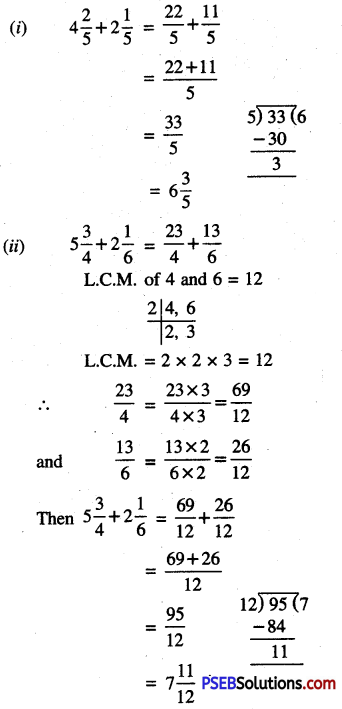
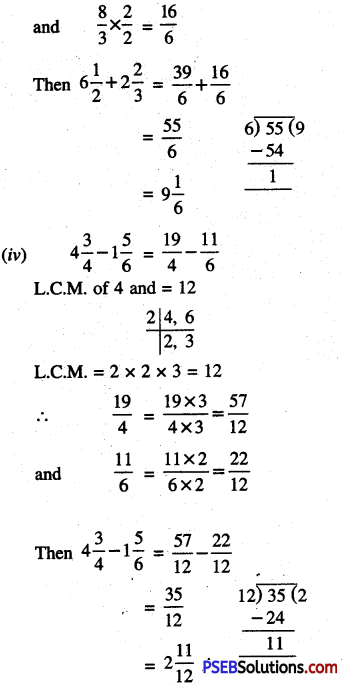
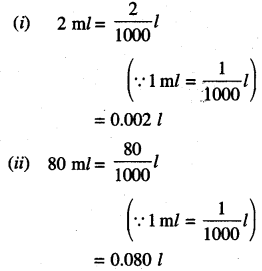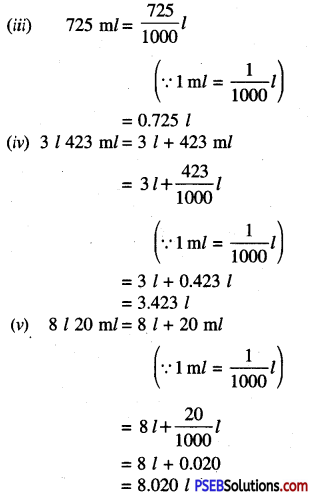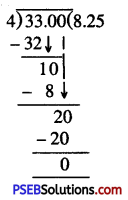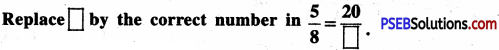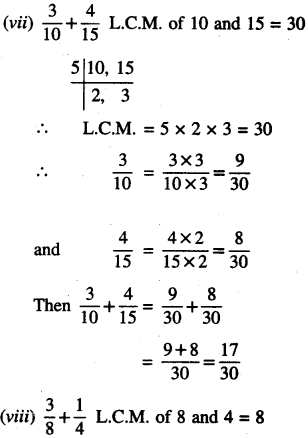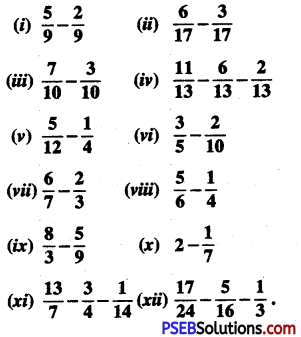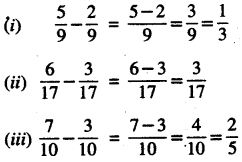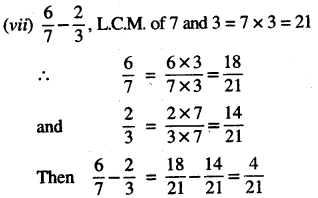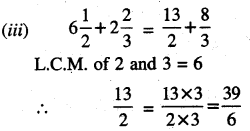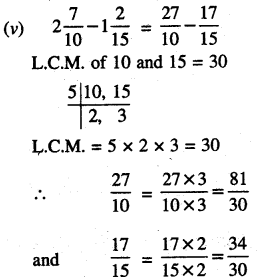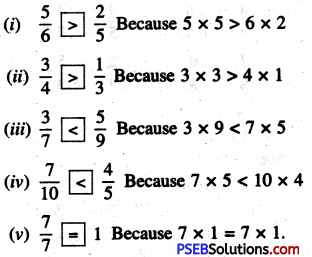Punjab State Board PSEB 6th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 6 Decimals Ex 6.3 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 6 Decimals Ex 6.3
1. Express as rupee using decimals:
Question (i)
35 paise
Solution:
35 paise = ₹ \(\frac {35}{100}\)
= ₹ 0.35
(∵ 1 paise = ₹ \(\frac {1}{100}\))
![]()
Question (ii)
4 paise
Solution:
4 paise = ₹ \(\frac {4}{100}\)
= ₹ 0.04
(∵ 1 paise = ₹ \(\frac {1}{100}\))
Question (iii)
240 paise
Solution:
240 paise = ₹ \(\frac {240}{100}\)
= ₹ 2.40
(∵ 1 paise = ₹ \(\frac {1}{100}\))
Question (iv)
12 rupees 25 paise
Solution:
= (12 rupees) + 25 paise
