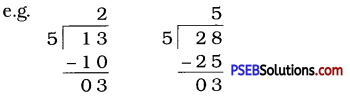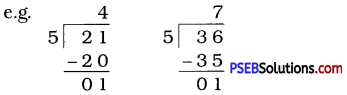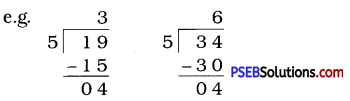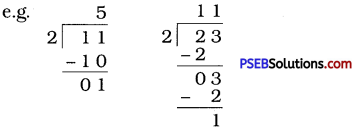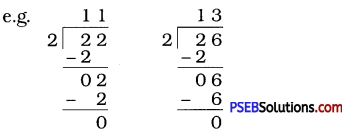Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 16 Playing with Numbers InText Questions and Answers.
PSEB 8th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 16 Playing with Numbers InText Questions
Try These : [Textbook Page No. 250]
1. Write the following numbers in generalised form:
Question (i)
- 25
- 73
- 129
- 302
Solution:
- 25 = 10 × 2 + 5 [ ∵ ab = 10a + b]
- 73 = 10 × 7 + 3 [ ∵ ab = 10a + b]
- 129 = 100 × 1 + 10 × 2 + 9 [ ∵ abc = 100a + 10b + c]
- 302 = 100 × 3 + 10 × 0 + 2 [ ∵ abc = 100a + 10b + c]

Question (ii)
Write the following in the usual form:
- 10 × 5 + 6
- 100 × 7 + 10 × 1 + 8
- 100 × a + 10 × c + b
Solution:
- 10 × 5 + 6 = 50 + 6 = 56
- 100 × 7 + 10 × 1 + 8
= 700 + 10 + 8 = 718
- 100 × a + 10 × c + b
= 100a + 10c + b = acb
Try These : [Textbook Page No. 251 ]
1. Check what the result would have been if Sundaram had chosen the numbers shown below:
Question (i)
1. 27
Solution:
Let Sundaram choose the number = 27
Then reversed number = 72
∴ Sum of these two numbers
= 27 + 72 = 99
Now, 99 = 11 (9) = 11 (2 + 7)
= 11 (Sum of the digits of the chosen number)
Question (ii)
2. 39
Solution:
Let Sundaram choose the number = 39
Then reversed number = 93
∴ Sum of these two numbers
= 39 + 93 = 132
Now, 132 = 11 (12) = 11 (3 + 9)
= 11 (Sum of the digits of the chosen number)

Question (iii)
3. 64
Solution:
Let Sundaram choose the number = 64
Then reversed number = 46
∴ Sum of these two numbers
= 64 + 46 = 110
Now, 110= 11 (10) = 11 (6+ 4)
= 11 (Sum of the digits of the chosen number)
Question (iv)
4. 17
Solution:
Let Sundaram choose the number =17
Then reversed number = 71
∴ Sum of these two numbers
= 17 + 71 = 88
Now, 88 = 11 (8) = 11 (1 + 7)
= 11 (Sum of the digits of the chosen number)
[Note: From above results, it is clear that sum of 2-digit number and number obtained by interchanging its digit is multiple of 11, i.e., is divisible by 11, leaving remainder 0.]
Try These [Textbook Page No. 251]
Check what the result would have been if Sundaram had chosen the numbers shown below:
Question (i)
1. 17
Solution:
Let Sundaram choose the number =17
Then reversed number = 71
∴ Difference of these numbers
= 71 – 17 = 54
Now, 54 = 9(6) = 9(7- 1)
= 9 (Difference of the digits of the chosen number)

Question (ii)
2. 21
Solution:
Let Sundaram choose the number = 21
Then reversed number =12
∴ Difference of these numbers
= 21 – 12 = 9
Now, 9 = 9(1) = 9(2 – 1)
= 9 (Difference of the digits of the chosen number)
Question (iii)
3. 96
Solution:
Let Sundaram choose the number = 96
Then reversed number = 69
∴ Difference of these numbers = 96 – 69 = 27
Now, 27 = 9 (3) = 9 (9-6)
= 9 (Difference of the digits of the chosen number)
Question (iv)
4. 37
Solution:
Let Sundaram choose the number = 37
Then reversed number = 73
∴ Difference of these numbers = 73 – 37 = 36
Now, 36 = 9(4) = 9(7 – 3)
= 9 (Difference of the digits of the chosen number)
[Note: From above results, it is clear that difference of 2-digit number and number obtained by interchanging its digit is a multiple of 9, i.e., is divisible by 9, leaving remainder 0.]

Try These: [Textbook Page No. 252]
Check what the result would have been if Minakshi had chosen the numbers shown below. In each case keep a record of the quotient obtained at the end:
Question (i)
1. 132
Solution:
Let Minakshi choose the number =132
Then reversed number = 231
∴ Difference of these numbers = 231 – 132 = 99
Now, 99 ÷ 99 = 1, so remainder = 0
Question (ii)
2. 469
Solution:
Let Minakshi choose the number = 469
Then reversed number = 964
∴ Difference of these numbers = 964 – 469 = 495
Now, 495 ÷ 99 = 5, so remainder = 0
Question (iii)
3. 737
Solution:
Let Minakshi choose the number = 737
Then reversed number = 737
∴ Difference of these numbers = 737 – 737 = 0
Now, 0 ÷ 99 = 0, so remainder = 0

Question (iv)
4. 901
Solution:
Let Minakshi choose the number = 901
Then reversed number =109
∴ Difference of these numbers = 901 – 109 = 792
Now, 792 ÷ 99 = 8, so remainder = 0
[Note: From above results, it is clear s that difference of 3-digit number and number obtained by reversing | its digits (Interchanging unit and ; hundred’s place) is multiple of 99, i.e., is divisible by 99, leaving ’ remainder 0.]
Try These : [Textbook Page No. 253]
Check what the result would have been if Sundaram had chosen the numbers shown below:
Question (i)
1. 417
Solution:
Let Sundaram choose the number = 417
By interchanging the digits, we get two ) numbers, which are 741 and 147.
∴ Sum of these three numbers = 417 + 741 + 174 = 1332
Now, dividing the sum by 37,
1332 ÷ 37 = 36, so remainder = 0
Question (ii)
2. 632
Solution:
Let Sundaram choose the number = 632
By interchanging digits, we get two numbers, which are 263 and 326.
∴ Sum of these three numbers = 632 + 263 + 326 = 1221
Now, dividing the sum by 37,
1221 ÷ 37 = 33, so remainder = 0

Question (iii)
3. 117
Solution:
Let Sundaram choose the number =117 By interchanging digits, we get two numbers, which are 711 and 171.
∴ Sum of these three numbers = 117 + 171 + 711 = 999
Now, dividing the sum by 37,
999 ÷ 37 = 27, so remainder = 0
Question (iv)
4. 937
Solution:
Let Sundaram choose the number = 937
By interchanging digits, we get two numbers, which are 379 and 793.
∴ Sum of these three numbers = 937 + 379 + 793 = 2109
Now, dividing the sum by 37,
2109 ÷ 37 = 57, so remainder = 0
[Note: Sum of 3-digit number and numbers formed by interchanging their digit is divisible by 37, leaving no remainder. ]
Try These : [Textbook Page No. 257]
Question (i)
If the division N ÷ 5 leaves a remainder of 3, what might be the ones digit of N? (The ones digit, when divided by 5, must leave a remainder of 3. So the ones digit must be either 3 or 8.)
Solution:
The ones digit, when divided by 5 leaves a remainder of 3. So the ones digit must be either 3 or 8.
(Given in textbook, but let us make it simple by solving numerically.)
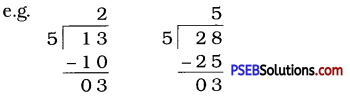

Question (ii)
If the division N ÷ 5 leaves a remainder of 1, what might be the ones digit of N?
Solution:
The ones digit, when divided by 5 leaves a remainder of 1. So the ones digit must be either 1 or 6.
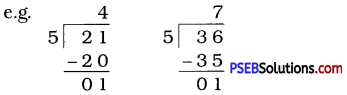
Question (iii)
If the division N ÷ 5 leaves a remainder of 4, what might be the ones digit of N?
Solution:
The ones digit, when divided by 5 leaves a remainder of 4. So the ones digit must be either 4 or 9.
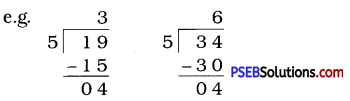
Try These : [Textbook Page No. 257 – 258]
Question (i)
If the division N ÷ 2 leaves a remainder of 1, what might be the ones digit of N? (N is odd; so its ones digit is odd. Therefore, the ones digit must be 1, 3, 5, 7 or 9.)
Solution:
N is odd, so its ones digit is odd. Therefore, the ones digit must be 1, 3, 5, 7 or 9.
(Given in textbook, but let us make it simple by solving numerically.)
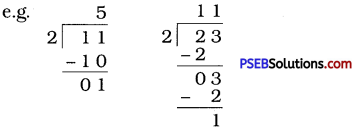

Question (ii)
If the division N ÷ 2 leaves no remainder (i.e., zero remainder), what might be the one’s digit of N?
Solution:
Here, the remainder = 0. So N is an even number, i.e., its ones digit is even. Therefore, the one’s digit must be 0, 2, 4, 6 or 8.
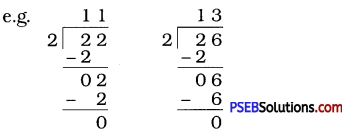
Question (iii)
Suppose that the division N ÷ 5 leaves a remainder of 4 and the division N ÷ 2 leaves a remainder of 1. What must be the ones digit of N?
Solution:
Here, the remainder is 4. So ones digit of N should be 4 or 9. Again, N ÷ 2 leaves a remainder 1.
So ones digit of N is odd, i.e., ones digit is one of these 1, 3, 5, 7 or 9.
∴ 9 is a common ones digit in both the cases.
Therefore, ones digit of N must be 9.

Try These : [Textbook Page No. 259]
Check the divisibility of the following numbers by 9:
Question (i)
1. 108
Solution:
Sum of digits of 108 = 1 + 0 + 8 = 9
Now, 9 ÷ 9 = 1 and remainder = 0
Thus, 108 is divisible by 9.

Question (ii)
2.616
Solution:
Sum of digits of 616 = 6 +1 + 6 = 13
Now, 13 ÷ 9 = 1 and remainder = 4
Thus, 616 is not divisible by 9.
Question (iii)
3. 294
Solution:
Sum of digits of 294 = 2 + 9 + 4 = 15
Now, 15 ÷ 9 = 1 and remainder = 6
Thus, 294 is not divisible by 9.
Question (iv)
4. 432
Solution:
Sum of digits of 432 = 4 + 3 + 2 = 9
Now, 9 ÷ 9 = 1 and remainder = 0
Thus, 432 is divisible by 9.
Question (v)
5. 927
Solution:
Sum of digits of 927 = 9 + 2 + 7 = 18
Now, 18 ÷ 9 = 2 and remainder = 0
Thus, 927 is divisible by 9.

Think, Discuss and Write: [Textbook Page No. 259]
1. You have seen that a number 450 is divisible by 10. It is also divisible by 2 and 5 which are factors of 10. Similarly, a number 135 is divisible 9. It is also divisible by 3 which is a factor of 9. Can you say that if a number is divisible by any number m, then it will also be divisible by each of the factors of m?
Solution:
Yes, if a number is divisible by any number m, then it will also be divisible by each of the factors of m. e.g. 12 is divisible by 6.
Factors of 6 are 2 and 3.
∴ 12 is also divisible by 2 and 3.
2.
Question (i)
Write a 3-digit number abc as 100a + 10b + c
= 99a + 11b + (a – b + c)
= 11 (9a + b) + (a – b + c)
If the number abc is divisible by 11, then what can you say about (a – b + c) ? Is it necessary that (a + c – b) should be divisible by 11?
Solution:
If the number abc is divisible by 11, then (a-b + c) is either 0 or a multiple of 11. Yes, it is necessary that (a + c-b) should be divisible by 11.
Question (ii)
Write a 4-digit number abed as 1000a + 100b + 10c + d = (1001a + 99b + 11c) – (a – b + c – d) = 11 (91a + 9b + c) + [(b + d) – (a + c)] If the number abed is divisible by 11, then what can you say about ((b + d) – (a + c)]?
Solution:
If the number abcd is divisible by 11, then [(b + d) – (a + c)] must be divisible by 11, i.e., [(b + d) – (a + c)] must be 0 or a multiple of 11.

Question (iii)
From (i) and (ii) above, can you say that a number will be divisible by 11 if the difference between the sum of digits at its odd places and that of digits at the even places is divisible by 11?
Solution:
Yes, we can say that a number will be divisible by 11, if the difference between the sum of digits at its odd places and that of digits at the even places is divisible by 11.
Try These : [Textbook Page No. 260]
Check the divisibility of the following numbers by 3:
Question (i)
1. 108
Solution:
Sum of digits of 108 = 1 + 0 + 8 = 9
Now, 9 is divisible by 3.
(∵ 9 ÷ 3 = 3, remainder = 0)
∴ 108 is divisible by 3.
Question (ii)
2. 616
Solution:
Sum of digits of 616 = 6 + 1 + 6 = 13
Now, 13 is not divisible by 3 leaving remainder 0.
(∵ 13 ÷ 3 = 4, remainder = 1)
∴ 616 is not divisible by 3.
Question (iii)
3. 294
Solution:
Sum of digits of 294 = 2 + 9 + 4 = 15
Now, 15 is divisible by 3.
(∵ 15 ÷ 3 = 5, remainder = 0)
∴ 294 is divisible by 3.

Question (iv)
4. 432
Solution:
Sum of digits of 432 = 4 + 3 + 2 = 9
Now, 9 is divisible by 3.
(∵ 9 ÷ 3 = 3, remainder = 0)
∴ 432 is divisible by 3.
Question (v)
5. 927
Solution:
Sum of digits of 927 = 9 + 2 + 7= 18
Now, 18 is divisible by 3.
(∵ 18 ÷ 3 = 6, remainder = 0)
∴ 927 is divisible by 3.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()