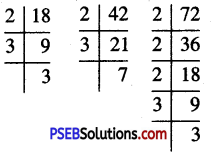
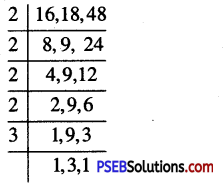
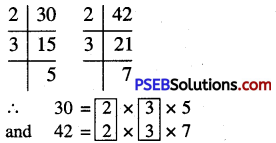
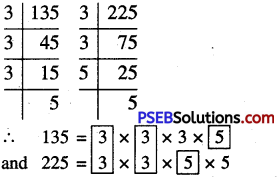
Punjab State Board PSEB 6th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 4 Integers Ex 4.1 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 4 Integers Ex 4.1
1. Write two examples from day-to-day life in which we can use positive and negative integers.
Solution:
1. If positive represents above sea level, then negative represents below sea level.
2. If positive represents a deposit, negative represents a withdrawal.
![]()
2. Write the opposite of the following:
Question (a)
A profit of ₹ 500
Solution:
A loss of ₹ 500
Question (b)
A withdrawal of ₹ 70 from bank account
Solution:
Deposit of ₹ 70 in bank account
Question (c)
A deposit of ₹ 1000
Solution:
Withdrawal of ₹ 1000
Question (d)
326 B.C
Solution:
326 AD
![]()
Question (e)
500 m below sea level
Solution:
500 m above sea level
Question (f)
25° above 0°C.
Solution:
25° below 0°C.
3. Represent the situations mentioned in integers.
Solution:
(a) + 500
(b) – 70
(c) + 1000
(d) – 326
(e) – 500 m
(f) + 25.
4. Represent the following situations in integers.
Question (a)
A deposit of ₹ 500.
Solution:
+ 500
![]()
Question (b)
An Aeroplane is flying at a height two thousand metre above the sea level.
Solution:
+ 2000
Question (c)
A withdrawal of ₹ 700 from Bank Account.
Solution:
– 700
Question (d)
A diver dives to a depth of 6 feet below ground level.
Solution:
– 6.
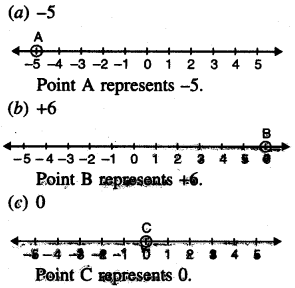
5. Represent the following numbers on number line.
Question (i)
(a) – 5
(b) + 6
(c) o
(d) + 1
(e) – 9
(f) – 4
(g) + 8
(h) + 3.
Solution:
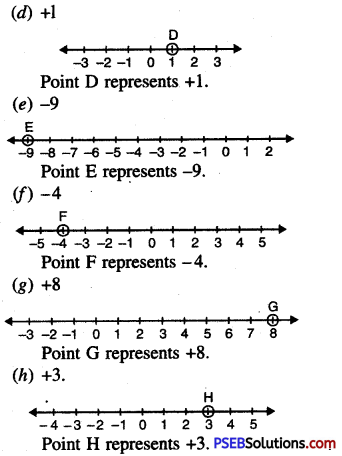
![]()
6. Integers are represented on a horizontal number line as shown where A represents – 2. With reference to the number line, answer the following questions:
![]()
(a) Which point represent – 3?
(b) Locate the point which represents the opposite of B and name it P.
(c) Write integers for the points C and E.
(d) Which point marked on the number line has the least value?
Solution:
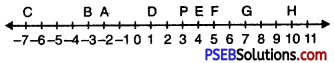
(a) Point B represents – 3.
(b) Point P represents + 3.
(c) Point C represents -7 and Point E represents + 4.
(d) Point C has the least value – 7.
7. In each of the following pairs, which number is to the right of other on the number line?
Question (i)
(a) 2 9
(b) -3, -8
(c) 0, -5
(d) -11, 10
(e) -9, 9
(f) 2, – 200.
Solution:
(a) 9
(b) – 3
(c) 0
(d) 10
(e) 9
(f) 2
![]()
8. Write all the integers between the given pairs (write them in increasing order)
Question (a)
0 and -6
Solution:
-5, -4, -3, -2, -1
Question (b)
-6 and +6
Solution:
-5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
Question (c)
-9 and -17
Solution:
-16, -15, -14, -13, -12, -11, -10
Question (d)
-19 and -5.
Solution:
-18, -17, -16, -15, -14, -13, -12, -11, -10, -9, -8, -7, -6.
9.
Question (a)
Write five negative integers greater than ‘-15’.
Solution:
Five negative integers greater than ‘-15’ are:
-14, -13, -12, -11, -10
![]()
Question (b)
Write five integers smaller than ‘-20’.
Solution:
Five integers smaller than ‘-20’ are:
-21, -22, -23, -24, -25
Question (c)
Write five integers greater than 0.
Solution:
Five integers greater than 0 are:
1,2, 3, 4, 5
Question (d)
Write five integers smaller than 0.
Solution:
Five integers smaller than 0 are:
-1, -2, -3, -4, -5.
10. Encircle the greater integer in each given pair.
(a) -5, -7
(b) 0,-3
(e) 5, 7
(d) -9, 0
(e) -9, -11
(f) -4, 4
(g) -10, -100
(h) 10, 100.
Solution:
(a) -5
(b) 0
(c) 7
(d) 0
(e) -9
(f) 4
(g) -10
(h) 100.
![]()
11. Arrange the following integers in ascending order:
Question (a)
0, -7, -9, 5, -3, 2, -4
Solution:
Ascending order of given integers is:
-9, -7, -4, -3, 0, 2, 5
Question (b)
8, -3, 7, 0, -9, -6.
Solution:
Ascending order of given integers is:
-9, -6, -3, 0, 7, 8.
12. Arrange the following integers in descending order:
Question (a)
-9, 3, 4, -6, 8, -3
Solution:
8, 4, 3, -3 -6, -9
![]()
Question (b)
4, 8,-3,-2, 5, 0.
Solution:
8, 5, 4, 0, -2, -3.