= ₹ 12 + ₹ \(\frac {25}{100}\)
(∵ 1 paise = ₹ \(\frac {1}{100}\))
= ₹ 12 + ₹ 0.25
= ₹ 12.25
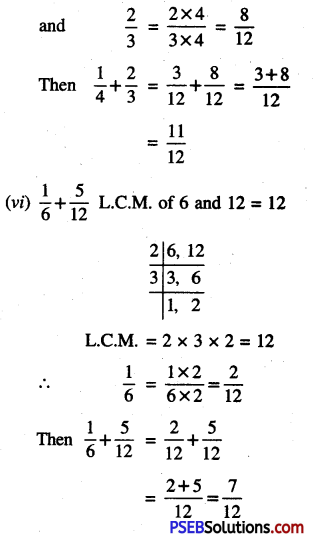
Question (v)
24 rupees 5 paise.
Solution:
(24 rupees) + (5 paise)
= ₹ 24 + ₹ \(\frac {5}{100}\)
(∵ 1 paise = ₹ \(\frac {1}{100}\))
= ₹ 24 + ₹ 0.05
= ₹ 24.05
![]()
2. Express as metre using decimals
Question (i)
5 cm
Solution:
5 cm = \(\frac {5}{100}\) m
= 0.05 m
(∵ 1cm =\(\frac {1}{100}\)m)
Question (ii)
62 cm
Solution:
62 cm = \(\frac {62}{100}\) m
= 0.62 m
(∵ 1cm =\(\frac {1}{100}\)m)
Question (iii)
135 cm
Solution:
135 cm = \(\frac {135}{100}\) m
= 1.35 m
(∵ 1cm =\(\frac {1}{100}\)m)
![]()
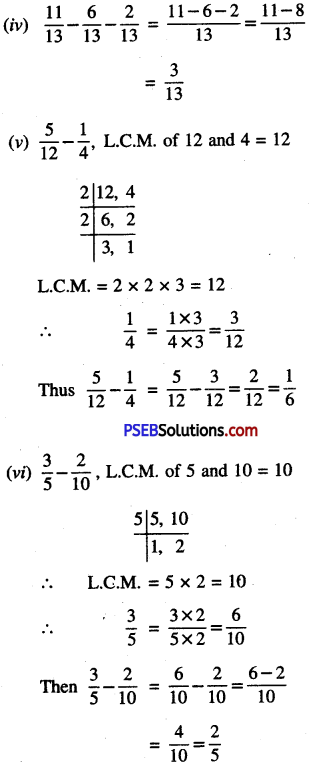
Question (iv)
5 m 20 cm
Solution:
= 5 m + 20 cm
(∵ 1cm = \(\frac {1}{100}\)m)
= 5m + 0.20m
= 5.20m
Question (v)
12 m 8 cm
Solution:
= 12 m + 8 cm
= 12 m + \(\frac {8}{100}\)m
(∵ 1cm = \(\frac {1}{100}\)m)
12 cm + 0.08 m
= 12.08 m
3. Express as centimetre using decimals:
Question (i)
2 mm
Solution:
2 mm = \(\frac {2}{10}\) cm
(∵ 1mm = \(\frac {1}{10}\)m)
= 0.2 cm
Question (ii)
28 mm
Solution:
28mm = \(\frac {28}{10}\)cm
(∵ 1mm = \(\frac {1}{10}\)m)
![]()
Question (iii)
8 cm 4 mm.
Solution:
8 cm 4 mm = 8 cm + 4 mm
= 8cm + \(\frac {4}{10}\)
= 8 cm + 0.4 cm
= 8.4 cm
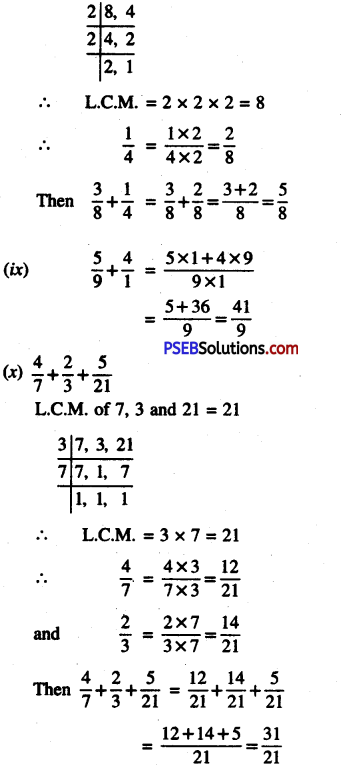
4. Express as kilometre using decimals:
Question (i)
7 m
Solution:
= \(\frac {7}{1000}\)
= (∵ 1m = \(\frac {1}{1000}\) km)
= 0.007 km
Question (ii)
50 m
Solution:
= \(\frac {50}{1000}\)
= (∵ 1m = \(\frac {1}{1000}\) km)
= 0.050 km
Question (iii)
425 m
Solution:
= \(\frac {425}{1000}\)
= (∵ 1m = \(\frac {1}{1000}\) km)
= 0.425 km
![]()
Question (iv)
2475 m
Solution:
= \(\frac {2475}{1000}\) km
= (∵ 1m = \(\frac {1}{1000}\) km)
= 2.475 km
Question (v)
3 km 225 m.
Solution:
= 3 km + 225 m
= 3 km + \(\frac {225}{1000}\)
= (∵ 1m = \(\frac {1}{1000}\) km)
= 3.225 km
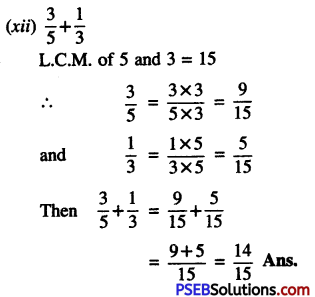
5. Express as kilogram using decimals:
Question (i)
5g
Solution:
5g = \(\frac {5}{1000}\)
= (∵ 1g = \(\frac {1}{1000}\) km)
= 0.005 kg
Question (ii)
75g
Solution:
75g = \(\frac {75}{1000}\)
= (∵ 1g = \(\frac {1}{1000}\) km)
= 0.075 kg
![]()
Question (iii)
423 g
Solution:
423 g = \(\frac {423}{1000}\)
= (∵ 1g = \(\frac {1}{1000}\) km)
= 0.423 kg
Question (iv)
1265 g
Solution:
1265 g = \(\frac {1265}{1000}\)
(∵ 1g = \(\frac {1}{1000}\) km)
= 1.265 kg
Question (v)
5 kg 418 g.
Solution:
= 5 kg + 418 g.
= 5 kg + \(\frac {418}{1000}\)
(∵ 1g = \(\frac {1}{1000}\) km)
= 5 kg + 0.418 kg
= 5.418 kg.
![]()
6. Express as litre using decimals:
(i) 2 ml
(ii) 80 ml
(iii) 725 ml
(iv) 3l 423 ml
(v) 8l 20 ml.
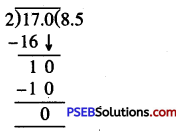
Solution: