਸਿਰ ਨਾ ਦਬਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ (Revolt was not suppressed in Time) – ਜਦੋਂ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਦੀ ਅੱਗ ਭੜਕੀ ਤਾਂ ਉਸ ’ਤੇ ਛੇਤੀ ਹੀ ਕਾਬੂ ਪਾਇਆ ਜਾ ਸਕਦਾ ਸੀ | ਅੱਠ ਮਹੀਨਿਆਂ ਤਕ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਨੂੰ ਫੈਲਣ ਦੇਣ ਪਿੱਛੇ ਇੱਕ ਡੂੰਘੀ ਰਾਜਸੀ ਚਾਲ ਸੀ । ਇਸ ਸਮੇਂ ਦੌਰਾਨ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ, ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਤੇ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਵੀ ਬਗ਼ਾਵਤ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤੀ । ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੱਡੀ ਸੈਨਿਕ ਕਾਰਵਾਈ ਕਰਨ ਦਾ ਬਹਾਨਾ ਮਿਲ ਗਿਆ ਅਤੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਉੱਤੇ ਕਬਜ਼ਾ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ ।
3. ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਸੰਧੀ ਦੀਆਂ ਸ਼ਰਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪੂਰਾ ਨਹੀਂ ਕੀਤਾ (British had not fulfilled the terms of the Treaty) – ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦਾ ਕਹਿਣਾ ਸੀ ਕਿ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਸੰਧੀ ਦੀਆਂ ਸ਼ਰਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪੂਰਾ ਕੀਤਾ ਹੈ । ਪਰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਸੰਧੀ ਦੀਆਂ ਕੇਵਲ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਸ਼ਰਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਹੀ ਪੂਰਾ ਕੀਤਾ, ਜਿਹੜੀਆਂ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਲਈ ਲਾਹੇਵੰਦ ਸਨ ।ਉਦਾਹਰਨ ਦੇ ਤੌਰ ‘ਤੇ ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦੀ ਸੰਧੀ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਇਹ ਸ਼ਰਤ ਮੰਨੀ ਸੀ ਕਿ ਉਹ ਦਸੰਬਰ, 1846 ਈ. ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਲਾਹੌਰ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਆਪਣੀਆਂ ਫ਼ੌਜਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਕੱਢ ਲੈਣਗੇ । ਜਦੋਂ ਇਹ ਸਮਾਂ ਆਇਆ ਤਾਂ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਭੈਰੋਵਾਲ ਦੀ ਸੰਧੀ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਇਸ ਸਮੇਂ ਨੂੰ ਵਧਾ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦਾ ਇਹ ਕਹਿਣਾ ਕਿ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਸੰਧੀ ਦੀਆਂ ਸਾਰੀਆਂ ਸ਼ਰਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪੂਰਾ ਕੀਤਾ ਹੈ, ਨਿਰਾ ਝੂਠ ਹੀ ਹੈ ।
4. ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦਰਬਾਰ ਨੇ ਸੰਧੀ ਦੀਆਂ ਸ਼ਰਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪੂਰਾ ਕਰਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਪੂਰਨ ਸਹਿਯੋਗ ਦਿੱਤਾ (Lahore Darbar gave full cooperation in fulfilling the terms of the Treaty) – ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦਰਬਾਰ ਤਾਂ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਉੱਤੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦਾ ਕਬਜ਼ਾ ਹੋਣ ਤਕ ਸੰਧੀ ਦੀਆਂ ਸ਼ਰਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਵਫ਼ਾਦਾਰੀ ਨਾਲ ਨਿਭਾਉਂਦਾ ਰਿਹਾ | ਲਾਹੌਰ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਰੱਖੀ ਹੋਈ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸੈਨਾ ਦਾ ਪੂਰਾ ਖ਼ਰਚਾ ਦੇ ਰਹੀ ਸੀ । ਉਸ ਨੇ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ, ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਤੇ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਕੀਤੀਆਂ ਗਈਆਂ ਬਗਾਵਤਾਂ ਦੀ ਨਿੰਦਿਆ ਕੀਤੀ ਅਤੇ ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਬਗਾਵਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਕੁਚਲਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਫ਼ੌਜਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪੂਰਾ ਸਹਿਯੋਗ ਵੀ ਦਿੱਤਾ ।
5. ਕਰਜ਼ੇ ਬਾਰੇ ਅਸਲੀਅਤ (Facts about Loan) – ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਲਗਾਇਆ ਇਹ ਦੋਸ਼ ਕਿ ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦਰਬਾਰ ਨੇ ਕਰਜ਼ੇ ਦੀ ਇੱਕ ਪਾਈ ਵੀ ਵਾਪਸ ਨਹੀਂ ਕੀਤੀ ਤੱਥਾਂ ਦੇ ਬਿਲਕੁਲ ਉਲਟ ਸੀ। ਲਾਹੌਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਰੈਜ਼ੀਡੈਂਟ ਫ਼ਰੈਡਰਿਕ ਕਰੀ ਨੇ ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਨੂੰ ਇੱਕ ਚਿੱਠੀ ਲਿਖੀ ਸੀ ਜਿਸ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਿਹਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ ਕਿ ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦਰਬਾਰ ਨੇ 13,56,837 ਰੁਪਏ ਦੇ ਮੁੱਲ ਦਾ ਸੋਨਾ ਜਮਾਂ ਕਰਵਾ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਹੈ । ਜੇ ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦਰਬਾਰ ਨੇ ਆਪਣਾ ਸਾਰਾ ਕਰਜ਼ਾ ਨਹੀਂ ਮੋੜਿਆ ਤਾਂ ਇਸ ਦੀ ਜ਼ਿੰਮੇਵਾਰੀ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਰੈਜ਼ੀਡੈਂਟ ਉੱਤੇ ਆਉਂਦੀ ਸੀ ।
6. ਪੂਰੀ ਸਿੱਖ ਸੈਨਾ ਅਤੇ ਲੋਕਾਂ ਨੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਨਹੀਂ ਕੀਤਾ ਸੀ (The whole Sikh Army and the People did not Revolt) – ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਨੇ ਇਹ ਦੋਸ਼ ਲਗਾਇਆ ਸੀ ਕਿ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੀ ਪੂਰੀ ਸਿੱਖ ਸੈਨਾ ਅਤੇ ਲੋਕਾਂ ਨੇ ਮਿਲ ਕੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਸੀ । ਪਰ ਇਸ ਕਥਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਜ਼ਰਾ ਵੀ ਸੱਚਾਈ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੈ । ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੇ ਕੇਵਲ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਅਤੇ ਹਜ਼ਾਰਾ ਪ੍ਰਾਂਤਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਹੀ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਹੋਇਆ ਸੀ | ਬਹੁਤੀ ਸਿੱਖ ਫ਼ੌਜ ਅਤੇ ਲੋਕ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਵਫ਼ਾਦਾਰ ਰਹੇ ।
7. ਪੰਜਾਬ ਉੱਤੇ ਕਬਜ਼ਾ ਇੱਕ ਵਿਸ਼ਵਾਸਘਾਤ ਸੀ (Annexation of the Punjab was a Breach of Trust) – ਦਸੰਬਰ, 1846 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਹੋਣ ਵਾਲੀ ਭੈਰੋਵਾਲ ਦੀ ਸੰਧੀ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਸਾਰਾ ਪ੍ਰਬੰਧ ਆਪਣੇ ਹੱਥਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਲੈ ਲਿਆ ਸੀ । ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਅਮਨ-ਅਮਾਨ ਕਾਇਮ ਰੱਖਣ ਦੇ ਉਦੇਸ਼ ਨਾਲ ਲਾਹੌਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸੈਨਾ ਵੀ ਰੱਖ ਲਈ ਸੀ । ਅਜਿਹੀ ਹਾਲਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਅਤੇ ਹਜ਼ਾਰਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਹੋਈ ਬਗ਼ਾਵਤ ਨੂੰ ਕੁਚਲਣ ਦੀ ਸਾਰੀ ਜ਼ਿੰਮੇਵਾਰੀ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਰੈਜ਼ੀਡੈਂਟ ਦੀ ਸੀ । ਜੇ ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਬਗਾਵਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਕੁਚਲਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਕੋਈ ਨਾਕਾਮ ਰਿਹਾ ਤਾਂ ਉਹ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਰੈਜ਼ੀਡੈਂਟ ਹੀ ਸੀ । ਆਪਣੇ ਕਸੂਰਾਂ ਲਈ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਸਜ਼ਾ ਦੇਣਾ ਇੱਕ ਬੇਇਨਸਾਫ਼ੀ ਵਾਲੀ ਗੱਲ ਸੀ । ਇਹ ਇੱਕ ਘੋਰ ਵਿਸ਼ਵਾਸਘਾਤ ਨਹੀਂ ਤਾਂ ਹੋਰ ਕੀ ਸੀ ।
ਉੱਪਰ ਲਿਖਿਤ ਵੇਰਵੇ ਤੋਂ ਇਹ ਸਪੱਸ਼ਟ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕਰਨਾ ਰਾਜਨੀਤਿਕ ਅਤੇ ਨੈਤਿਕ ਦ੍ਰਿਸ਼ਟੀ ਤੋਂ ਬਿਲਕੁਲ ਨਾਜਾਇਜ਼ ਸੀ । ਅੰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਅਸੀਂ ਮੇਜਰ ਈਵਾਨਜ਼ ਬੈੱਲ ਦੇ ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਸ਼ਬਦਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਸਹਿਮਤ ਹਾਂ,
“ਇਹ ਅਸਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਕੋਈ ਜਿੱਤ ਨਹੀਂ ਬਲਕਿ ਘੋਰ ਵਿਸ਼ਵਾਸਘਾਤ ਸੀ ।” 1

ਸੰਖੇਪ ਉੱਤਰਾਂ ਵਾਲੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ (Short Answer Type Questions)
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨਾਂ ਦਾ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਵਰਣਨ ਕਰੋ । (Explain in brief the causes of Second Anglo-Sikh War.)
ਜਾਂ
ਦੁਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨਾਂ ਦਾ ਵਰਣਨ ਕਰੋ । (Describe major causes of the Second Anglo-Sikh War.)
ਜਾਂ
ਦੂਜੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਤਿੰਨ ਮੁੱਖ ਕਾਰਨ ਕੀ ਸਨ ? (What were the three main causes for Second Anglo-Sikh War ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
- ਸਿੱਖ ਪਹਿਲੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਵਿੱਚ ਹੋਈ ਹਾਰ ਦਾ ਬਦਲਾ ਲੈਣਾ ਚਾਹੁੰਦੇ ਸਨ ।
- ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਜੋ ਅਪਮਾਨਜਨਕ ਸਲੂਕ ਕੀਤਾ, ਉਸ ਨਾਲ ਸਿੱਖ ਭੜਕ ਉੱਠੇ ।
- ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਦਾ ਝੰਡਾ ਬੁਲੰਦ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ।
- ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਛੇਤੀ ਤੋਂ ਛੇਤੀ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕਰਨਾ ਚਾਹੁੰਦਾ ਸੀ ।
- ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਤੇ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਨੇ ਬਲਦੀ ‘ਤੇ ਤੇਲ ਪਾਉਣ ਦਾ ਕੰਮ ਕੀਤਾ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ‘ਤੇ ਇੱਕ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਨੋਟ ਲਿਖੋ । (Write a short note on the revolt of Diwan Mool Raj.)
ਜਾਂ
ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਸੰਬੰਧੀ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਜਾਣਕਾਰੀ ਦਿਓ । (Give a brief account of the revolt of Diwan Mool Raj of Multan.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ 1844 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਵਿੱਚ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦਾ ਨਵਾਂ ਗਵਰਨਰ ਨਿਯੁਕਤ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ । ਉਸ ਤੋਂ ਵਸੂਲ ਕੀਤਾ ਜਾਣ ਵਾਲਾ ਸਲਾਨਾ ਲਗਾਨ ਬਹੁਤ ਵਧਾ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ । ਸਿੱਟੇ ਵਜੋਂ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਨੇ ਆਪਣੇ ਅਹੁਦੇ ਤੋਂ ਅਸਤੀਫ਼ਾ ਦੇ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਨਵੇਂ ਰੈਜ਼ੀਡੈਂਟ ਨੇ ਕਾਹਨ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦਾ ਨਵਾਂ ਗਵਰਨਰ ਨਿਯੁਕਤ ਕਰਨ ਦਾ ਫੈਸਲਾ ਕੀਤਾ । ਦੋ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਅਫ਼ਸਰਾਂ ਐਗਨਿਯੁ ਅਤੇ ਐਂਡਰਸਨ ਨੂੰ ਉਸ ਦੀ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਲਈ ਭੇਜਿਆ ਗਿਆ । ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਕਤਲ ਦਾ ਝੂਠਾ ਇਲਜ਼ਾਮ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ’ਤੇ ਪਾਇਆ । ਸਿੱਟੇ ਵਜੋਂ ਉਹ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਮਜਬੂਰ ਹੋ ਗਿਆ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਹਜ਼ਾਰਾ ਦੇ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਬਾਰੇ ਤੁਸੀਂ ਕੀ ਜਾਣਦੇ ਹੋ ? (What do you know about the revolt of Chattar Singh of Hazara ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਟਾਰੀਵਾਲਾ ਹਜ਼ਾਰਾ ਦਾ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ ਸੀ । ਕੈਪਟਨ ਐਬਟ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਭੜਕਾਏ ਗਏ ਹਜ਼ਾਰਾ ਦੇ ਮੁਸਲਮਾਨਾਂ ਨੇ 6 ਅਗਸਤ, 1848 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਰਿਹਾਇਸ਼ਗਾਹ ‘ਤੇ ਹਮਲਾ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਇਹ ਵੇਖ ਕੇ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਕਰਨਲ ਕੈਨੋਰਾ ਨੂੰ ਵਿਦਰੋਹੀਆਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਕਾਰਵਾਈ ਕਰਨ ਦਾ ਹੁਕਮ ਦਿੱਤਾ ! ਕਰਨਲ ਕੈਨੋਰਾ ਨੇ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਹੁਕਮ ਨੂੰ ਮੰਨਣ ਤੋਂ ਇਨਕਾਰ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਕੈਪਟਨ ਐਬਟ ਨੇ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਅਹੁਦੇ ਤੋਂ ਹਟਾ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਇਸ ਕਾਰਨ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦਾ ਖੂਨ ਉਬਲ ਗਿਆ ਤੇ ਉਸ ਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਬਗ਼ਾਵਤ ਕਰਨ ਦਾ ਐਲਾਨ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਚਿਲ੍ਹਿਆਂਵਾਲਾ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ‘ਤੇ ਇੱਕ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਨੋਟ ਲਿਖੋ। (Write a note on the battle of Chillianwala.)
ਜਾਂ
ਚਿਲ੍ਹਿਆਂਵਾਲਾ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਬਾਰੇ ਤੁਸੀਂ ਕੀ ਜਾਣਦੇ ਹੋ ? (What do you know about the battle of Chillianwala ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਚਿਆਂਵਾਲਾ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਦੁਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੀ ਇੱਕ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਨ ਲੜਾਈ ਸੀ । ਲਾਰਡ ਹਿਊਗ ਗਫ਼ ਜੋ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਫ਼ੌਜਾਂ ਦਾ ਸੈਨਾਪਤੀ ਸੀ, ਨੂੰ ਇਹ ਸੂਚਨਾ ਮਿਲੀ ਕਿ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਲਈ ਆ ਰਿਹਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਲਾਰਡ ਹਿਊਗ ਗਫ਼ ਨੇ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਪਹੁੰਚਣ ਤੋਂ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਹੀ 13 ਜਨਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਜ਼ਿਲ੍ਹਿਆਂਵਾਲਾ ਵਿਖੇ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀਆਂ ਫ਼ੌਜਾਂ ‘ਤੇ ਹਮਲਾ ਬੋਲ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਇਸ ਘਮਸਾਨ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦੇ ਚੰਗੇ ਛੱਕੇ ਛੁਡਵਾਏ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 5.
ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਸਮੇਂ ਹੋਈ ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਦਾ ਕੀ ਮਹੱਤਵ ਸੀ ? (What was the importance of the battle of Gujarat in the Second Anglo-Sikh War ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਦੁਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੀ ਆਖਰੀ ਅਤੇ ਫੈਸਲਾਕੁੰਨ ਲੜਾਈ ਸੀ ।ਇਹ ਲੜਾਈ 21 ਫ਼ਰਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਲੜੀ ਗਈ ਸੀ । ਇਸ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਿੱਖ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਦੀ ਗਿਣਤੀ 40,000 ਸੀ ਅਤੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਅਗਵਾਈ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ, ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਤੇ ਮਹਾਰਾਜ ਸਿੰਘ ਕਰ ਰਹੇ ਸਨ । ਦੂਜੇ ਪਾਸੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦੇ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਦੀ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਲਗਪਗ 68,000 ਸੀ ਅਤੇ ਲਾਰਡ ਹਿਊਗ ਗਫ਼ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਅਗਵਾਈ ਕਰ ਰਿਹਾ ਸੀ । ਇਸ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦੀ ਹਾਰ ਹੋਈ । ਸਿੱਟੇ ਵਜੋਂ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ 29 ਮਾਰਚ, 1849 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ ਗਿਆ ।

ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 6.
ਦੁਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਕੀ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ ਪਏ ? (What were the results of Second Anglo-Sikh War ?)
ਜਾਂ
ਦੂਜੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਕੋਈ ਤਿੰਨ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵਾਂ ਦਾ ਵਰਣਨ ਕਰੋ । (Explain any three effects of Second Anglo-Sikh War.)
ਜਾਂ
ਦੂਜੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਕੋਈ ਤਿੰਨ ਨਤੀਜੇ ਦੱਸੋ । (Explain any three results of Second Anglo-Sikh War.)
ਜਾਂ
ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਕੀ ਸਿੱਟੇ ਨਿਕਲੇ ? (What were the results of Second Anglo-Sikh War ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
- ਦੁਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਨ ਸਿੱਟਾ ਇਹ ਨਿਕਲਿਆ ਕਿ 29 ਮਾਰਚ, 1849 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ ਗਿਆ ।
- ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੇ ਅੰਤਿਮ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ 50,000 ਪੌਂਡ ਸਾਲਾਨਾ ਪੈਨਸ਼ਨ ਦੇ ਕੇ ਗੱਦੀਓਂ ਲਾਹ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ ।
- ਸਿੱਖ ਸੈਨਾ ਨੂੰ ਤੋੜ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ ।
- ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਅਤੇ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਦੇਸ਼ ਨਿਕਾਲੇ ਦੀ ਸਜ਼ਾ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਗਈ ।
- ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਪ੍ਰਬੰਧ ਚਲਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਾਸਨਿਕ ਬੋਰਡ ਦੀ ਸਥਾਪਨਾ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 7.
ਕੀ ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਲਾਉਣਾ ਉੱਚਿਤ ਸੀ ? ਆਪਣੇ ਪੱਖ ਵਿੱਚ ਦਲੀਲਾਂ ਦਿਓ । (Was it proper of Lord Dalhousie to annex Punjab to the British Empire ? Give arguments in support of your answer.)
ਜਾਂ
“ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਲਾਉਣਾ ਇੱਕ ਘੋਰ ਵਿਸ਼ਵਾਘਾਤ ਸੀ ।” ਵਿਆਖਿਆ ਕਰੋ । (“Annexation of Punjab was a violent breach of trust.” Explain.)
ਜਾਂ
ਕੀ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਸੰਯੋਜਨ ਨਿਆਂ ਸੰਗਤ ਸੀ ? ਕਾਰਨ ਦੱਸੋ । (Was the annexation of Punjab justified ? Give reasons.)
ਜਾਂ
ਕੀ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਸੰਯੋਜਨ ਨਿਆਂ ਸੰਗਤ ਸੀ ? ਕਾਰਨ ਦੱਸੋ । (Was the annexation of Punjab justified ? Give reasons.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਲਾਉਣਾ ਕਿਸੇ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਵੀ ਉੱਚਿਤ ਨਹੀਂ ਸੀ । ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦੀ ਸੰਧੀ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੇ ਕਈ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਨ ਇਲਾਕੇ ਖੋਹ ਲਏ । ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦਰਬਾਰ ਦੀ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾਤਰ ਫ਼ੌਜ ਨੂੰ ਤੋੜ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਜਿਸ ਕਾਰਨ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਰੋਸ ਪੈਦਾ ਹੋ ਗਿਆ । ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਖ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਗਵਰਨਰ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਅਤੇ ਹਜ਼ਾਰਾ ਦੇ ਗਵਰਨਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਲਈ ਭੜਕਾਇਆ ਤਾਂ ਕਿ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਬਹਾਨਾ ਬਣਾ ਕੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਕਬਜ਼ੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਰ ਸਕਣ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 8.
ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਦੇ ਇਸ ਪੱਖ ਵਿੱਚ ਦਲੀਲਾਂ ਦਿਓ ਕਿ ਉਸ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਲਾਉਣਾ ਉੱਚਿਤ ਸੀ । (Give arguments in favour of Dalhousie’s annexation of the Punjab to the British empire.)
ਜਾਂ
ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਦੀ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਉੱਤੇ ਕਬਜ਼ੇ ਦੀ ਨੀਤੀ ਦੇ ਪੱਖ ਵਿੱਚ ਦਲੀਲਾਂ ਦਿਓ । (Give arguments in favour of Dalhousie’s policy of the annexation of Punjab.)
ਜਾਂ
ਕੀ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਲਾਉਣਾ ਉੱਚਿਤ ਸੀ ? ਕਾਰਨ ਦੱਸੋ । (Was the annexation of Punjab justified ? Give reasons.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
- ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨੇ ਭੈਰੋਵਾਲ ਦੀ ਸੰਧੀ ਦੀਆਂ ਸ਼ਰਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਤੋੜਿਆ ਸੀ ।
- ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਬਗ਼ਾਵਤ ਕੀਤੀ ਸੀ ।
- ਪੰਜਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਂਤੀ ਸਥਾਪਿਤ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਇਸ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਲਾਉਣਾ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਸੀ ।
- ਪੰਜਾਬ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਲਈ ਇੱਕ ਖ਼ਤਰਾ ਬਣ ਸਕਦਾ ਸੀ ।
- ਪੰਜਾਬ ’ਤੇ ਕਬਜ਼ਾ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਲਈ ਲਾਭਦਾਇਕ ਸਿੱਧ ਹੋ ਸਕਦਾ ਸੀ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 9.
ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ‘ਤੇ ਇੱਕ ਨੋਟ ਲਿਖੋ । (Write a note on Maharaja Dalip Singh.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਛੋਟਾ ਪੁੱਤਰ ਸੀ । ਉਹ 15 ਸਤੰਬਰ, ‘ 1843 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਨਵਾਂ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਬਣਿਆ ਸੀ । ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਲਾਲ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਪ੍ਰਧਾਨ ਮੰਤਰੀ ਦੇ ਅਹੁਦੇ ‘ਤੇ ਨਿਯੁਕਤ ਕੀਤਾ ਪਰ ਉਹ ਗੱਦਾਰ ਨਿਕਲਿਆ । ਸਿੱਟੇ ਵਜੋਂ ਪਹਿਲੇ ਅਤੇ ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਹਾਰ ਦਾ ਮੂੰਹ ਦੇਖਣਾ ਪਿਆ | ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਗੱਦੀ ਤੋਂ ਲਾਹ ਦਿੱਤਾ । 22 ਅਕਤੂਬਰ, 1893 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਪੈਰਿਸ ਵਿਖੇ ਮੌਤ ਹੋ ਗਈ ਸੀ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 10.
ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਜਾਂ ਜਿੰਦ ਕੌਰ ‘ਤੇ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਨੋਟ ਲਿਖੋ । (Write a brief note on Maharani Jindan or Jind Kaur.)
ਜਾਂ
ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਬਾਰੇ ਤੁਸੀਂ ਕੀ ਜਾਣਦੇ ਹੋ ? (What do you know about Maharani Jindan ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ, ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਰਾਣੀ ਸੀ ਉਸ ਨੂੰ 15 ਸਤੰਬਰ, 1843 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੇ ਨਵੇਂ ਨਿਯੁਕਤ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਦਾ ਸਰਪ੍ਰਸਤ ਨਿਯੁਕਤ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਦਸੰਬਰ, 1846 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਹੋਈ ਭੈਰੋਵਾਲ ਦੀ ਸੰਧੀ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਸਾਰੀਆਂ ਸ਼ਕਤੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਖੋਹ ਲਿਆ ਸੀ । ਅਪਰੈਲ, 1849 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਭੇਸ ਬਦਲ ਕੇ ਨੇਪਾਲ ਪਹੁੰਚਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਫਲ ਹੋ ਗਈ । ਅੰਤ 1 ਅਗਸਤ, 1863 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਇੰਗਲੈਂਡ ਵਿੱਚ ਇਸ ਸੰਸਾਰ ਨੂੰ ਹਮੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਲਈ ਅਲਵਿਦਾ ਕਹਿ ਗਈ ।

ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 11.
ਭਾਈ ਮਹਾਰਾਜ ਸਿੰਘ ‘ਤੇ ਇੱਕ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਨੋਟ ਲਿਖੋ । (Write a brief note on Bhai Maharaj Singh.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਭਾਈ ਮਹਾਰਾਜ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੌਰੰਗਾਬਾਦ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਸੰਤ ਭਾਈ ਬੀਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਚੇਲੇ ਸਨ । ਉਹ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੀ ਸੁਤੰਤਰਤਾ ਦੇ ਹੱਕ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਨ । ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੁਲਜ, ਹਜ਼ਾਰਾ ਦੇ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਟਾਰੀਵਾਲਾ ਅਤੇ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਪੁੱਤਰ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਦਾ ਝੰਡਾ ਬੁਲੰਦ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਪ੍ਰੇਰਿਤ ਕੀਤਾ । ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਦੂਜੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੀਆਂ ਸਾਰੀਆਂ ਲੜਾਈਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਹਿੱਸਾ ਲਿਆ । ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਸਿੰਘਾਪੁਰ ਜੇਲ੍ਹ ਵਿੱਚ 5 ਜੁਲਾਈ, 1856 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਮੌਤ ਹੋ ਗਈ ਸੀ ।
ਵਸਤੁਨਿਸ਼ਠ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ (Objective Type Questions)
ਇੱਕ ਸ਼ਬਦ ਤੋਂ ਇੱਕ ਵਾਕ ਵਿੱਚ ਉੱਤਰ (Answer in one Word to one Sentence)
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਦੂਸਰਾ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਕਦੋਂ ਲੜਿਆ ਗਿਆ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
1848-49 ਈ. ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਗਵਰਨਰ-ਜਨਰਲ ਕੌਣ ਸੀ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦਾ ਕੋਈ ਇੱਕ ਕਾਰਨ ਲਿਖੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਸਿੱਖ ਪਹਿਲੇ ਯੁੱਧ ਵਿੱਚ ਹੋਈ ਆਪਣੀ ਹਾਰ ਦਾ ਬਦਲਾ ਲੈਣਾ ਚਾਹੁੰਦੇ ਸਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਕੌਣ ਸੀ ?
ਜਾਂ
ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ (ਜਿੰਦ ਕੌਰ) ਕੌਣ ਸੀ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਮਾਂ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 5.
ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਕੌਣ ਸੀ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦਾ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ ਗਵਰਨਰ ਸੀ ।

ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 6.
ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਕਰਨ ਦਾ ਕੋਈ ਇੱਕ ਕਾਰਨ ਦੱਸੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਵੱਲੋਂ ਵਸੂਲ ਕੀਤੇ ਜਾਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਸਾਲਾਨਾ ਲਗਾਨ ਦੀ ਰਕਮ ਕਾਫ਼ੀ ਵਧਾ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਸੀ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 7.
ਸਾਵਨ ਮਲ ਕੌਣ ਸੀ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਦਾ ਪਿਤਾ ਅਤੇ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦਾ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 8.
ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਟਾਰੀਵਾਲਾ ਕੌਣ ਸੀ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਹਜ਼ਾਰਾ ਦਾ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 9.
ਸਰਦਾਰ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਕੌਣ ਸੀ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਟਾਰੀਵਾਲਾ ਦਾ ਪੁੱਤਰ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 10.
ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਬਗਾਵਤ ਦਾ ਝੰਡਾ ਕਿਉਂ ਬੁਲੰਦ ਕੀਤਾ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਉਸਦੇ ਪਿਤਾ ਨਾਲ ਕੀਤੇ ਗਏ ਦੁਰਵਿਹਾਰ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 11.
ਭਾਈ ਮਹਾਰਾਜ ਸਿੰਘ ਕੌਣ ਸੀ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਉਹ ਨੌਰੰਗਾਬਾਦ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਸੰਤ ਸਨ ।

ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 12.
ਦੂਸਰਾ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਕਿਸ ਦੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਨਾਲ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਹੋਇਆ ?
ਜਾਂ
ਕਿਸ ਦੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਨੇ ਦੂਜੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਕੀਤਾ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 13.
ਰਾਮਨਗਰ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਕਦੋਂ ਹੋਈ ਸੀ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
22 ਨਵੰਬਰ, 1848 ਈ. ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 14.
ਚਿਲਿਆਂਵਾਲਾ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਕਦੋਂ ਲੜੀ ਗਈ ਸੀ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
13 ਜਨਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ. ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 15.
ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੀ ਆਖਰੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਕਿਹੜੀ ਸੀ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 16.
ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਕਦੋਂ ਲੜੀ ਗਈ ਸੀ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
21 ਫ਼ਰਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ. ।

ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 17.
ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਦੌਰਾਨ ਲੜੀ ਗਈ ਉਸ ਲੜਾਈ ਦਾ ਨਾਂ ਦੱਸੋ ਜਿਹੜੀ ਇਤਿਹਾਸ ਵਿੱਚ ਤੋਪਾਂ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਦੇ ਨਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 18.
ਦੁਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦਾ ਕੋਈ ਇੱਕ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਨ ਸਿੱਟਾ ਦੱਸੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ ਗਿਆ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 19.
ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਦੋਂ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ?
ਜਾਂ
ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਦੋਂ ਮਿਲਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
29 ਮਾਰਚ, 1849 ਈ. ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 20.
ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕਰਨ ਦੇ ਪੱਖ ਵਿੱਚ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਜਾਣ ਵਾਲੀ ਕੋਈ ਇੱਕ ਦਲੀਲ ਦੱਸੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕਰਨਾ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੇ ਲੋਕਾਂ ਲਈ ਲਾਭਦਾਇਕ ਸੀ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 21.
ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕਰਨ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਜਾਣ ਵਾਲੀ ਕੋਈ ਇੱਕ ਦਲੀਲ ਲਿਖੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਬਗਾਵਤ ਲਈ ਭੜਕਾਇਆ ਸੀ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 22.
ਭਾਈ ਮਹਾਰਾਜ ਸਿੰਘ ਕੌਣ ਸੀ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਉਹ ਨੌਰੰਗਾਬਾਦ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਸੰਤ ਭਾਈ ਬੀਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦਾ ਚੇਲਾ ਸੀ ।

ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 23.
ਭਾਈ ਮਹਾਰਾਜ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਮੌਤ ਕਦੋਂ ਹੋਈ ਸੀ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
1856 ਈ. ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 24.
ਭਾਈ ਮਹਾਰਾਜ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਮੌਤ ਕਿੱਥੇ ਹੋਈ ਸੀ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਸਿੰਘਾਪੁਰ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 25.
ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਆਖ਼ਰੀ ਸਿੱਖ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਕੌਣ ਸੀ ?
ਜਾਂ
ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਆਖ਼ਰੀ ਸਿੱਖ ਸ਼ਾਸਕ ਕੌਣ ਸੀ ?
ਜਾਂ
ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦਾ ਅੰਤਿਮ ਸਿੱਖ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਕੌਣ ਸੀ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 26.
ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਮੌਤ ਕਿੱਥੇ ਹੋਈ ਸੀ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਪੈਰਿਸ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 27.
ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਮੌਤ ਕਦੋਂ ਹੋਈ ਸੀ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
1893 ਈ. ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 28.
ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਦੀ ਮੌਤ ਕਦੋਂ ਹੋਈ ਸੀ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
1863 ਈ. ।

ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 29.
ਸਿੱਖ ਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਪਤਨ ਦਾ ਕੋਈ ਇੱਕ ਕਾਰਨ ਦੱਸੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਉੱਤਰਾਧਿਕਾਰੀ ਕਮਜ਼ੋਰ ਨਿਕਲੇ ।
ਖ਼ਾਲੀ ਥਾਂਵਾਂ ਭਰੋ (Fill in the Blanks)
ਨੋਟ :-ਖ਼ਾਲੀ ਥਾਂਵਾਂ ਭਰੋ :
1. ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਵਿਚਕਾਰ ਦੂਜੀ ਲੜਾਈ …………………… ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਹੋਈ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(1848-49)
2. ਦੁਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਗਵਰਨਰ ਜਨਰਲ …………………….. ਸੀ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ)
3. ਦੁਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਸਮੇਂ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ …………………….. ਸੀ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ)
4. ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਮਾਂ ਦਾ ਨਾਂ ……………………….. ਸੀ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ)
5. 1844 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ …………………………. ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦਾ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ ਨਿਯੁਕਤ ਹੋਇਆ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ)

6. ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਟਾਰੀਵਾਲਾ ………………………… ਦਾ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ ਸੀ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(ਹਜ਼ਾਰਾ)
7. ਦੁਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੀ ਪਹਿਲੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਦਾ ਨਾਂ ……………………… ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਸੀ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(ਰਾਮਨਗਰ)
8. ਰਾਮਨਗਰ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ …………………………. ਨੂੰ ਹੋਈ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(22 ਨਵੰਬਰ, 1848 ਈ.)
9. ਚਿਲ੍ਹਿਆਂਵਾਲਾ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ …………………………. ਨੂੰ ਹੋਈ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(13 ਜਨਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ.)
10. ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਇਤਿਹਾਸ ਵਿੱਚ ………………………… ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਦੇ ਨਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਹੈ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(ਤੋਪਾਂ)
11. ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਆਪਣੇ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ………………………….. ਨੂੰ ਮਿਲਾਇਆ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(29 ਮਾਰਚ, 1849 ਈ.)

ਠੀਕ ਜਾਂ ਗਲਤ (True or False)
ਨੋਟ :-ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਠੀਕ ਜਾਂ ਗਲਤ ਦੀ ਚੋਣ ਕਰੋ-
1. ਦੁਸਰਾ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ 1848-49 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਲੜਿਆ ਗਿਆ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਠੀਕ
2. ਦੁਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਗਵਰਨਰ-ਜਨਰਲ ਸੀ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਠੀਕ
3. ਦੁਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਸੀ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਠੀਕ
4. ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਮਾਂ ਸੀ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਠੀਕ
5. ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ 1846 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦਾ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ ਬਣਿਆ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਗਲਤ
6. ਦੂਸਰਾ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਰਾਮਨਗਰ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਨਾਲ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਹੋਇਆ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਠੀਕ

7. ਰਾਮਨਗਰ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ 12 ਨਵੰਬਰ, 1846 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਹੋਈ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਗ਼ਲਤ
8. ਚਿਲਿਆਂਵਾਲਾ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ 13 ਜਨਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਹੋਈ ਸੀ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਠੀਕ
9. ਚਿਲਿਆਂਵਾਲਾ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸੈਨਾ ਨੂੰ ਇੱਕ ਕਰਾਰੀ ਹਾਰ ਦਾ ਸਾਹਮਣਾ ਕਰਨਾ ਪਿਆ ਸੀ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਠੀਕ
10. ਦੁਸਰਾ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਨਾਲ ਸਮਾਪਤ ਹੋ ਗਿਆ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਠੀਕ
11. ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ 21 ਫ਼ਰਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਹੋਈ ਸੀ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਠੀਕ
12. ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ 29 ਮਾਰਚ, 1849 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਠੀਕ

13. ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਉਸਦੇ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਦੀ ਵਾਗਡੋਰ ਸੰਭਾਲੀ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਗਲਤ
14. ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਆਖਰੀ ਸਿੱਖ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਸੀ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਠੀਕ
15. ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦਾ ਅੰਤਿਮ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਸੀ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਗ਼ਲਤ
ਬਹੁਪੱਖੀ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ (Multiple Choice Questions)
ਨੋਟ :-ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਠੀਕ ਉੱਤਰ ਦੀ ਚੋਣ ਕਰੋ-
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਦੂਸਰਾ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਕਦੋਂ ਲੜਿਆ ਗਿਆ ?
(i) 1844-45 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ
(ii) 1845-46 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ
(iii) 1847-48 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ
(iv) 1848-49 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(iv) 1848-49 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਗਵਰਨਰ-ਜਨਰਲ ਕੌਣ ਸੀ ?
(i) ਲਾਰਡ ਲਿਟਨ
(ii) ਲਾਰਡ ਰਿਪਨ
(iii) ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ
(iv) ਲਾਰਡ ਹਾਰਡਿੰਗ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(iii) ਲਾਰਡ ਡਲਹੌਜ਼ੀ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਦੁਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਸਮੇਂ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਕੌਣ ਸੀ ?
(i) ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ
(ii) ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ
(iii) ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ
(iv) ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਖੜਕ ਸਿੰਘ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(iii) ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ।

ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਮਹਾਰਾਣੀ ਜਿੰਦਾਂ ਕੌਣ ਸੀ ?
(i) ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਮਾਂ
(ii) ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਖੜਕ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਭੈਣ
(iii) ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਪਤਨੀ
(iv) ਰਾਜਾ ਗੁਲਾਬ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਪੁੱਤਰੀ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(i) ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਮਾਂ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 5.
ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਕੌਣ ਸੀ ?
(i) ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦਾ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ
(ii) ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦਾ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ
(iii) ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ ਦਾ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ
(iv) ਪਿਸ਼ਾਵਰ ਦਾ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ
ਉੱਤਰ-
(ii) ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦਾ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 6.
ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਕਦੋਂ ਕੀਤਾ ਸੀ ?
(i) 1844 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ
(ii) 1845 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ
(iii) 1846 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ
(iv) 1848 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(iv) 1848 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 7.
ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਟਾਰੀਵਾਲਾ ਕਿੱਥੋਂ ਦਾ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ ਸੀ ?
(i) ਹਜ਼ਾਰਾ
(ii) ਮੁਲਤਾਨ
(iii) ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ
(iv) ਪਿਸ਼ਾਵਰ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(i) ਹਜ਼ਾਰਾ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 8.
ਦੂਸਰਾ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਕਿਸ ਲੜਾਈ ਨਾਲ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਹੋਇਆ ਸੀ ?
(i) ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ
(ii) ਚਿਲਿਆਂਵਾਲਾ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ
(iii) ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ
(iv) ਰਾਮਨਗਰ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(iv) ਰਾਮਨਗਰ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ।

ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 9.
ਰਾਮਨਗਰ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਕਦੋਂ ਹੋਈ ਸੀ ?
(i) 12 ਨਵੰਬਰ, 1846 ਈ.
(ii) 15 ਨਵੰਬਰ, 1847 ਈ.
(iii) 17 ਨਵੰਬਰ, 1848 ਈ.
(iv) 22 ਨਵੰਬਰ, 1848 ਈ. ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(iv) 22 ਨਵੰਬਰ, 1848 ਈ. ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 10.
ਚਿਲ੍ਹਿਆਂਵਾਲਾ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਕਦੋਂ ਹੋਈ ?
(i) 22 ਨਵੰਬਰ, 1848 ਈ.
(ii) 3 ਜਨਵਰੀ, 1848 ਈ.
(iii) 10 ਜਨਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ.
(iv) 13 ਜਨਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ. ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(iv) 13 ਜਨਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ. ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 11.
ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦਾ ਯੁੱਧ ਕਦੋਂ ਖ਼ਤਮ ਹੋਇਆ ?
(i) 22 ਜਨਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ.
(ii) 23 ਜਨਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ.
(ii) 24 ਜਨਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ.
(iv) 25 ਜਨਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ. ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(i) 22 ਜਨਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ. ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 12.
ਦੂਸਰਾ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਕਿਸ ਲੜਾਈ ਨਾਲ ਖ਼ਤਮ ਹੋਇਆ ?
ਜਾਂ
ਉਸ ਲੜਾਈ ਦਾ ਨਾਂ ਦੱਸੋ ਜਿਹੜੀ ਇਤਿਹਾਸ ਵਿੱਚ ‘ਤੋਪਾਂ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਦੇ ਨਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਹੈ ?
(i) ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ
(ii) ਰਾਮਨਗਰ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ
(iii) ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ
(iv) ਚਿਲ੍ਹਿਆਂਵਾਲਾਂ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(iii) ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 13.
ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਕਦੋਂ ਲੜੀ ਗਈ ਸੀ ?
(i) 22 ਨਵੰਬਰ, 1848 ਈ.
(ii) 13 ਜਨਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ.
(iii) 22 ਜਨਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ.
(iv) 21 ਫਰਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ. ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(iv) 21 ਫਰਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ. ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 14.
ਪੰਜਾਬ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਦੋਂ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ ?
(i) 1849 ਈ.
(ii) 1850 ਈ.
(iii) 1848 ਈ.
(iv) 1947 ਈ. ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(i) 1849 ਈ. ।

ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 15.
ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦਾ ਆਖ਼ਰੀ ਸਿੱਖ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ, ਕੌਣ ਸੀ ?
(i) ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ
(ii) ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ
(iii) ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਖੜਕ ਸਿੰਘ
(iv) ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(i) ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 16.
ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਮੌਤ ਕਦੋਂ ਹੋਈ ਸੀ ?
(i) 1857 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ
(ii) 1893 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ
(iii) 1849 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ
(iv) 1892 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(ii) 1893 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 17.
ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਦਲੀਪ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਮੌਤ ਕਿੱਥੇ ਹੋਈ ਸੀ ?
(i) ਪੰਜਾਬ
(ii) 1893 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ
(iii) ਨੇਪਾਲ
(iv) ਲੰਡਨ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(ii) 1893 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ।
Source Based Questions
ਨੋਟ-ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਪੈਰਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਧਿਆਨ ਨਾਲ ਪੜ੍ਹੋ ਅਤੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਅੰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਦਿੱਤੇ ਗਏ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨਾਂ ਦੇ ਉੱਤਰ ਦਿਓ-
1. ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਨੂੰ ਆਰੰਭ ਕਰਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਨੂੰ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ ਸਥਾਨ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਹੈ । ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਸਿੱਖ-ਰਾਜ ਦਾ ਇੱਕ ਸੂਬਾ ਸੀ । 1844 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਇੱਥੋਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ (ਗਵਰਨਰ) ਸਾਵਨ ਮਲ ਦੀ ਮੌਤ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਪੁੱਤਰ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦਾ ਨਵਾਂ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ ਬਣਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ । ਇਸ ਮੌਕੇ ‘ਤੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਰੈਜ਼ੀਡੈਂਟ ਨੇ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਸੂਬੇ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਲਾਹੌਰ ਦਰਬਾਰ ਨੂੰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਜਾਣ ਵਾਲਾ ਸਾਲਾਨਾ ਲਗਾਨ 13,47,000 ਰੁਪਏ ਤੋਂ ਵਧਾ ਕੇ 19,71,500 ਰੁਪਏ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ । 1846 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਇਸ ਨੂੰ ਵਧਾ ਕੇ 30 ਲੱਖ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ । ਦੂਜੇ ਪਾਸੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਿਕਣ ਵਾਲੀਆਂ ਕੁਝ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਵਸਤਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਕਰ ਹਟਾ ਲਿਆ ਅਤੇ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦਾ 1/3 ਹਿੱਸਾ ਵੀ ਵਾਪਸ ਲੈ ਲਿਆ । ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਕਾਰਨਾਂ ਕਰਕੇ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਨੂੰ ਵਧਿਆ ਹੋਇਆ ਲਗਾਨ ਨਹੀਂ ਦੇ ਸਕਦਾ ਸੀ ।
ਇਸ ਸੰਬੰਧੀ ਉਸ ਨੇ ਬਿਟਿਸ਼ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਨੂੰ ਕਈ ਵਾਰ ਕਿਹਾ ਪਰ ਉਹ ਨਾ ਮੰਨੀ । ਅੰਤ ਮਜਬੂਰ ਹੋ ਕੇ ਦਸੰਬਰ, 1847 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਨੇ ਆਪਣਾ ਅਸਤੀਫ਼ਾ ਦੇ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਮਾਰਚ, 1848 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਨਵੇਂ ਰੈਜ਼ੀਡੈਂਟ ਫ਼ਰੈਡਰਿਕ ਕਰੀ ਨੇ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਕਾਹਨ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦਾ ਨਵਾਂ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ ਨਿਯੁਕਤ ਕਰਨ ਦਾ ਫੈਸਲਾ ਕੀਤਾ । ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਤੋਂ ਚਾਰਜ ਲੈਣ ਲਈ ਕਾਹਨ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਦੋ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਅਫਸਰਾਂ ਵੈਨਸ ਐਗਨਿਯੂ ਅਤੇ ਐਂਡਰਸਨ ਨੂੰ ਭੇਜਿਆ ਗਿਆ । ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਨੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦਾ ਚੰਗਾ ਸਵਾਗਤ ਕੀਤਾ 19 ਅਪਰੈਲ ਨੂੰ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਨੇ ਕਿਲ੍ਹੇ ਦੀਆਂ ਚਾਬੀਆਂ ਕਾਹਨ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਹਵਾਲੇ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤੀਆਂ | ਪਰ ਅਗਲੇ ਦਿਨ 20 ਅਪਰੈਲ ਨੂੰ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਕੁਝ ਸਿਪਾਹੀਆਂ ਨੇ ਹਮਲਾ ਕਰਕੇ ਦੋਹਾਂ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਅਫਸਰਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਕਤਲ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਅਤੇ ਕਾਹਨ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਗ੍ਰਿਫ਼ਤਾਰ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ । ਫ਼ਰੈਡਰਿਕ ਕਰੀ ਨੇ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਦੀ ਸਾਰੀ ਜ਼ਿੰਮੇਵਾਰੀ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਸਿਰ ਪਾਈ ।
1. ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ ਕਦੋਂ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦਾ ਨਵਾਂ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ ਨਿਯੁਕਤ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ ?
2. ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਨੇ ਕਿਹੜੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਕਰਕੇ ਆਪਣਾ ਅਸਤੀਫ਼ਾ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਸੀ ?
3. 1848 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਰੈਜ਼ੀਡੈਂਟ ਫ਼ਰੈਡਰਿਕ ਕਰੀ ਨੇ ਕਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦਾ ਨਵਾਂ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ ਨਿਯੁਕਤ ਕੀਤਾ ?
4. ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਕਿਹੜੇ ਦੋ ਅਫ਼ਸਰਾਂ ਦੇ ਕਤਲ ਦੀ ਜ਼ਿੰਮੇਵਾਰੀ ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੁਲਰਾਜ ’ਤੇ ਪਾਈ ?
5. ਫ਼ਰੈਡਰਿਕ ਕਰੀ ਨੇ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਵਿਦਰੋਹ ਦੀ ਸਾਰੀ ਜ਼ਿੰਮੇਵਾਰੀ …………………. ਦੇ ਸਿਰ ਪਾਈ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
1. ਦੀਵਾਨ ਮੂਲਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ 1844 ਈ. ਵਿੱਚ ਮੁਲਤਾਨ ਦਾ ਨਵਾਂ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ ਨਿਯੁਕਤ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ ।
2. ਉਸ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਦਿੱਤੇ ਜਾਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਸਲਾਨਾ ਲਗਾਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਬਹੁਤ ਵਾਧਾ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ ।
3. ਸਰਦਾਰ ਕਾਹਨ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ।
4. ਵੈਨਸ ਐਗਨਿਯੂ ਅਤੇ ਐਂਡਰਸਨ ।
5. ਮੁਲਰਾਜੇ ।
2. ਚਿਲਿਆਂਵਾਲਾ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੀਆਂ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਨ ਲੜਾਈਆਂ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਇੱਕ ਸੀ । ਇਹ ਲੜਾਈ 13 ਜਨਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਲੜੀ ਗਈ ਸੀ । ਹਿਊਗ ਗਫ਼ ਦਾ ਇਹ ਵਿਚਾਰ ਸੀ ਕਿ ਉਸ ਕੋਲ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦਾ ਮੁਕਾਬਲਾ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਸ਼ਕਤੀਸ਼ਾਲੀ ਫ਼ੌਜ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਉਹ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਸੈਨਿਕ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਪਹੁੰਚਣ ਦੀ ਉਡੀਕ ਕਰਨ ਲੱਗਾ । ਜਦੋਂ ਗਫ਼ ਨੂੰ ਇਹ ਖ਼ਬਰ ਮਿਲੀ ਕਿ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਆਪਣੇ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਸਮੇਤ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਲਈ ਪਹੁੰਚ ਰਿਹਾ ਹੈ ਤਾਂ ਉਸ ਨੇ 13 ਜਨਵਰੀ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ‘ਤੇ ਹਮਲਾ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਇਹ ਲੜਾਈ ਬਹੁਤ ਭਿਆਨਕ ਸੀ । ਇਸ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਸੈਨਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਤਬਾਹੀ ਮਚਾ ਦਿੱਤੀ । ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦੇ 695 ਸੈਨਿਕ ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ 132 ਅਫ਼ਸਰ ਸਨ, ਇਸ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਾਰੇ ਗਏ ਅਤੇ 1651 ਹੋਰ ਸੈਨਿਕ ਜ਼ਖ਼ਮੀ ਹੋਏ | ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ 4 ਤੋਪਾਂ ਵੀ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦੇ ਹੱਥ ਆ ਗਈਆਂ ।
1. ਦੁਸਰੇ-ਐਂਗਲੋ ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੀ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਨ ਲੜਾਈ ਕਿਹੜੀ ਸੀ ?
2. ਚਿਲਿਆਂਵਾਲਾ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਕਦੋਂ ਹੋਈ ?
3. ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਕੌਣ ਸੀ?
4. ਚਿਲਿਆਂਵਾਲਾ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਿਸ ਦੀ ਹਾਰ ਹੋਈ ?
5. ਚਿਲਿਆਂਵਾਲਾ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਿੰਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਅਫ਼ਸਰ ਮਾਰੇ ਗਏ ਸਨ ?
(i) 132
(ii) 142
(iii) 695
(iv) 1651.
ਉੱਤਰ-
1. ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੀ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਨ ਲੜਾਈ ਚਿਲਿਆਂਵਾਲਾ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਸੀ ।
2. ਇਹ ਲੜਾਈ 13 ਜਨਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਹੋਈ ।
3. ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਹਜ਼ਾਰਾ ਦੇ ਨਾਜ਼ਿਮ ਸਰਦਾਰ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦਾ ਪੁੱਤਰ ਸੀ ।
4. ਚਿਲਿਆਂਵਾਲਾ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਦੀ ਹਾਰ ਹੋਈ ।
5. 132.

3. ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੀ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਨ ਅਤੇ ਨਿਰਣਾਇਕ ਲੜਾਈ ਸਿੱਧ ਹੋਈ । ਇਸ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਚਤਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਸੈਨਿਕ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਆਣ ਮਿਲੇ ਸਨ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਲਈ । ਭਾਈ ਮਹਾਰਾਜ ਸਿੰਘ ਵੀ ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਪਹੁੰਚ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ । ਇਸ ਤੋਂ ਇਲਾਵਾ ਅਫ਼ਗਾਨਿਸਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਬਾਦਸ਼ਾਹ ਦੋਸਤ ਮੁਹੰਮਦ ਖ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਵੀ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦੀ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਲਈ ਆਪਣੇ ਪੁੱਤਰ ਅਕਰਮ ਖਾਂ ਦੀ ਅਗਵਾਈ ਹੇਠ 3,000 ਘੋੜਸਵਾਰ ਸੈਨਾ ਭੇਜੀ ਸੀ । ਇਸ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦੀ ਕੁੱਲ ਫ਼ੌਜ 40,000 ਸੀ । ਦੂਜੇ ਪਾਸੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸੈਨਾ ਦੀ ਅਗਵਾਈ ਅਜੇ ਵੀ ਲਾਰਡ ਹਿਊਗ ਗ ਹੀ ਕਰ ਰਿਹਾ ਸੀ ਕਿਉਂਕਿ ਸਰ ਚਾਰਲਸ ਨੇਪੀਅਰ ਅਜੇ ਭਾਰਤ ਨਹੀਂ ਪੁੱਜਾ ਸੀ । ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਕੋਲ 68,000 ਸੈਨਿਕ ਸਨ ।
ਇਸ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਦੋਹਾਂ ਪਾਸਿਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਤੋਪਾਂ ਦੀ ਕਾਫ਼ੀ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ ਸੀ ਜਿਸ ਕਾਰਨ ਇਹ ਲੜਾਈ ਇਤਿਹਾਸ ਵਿੱਚ ‘ਤੋਪਾਂ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਦੇ ਨਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਲੜਾਈ 21 ਫ਼ਰਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਸਵੇਰੇ 7.30 ਵਜੇ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਹੋਈ । ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਤੋਪਾਂ ਦਾ ਬਾਰੂਦ ਛੇਤੀ ਮੁੱਕ ਗਿਆ । ਜਦੋਂ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਇਸ ਬਾਰੇ ਪਤਾ ਲੱਗਿਆ ਤਾਂ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਆਪਣੀਆਂ ਤੋਪਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਸਿੱਖ ਸੈਨਾ ‘ਤੇ ਜ਼ਬਰਦਸਤ ਹਮਲਾ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਸਿੱਖ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਨੇ ਆਪਣੀਆਂ ਤਲਵਾਰਾਂ ਕੱਢ ਲਈਆਂ ਪਰ ਉਹ ਤੋਪਾਂ ਦਾ ਮੁਕਾਬਲਾ ਕਿੰਨਾ ਕੁ ਚਿਰ ਕਰਦੇ । ਇਸ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਿੱਖ ਸੈਨਾ ਦਾ ਭਾਰੀ ਨੁਕਸਾਨ ਹੋਇਆ ।
1. ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਦੂਸਰੇ ਐਂਗਲੋ-ਸਿੱਖ ਯੁੱਧ ਦੀ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਨ ਅਤੇ …………………… ਲੜਾਈ ਸਿੱਧ ਹੋਈ ।
2. ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਕਦੋਂ ਲੜੀ ਗਈ ਸੀ ?
3. ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸੈਨਾ ਦੀ ਅਗਵਾਈ ਕੌਣ ਕਰ ਰਿਹਾ ਸੀ ?
4. ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਨੂੰ ਤੋਪਾਂ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਕਿਉਂ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਸੀ ?
5. ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਕੌਣ ਜੇਤੂ ਰਿਹਾ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
1. ਨਿਰਣਾਇਕ ।
2. ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ 21 ਫ਼ਰਵਰੀ, 1849 ਈ. ਨੂੰ ਲੜੀ ਗਈ ਸੀ ।
3. ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸੈਨਾ ਦੀ ਅਗਵਾਈ ਲਾਰਡ ਹਿਊਗ ਗਫ਼ ਕਰ ਰਿਹਾ ਸੀ ।
4. ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਨੂੰ ਤੋਪਾਂ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਇਸ ਕਰਕੇ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਕਿਉਂਕਿ ਇਸ ਵਿੱਚ ਦੋਹਾਂ ਪਾਸਿਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਭਾਰੀ ਤੋਪਾਂ ਦੀ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ ਸੀ ।
5. ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ ਜੇਤੂ ਰਹੇ ।
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()