Punjab State Board PSEB 6th Class Social Science Book Solutions History Chapter 15 ਗੁਪਤ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Social Science History Chapter 15 ਗੁਪਤ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ
SST Guide for Class 6 PSEB ਗੁਪਤ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ Textbook Questions and Answers
ਅਭਿਆਸ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ
I. ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨਾਂ ਦੇ ਉੱਤਰ ਲਿਖੋ :
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਸਮੁਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਦੀਆਂ ਜਿੱਤਾਂ ਦਾ ਵਰਣਨ ਕਰੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਸਮੁਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਇੱਕ ਮਹਾਨ ਜੇਤੂ ਸੀ । ਉਸ ਦੀਆਂ ਮੁੱਖ ਜਿੱਤਾਂ ਦਾ ਵਰਣਨ ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਹੈ-
- ਸਮੁਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਨੇ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਉੱਤਰੀ ਭਾਰਤ (ਆਰੀਆਵਰਤ) ਤੋਂ ਆਏ ਤਿੰਨ ਰਾਜਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਹਰਾਇਆ ਅਤੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ ਗੁਪਤ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਲਾ ਲਿਆ ।
- ਸਮੁਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਦੀ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡੀ ਜਿੱਤ ਦੱਖਣੀ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਜਿੱਤ ਸੀ । ਉਸ ਨੇ ਦੱਖਣ ਦੇ 12 ਰਾਜਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਹਰਾਇਆ, ਪਰ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਅਧੀਨਤਾ ਸਵੀਕਾਰ ਕਰਨ ਤੇ ਉਸ ਨੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਰਾਜ ਵਾਪਸ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤੇ ।
- ਕੁਝ ਜੰਗਲੀ ਜਾਤੀਆਂ ਨੇ ਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਅਸ਼ਾਂਤੀ ਫੈਲਾ ਰੱਖੀ ਸੀ । ਇਹ ਜਾਤੀਆਂ ਆਮ ਤੌਰ ‘ਤੇ ਉੜੀਸਾ ਦੇ ਜੰਗਲਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਰਹਿੰਦੀਆਂ ਸਨ । ਸਮੁਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਨੇ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਜਾਤੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਯੁੱਧ ਵਿੱਚ ਹਰਾ ਕੇ ਸ਼ਾਂਤੀ ਸਥਾਪਤ ਕੀਤੀ ।
ਅਸਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਮੁਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਨੇ ਫ਼ਰਾਂਸ ਦੇ ਸ਼ਾਸਕ ਅਤੇ ਸੈਨਾਪਤੀ ਨੈਪੋਲੀਅਨ ਵਾਂਗ ਅਨੇਕਾਂ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ‘ਤੇ ਜਿੱਤ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਕੀਤੀ । ਇਸੇ ਲਈ ਉਸ ਨੂੰ ‘ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਨੈਪੋਲੀਅਨ` ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਵਿਕਰਮਾਦਿੱਤਿਆ ਬਾਰੇ ਤੁਸੀਂ ਕੀ ਜਾਣਦੇ ਹੋ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਵਿਕਰਮਾਦਿੱਤਿਆ ਸਮੁਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਦਾ ਪੁੱਤਰ ਸੀ ।ਉਸਨੂੰ ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਦੂਜਾ ਵੀ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਉਹ ਗੁਪਤ ਵੰਸ਼ ਦਾ ਇਕ ਪ੍ਰਤਾਪੀ ਰਾਜਾ ਸੀ । ਉਸਨੇ ਲਗਪਗ 380 ਈ: ਤੋਂ 412 ਈ: ਤੱਕ ਰਾਜ ਕੀਤਾ ।
- ਉਸਨੇ ਪੱਛਮੀ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਸ਼ਕਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਹਰਾਇਆ । ਉਸਨੇ ਆਪਣੀ ਸੈਨਿਕ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਆਪਣੇ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ ਅਰਬ ਸਾਗਰ ਤੱਕ ਵਧਾਇਆ ਅਤੇ ਸੌਰਾਸ਼ਟਰ ਤੇ ਕਾਠੀਆਵਾੜ ਨੂੰ ਜਿੱਤਿਆ ।
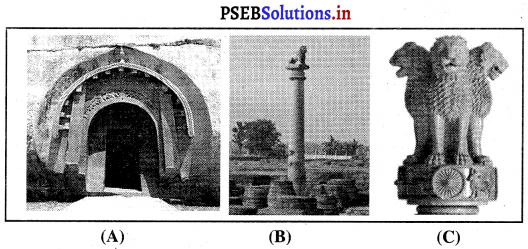
- ਉਸਨੇ ਦਿੱਲੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਕੁਤੁਬਮੀਨਾਰ ਦੇ ਕੋਲ ਲੋਹੇ ਦਾ ਵਿਸ਼ਾਲ ਸਤੰਭ ਬਣਵਾਇਆ, ਜਿਸ ‘ਤੇ ਲਿਖੇ ਲੇਖ ਵਿੱਚ ਉਸ ਦੀਆਂ ਸਫਲਤਾਵਾਂ ਦਾ ਵਰਣਨ ਹੈ ।
- ਉਸਨੇ ਕਲਾ ਅਤੇ ਸਾਹਿਤ ਨੂੰ ਉਤਸ਼ਾਹ ਦਿੱਤਾ । ਉਸਦੇ ਦਰਬਾਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਨੌਂ ਵਿਦਵਾਨ ਸਨ ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ‘ਨੌਂ ਰਤਨ’ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਸੀ ।
- ਉਹ ਧਾਰਮਿਕ ਦ੍ਰਿਸ਼ਟੀ ਤੋਂ ਬਹੁਤ ਸਹਿਣਸ਼ੀਲ ਸੀ । ਉਹ ਆਪ ਭਗਵਾਨ ਵਿਸ਼ਨੂੰ ਦਾ ਭਗਤ ਸੀ ਪਰ ਸਾਰੇ ਧਰਮਾਂ ਦਾ ਸਨਮਾਨ ਕਰਦਾ ਸੀ । ਉਸਨੇ ਵੱਡੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਸੋਨੇ, ਚਾਂਦੀ ਅਤੇ ਤਾਂਬੇ ਦੇ ਸਿੱਕੇ ਚਲਾਏ ।
- ਉਸਦੇ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਕਾਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਹੀ ਚੀਨੀ ਯਾਤਰੀ ਫ਼ਾਹਿਆਨ ਭਾਰਤ ਆਇਆ ਸੀ ।
- ਉਸਨੇ ਵਿਕਰਮਾਦਿੱਤਿਆ ਦੀ ਉਪਾਧੀ ਧਾਰਨ ਕੀਤੀ ਸੀ, ਜਿਸਦਾ ਅਰਥ ਹੈ ‘ਬਹਾਦਰੀ ਦਾ ਸੂਰਜ’ ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਕਾਲੀਦਾਸ ਬਾਰੇ ਇੱਕ ਨੋਟ ਲਿਖੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਕਾਲੀਦਾਸ ਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤ ਦੇ ਇੱਕ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਕਵੀ ਸਨ ।ਉਹ ਗੁਪਤ ਸਮਰਾਟ ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਵਿਕਰਮਾਦਿੱਤਿਆ ਦੇ ਦਰਬਾਰ ਦੇ ਨੌਂ ਰਤਨਾਂ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਇੱਕ ਸਨ । ਉਹਨਾਂ ਨੇ ਬਹੁਤ ਸਾਰੇ, ਨਾਟਕਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਕਵਿਤਾਵਾਂ ਦੀ ਰਚਨਾ ਕੀਤੀ । ਸ਼ਕੁੰਤਲਾ, ਰਘੂਵੰਸ਼, ਕੁਮਾਰ ਸੰਭਵ ਅਤੇ ਮੇਘਦੂਤ ਆਦਿ ਉਹਨਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਅਮਰ ਰਚਨਾਵਾਂ ਹਨ । ‘ਸ਼ਕੁੰਤਲਾ’ ਨਾਟਕ ਸੰਸਾਰ ਭਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਗੁਪਤ ਕਾਲ ਦੇ ਆਰਥਿਕ ਜੀਵਨ ਬਾਰੇ ਤੁਸੀਂ ਕੀ ਜਾਣਦੇ ਹੋ ? ਉੱਤਰ-ਗੁਪਤ ਕਾਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਰਥਿਕ ਜੀਵਨ ਬਹੁਤ ਖੁਸ਼ਹਾਲ ਸੀ ।
- ਟੈਕਸ ਬਹੁਤ ਘੱਟ ਸਨ ਅਤੇ ਰੋਜ਼ਾਨਾ ਜ਼ਰੁਰਤ ਦੀਆਂ ਵਸਤਾਂ ਬਹੁਤ ਸਸਤੀਆਂ ਸਨ । ਆਮ ਲੋਕ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਖ਼ਰੀਦਣ ਲਈ ਕੌਡੀਆਂ ਜਾਂ ਤਾਂਬੇ ਦੇ ਸਿੱਕਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਕਰਦੇ ਸਨ । ਪਰ ਇਸ ਕਾਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਧ ਸੋਨੇ ਦੇ ਸਿੱਕੇ ਚਲਾਏ ਗਏ । ਅਜਿਹੇ ਸਿੱਕਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਦੀਨਾਰ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਸਨ ।
- ਲੋਕਾਂ ਦਾ ਮੁੱਖ ਕਿੱਤਾ ਖੇਤੀਬਾੜੀ ਸੀ । ਕਈ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਅਨਾਜਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਇਲਾਵਾ ਫਲਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਤੇਲ-ਬੀਜਾਂ ਦੀ ਖੇਤੀ ਵੀ ਕੀਤੀ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਸੀ ।
- ਦੇਸੀ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਦੇਸ਼ੀ, ਦੋਹਾਂ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਦਾ ਵਪਾਰ ਉੱਨਤ ਸੀ । ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਦੱਖਣ-ਪੂਰਬੀ ਏਸ਼ੀਆ, ਚੀਨ, ਮੱਧ ਏਸ਼ੀਆ ਅਤੇ ਯੂਰਪੀ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਵਪਾਰਕ ਸੰਬੰਧ ਸਨ ।
- ਸ਼ਾਹੂਕਾਰਾਂ, ਵਪਾਰੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਉਤਪਾਦਕਾਂ ਦੇ ਆਪਣੇ-ਆਪਣੇ ਸੰਗਠਨ ਸਨ, ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ੇਣੀ ਜਾਂ ਨਿਗਮ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਸਨ ।
- ਪਸ਼ੂ-ਪਾਲਣ ਅਤੇ ਉਦਯੋਗਿਕ-ਧੰਦੇ ਹੋਰ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਕਿੱਤੇ ਸਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 5.
ਗੁਪਤ ਕਾਲ ਨੂੰ ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ‘ਸੁਨਹਿਰੀ ਯੁੱਗ’ ਕਿਉਂ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਗੁਪਤ ਕਾਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਜੀਵਨ ਦੇ ਹਰੇਕ ਖੇਤਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਬਹੁਤ ਉੱਨਤੀ ਹੋਈ ਸੀ, ਜਿਸ ਕਾਰਨ ਇਸਨੂੰ ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ‘ਸੁਨਹਿਰੀ ਯੁੱਗ’ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਗੁਪਤ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਦਾ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਪ੍ਰਬੰਧ ਬਹੁਤ ਵਧੀਆ ਸੀ । ਰਾਜਾ ਮੰਤਰੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਅਧਿਕਾਰੀਆਂ ਦੀ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਨਾਲ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਚਲਾਉਂਦਾ ਸੀ ।
- ਲੋਕ ਖ਼ੁਸ਼ਹਾਲ, ਸੁਖੀ ਅਤੇ ਇਮਾਨਦਾਰ ਸਨ । ਕਰ ਬਹੁਤ ਘੱਟ ਸਨ । ਰੋਜ਼ਾਨਾ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਚੀਜ਼ਾਂ ਬਹੁਤ ਸਸਤੀਆਂ ਸਨ । ਇਸ ਕਾਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਸੋਨੇ ਦੇ ਸਿੱਕੇ ਵੱਡੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਚਲਾਏ ਗਏ ।
- ਖੇਤੀਬਾੜੀ ਅਤੇ ਵਪਾਰ ਦਾ ਬਹੁਤ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਹੋਇਆ ਸੀ ।
- ਗੁਪਤ ਕਾਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਉੱਚ ਦਰਜੇ ਦੇ ਸਾਹਿਤ ਅਤੇ ਕਲਾ ਦੀ ਰਚਨਾ ਹੋਈ । ਸਾਹਿਤਕਾਰਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਕਲਾਕਾਰਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਰਾਜਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਸਰਪ੍ਰਸਤੀ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਸੀ ।
- ਸਾਰੇ ਧਰਮਾਂ ਦਾ ਸਨਮਾਨ ਕੀਤਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਸੀ । ਭਾਵੇਂ ਗੁਪਤ ਰਾਜੇ ਆਪ ਹਿੰਦੂ ਧਰਮ ਨੂੰ ਮੰਨਦੇ ਸਨ ਪਰ ਉਹ ਸਾਰੇ ਧਰਮਾਂ ਦੇ ਲੋਕਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਸਨਮਾਨ-ਪੂਰਵਕ ਵਿਵਹਾਰ ਕਰਦੇ ਸਨ | ਸਾਰੇ ਲੋਕਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪੂਰੀ ਧਾਰਮਿਕ ਸੁਤੰਤਰਤਾ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਸੀ ।
- ਗੁਪਤ ਕਾਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਿਗਿਆਨ ਅਤੇ ਤਕਨੀਕ ਦਾ ਬਹੁਤ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਹੋਇਆ ਸੀ । ਆਰੀਆ ਭੱਟ, ਵਰਾਹਮਿਹਿਰ, ਬ੍ਰਹਮਗੁਪਤ ਅਤੇ ਬਾਣਭੱਟ ਇਸ ਕਾਲ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਵਿਗਿਆਨੀ ਸਨ ।
- ਸਿੱਖਿਆ ਦੇ ਖੇਤਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੀ ਬਹੁਤ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਹੋਇਆ ਸੀ । ਬ੍ਰਾਹਮਣ ਅਤੇ ਭਿਕਸ਼ੂ ਅਧਿਆਪਕ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਸਨ ਜਿਹੜੇ ਆਮ ਤੌਰ ‘ਤੇ ਮੰਦਰਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਮੱਠਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਿੱਖਿਆ ਦਿੰਦੇ ਸਨ । ਤਕਸ਼ਿਲਾ, ਸਾਰਨਾਥ` ਅਤੇ ਨਾਲੰਦਾ ਗੁਪਤ ਕਾਲ ਦੇ ਵਿਸ਼ਵਵਿਦਿਆਲੇ ਸਨ ।
- ਗੁਪਤ ਕਾਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਸਭਿਆਚਾਰ ਅਤੇ ਸਭਿਅਤਾ ਦਾ ਵਿਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਪ੍ਰਚਾਰ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ।
II. ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਵਾਕਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਖ਼ਾਲੀ ਥਾਂਵਾਂ ਭਰੋ :
(1) ਸਮੁਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਇਕ ………………………. ਅਤੇ …………………… ਸੀ ।
(2) ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਦੂਜੇ ਨੇ ਬਹੁਤ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਵਿਚ ……………………, ………………….. ਅਤੇ …………………… ਦੇ ਸਿੱਕੇ ਜਾਰੀ ਕੀਤੇ ।
(3) ਗੁਪਤ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਕਈ ਸੂਬਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਵੰਡਿਆ ਹੋਇਆ ਸੀ, ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ …………………………… ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਸਨ ।
(4) ਗੁਪਤਕਾਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਜ਼ਿਲ੍ਹਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ……………………… ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਸਨ ।
(5) ਕਾਲੀਦਾਸ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਲਿਖਿਆ ਨਾਟਕ …………………………. ਅਤੇ ਕਾਵਿ …………………… ਬਹੁਤ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਹਨ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(1) ਮਹਾਨ ਯੋਧਾ, ਸ਼ਾਸਕ
(2) ਸੋਨੇ, ਚਾਂਦੀ
(3) ਭੁਕਤੀ
(4) ਵਿਸ਼
(5) ਸ਼ਕੁੰਤਲਾ, ਮੇਘਦੂਤ ।
![]()
III. ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਵਾਕਾਂ ਦੇ ਸਹੀ ਜੋੜੇ ਬਣਾਓ :
| (1) ਆਰੀਆਵਤ | (ਉ) ਪੰਜਾਬ |
| (2) ਮੁਕ | (ਅ) ਉੱਤਰੀ ਭਾਰਤ |
| (3) ਲੋਹ-ਸਤੰਭ | (ੲ) ਇੱਕ ਅਫ਼ਸਰ |
| (4) ਕੁਮਾਰਾਮਾਤਯ | (ਸ) ਦਿੱਲੀ |
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਸਹੀ ਜੋੜੇ-
| (1) ਆਰੀਆਵਤ | (ਅ) ਉੱਤਰੀ ਭਾਰਤ |
| (2) ਮੁਕ | (ਉ) ਪੰਜਾਬ |
| (3) ਲੋਹ-ਸਤੰਭ | (ਸ) ਦਿੱਲੀ |
| (4) ਕੁਮਾਰਾਮਾਤਯ | (ੲ) ਇੱਕ ਅਫ਼ਸਰ |
IV. ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਵਾਕਾਂ ਦੇ ਸਾਹਮਣੇ ਸਹੀ (√) ਇੱਕ ਅਫ਼ਸਰ ) ਜਾਂ ਗ਼ਲਤ (×) ਦਾ ਨਿਸ਼ਾਨ ਲਗਾਓ :
(1) ਮਹਾਰਾਜ ਗੁਪਤ, ਗੁਪਤ ਵੰਸ਼ ਦਾ ਪਹਿਲਾ ਰਾਜਾ ਸੀ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(√)
(2) ਵਿਕਰਮਾਦਿੱਤਿਆ ਨੇ ਸਮੁਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਦੀ ਉਪਾਧੀ ਧਾਰਨ ਕੀਤੀ ਸੀ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(×)
(3) ਯੌਧੇਅ ਦੱਖਣੀ ਭਾਰਤ ‘ਤੇ ਰਾਜ ਕਰਦੇ ਸਨ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(×)
(4) ਫ਼ਾਹਿਯਾਨ ਯੂਨਾਨੀ ਲੇਖਕ ਸੀ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(×)
![]()
(5) ਗੁਪਤ ਰਾਜਿਆਂ ਨੇ ਸੋਨੇ ਦੇ ਸਿੱਕੇ ਜਾਰੀ ਕੀਤੇ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(√)
(6) ਆਰੀਆਭੱਟ ਇੱਕ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਵਿਗਿਆਨੀ ਸੀ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(√)
PSEB 6th Class Social Science Guide ਗੁਪਤ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ Important Questions and Answers
ਵਸਤੂਨਿਸ਼ਠ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ
ਘੱਟ ਤੋਂ ਘੱਟ ਸ਼ਬਦਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਉੱਤਰ ਵਾਲੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਗੁਪਤਵੰਸ਼ ਦੇ ਪਹਿਲੇ ਮਹਾਨ ਸ਼ਾਸਕ ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਪ੍ਰਧਾਨ ਨੇ ਇਕ ਲਿਚਛਵੀ ਰਾਜ ‘ਕੁਮਾਰੀ ਨਾਲ ਵਿਆਹ ਕੀਤਾ ਸੀ । ਉਸਦਾ ਕੀ ਨਾਂ ਸੀ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਕੁਮਾਰ ਦੇਵੀ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਸਮੁਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਦੀਆਂ ਉਪਲੱਬਧੀਆਂ ਨਾਲ ਜੁੜੇ ਇਲਾਹਾਬਾਦ ਸਤੰਬ ਦਾ ਲੇਖਕ ਕੌਣ ਸੀ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਹਰੀਸ਼ੇਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਮਹਿਰੌਲੀ ਵਿਚ ਕੁਤੁਬਮੀਨਾਰ ਦੇ ਨੇੜੇ ਸਥਿਤ ਲੋਹ-ਸਤੰਬ ਇਤਿਹਾਸ ਵਿਚ ਕਿਹੜੇ ਰਾਜਵੰਸ਼ ਦੇ ਕਾਲ ਵਿਚ ਬਣਿਆ ਸੀ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਗੁਪਤ ਵੰਸ਼ ।
ਬਹੁ-ਵਿਕਲਪੀ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਗੁਪਤ ਵੰਸ਼ ਦੇ ਪਤਨ ਵਿਚ ਹੇਠਾਂ ਲਿਖਿਆਂ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਕਿਹੜੇ ਹਮਲਾਵਰਾਂ ਦੀ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ ਭੂਮਿਕਾ ਰਹੀ ?
(ਉ) ਹੁਨ
(ਅ) ਮੰਗੋਲ
(ੲ) ਆਰੀਆ
ਉੱਤਰ-
(ਉ) ਹੁਨ
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਅਜੰਤਾ ਦੀਆਂ ਗੁਫ਼ਾਵਾਂ ਆਪਣੀ ਕਿਹੜੀ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ਤਾ ਦੇ ਲਈ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਹਨ ?
(ਉ) ਸੁੰਦਰ ਢਿੱਤੀ-ਚਿੱਤਰ
(ਅ) ਹਿੰਦੂ ਦੇਵੀ-ਦੇਵਤਾਵਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਮੂਰਤੀਆਂ
(ੲ) ਵਿਸ਼ਾਲ ਤੋਰਨ ਦਵਾਰ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(ਉ) ਸੁੰਦਰ ਢਿੱਤੀ-ਚਿੱਤਰ
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਕਾਲੀਦਾਸ ਨੇ ਮੇਘਦੂਤ ਅਤੇ ਸ਼ਕੁੰਤਲਾ ਵਰਗੇ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਗ੍ਰੰਥਾਂ ਦੀ ਰਚਨਾ ਕੀਤੀ । ਉਹ ਹੇਠਾਂ ਲਿਖਿਆਂ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਕਿਹੜੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ ਦਾ ਕਵੀ ਸੀ ?
(ਉ) ਬ੍ਰਜ
(ਅ) ਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤ
(ੲ) ਪਾਲੀ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(ੲ) ਪਾਲੀ ।
ਬਹੁਤ ਛੋਟੇ ਉੱਤਰਾਂ ਵਾਲੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਗੁਪਤ ਵੰਸ਼ ਦੀ ਜਾਣਕਾਰੀ ਦੇਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਚਾਰ ਸਰੋਤਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਂ ਦੱਸੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਗੁਪਤ ਵੰਸ਼ ਦੀ ਜਾਣਕਾਰੀ ਦੇਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਚਾਰ ਸਰੋਤ ਹਨ-
- ਪੁਰਾਣ,
- ਕਾਲੀਦਾਸ ਦੇ ਨਾਟਕ,
- ਚੀਨੀ ਯਾਤਰੀ ਸ਼ਾਹਿਬਾਨ ਦਾ ਬਿਰਤਾਂਤ,
- ਸ਼ਿਲਾਲੇਖ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਗੁਪਤ ਵੰਸ਼ ਦਾ ਪਹਿਲਾ ਸੁਤੰਤਰ ਰਾਜਾ ਕੌਣ ਸੀ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਗੁਪਤ ਵੰਸ਼ ਦਾ ਪਹਿਲਾ ਸੁਤੰਤਰ ਰਾਜਾ ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਪਹਿਲਾ ਸੀ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਪਹਿਲੇ ਨੇ ਕਿਹੜੇ ਰਾਜਵੰਸ਼ ਨਾਲ ਵਿਆਹ ਸੰਬੰਧ ਬਣਾਏ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਪਹਿਲੇ ਨੇ ਸਿੱਛਵੀ ਵੰਸ਼ ਨਾਲ ਵਿਆਹ ਸੰਬੰਧ ਬਣਾਏ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਪਹਿਲੇ ਦਾ ਰਾਜਕਾਲ ਦੱਸੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਪਹਿਲੇ ਦਾ ਰਾਜਕਾਲ 319 ਈ: ਤੋਂ 335 ਈ: ਤੱਕ ਸੀ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 5.
ਸਮੁਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਰਾਜਗੱਦੀ ‘ਤੇ ਕਦੋਂ ਬੈਠਾ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਸਮੁਦਰਗੁਪਤ 335 ਈ: ਵਿੱਚ ਰਾਜਗੱਦੀ ‘ਤੇ ਬੈਠਾ ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 6.
ਸਮੁਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਨੇ ਕਿਹੜੇ ਨਾਗ ਰਾਜਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਹਰਾਇਆ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਸਮੁਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਨੇ ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨਾਗ ਰਾਜਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਹਰਾਇਆ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਂ ਸਨਅਚਯੁਤ ਨਾਗ, ਨਾਗਸੈਨ ਅਤੇ ਗਣਪਤੀ ਨਾਗ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 7.
ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਨੈਪੋਲੀਅਨ ਕਿਹੜੇ ਰਾਜੇ ਨੂੰ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਸਮੁਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਨੂੰ ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਨੈਪੋਲੀਅਨ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 8.
ਸਮੁਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਨੇ ਕਿਹੜੇ ਵਿਦੇਸ਼ੀ ਰਾਜੇ ਨਾਲ ਮਿੱਤਰਤਾ ਕੀਤੀ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਸਮੁਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਨੇ ਸ੍ਰੀ ਲੰਕਾ ਦੇ ਰਾਜੇ ਮੇਘਵਰਮਨ ਨਾਲ ਮਿੱਤਰਤਾ ਕੀਤੀ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 9.
ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਵਿਕਰਮਾਦਿੱਤਿਆ ਦਾ ਰਾਜਕਾਲ ਦੱਸੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਵਿਕਰਮਾਦਿੱਤਿਆ ਦਾ ਰਾਜਕਾਲ 380 ਈ: ਤੋਂ 412 ਈ: ਤੱਕ ਸੀ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 10.
ਪੰਚਤੰਤਰ ਦਾ ਲੇਖਕ ਕੌਣ ਸੀ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਪੰਚਤੰਤਰ ਦਾ ਲੇਖਕ ਵਿਸ਼ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ਰਮਾ ਸੀ ।
![]()
ਛੋਟੇ ਉੱਤਰਾਂ ਵਾਲੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਪਹਿਲੇ ਦੀਆਂ ਜਿੱਤਾਂ ਬਾਰੇ ਲਿਖੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਪਹਿਲੇ ਨੇ ਸਿੱਛਵੀ ਵੰਸ਼ ਦੀ ਰਾਜਕੁਮਾਰੀ ਦੇਵੀ ਨਾਲ ਵਿਆਹ ਕੀਤਾ । ਲਿੱਛਵੀ ਵੰਸ਼ ਰਾਜਨੀਤਿਕ ਤੌਰ ‘ਤੇ ਸ਼ਕਤੀਸ਼ਾਲੀ ਸੀ । ਇਸ ਵੰਸ਼ ਦੀ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਨਾਲ ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਪਹਿਲੇ ਨੇ ਮਗਧ, ਬਿਹਾਰ ਅਤੇ ਇਲਾਹਾਬਾਦ ਦੇ ਨੇੜਲੇ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਜਿੱਤ ਲਿਆ ਉਸ ਨੇ ਆਪਣੇ ਨਾਂ ‘ਤੇ ਇੱਕ ਸੰਵਤ ਵੀ ਚਲਾਇਆ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਸਮੁਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਦੀ ਕਲਾ ਦੇ ਖੇਤਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਕੀ ਦੇਣ ਸੀ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਸਮੁਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਨੇ ਕਲਾ ਅਤੇ ਸਾਹਿਤ ਨੂੰ ਪੂਰੀ ਸੁਰੱਖਿਆ ਦਿੱਤੀ । ਉਸਨੂੰ ਸੰਗੀਤ ਨਾਲ ਬਹੁਤ ਲਗਾਓ ਸੀ । ਉਸ ਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਕੁਝ ਸਿੱਕਿਆਂ ‘ਤੇ ਉਸ ਨੂੰ ਵੀਣਾ ਵਜਾਉਂਦੇ ਹੋਏ ਦਿਖਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ । ਹਰੀਸ਼ੇਨ ਉਸ ਦਾ ਦਰਬਾਰੀ ਕਵੀ ਸੀ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਗੁਪਤ ਕਾਲ ਦੀ ਵਿਗਿਆਨਿਕ ਉੱਨਤੀ ਦਾ ਵੇਰਵਾ ਦਿਓ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਗੁਪਤ ਕਾਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਿਗਿਆਨ ਦੇ ਖੇਤਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਬਹੁਤ ਉੱਨਤੀ ਹੋਈ । ਆਰੀਆ ਭੱਟ ਇਸ ਕਾਲ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਜੋਤਸ਼ੀ ਅਤੇ ਗਣਿਤ ਦਾ ਵਿਦਵਾਨ ਸੀ । ਉਸ ਨੇ ਸੰਸਾਰ ਨੂੰ ਸਿਫ਼ਰ ਅਤੇ ਸੂਰਜ ਗ੍ਰਹਿਣ ਦੀ ਜਾਣਕਾਰੀ ਦਿੱਤੀ । ਮਗੁਪਤ ਗਣਿਤ ਅਤੇ ਬੀਜ ਗਣਿਤ ਦਾ ਵਿਦਵਾਨ ਸੀ । ਵਰਾਹਮਿਹਿਰ ਬਨਸਪਤੀ ਵਿਗਿਆਨ ਅਤੇ ਭੂਗੋਲ ਦਾ ਵਿਦਵਾਨ ਸੀ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਸਮੁਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਦੀਆਂ ਦੱਖਣੀ ਜਿੱਤਾਂ ਬਾਰੇ ਲਿਖੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਸਮੁਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਦੀ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਮਹਾਨ ਜਿੱਤ ਦੱਖਣੀ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਜਿੱਤ ਸੀ । ਉਸ ਨੇ ਦੱਖਣੀ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ 12 ਰਾਜਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਹਰਾਇਆ | ਉਸ ਨੇ ਉੱਤਰੀ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਾਰੇ ਜਿੱਤੇ ਹੋਏ ਦੋਸ਼ਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਆਪਣੇ ਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਲਾਇਆ ਸੀ ਪਰ ਦੱਖਣ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਸਾਰੇ ਜਿੱਤੇ ਹੋਏ ਦੇਸ਼ ਉਸ ਨੇ ਉੱਥੋਂ ਦੇ ਰਾਜਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਵਾਪਸ ਦੇ ਦਿੱਤੇ । ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਉਹ ਕੇਵਲ ਕਰ ਵਸੂਲ ਕਰਦਾ ਸੀ ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 5.
ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਦੂਜੇ ਦੇ ਦੂਜੇ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਸੰਬੰਧਾਂ ਦੀ ਜਾਣਕਾਰੀ ਦਿਓ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਨੇ ਇੱਕ ਸ਼ਕਤੀਸ਼ਾਲੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਦੀ ਸਥਾਪਨਾ ਕਰਕੇ ਵਿਕਰਮਾਦਿੱਤਿਆ ਦੀ ਉਪਾਧੀ ਧਾਰਨ ਕੀਤੀ । ਉਸਨੇ ਆਪਣੇ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਗੁਆਂਢੀ ਰਾਜਿਆਂ ਨਾਲ ਵਿਆਹ ਸੰਬੰਧ ਸਥਾਪਤ ਕੀਤੇ । ਉਸਨੇ ਆਪਣੀ ਪੁੱਤਰੀ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵਤੀ ਦਾ ਵਿਆਹ ਵਾਕਾਟਕ ਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਰਾਜਕੁਮਾਰ ਰੁਦਰਸੇਨ ਦੂਜੇ ਨਾਲ ਕੀਤਾ | ਪਰ ਬਦਕਿਸਮਤੀ ਨਾਲ ਰੁਦਰਸੇਨ ਦੂਜੇ ਦੀ ਜਲਦੀ ਹੀ ਮੌਤ ਹੋ ਗਈ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਨੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵਤੀ ਅਤੇ ਆਪਣੇ ਗੁਪਤ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਨਬਾਲਗ ਦੋਹਤਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਵਾਕਾਟਕ ਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ ਸੰਭਾਲਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਕੀਤੀ । ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਦੀ ਇਸ ਨੀਤੀ ਕਾਰਨ ਵਾਕਾਟਕ ਰਾਜ ਦੀ ਜਨਤਾ ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਦੀ ਅਹਿਸਾਨਮੰਦ ਹੋ ਗਈ । ਗੁਪਤ ਰਾਜਿਆਂ ਨੇ ਕੁੰਤਲ ਦੇ ਕਾਂਵ ਸ਼ਾਸਕ ਦੀਆਂ ਪੁੱਤਰੀਆਂ ਨਾਲ ਵੀ ਵਿਆਹ ਕੀਤੇ । ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਦੂਜੇ ਨੇ ਆਪਣੀ ਸਥਿਤੀ ਨੂੰ ਹੋਰ ਸ਼ਕਤੀਸ਼ਾਲੀ ਬਣਾ ਲਿਆ ।
ਵੱਡੇ ਉੱਤਰਾਂ ਵਾਲੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਫ਼ਾਹਿਆਨ ਦੇ ਬਿਰਤਾਂਤ ਦਾ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਵੇਰਵਾ ਦਿਓ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਫ਼ਾਰਿਆਨ ਇੱਕ ਚੀਨੀ ਯਾਤਰੀ ਸੀ । ਉਹ ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਵਿਕਰਮਾਦਿੱਤਿਆ ਦੇ ਰਾਜਕਾਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤ ਆਇਆ । ਉਹ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿਚ ਬੋਧੀ ਤੀਰਥ ਸਥਾਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਯਾਤਰਾ ਕਰਨ ਅਤੇ ਬੋਧੀ ਗ੍ਰੰਥਾਂ ਦੀ ਖੋਜ ਲਈ ਭਾਰਤ ਆਇਆ ਸੀ ।
ਉਸਨੇ ਆਪਣੇ ਬਿਰਤਾਂਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੀਆਂ ਗੱਲਾਂ ਦਾ ਵਰਣਨ ਕੀਤਾ ਹੈ-
- ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਵਿਕਰਮਾਦਿੱਤਿਆ ਦੇ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਬਾਰੇ – ਫ਼ਾਰਿਆਨ ਨੇ ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਵਿਕਰਮਾਦਿੱਤਿਆ ਦੇ ਉਦਾਰਵਾਦੀ ਰਾਜ ਪ੍ਰਬੰਧ ਦਾ ਵਰਣਨ ਕੀਤਾ ਹੈ । ਉਹ ਲਿਖਦਾ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਸਜ਼ਾ ਨਰਮ ਸੀ, ਫਿਰ ਵੀ ਅਪਰਾਧ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਸਨ । ਸੜਕਾਂ ਸੁਰੱਖਿਅਤ ਸਨ । ਰਾਜ ਪ੍ਰਬੰਧ ਨੂੰ ਸੁਚਾਰੂ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਚਲਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ ਪ੍ਰਾਂਤਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੰਡਿਆ ਹੋਇਆ ਸੀ | ਪ੍ਰਾਂਤਾਂ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਬੰਧ ਗਵਰਨਰਾਂ ਦੇ ਹੱਥ ਵਿੱਚ ਸੀ ।
- ਲੋਕਾਂ ਬਾਰੇ – ਫ਼ਾਹਿਆਨ ਦੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਗੁਪਤ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਲੋਕ ਖ਼ੁਸ਼ਹਾਲ, ਇਮਾਨਦਾਰ ਅਤੇ ਚੰਗੇ ਨਾਗਰਿਕ ਸਨ । ਉਹ ਕਾਨੂੰਨ ਦੀ ਪਾਲਣਾ ਕਰਦੇ ਸਨ । ਉਹਨਾਂ ਦਾ ਨੈਤਿਕ ਜੀਵਨ ਉੱਚਾ ਸੀ । ਲੋਕ ਮੁੱਖ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਕਾਹਾਰੀ ਸਨ । ਚੰਡਾਲਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਨਫ਼ਰਤ ਦੀ ਨਜ਼ਰ ਨਾਲ ਵੇਖਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਸੀ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਉਹ ਨਗਰ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਹਰ ਰਹਿੰਦੇ ਸਨ ।
- ਧਰਮ ਬਾਰੇ – ਫ਼ਾਹਿਆਨ ਦੇ ਬਿਰਤਾਂਤ ਤੋਂ ਪਤਾ ਲੱਗਦਾ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਗੁਪਤ ਕਾਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਬੁੱਧ ਧਰਮ ਬਹੁਤ ਵਿਕਸਿਤ ਸੀ । ਪਰ ਗੁਪਤ ਸ਼ਾਸਕ ਆਪ ਹਿੰਦੂ ਧਰਮ ਨੂੰ ਮੰਨਦੇ ਸਨ । ਉਹ ਵਿਸ਼ਨੂੰ ਦੇ ਪੁਜਾਰੀ ਸਨ | ਪਰ ਉਹ ਦੂਜੇ ਧਰਮਾਂ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਉਦਾਰਵਾਦੀ ਸਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਗੁਪਤ ਕਾਲ ਦੇ ਸਾਹਿਤ ਦੀ ਜਾਣਕਾਰੀ ਦਿਓ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਗੁਪਤ ਕਾਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਰਾਜ ਦਰਬਾਰ ਦੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ ਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤ ਸੀ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ ਅਤੇ ਸਾਹਿਤ ਨੇ ਇਸ ਕਾਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ ਉੱਨਤੀ ਕੀਤੀ ।
- ਇਸ ਕਾਲ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਲੇਖਕ ਕਾਲੀਦਾਸ ਨੇ ਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਅਨੇਕਾਂ ਨਾਟਕ ਅਤੇ ਕਵਿਤਾਵਾਂ ਲਿਖੀਆਂ । ਸ਼ਕੁੰਤਲਾ, ਰਘੂਵੰਸ਼, ਮੇਘਦੂਤ ਅਤੇ ਰਿਤੁਸੰਹਾਰ ਉਹਨਾਂ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਲਿਖੇ ਗਏ ਮੁੱਖ ਨਾਟਕ ਹਨ । ਕਾਲੀਦਾਸ, ਚੰਦਰਗੁਪਤ ਦੂਜੇ ਦੇ ਨੌਂ ਰਤਨਾਂ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਇੱਕ ਸਨ । ਉਹਨਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਸ਼ੈਕਸਪੀਅਰ ਵੀ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਸਮੁਦਰ ਗੁਪਤ ਦੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਹਰੀਸ਼ਨ ਇੱਕ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਸਾਹਿਤਕਾਰ ਸੀ ।
- ਵਿਸ਼ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ਰਮਾ ਦਾ ਪੰਚਤੰਤਰ, ਵਿਸ਼ਾਖਦੱਤ ਦਾ ਮੁਦਰਾਖਸ਼ਸ਼ ਅਤੇ ਅਮਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦਾ ਅਮਰਕੋਸ਼ ਵੀ ਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ ਦੀਆਂ ਅਨਮੋਲ ਰਚਨਾਵਾਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਗੁਪਤਕਾਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਨਾਲੰਦਾ, ਸਾਰਨਾਥ, ਤਕਸ਼ਿਲਾ, ਪਾਟਲੀਪੁੱਤਰ, ਬਨਾਰਸ, ਮਥੁਰਾ ਆਦਿ ਸਿੱਖਿਆ ਦੇ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਨ ਕੇਂਦਰ ਸਨ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਕੇਂਦਰਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਾਹਿਤ, ਧਰਮ, ਦਰਸ਼ਨ, ਵੇਦਾਂ ਆਦਿ ਦੀ ਸਿੱਖਿਆ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਸੀ।