Punjab State Board PSEB 9th Class Hindi Book Solutions Hindi Grammar patra lekhan पत्र-लेखन Exercise Questions and Answers, Notes.
PSEB 9th Class Hindi Grammar पत्र-लेखन
1. आपका नाम शैली है। आप 235, सेक्टर-16 करनाल में रहती हैं। आप अपनी सखी डिम्पी की बहन की शादी में व्यस्तता के कारण नहीं जा सकीं। डिम्पी को एक बधाई पत्र लिखिए।
235, सेक्टर-16
करनाल।
प्रिय सखी डिम्पी,
सप्रेम नमस्ते।
आज ही मेरी वार्षिक परीक्षाएँ समाप्त हुई हैं इसलिए मैं तुम्हारी बहन की शादी में नहीं पहुँच सकी। इसके लिए मैं तुमसे माफी मांगती हूँ। मैं अपनी और माता-पिता की तरफ से तुम्हें हार्दिक बधाई देती हूँ। प्रभु से तुम्हारी बहन के वैवाहिक मंगल जीवन की प्रार्थना करती हूँ।
तुम इस शादी में बहुत व्यस्त रही होगी। घर में बहुत काम बढ़ गया होगा। मैं जानती हूँ कि तुम्हें शादी में मेरी याद अवश्य आई होगी किंतु मैं इस अवस्था में नहीं पहुँच सकी परंतु हमारी अन्य सखियां तो आई होगी। आशा है तुम सबने मिलकर मनोरंजन किया होगा। . – मेरी तरफ से आपके पूरे परिवार को बहुत बधाई। माता-पिता को मेरी ओर से सादर प्रणाम तथा रवि को प्यार।
तुम्हारी सखी,
डिम्पी।

2. आपका नाम सुधीर वर्मा है। आप 2561, सेक्टर-22 नोएडा में रहते हैं। आपको सूचना मिली है कि आपके मित्र के पिता जी की अचानक मृत्यु हो गयी है। इस संबंध में उसे सांत्वना देते हुए पत्र लिखिए।
2561, सेक्टर-22,
नोएडा। 5 मई,
20…… प्रिय मित्र,
सप्रेम नमस्ते।
आज ही आपका पत्र मिला। पढ़कर बहुत दुःख हुआ कि अचानक आपके पिता जी की मृत्यु हो गई। यह तुम्हारे लिए ही नहीं बल्कि पूरे परिवार के लिए दुःख की घड़ी है। किंतु जीवन में सुख-दुःख आते-जाते रहते हैं। इससे तुम्हें शिक्षा लेकर धैर्य रखना चाहिए। तुम अपने भाइयों में बड़े हो इसलिए तुम्हें सबको धैर्य देना चाहिए। धीरे-धीरे सब कुछ ठीक हो जाएगा। तुम अपनी पढ़ाई जारी रखना।
माता जी को प्रणाम तथा गौरव को प्यार।
आपका प्रिय मित्र,
सुधीर वर्मा।
3. आपका नाम मयंक गुप्ता है। आप मेरठ पब्लिक स्कूल, मेरठ में नौवीं कक्षा में पढ़ते हो और छात्रावास में रहते हो। आप अपनी माता जी को छात्रावास के जीवन के बारे में बताते हुए पत्र लिखें।
नेता जी छात्रावास,
मेरठ पब्लिक स्कूल,
मेरठ।
5 मई, 20……
आदरणीया माता जी,
चरण स्पर्श।
मैं यहाँ कुशलपूर्वक हूँ। आशा है कि आप भी कुशल होंगे। हमारे छात्रावास में कुल पचास विद्यार्थी रहते हैं। सभी देश के कोने-कोने से हैं। अलग-अलग राज्यों से होने पर भी हम सब मिल-जुल कर रहते हैं। हमारे छात्रावास में पच्चीस कमरे हैं। प्रत्येक कमरे में दो छात्र रहते हैं। श्री मुरली प्रसाद हमारे छात्रावास के इंचार्ज हैं। वे पूर्व सैनिक हैं इसलिए नियमों के कड़े हैं। उन्हें अनुशासन बहुत प्रिय है। इसी कारण यहाँ सभी छात्र अनुशासन में रहते हैं। अनुशासन तोड़ने पर कड़ी सजा मिलती है। हमारे इंचार्ज किसी के साथ भी ढील नहीं छोड़ते।।
छात्रावास में सभी छात्र सुबह पाँच बजे जाग जाते हैं। स्नान आदि करने के बाद सैर करते हैं उसके बाद आधा घंटा योग कक्षा लगती है। सात बजे कैंटीन में नाश्ता होता है। उसके बाद सभी कक्षाओं में चले जाते हैं। छुट्टी के पश्चात् भोजन करके सभी की अन्य कक्षाएं होती हैं। शाम को पांच बजे हम स्कूल के खेल के मैदान में पहुँच जाते हैं। वहाँ हम सात बजे तक खेलते हैं। इसके बाद रात्रि भोजन कर सभी सोने के लिए अपने अपने कमरों में चले जाते हैं।
मैं अपने मित्रों के साथ बहुत खुश हूँ। पिता जी को सादर प्रणाम।
अमृत को प्यार।
आपका पुत्र,
मयंक गुप्ता।
4. आपका नाम रिदम है। आप 525, मयूर विहार, दिल्ली में रहती हैं। आपकी दादी आपके पास पंद्रह दिन के लिए आने वाली हैं। उन्हें अपनी मनपसंद वस्तुओं की फरमाइश करते हुए पत्र लिखें।
525, मयूर विहार,
दिल्ली।
5 अगस्त, 20……
आदरणीया दादी जी,
चरण स्पर्श।
मुझे यह जानकर बहुत खुशी हुई कि आप हमारे पास पंद्रह दिन के लिए रहने आ रही है। इससे मैं ही नहीं बल्कि पूरा परिवार गदगद है। मुझे पता है कि आप अमृतसर से आते हुए बहुत सारी वस्तुएँ लेकर आएंगी। आप मेरे लिए मेरी मनपसंद गुड़िया, पापड़ और दुपट्टे ज़रूर लेकर आना। मुझे अमृतसरी मिठाई भी पसंद है। इसलिए आप खूब सारी मिठाई अवश्य लेकर आना। अमृतसरी कुर्ता-सलवार हमारे यहाँ बहुत प्रसिद्ध है। मैं ही नहीं सभी लोग इसे पसंद करते हैं। आप इसे ज़रूर सिलवाकर लाना।
पूज्य दादा जी को चरण स्पर्श तथा चाचा-चाची को सादर प्रणाम।
चरणजीत और डॉली को प्यार।
तुम्हारी पोती,
रिदम।
5. आपका नाम तनजीत कौर है। आप ए-10, शांति नगर, लुधियाना में रहती हैं। अपने बड़े भाई जो मुम्बई में रहते हैं, को अपने जीवन की भावी योजनाओं के विषय में पत्र लिखिए।
ए-10, शांति नगर,
लुधियाना।
1 जनवरी, 20……
प्रिय भैया,
सादर प्रणाम।
मैं यहां कुशलता से हूँ। आशा है कि आप भी मुंबई में खुश होंगे। आपको जानकर बहुत खुशी होगी कि इस वर्ष मैं नौवीं कक्षा में स्कूल में प्रथम आई हूँ। आगे मैं उच्च शिक्षा के लिए चंडीगढ़ जाना चाहती हूँ। ताकि मैं वहाँ जाकर पढ़ाई के साथ-साथ आई० ए० एस० की शुरू से ही तैयारी कर सकू। मैं बड़ी होकर देश की आई० ए० एस० अफसर बनना चाहती हूँ। इसके लिए मुझे दसवीं कक्षा के साथ-साथ आई० ए० एस० की भी तैयारी करनी होगी।
मैं आपको विश्वास दिलाती हूँ कि मैं सदा खूब मेहनत से पढूंगी और एक दिन अपना सपना ज़रूर पूरा करूँगी।
आपकी प्रिय बहन,
तनजीत कौर।
6. आपका नाम प्रवीण शर्मा है। आप 256, आशियाना सोसाइटी, नंगल में रहते हैं। आपका खोया हुआ बैग लौटाने वाले नीरज वर्मा को आभार व्यक्त करते हुए पत्र लिखें।
256, आशियाना सोसाइटी,
नंगल।
प्रिय मित्र नीरज वर्मा,
सप्रेम नमस्ते।
मुझे आज ही तुम्हारा पार्सल मिला। खोलकर देखा तो उसमें से एक बैग निकला। मैं इसे देखकर हैरान रह गया कि यह मेरा खोया हुआ बैग था। मैं आज बहुत खुश भी हूँ कि आज भी हमारे देश में तुम जैसे ईमानदार लोग हैं। यदि तुम चाहते तो इसे अपने पास रख सकते थे किंतु तुमने ऐसा नहीं किया। मेरा खोया हुआ बैग लौटाने के लिए मैं तुम्हारा बहुत आभारी हूँ। मैं सदा आपकी इस ईमानदारी को याद रखूगा। तुम्हारा बहुत धन्यवाद।
मैं प्रभु से तुम्हारे उज्ज्वल भविष्य की प्रार्थना करता हूँ। अपने माता-पिता जी को मेरी तरफ से सादर प्रणाम कहना।
आपका प्रिय,
प्रवीण शर्मा।
परीक्षोपयोगी अन्य पत्र।
1. अपने छोटे भाई को समाचार पात्र पटाने की प्रेरण देते हुए एक पात्र लिखिए
69-टैगोर नगर,
अमृतसर।
दिनांक………….
प्रिय भाई राकेश,
सस्नेह नमस्ते।
अभी-अभी प्राप्त हुए तुम्हारे पत्र से पता चला कि तुमने क्विज प्रतियोगिता में भाग लिया था लेकिन विषय में ज्ञान कम होने से प्रतियोगिता से बाहर हो गए। इससे पता चलता है कि तुम्हारा सामान्य ज्ञान बहुत कमज़ोर है। मेरे भाई आप को तो पता ही है कि आजकल प्रत्येक प्रतियोगिता में जो प्रश्न पूछे जाते हैं उनमें व्यक्ति का सामान्य ज्ञान बहुत होना चाहिए। मैं इस पत्र में अपना सामान्य ज्ञान बढ़ाने का एक उपाय बता रहा हूँ।
मेरा सुझाव यह है कि तुम अंग्रेजी और हिंदी के समाचार-पत्र नियमित रूप से पढ़ा करो। इससे तुम्हारा सामान्य ज्ञान काफ़ी हद तक ठीक हो जायेगा। अंग्रेजी के समाचार-पत्र से तुम्हारा अंग्रेज़ी का ज्ञान भी बढ़ेगा। हिंदी के तो आजकल पंजाब में कई दैनिक समाचार-पत्र प्रकाशित होने लगे हैं। समाचार-पत्रों से तुम्हें देश-विदेश में होने वाली घटनाओं की तो जानकारी होगी ही साथ ही धर्म, विज्ञान, खेल, व्रत त्योहारों की भी पूरी जानकारी प्राप्त होगी। हिंदी के समाचारपत्रों में प्रत्येक दिन इन सभी विषयों पर विस्तृत जानकारी दी गई होती है।
मेरी सलाह मानोगे तो महीने भर में ही तुम्हें पता चल जाएगा कि तुम्हारा सामान्य ज्ञान कितना बढ़ गया है। यह ज्ञान भविष्य में भी तुम्हारे काम आएगा। यदि हो सके तो ऐसी ही सलाह तुम अपने मित्रों को भी दे सकते हो।
स्नेह सहित,
तुम्हारा भाई.

2. अपनी माता जी को एक पत्र लिखिए जिसमें छात्रावास का विवरण दिया गया हो।
12-टैगोर भवन,
पंजाब विश्वविद्यालय,
चंडीगढ़।
दिनांक 12-10-20…
पूज्य माता जी,
सादर प्रणाम!
आपका पत्र मिला जिसमें आपने मेरे घर से बाहर रहने और सही भोजन न मिलने के बारे में चिंता व्यक्त की है। पूज्य माता जी, मुझे छात्रावास में किसी प्रकार का कोई कष्ट नहीं है। यह ठीक है कि घर से दूर होने पर मुझे आप सबकी बहुत याद आती है किन्तु अपना भविष्य बनाने के लिए इतना कष्ट तो सहना ही पड़ेगा।
मैं आप को अपने छात्रावास की दिनचर्या का विवरण लिख रहा हूँ जिसे पढ़कर सम्भव है आपके मन को शान्ति मिल सके। हमारे छात्रावास में एक सौ दस कमरे हैं। प्रत्येक कमरे में दो-दो विद्यार्थियों के रहने की व्यवस्था है। संयोग से मेरे कमरे में मेरे ही गाँव का विद्यार्थी ठहरा है। छात्रावास में एक भोजनालय है जिसमें सभी विद्यार्थी मिलकर भोजन करते हैं। भोजनालय में ही एक तरफ मनोरंजन के लिए एक बड़ा टेलीविज़न भी रखा है। छात्रावास परिसर के साथ ही जुड़ा है।
छात्रावास में आकर मेरा जीवन भी नियमित हो गया है। छात्रावास के वार्डन छात्रों को प्रात: पाँच बजे जगा देते हैं। कोई एक घंटे के लिए हमें योग और प्राणायाम का प्रशिक्षण दिया जाता है। स्नानादि के बाद हम अल्पाहार करके विश्वविद्यालय चले जाते हैं। विश्वविद्यालय से वापस आकर कुछ देर के लिए हम इनडोर खेलें खेलते हैं फिर शाम को चाय पीते हैं। रात को हमें आठ बजे तक भोजन मिल जाता है। भोजन में हमें एक सब्जी, एक दाल और मिष्ठान दिया जाता है। रात को ग्यारह बजे तक हमें पढ़ना होता है। उसके बाद छात्रावास की सारी बत्तियाँ बुझा दी जाती हैं।
छात्रावास का जीवन मुझे बहुत पसंद है। मेरा पूरी तरह से यहाँ दिल लग गया है मैं पढ़ाई भी नियमित रूप से करने लगा हूँ। आप मेरी ओर से पूर्णत: निश्चिन्त हो जाएँ।
पूज्य पिता जी को मेरा प्रणाम कहिएगा। रुचि को स्नेह।
आपका प्रिय पुत्र,
आदीश।
3. पिता की ओर से पुत्र को पत्र जिसमें पढ़ाई के साथ-साथ जीवन में खेलों के महत्त्व पर भी प्रकाश डाला गया हो।
39-माडल टाऊन,
पटियाला।
दिनांक. ………..
प्रिय संजीव,
आशीर्वाद।
आज ही तुम्हारे अध्यापक का पत्र मिला जिसमें उन्होंने शिकायत की है कि तुम्हारा स्वास्थ्य ठीक नहीं रहता। इसका कारण उन्होंने यह दिया है कि तुम केवल पढ़ाई में ही लगे रहते हो, खेलों में बिलकुल भी भाग नहीं लेते।
तुम्हें मालूम होना चाहिए कि जीवन में जितना महत्त्व पढ़ाई का है उतना ही खेलों का भी है। खेलों में भाग लेने पर व्यक्ति का एक तरह से व्यायाम हो जाता है जिससे उसका स्वास्थ्य ठीक रहता है। व्यक्ति को खूब भूख लगती है और भोजन पचाने में भी खेलें सहायक होती हैं। याद रखो अच्छी तरह पढ़ाई वही कर सकता है जिसका स्वास्थ्य ठीक हो। खेलें हमें जीवन में अनुशासन में रहना भी सिखाती हैं और हम में टीम भावना भी पैदा करती हैं। अत: मेरी तुम्हें सलाह है कि स्कूल में होने वाली खेलों में से अपनी रुचि के अनुसार किसी भी खेल में अवश्य भाग लेना चाहिए। खेलों में भाग लेने पर तुम्हारा व्यायाम भी स्वयं ही हो जाएगा और स्वास्थ्य भी ठीक रहेगा और सबसे बड़ी बात यह है कि तुम्हारा पढ़ाई में भी मन लगेगा।
आशा है तुम मेरे इन विचारों से सहमत होवोगे।
शुभकामनाओं सहित,
तुम्हारा पिता,
4. रक्षाबन्धन के पवित्र अवसर पर भाई ने जो उपहार भेजा है, उसकी उपयोगिता बताते हुए उसका धन्यवाद कीजिए।
29-मॉडल कालोनी,
फगवाड़ा।
दिनांक …………
आदरणीय भाई जी,
नमस्कार।
आज ही आप का भेजा पत्र प्राप्त हुआ जिसमें आपने राखी भेजने के लिए मेरा धन्यवाद करते हुए उपहार स्वरूप मुंशी प्रेमचन्द की कहानियों का पूरा सैट मानसरोवर (आठ भाग) भेजा है। इस अनुपम उपहार के लिए मैं आपका हृदय से धन्यवाद करती हूँ। मेरे लिए यह उपहार किसी सोने के गहने से कम नहीं है। पुस्तकें सदा से ही एक सुन्दर उपहार मानी जाती हैं। इन कहानियों को पढ़ कर यहाँ मुझे अपना सामान्य ज्ञान बढ़ाने में मदद मिलेगी वहाँ मेरा दिल भी लगा रहेगा। यह एक ऐसा उपहार है जो सदा मेरे पास रहेगा। भैया आप का जितना भी धन्यवाद करूं उतना ही कम है।
मेरी ओर से आदरणीय भाभी जी को नमस्ते कहिएगा।
शुभकामनाओं सहित,
आपकी प्रिय बहन,
राधिका।
5. गर्मियों की छुट्टियाँ इकट्ठे बिताने के लिए अपने मित्र को एक पत्र लिखिए।
राजगढ़ रोड़,
सोलन।
दिनांक…………….
प्रिय मित्र कुलदीप,
नमस्ते।
इस पत्र के द्वारा न मैं तुम्हें गर्मियों की छुट्टियाँ हमारे साथ हिमाचल में साथ बिताने का निमंत्रण दे रहा हूँ। इन छुट्टियों में हम हिमाचल प्रदेश के सभी दर्शनीय स्थलों की यात्रा करेंगे। इस पत्र में मैं तुम्हें हिमाचल के कुछ दर्शनीय स्थलों का वर्णन दे रहा हूँ ताकि तुम्हारे मन में जिज्ञासा और उत्सुकता जागृत हो सके और तुम छुट्टियाँ होते ही सोलन पहुँच जाओ। कसम से तुम्हारे साथ होने से भ्रमण का मज़ा दुगुना हो जाएगा।
हिमाचल प्रदेश अपनी प्राकृतिक सुषमा के लिए प्रसिद्ध है। हिमाचल प्रदेश की राजधानी शिमला तो पर्यटकों का लोकप्रिय स्थल है। यहाँ का मालरोड, जाखू का हनुमान जी का मंदिर विशेष रूप से आकर्षण के केन्द्र हैं। शिमला से आगे बिलासपुर शहर है जो अब गोबिंद सागर झील के किनारे बसा है। पर्यटक यहाँ नौका विहार का मज़ा लेते हैं। बिलासपुर से आगे मंदिरों का शहर मंडी है जहाँ मनाया जाने वाला शिवरात्रि का त्योहार प्रसिद्ध है। मंडी के बाद कुल्लू मनाली आता है जो अपनी प्राकृतिक सुषमा के लिए जगत प्रसिद्ध है। मनाली स्थित हिडंबा देवी का मंदिर वास्तुकला का अद्भुत नमूना है। यदि समय मिला तो हम डलहौज़ी, चंबा और धर्मशाला भी जाएँगे।
उपर्युक्त विवरण को पढ़ने से मुझे पूर्ण विश्वास है कि तुम इन गर्मियों की छुट्टियों में हमारे साथ हिमाचल दर्शन के लिए अवश्य हमारे साथ शामिल हो जाओगे।
घर पर सभी को मेरा प्रणाम कहना।
तुम्हारा मित्र,
संजीव।
6. दीपावली की छुट्टियों में किसी दर्शनीय स्थल की यात्रा पर जाने के कार्यक्रम की सूचना देते हुए अपने मित्र को एक पत्र लिखिए।
12, गीता भवन,
लाजपतराय मार्ग,
जालन्धर।
दिनांक ………..
प्रिय मित्र आशीष,
नमस्ते।
तुम्हारा पत्र मिला। यह जान कर खुशी हुई है कि इस बार की दीपावली की छुट्टियों में तुम कन्या कुमारी जा रहे हो। हमने भी इस बार मैसूर और बेंगलुरू जाने का कार्यक्रम बनाया है। परिवार के सभी सदस्य इस बार इकट्ठे जा रहे हैं।
हम बीस अक्तूबर को जालंधर से चलेंगे। गाड़ी सात बजे चलेगी। तीसरे दिन हम बंगलौर पहुंच जाएँगे। वहाँ एक यात्री निवास में ठहरने का हमारा प्रबंध पहले से ही मेरे पिता जी के एक मित्र ने कर रखा है।
ये दोनों बहुत सुन्दर और ऐतिहासिक शहर हैं। यहाँ वृंदावन गार्डन, राजमहल, चामुंडेश्वरी का मंदिर देखने योग्य स्थान हैं। यहाँ के संग्रहालय भी बहुत प्रसिद्ध हैं। सुना है कि वहाँ अति प्राचीन वस्तुएँ संभाल कर रखी गई हैं।
हमारा कार्यक्रम सबसे पहले वृंदावन गार्डन देखने का है। यह बाग भारत भर में प्रसिद्ध है और इसे देखने देश-विदेश से लोग आते हैं। उसके बाद हम चामुंडेश्वरी देवी के मंदिर में देवी-दर्शन के लिए जाएँगे। तुम तो जानते ही हो कि ये स्थान चंदन की लकड़ी के लिए संसार भर में जाने जाते हैं। चंदन की लकड़ी से सुंदर मूर्तियाँ बनाने के यहाँ कई कारखाने हैं। इन मूर्तियों की मांग विदेशों में बहुत है। मैसूर चंदन की अगरबत्तियों और साबुन के लिए भी प्रसिद्ध है।
हम ठीक दीवाली वाले दिन यहाँ पहुँचेंगे। यहाँ के राजमहल की दीपमाला देखने योग्य होती है। हम वह अवश्य देखने जाएंगे। यात्रा से लौटकर मैं तुम्हें अपने अनुभवों के बारे में ब्योरे में लिखूगा। तुम भी मुझे अपनी यात्रा के अनुभव लिखना।
घर में सभी को मेरी नमस्ते कहना।
तुम्हारा प्रिय मित्र,
सुखदेव सिंह।

7. स्वास्थ्य का महत्त्व समझाते हुए छोटे भाई को पत्र लिखिए।
720, सैक्टर 9,
अमृतसर।
26-12-20 ……..
प्रिय भाई हार्दिक
स्नेहाशिष।
आज ही पूज्य पिता जी का पत्र मिला, जिसे पढ़कर दुःख हुआ कि तुम्हारा स्वास्थ्य ठीक नहीं रहता। प्रिय भाई, तुम्हें अपने स्वास्थ्य का विशेष रूप से ध्यान रखना चाहिए। परीक्षा सिर पर है। ऐसा न हो कि तुम्हारी सारे साल की मेहनत पर पानी फिर जाए।
मेरा विचार है कि तुम प्रतिदिन सुबह सवेरे उठा करो। प्रातः वेला में थोड़ी सैर भी किया करो। उस समय हमें शुद्ध एवं प्रदूषण रहित वायु मिलती है जो सारा दिन हमें चुस्त बनाये रखती है। प्रातः भ्रमण के बाद थोड़ा व्यायाम भी किया करो। सुबह सवेरे सूर्योदय के समय उसकी लालिमा के सामने आँखें बन्द कर पांच-दस मिनट अवश्य खड़े हुआ करो। इससे तुम्हारा शरीर भी स्वस्थ रहेगा और तुम्हारी आँखों की ज्योति भी कमजोर नहीं होगी। देर तक पढ़ाई करने वाले विद्यार्थी के लिए यह अति उत्तम उपाय है।
तुम अपने खाने, सोने, पढ़ने और खेलने का ध्यान अवश्य रखो। हर काम समय पर करो। भोजन के मामले में तुम्हें विशेष ध्यान रखना चाहिए। भोजन नियत समय पर ही करना चाहिए। इस तरह तुम्हारा पेट ठीक रहेगा। बहुत से रोग .. आदमी का पेट ठीक न होने के कारण होते हैं। सही समय पर भोजन करना हमें कई रोगों से बचाता है।
तुम शाम को खेलकूद में अवश्य भाग लिया करो। व्यक्ति का मन के साथ-साथ शरीर भी स्वास्थ्य होना चाहिए। रोगी, शरीर वाला कोई भी काम ठीक ढंग से नहीं कर सकता।
मुझे पूरी आशा है कि तुम मेरी इन बातों की तरफ अवश्य ध्यान दोगे और नियमपूर्वक इनका पालन करोगे। मेरी शुभ कामनाएँ तुम्हारे साथ हैं।
तुम्हारा भाई,
चैतन्य।
8. मन लगाकर पढ़ाई करने की शिक्षा देते हुए छोटे भाई को पत्र लिखें।
………………… पता
………………… शहर
दिनांक……………..
प्रिय भाई………….
नमस्ते।
आज ही तुम्हारे अध्यापक श्री…………का पत्र मुझे मिला, जिसमें उन्होंने तुम्हारी शिकायत की है कि तुम पढ़ाई में बहुत कम ध्यान देने लगे हो। अर्धवार्षिक परीक्षा में तुम्हारे अंक भी बहुत कम आये हैं। प्यारे भाई तुम्हें पता ही है कि इस वर्ष तुम्हारी मैट्रिक की पढ़ाई है। पुराने ज़माने में इसे एंटरस की परीक्षा कहते थे। कारण यह है कि इस परीक्षा को पास करके ही विद्यार्थी वास्तव में अपने भावी जीवन का निर्माण करता है। यह परीक्षा जीवन का प्रवेश द्वार है।
आज प्रतियोगिता और मैरिट का ज़माना है। इन दोनों में सफलता पाने के लिए मन लगाकर पढ़ना ज़रूरी है। पढ़लिख कर जब तुम कुछ बन जाओगे तो सारा जीवन ऐश करने के लिए ही है। किन्तु यदि पढ़ाई ठीक ढंग से नहीं की तो जीवन भर पछताना पड़ेगा। विद्यार्थी जीवन और पढ़ाई का यह अवसर लौटकर नहीं आएंगे।
हमारा परिवार एक मध्यवर्गीय परिवार है। आज वह जमाना नहीं रहा कि एक कमाता था तो सब खाते थे। आज तो सभी कमाएँ तो अच्छी तरह से खा सकते हैं। अपने परिवार की आर्थिक स्थिति तुम से छिपी नहीं है। हम सब को तुम पर बड़ी आशाएँ हैं। हम पिता-पुत्र अपनी गाढ़े पसीने की कमाई तुम्हारी पढ़ाई पर इसीलिए खर्च कर रहे हैं कि तुम पढ़-लिखकर कुछ बन जाओ और परिवार का नाम रोशन करो।
मुझे पूर्ण आशा है कि थोड़े कहे को अधिक समझते हुए, तुम पूरी तरह मन लगाकर पढ़ोगे और पहले की तरह ही कक्षा में प्रथम आकर दिखाओगे। हम सब की शुभ कामनाएँ और आशीर्वाद तुम्हारे साथ है।
पूज्य माता जी और पिता जी तुम्हें ढेर सारा प्यार भेजते हैं।
तुम्हारा भाई,
………….।
9. नैतिक मूल्यों का महत्त्व समझाते हुए छोटे भाई को पत्र लिखें।
……………पता
…………..शहर
दिनांक…………..
प्रिय भाई…
नमस्ते।
तुम्हारा पत्र प्राप्त हुआ। पढ़ कर प्रसन्नता हुई कि तुम नैतिक मूल्यों के बारे में जानकारी प्राप्त करना चाहते हो। इस पत्र में मैं तुम्हें कुछ महत्त्वपूर्ण बातों की जानकारी दे रहा हूँ। याद रखना इन पर अमल करने वाला विद्यार्थी जीवन भर सुखी रहता है। सबसे पहली बात यह है कि तुम्हें समय का सद्उपयोग करना चाहिए। समय से मूल्यवान् वस्तु कोई नहीं है। एक चित्रकार ने समय का चित्र बनाते समय उसके माथे पर बालों का गुच्छा दिखाया था और उसे सिर के पीछे से गंजा दिखाया था। इसका मतलब यह है कि समय को सदा सामने से ही पकड़ो। उसके बीत जाने पर तो तुम्हारा हाथ उसके गंज पर पड़ेगा और तुम्हारे हाथ कुछ न आयेगा। किसी ने ठीक ही कहा है-‘अब पछताय क्या होत जब चिड़िया चुग गई खेत।’ इसलिए समय के मूल्य को समझो। संसार में जितने भी महान् व्यक्ति हुए हैं उन सभी ने समय के मूल्य को समझा और उसका पालन किया है। तुम्हें समय पर पढ़ाई करना, खेलना, खाना, सोना आदि काम करने चाहिएं।
दूसरी.विशेष बात है-सच्चरित्रता। कहते हैं कि ईश्वर भी उसी का साथ देता है जिसका आचरण सच्चा होता है। सच्चरित्र व्यक्ति जीवन में सदा सफल होता है। आजकल टेलीविज़न, फिल्में आदि व्यक्ति के चरित्र को बनाने की बजाए बिगाड़ रहे हैं। चरित्र बिगड़ जाने पर व्यक्ति का सब कुछ नष्ट हो जाता है। मैं टेलीविज़न या फिल्म देखने से तुम्हें रोकना नहीं चाहता बल्कि चाहता हूँ कि टेलीविज़न पर अच्छे और ज्ञानवर्धक कार्यक्रम देखो। फिल्म देखो तो उससे बुरी बातें नहीं अच्छी बातें सीखो।
तीसरी बात है, अपने कर्त्तव्य का पालन करना चाहिए। हमारा पहला कर्त्तव्य अपने देश के प्रति है फिर राज्य, जाति या समाज के लिए। हमें सदा दूसरों का भला करने की बात सोचनी चाहिए। गरीबों की, असहायों की मदद करनी चाहिए। हर व्यवसाय में कर्त्तव्य पालन करना ज़रूरी है। सूर्य, चन्द्रमा समय पर उदय होकर और अस्त होकर अपने कर्तव्य का ही तो पालन करते हैं। कर्त्तव्य पालन हमें जीवन में सुख और उन्नति प्रदान करता है।
तुम्हारा भाई,
…………….
10. समय का महत्त्व समझाते हुए मित्र/सखी को पत्र लिखें।
……….. पता
………… नगर का नाम
दिनांक………….
प्रिय उमेश,
नमस्ते।
आशा है तुम स्वस्थ एवं प्रसन्न होगे और छात्रावास में तुम्हारा मन लग गया होगा। मुझे कल ही तुम्हारे एक मित्र का पत्र मिला है जिसमें उसने तुम्हारी शिकायत करते हुए लिखा है कि तुम पढ़ाई की तरफ कम ध्यान देते हो और बहुतसा समय आवारागर्दी में बिता देते हो। तुम्हारे मित्र ने मुझे तुम्हें समझाने की सलाह दी है।
इस पत्र में मैं तुम्हें समय के महत्त्व पर कुछ बातें लिख रहा हूँ। मुझे पूर्ण आशा है कि तुम मेरी बातों पर ध्यान देते हुए अपने आचरण में सुधार करोगे। समय बड़ा कीमती धन है जो इसकी कदर नहीं करता वह सारी उमर पछताता रहता है। क्योंकि बीता हुआ समय लौट कर नहीं आता। विद्यार्थी जीवन में तो इसका बड़ा महत्त्व है। ज़रा सोचो यदि तुम अपने सहपाठियों से एक वर्ष पीछे रह गए तो क्या इस बीते समय की तुम भरपाई कर पाओगे। याद रखो समय कभी किसी की प्रतीक्षा नहीं करता। जीवन में वही लोग सफल होते हैं जो समय के महत्त्व को पहचानते हैं।
विद्यार्थी जीवन में तो समय का ध्यान रखना बहुत ज़रूरी है। समय पर सोना, समय पर जागना, समय पर भोजन करना, समय पर खेलना, समय पर पढ़ाई करना एक विद्यार्थी के स्वास्थ्य को तो सही रखता ही है उसकी बुद्धि को भी तीक्ष्ण करता है। समय पर किया गया हर कार्य मनुष्य के जीवन को सुखमय बनाने में सहायक होता है।
प्रिय मित्र, थोड़े कहे को अधिक समझो। मुझे पूर्ण आशा है कि तुम अपने परिवार की आर्थिक स्थिति को तथा अपने भविष्य को ध्यान में रखते हुए समय के महत्त्व को समझोगे और अपनी दिनचर्या को बदलने का प्रयास करोगे। मेरी शुभकामनाएँ तुम्हारे साथ हैं।
तुम्हारा मित्र,
रमेश यादव।
11. व्यायाम के महत्त्व पर प्रकाश डालते हुए सखी को पत्र लिखें।
……………..पता
……………..शहर का नाम
दिनांक…………
प्रिय सुरभि,
नमस्ते।
आज ही तुम्हारा पत्र प्राप्त हुआ। यह जान कर दुःख हुआ कि तुम्हारा स्वास्थ्य कुछ ठीक नहीं रहता। पिछले वर्ष जब मैं तुमसे मिलने अमरावती आई थी तो तुम्हारी माता जी ने इस बात की शिकायत की थी कि तुम सारा दिन सुस्त सी रहती हो। न कोई व्यायाम करती हो और न ही स्कूल की किसी खेल में हिस्सा लेती हो।।
तुम्हें तो मालूम ही है कि स्वास्थ्य ही धन है और अच्छे स्वास्थ्य के लिए व्यायाम बहुत ज़रूरी है। व्यायाम का यह मतलब कभी न लेना कि यह पहलवानों की तरह कसरत करना ही व्यायाम होता है। बल्कि एक लड़की के लिए तो घर का काम काज करना भी एक तरह का व्यायाम ही है। सुबह सवेरे उठकर सैर करना, घर की सफाई करना, झाड़ आदि देना, कपड़े धोना, खाना बनाना ये सब व्यायाम के ही अंग हैं। आजकल लोग विशेषकर बच्चे सारा-सारा दिन दूरदर्शन के कार्यक्रम देखते रहते हैं। इस तरह वे अपना समय और स्वास्थ्य खराब करते हैं। तुम भी दूरदर्शन देखना कम करके अपनी दैनिक दिनचर्या को थोड़ा बदलो। प्रात: जल्दी उठा करो और रात को जल्दी सो जाया करो। सुबह सवेरे खुली हवा में सैर करना और हल्के व्यायाम करना भी तुम्हारे लिए लाभदायक सिद्ध होगा। घर में अपनी माता जी के साथ काम में हाथ बटाया करो। घरेलू काम भी व्यायाम ही हैं। पुराने ज़माने में औरतें चक्की पीसती थीं, कुएं से पानी खींचती थीं और सिर पर पानी का घड़ा रखकर घर लाती थीं। इन घरेलू कामों के कारण पुराने समय की औरतें स्वस्थ रहा करती थीं। आज महानगरों में बड़े-बड़े स्वास्थ्य क्लबों में यही सब व्यायाम करवाये जाते हैं।
इन व्यायामों से कोई भी लड़की सुंदर, स्वस्थ, सुगठित शरीर वाली बनी रह सकती है। व्यायाम करने से चेहरे पर एक तेज आ जाता है, जो स्त्री के व्यक्तित्व को आकर्षक बनाने में सहायक होता है। क्या कोई रोनी सूरत वाली उदासउदास दिखने वाली लड़की की तरफ देखना पसन्द करेगा? नहीं, कदापि नहीं। ऐसी लड़की को तो कोई अपनी सहेली भी बनाने को तैयार नहीं होता।
मेरा तुम से आग्रह है कि अभी भी कुछ नहीं बिगड़ा है, नियमित रूप से व्यायाम करो, सदा खुश रहो, गुस्सा कम करो। थोड़े ही दिनों में तुम देखोगी कि तुम्हारे रूप पर निखार आना शुरू हो जाएगा और तुम बहुत से ऐसे रोगों से बची रहोगी जिन से प्रायः लड़कियाँ परेशान रहा करती हैं। इस सम्बन्ध में अपनी माता जी की भी घर पर सहायता लो। अपने माता-पिता को मेरा नमस्कार कहना। छोटे भाई को मेरा प्यार कहना।
तुम्हारी सखी,
मोहिनी।

12. वृक्षों का महत्त्व समझाते हुए सखी को पत्र लिखें।
……………….पता
………………शहर का नाम
दिनांक………….
प्रिय सखी रूपाली,
नमस्ते।
तुम्हें यह जान कर प्रसन्नता होगी कि कल हमारे नगर में वन महोत्सव बड़ी धूमधाम से मनाया गया। इस महोत्सव में नगर के सभी स्कूली बच्चों ने बड़े उत्साह एवं चाव से भाग लिया। मैंने भी रेलवे स्टेशन के सामने पड़ी खाली भूमि में दो नीम के पेड़ लगाये। इस दिन वृक्षों के सम्बन्ध में कई नई बातों की जानकारी प्राप्त हुई जो मैं तुम्हें लिख रही हूँ।
आप तो जानती ही हैं कि वृक्ष पर्यावरण को शुद्ध रखने और हमें प्रदूषण से सुरक्षित रखने में कितने सहायक होते हैं। हमने ईंधन और इमारती लकड़ी के लिए वृक्षों की जो अंधाधुंध कटाई शुरू कर दी है उसी के कारण हमें अनेक मुसीबतों का सामना करना पड़ रहा है। अभी पिछले वर्ष ही उत्तर प्रदेश में भूस्खलन और बाढ़ के कारण जो जान माल की हानि हुई है उसकी जानकारी तो तुम्हें दूरदर्शन और समाचार-पत्रों के माध्यम से मिल ही चुकी होगी।
वृक्ष हमें शुद्ध वायु प्रदान करने के साथ-साथ प्रदूषित वायु को शुद्ध करने का कार्य भी करते हैं जैसे कि नीम, पीपल, बड़ के वृक्ष। वृक्षों से हमें अनेक प्रकार की औषधियाँ भी प्राप्त होती हैं। इसी कारण हमारे बुजुर्गों ने कुछ वृक्षों को देवता का स्वरूप भी माना है। अतः हमें यह प्रण करना चाहिए कि वृक्षों की कटाई को बंद करके हर वर्ष कमसे-कम एक वृक्ष अवश्य लगाना चाहिए। भारत सरकार का यह नारा सही है कि हम एक अनपढ़ को अवश्य पढ़ाएं और एक वृक्ष अवश्य लगायें। भारत की 125 करोड़ जनसंख्या में से यदि 50 करोड़ लोग भी हर वर्ष एक-एक वृक्ष लगाये तो हर वर्ष हम 50 करोड़ नए वृक्ष लगा सकते हैं।
मुझे पूरी आशा है कि तुम अपने आस पड़ोस में भी वृक्षों के महत्त्व से लोगों को परिचित करवा कर उन्हें वृक्षारोपण के लिए प्रेरित करोगी। इस तरह तुम अपनी ही नहीं देश की भी भलाई करोगी।
तुम्हारी सखी
………… नाम
13. बुरी संगति से बचने की सलाह देते हुए छोटे भाई को पत्र लिखें।
………………पता
……………..शहर का नाम
दिनांक…………….
प्रिय भाई राकेश,
स्नेह।
आज ही तुम्हारी अक्तूबर महीने की स्कूली परीक्षा का परिणाम प्राप्त हुआ। साथ ही तुम्हारे अध्यापक महोदय का पिता जी के नाम एक पत्र भी मिला, जिसमें उन्होंने तुम्हारी शिकायत की है कि तुम पढ़ाई में पूरा ध्यान नहीं देते। अध्यापक महोदय ने यह शिकायत भी की है कि तुम्हारी संगति अच्छे लड़कों से नहीं है। तुम्हारा परीक्षा परिणाम इस बात की पुष्टि करता है।
मुझे इस बात की जानाकरी से काफ़ी हैरानी हुई है कि तुम पिछले वर्ष अपनी कक्षा में दूसरे स्थान पर रहे थे और इस वर्ष तुम चार-चार विषयों में फेल हो। गणित में तुमने मात्र दस अंक प्राप्त किये हैं। यह इस बात का प्रमाण है कि तुम्हारा ध्यान पढ़ाई की ओर नहीं रहा। मुझे लगता है कि यह सब तुम्हारे बुरे लड़कों की संगति का ही परिणाम है।
तुम तो जानते ही हो कि व्यक्ति अपनी संगति से ही पहचाना जाता है। अच्छों की संगति करने से वह अच्छा और बुरों की संगति से बुरा समझा जाता है। बुरी संगति में पड़ कर भले ही थोड़ी देर के लिए आनन्द अनुभव हो पर इस तरह तुम अपना भविष्य बिगाड़ लोगे। जीवन का एक वर्ष भी यदि तुमने गंवा दिया तो सारी उमर पछताते रहोगे।
यह प्रतियोगिता का युग है। यदि परीक्षा में तुमने अच्छे अंक न प्राप्त किए तो आगे कैसे पढ़ सकोगे। पढ़ोगे नहीं तो करोगे क्या? हमारे पिता जी की कोई ज़मीन-जायदाद या कारोबार. तो है नहीं जो बिना पढ़ाई पर उनकी हट्टी पर बैठ जाओगे। बिना पढ़े तुम अपना जीवन निर्वाह कैसे करोगे? इसलिए मेरी तुम्हें सलाह है कि अपना भला-बुरा स्वयं विचार करो और बुरे लड़कों की संगति छोड़ दो। पढ़ाई में दिल लगाओ। यही तुम्हारी सारी उमर साथ देगी। बुरे मित्र तुम्हारा साथ जीवन भर नहीं देंगे।
मुझे पूर्ण आशा है कि तुम मेरी सलाह पर ध्यान देकर पढ़ाई में दिल लगाओगे और कक्षा में पहले जैसा स्थान प्राप्त करोगे।
तुम्हारा भाई,
…………. नाम
14. शैक्षणिक यात्रा में जाने की अनुमति माँगते हुए तथा रुपए भेजने की प्रार्थना करते हुए पिता जी को पत्र लिखें।
……………..पता
……………शहर का नाम
दिनांक…………..
पूज्य पिता जी,
सादर प्रणाम।
आप का पत्र कल ही मुझे मिला। परिवार का कुशल समाचार पढ़कर प्रसन्नता हुई। पूज्य पिता जी, मैं यहाँ पूर्ण रूप से स्वस्थ हूँ और दिल लगाकर पढ़ाई कर रहा हूँ। मेरे बारे में आप कोई चिन्ता न करें।
अगले महीने बड़े दिनों की छुट्टियाँ हो रही हैं। इन छुट्टियों में हमारे स्कूल की ओर से एक शैक्षणिक यात्रा का आयोजन किया जा रहा है। इस यात्रा में छात्रों को राजस्थान के कुछ ऐतिहासिक स्थानों की सैर करवाई जाएगी। इन स्थानों में देश के महान् सपूत महाराणा प्रताप के जीवन से जुड़े स्थानों के दर्शन भी शामिल होंगे। इस यात्रा में जयपुर, जोधपुर, अजमेर, आबू आदि स्थानों की सैर भी करवायी जाएगी।
यदि आप की आज्ञा हो तो मैं इस यात्रा में जाने वाले विद्यार्थियों में अपना नाम लिखवा दूं। इसके मुझे तीन सौ रुपए जमा करवाने होंगे। यदि आप की सहमति हो तो कृपया मुझे तीन सौ रुपए तुरन्त मनी आर्डर द्वारा भेज दें। साथ ही प्रधानाचार्य जी के नाम अपनी अनुमति का पत्र भी भेज दें। पूज्य पिता जी, मेरा विचार है कि मुझे इस सुनहरी अवसर को हाथ से नहीं जाने देना चाहिए।
घर पर पूज्य माता जी को मेरा प्रणाम कहिएगा तथा छोटे भाई-बहनों को प्यार।
आपकी अनुमति एवं मनीआर्डर की प्रतीक्षा में।
आपका आज्ञाकारी बेटा,
……………..नाम
दिनांक…………..
15. गाँव में लगी कृषि प्रदर्शनी का वर्णन करते हुए मित्र को पत्र लिखें।
…………….पता
………………शहर का नाम
दिनांक …………
प्रिय मित्र…………..
नमस्ते।
तुम्हारा पत्र मिला, घर पर सबकी कुशलता जान पर प्रसन्नता हुई। प्रिय मित्र पिछले दिनों हमारे गाँव में पंजाब सरकार की कृषि मंत्रालय और कृषि विश्वविद्यालय लुधियाना की ओर से एक कृषि-प्रदर्शनी का आयोजन किया गया था। इस पत्र में मैं तुम्हें उसी की संक्षिप्त जानकारी लिख रहा हूँ।
कृषि प्रदर्शनी हमारे गाँव के बाहर एक खुले मैदान में लगायी गई थी। सारे मैदान को दुल्हन की तरह सजाया गया था। इस प्रदर्शनी की जानकारी मुनादी द्वारा आसपास के कई गाँवों में दी गई थी। इस प्रदर्शनी का उद्घाटन पंजाब सरकार के कृषि मंत्री जी ने प्रात: नौ बजे किया। प्रदर्शनी देखने आसपास के कई गाँवों से हजारों की संख्या में किसान आए थे। किसानों के अतिरिक्त महिलाएँ और बच्चे भी बड़ी संख्या में प्रदर्शनी देखने आए। इस प्रदर्शनी में खेती बाड़ी से जुड़े अनेक अत्याधुनिक यन्त्र भी रखे गये थे। इस पंडाल में कृषि अधिकारी किसानों को इन यन्त्रों के प्रयोग और लाभ संबंधी जानकारी दे रहे थे। एक पंडाल में पंजाब प्रदेश में तैयार किए जाने वाले ट्रैक्टर से लेकर छोटे से छोटे यन्त्र प्रदर्शित किये गये थे। इस पंडाल में जाकर हमें पता चला कि पंजाब में बने स्वराज और सोनालीका जैसे ट्रैक्टर अन्तर्राष्ट्रीय स्तर पर बिक रहे हैं। एक पंडाल में किसानों को अपने उत्पाद में वृद्धि के लिए कई तरह के बीज रखे गये थे। नमूने के तौर पर प्रत्येक किसान को पाँच किलो बढ़िया उत्पाद देने वाले बीज मुफ्त बाँटे जा रहे थे। इस पंडाल में हमें पता चला कि अब टमाटर, करेले बेलों में भी लगते हैं तथा घिया या लौकी के पेड़ भी उगाये जा सकते हैं।
मुझे ही नहीं हमारे क्षेत्र के प्रत्येक किसान को इस प्रदर्शनी से बहुत सी लाभप्रद जानकारी प्राप्त हुई। मेरा मानना है कि ऐसी प्रदर्शनियाँ हमें अपने उत्पाद में वृद्धि करने में काफ़ी सहायक हो सकती हैं। इस तरह हमारा पंजाब जो अन्न उत्पादन में सबसे आगे है, फल और सब्जियों के उत्पादन में सबसे आगे निकल जाएगा।
घर पर सबको मेरी तरफ से नमस्ते कहना।
तुम्हारा मित्र,
………….
16. आपका मित्र बोर्ड की परीक्षा में प्रथम रहा है। उसे बधाई देते हुए एक पत्र लिखिए।
269, संतोखपुरा,
………….शहर का नाम।
दिनांक …………
प्रिय मित्र………….
नमस्कार।
आज ही दैनिक जागरण में तुम्हारा चित्र छपा देखकर तथा यह जानकर कि तुम पंजाब स्कूल बोर्ड की मैट्रिक की परीक्षा में प्रथम रहे हो, हृदय प्रसन्नता से झूम उठा। प्रिय मित्र, तुम से यही आशा थी। तुम ने अपनी माता-पिता और अध्यापकों के सपनों को साकार कर दिया है। इस शानदार सफलता के लिए मेरी हार्दिक बधाई स्वीकार करें।
आज हम सब तुम्हारे ऊपर गर्व का अनुभव कर रहे हैं। तुम्हारे माता-पिता, भाई-बहन कितने प्रसन्न होंगे इसका अनुमान सहज ही लगाया जा सकता है। तुम ने यह सिद्ध कर दिया है कि कठोर परिश्रम और सच्ची लगन से कुछ भी प्राप्त किया जा सकता है।
तुम्हारी इस शानदार सफलता पर मैं तथा मेरे माता-पिता तुम्हारे माता-पिता को भी अपनी ओर से हार्दिक बधाई प्रस्तुत करते हैं और आशा करते हैं कि भविष्य में भी तुम ऐसी ही सफलताएँ प्राप्त करते रहो।
शुभकामनाओं सहित,
तुम्हारा मित्र,
…………..नाम।

17. अपने/अपनी मित्र/सखी को उसके जन्म दिन पर बधाई पत्र लिखिए।
561, मॉडल टाऊन,
लुधियाना।
दिनांक: 10 अक्तूबर, ……….
प्रिय सखी उर्वशी,
स्नेह।
आज ही तुम्हारा पत्र प्राप्त हुआ। यह जानकार प्रसन्नता हुई कि 12 अक्तूबर को तुम अपना जन्म दिन मना रही हो। तुम ने इस अवसर पर मुझे भी निमन्त्रण दिया है, उसके लिए बहुत-बहुत धन्यवाद।। मेरा जी तो करता था कि इस शुभ अवसर पर स्वयं उपस्थित होकर अपनी शुभकामनाएँ प्रस्तुत करती किन्तु कुछ कारणों से मैं उपस्थित न हो सकूँगी। मैं अपनी शुभ कामनाएँ तुम्हें भेज रही हूँ, इस प्रार्थना के साथ कि तुम जियो हज़ारों साल, साल के दिन हो साठ हज़ार। मेरी परम पिता परमेश्वर से यह प्रार्थना है कि आप अपने भावी जीवन में हर कदम पर सफलताओं का मुँह देखो और तुम्हारा भावी जीवन उल्लास भरा हो, नई उमंगों और नई आशाओं भरा हो।
अपनी ओर से एक छोटी-सी भेंट तुम्हें भेज रही हूँ। स्वीकार करें। अपने माता-पिता को भी मेरी ओर से इस अवसर पर बधाई कहना।
शुभ कामनाओं सहित,
तुम्हारी प्रिय सहेली,
रूपन घुम्मन।
18. अपने मित्र/अपनी सहेली को पंजाब जूडो कराटे प्रतियोगिता में प्रथम पुरस्कार प्राप्त करने पर एक बधाई पत्र लिखिए।
494-सुभाष नगर,
पटियाला-147001
दिनांक ……………
प्रिय सखी जसप्रीत,
स्नेह।
आज ही समाचार-पत्र में चण्डीगढ़ में आयोजित पंजाब जूडो कराटे प्रतियोगिता में तुम्हारे प्रथम स्थान प्राप्त करने का समाचार पढ़ा। पढ़ कर हृदय प्रफुल्लित हो उठा। मेरी तरफ से इस सम्मान को प्राप्त करने पर तुम्हें बहुत-बहुत बधाई हो।
मुझे पूर्ण आशा है कि तुम से प्रेरणा लेकर अन्य स्कूली छात्राएँ भी इस कला को सीखने में रुचि लेना शुरू कर देंगी। . क्योंकि इस कला में प्रवीण लड़की बड़ी आसानी से राह चलते मजनुओं, छेड़खानी करने वालों से अपनी सुरक्षा भी कर सकती है और उन्हें धूल भी चटा सकती है।
मैं ईश्वर से प्रार्थना करती हूँ कि भविष्य में तुम राष्ट्रीय एवं अन्तर्राष्ट्रीय स्तर पर इस कला में सम्मान प्राप्त करो।
शुभकामनाओं सहित,
तुम्हारी सखी,
इंद्रजीत कौर।
19. भाषण प्रतियोगिता में प्रथम स्थान प्राप्त करने पर बधाई देते हुए मित्र/सखी को पत्र लिखें।
315-कीर्ति नगर,
…………नगर का नाम
दिनांक……………..
प्रिय सखी मंजुला,
नमस्ते।
आज ही दैनिक पंजाब केसरी में जालन्धर में हुई अंतर्विद्यालीय भाषण प्रतियोगिता के परिणाम प्रकाशित हुए हैं। विजेताओं की सूची में तुम्हारे स्कूल द्वारा चल वैजयंती (Running Trophy) जीतने के समाचार के साथ ही तुम्हारे द्वारा प्रथम पुरस्कार प्राप्त करने का समाचार पढ़ कर बड़ी प्रसन्नता हुई। तुम्हारी इस उपलब्धि और सम्मान प्राप्त करने पर मैं तुम्हें अपनी ओर से हार्दिक बधाई प्रस्तुत करती हूँ।
मैं यह अनुमान लगा सकती हूँ कि तुम्हारा भाषण कितना जोरदार रहा होगा। मुझे इस बात की और भी अधिक प्रसन्नता है कि इस तरह की प्रतियोगिताओं में लड़कियाँ भी बढ़-चढ़ कर भाग लेने लगी हैं। आज हमारे देश को अच्छे वक्ताओं की अच्छे नेताओं की ज़रूरत है। मेरी मनोकामना है कि तुम भारत कोकिला श्रीमती सरोजनी नायडू जैसी वक्ता बनो। निश्चय ही आप की यह उपलब्धि आप के लिए, आप के स्कूल के लिए और आपके माता-पिता और अध्यापकों के लिए गौरव की बात है।
मेरी शुभकामनाएँ सदा तुम्हारे साथ हैं।
आप की प्रिय सखी,
………….. नाम
20. आपके बड़े भाई ने आपके जन्म दिन के अवसर पर आपको उपहार स्वरूप कुछ पुस्तकें भेजी हैं। उनका धन्यवाद करते हुए पत्र।
………….पता
…………शहर
दिनांक………….
आदरणीय भाई साहिब,
सादर प्रणाम।
कल जब मेरे जन्म दिन की पार्टी चल रही थी तो कोरियर वाला आपके द्वारा भेजा गया एक पार्सल दे गया। मेरे सभी मित्र यह जानने के लिए उत्सुक थे कि आपने मुझे कौन-सा उपहार भेजा है। पार्सल खोलने पर पता चला कि आपने हिन्दी के महान् लेखक प्रेम चंद जी की कहानियों का पूरा सैट-मानसरोवर 8 भाग भेजा है। सच जानिए, भाई साहब मेरी और मेरे मित्रों की प्रसन्नता का कोई पारावार न रहा। आपने यह अनमोल उपहार भेज कर बड़ी कृपा की। मैं आपका हृदय से आभार व्यक्त करता हूँ।
आदरणीय भाई साहिब हमारी पाठ्य-पुस्तक में प्रेमचंद जी द्वारा लिखित ‘बड़े भाई साहिब’ कहानी संकलित है। इस प्रेरणादायक कहानी को पढ़ कर मेरा मन करता था कि प्रेमचंद जी की अन्य कहानियाँ भी पढूँ। आपने मेरी यह इच्छा पूरी कर दी। आपका बहुत-बहुत धन्यवाद। मेरे मित्रों ने भी इस उपहार को अमूल्य बताया है। निश्चय ही पुस्तकों का उपहार अन्य सभी सांसारिक वस्तुओं से अधिक मूल्यवान् है।
धन्यवाद सहित,
आपका छोटा भाई,
………….नाम
21. बड़ी बहन के विवाह के अवसर पर सखी को शामिल होने का निमन्त्रण पत्र।
51-कृष्णा नगर,
गली नं. 12
पठानकोट।
दिनांक………
प्रिय सखी ………
नमस्ते।
आप को यह जानकर हार्दिक प्रसन्नता होगी कि मेरी बड़ी बहन सुकीर्ति का शुभ विवाह दिनांक………… मंगलवार को होना निश्चित हो गया है। बारात रात ठीक आठ बजे हमारे घर पहुँचेगी तथा डोली की रस्म अगली सुबह 8 बजे होगी।
आप से प्रार्थना है कि इस अवसर पर आप अवश्य पधारें। यदि विवाह से एक-दो दिन पहले आने की कृपा करो तो आभारी हूँगी। क्योंकि तब तुम मेरे साथ काम में हाथ बटा सकोगी।
इस पत्र के साथ ही आपके माता-पिता के नाम औपचारिक निमन्त्रण पत्र भी भेज रही हूँ। हो सके तो उन्हें भी मेरी ओर से प्रार्थना करें कि वे भी इस शुभ अवसर पर दर्शन दें।
तुम्हारी सखी,
………….नाम।
22. अपने किसी मित्र की माता की मृत्यु हो जाने पर उसे संवेदना प्रकट करते हुए एक पत्र लिखिए।
…………..पता
………….शहर
दिनांक………….
प्रिय मित्र ………..
स्नेह।
अभी-अभी तुम्हारी पूज्य माता जी के अचानक स्वर्ग सिधार जाने का दुखद समाचार मिला। जानकर दिल को भारी धक्का लगा। यह शोक समाचार सुन कर मेरे माता-पिता भी शोक विह्वल हो उठे। इस दुःख की घड़ी में मैं तुम्हारा भागीदार हूँ। मैं तथा मेरे माता-पिता अपनी हार्दिक संवेदना प्रस्तुत करते हैं। . प्रिय मित्र, जीवन और मृत्यु ऐसी चीजें हैं जिन पर मनुष्य का अपना कोई अधिकार नहीं है। ईश्वर की लीला बड़ी विचित्र है। पूज्य माता जी की जिस समय परिवार को अधिक आवश्यकता थी, ईश्वर ने उन्हें अपने पास बुला लिया। इस दैवी आघात को सहन करने के अतिरिक्त हमारे पास दूसरा कोई चारा नहीं। माँ का रिश्ता दुनिया में ऐसा रिश्ता है जिसकी तुलना किसी दूसरे रिश्ते से नहीं की जा सकती। मैं भी उनके स्नेहमयी व्यवहार को कभी भूल नहीं पाऊँगा।
उस परमपिता परमात्मा से प्रार्थना है कि वह पूज्य माता जी की आत्मा को शान्ति और सद्गति प्रदान करे और आप सब को इस भीषण दुःख को सहन करने की शक्ति और सामर्थ्य प्रदान करें।
तुम्हारा अभिन्न मित्र,
……………… नाम।
संचार माध्यम के रूप में पत्र की बहुत उपयोगिता है। वर्तमान समय में टेलीफोन, मोबाइल, फैक्स और इंटरनेट ने संचार-क्षेत्र में क्रांति ला दी है। आज तो विश्व के किसी भी कोने में घर बैठे-बैठे कुछ ही सैकिंडों में बात हो जाती है। टेलीफ़ोन, मोबाइल, इंटरनेट प्रत्येक माध्यम की अपनी विशेष भूमिका है। ई-मेल, एस० एम० एस०, एम० एम० एस० आदि पत्र के ही नये रूप हैं। यह परस्पर विचारों के आदान-प्रदान का नया माध्यम है। किंतु पत्रलेखन का संचार क्षेत्र में अपना अनूठा महत्त्व है। आज भी उसकी महत्ता बनी हुई है। यह एक ऐसा माध्यम है जिसके द्वारा हम अपने मन के भावों को उचित रूप से प्रस्तुत कर सकते हैं। जिन बातों को हम मोबाइल फ़ोन आदि पर बोलने में संकोच करते हैं। उन बातों को पत्र में आसानी से लिख सकते हैं। रिश्तों की मधुरता और निकटता को बनाए रखने में पत्र की महत्त्वपूर्ण भूमिका है।
पत्र-लेखन व्यक्तिगत ही नहीं बल्कि सरकारी, गैर-सरकारी और निजी संस्थानों में निरंतर चल रहा है। कार्यालयों द्वारा भेजे गए पत्रों के रिकार्ड तो कार्यालय के डायरी रजिस्टर में भी रहते हैं। इस प्रकार पत्र लेखन एक अनूठी कला हैं।

अच्छे पत्र के गुण
अच्छे पत्र में निम्नलिखित गुण होने चाहिएं-
1. सरल भाषा-शैली-पत्र में साधारणतः सरल और बोलचाल की भाषा होनी चाहिए। शब्द बड़ी सावधानी से प्रयोग में लाए जाएं। थोड़े में बहुत कहने की रीति को अपनाया गया हो। बात सीधे-साधे ढंग से कही जाए। घुमा-फिरा कर लिखने से पत्र की शोभा बिगड़ जाती है।
2. संक्षिप्त विवरण-पत्र में व्यर्थ की व्याख्या नहीं होनी चाहिए। जितनी बात प्रश्न में पूछी गई है उसी की व्याख्या करनी चाहिए। इधर-उधर की हाँकने से पत्र में दोष आ जाता है। पत्र को पढ़ने वाले के दिमाग में सारी बात स्पष्ट हो जानी चाहिए, यह न हो कि वह किसी प्रकार की उलझन में फंसा रहे।
3. प्रभावोत्यादक-पत्र ऐसा होना चाहिए कि जिसको पढ़कर पढ़ने वाले पर प्रभाव पड़े। इसके लिए उसे पत्र के आरम्भ और अन्त को ध्यानपूर्वक लिखना चाहिए। इसके लिए पत्र लिखने के नियमों का पूरा पालन किया गया हो।
पत्रों के प्रकार-मुख्यतः पत्र दो तरह के होते हैं-
(1) अनौपचारिक पत्र
(2) औपचारिक पत्र।।
1. अनौपचारिक पत्र-ऐसे पत्रों में निजी या पारिवारिक पत्र आते हैं। इन पत्रों को लिखते समय व्यक्ति को खुली छूट होती है कि वह जैसे चाहे पत्र लिख सकता है। ऐसे पत्र प्रायः अपने परिवार के सदस्यों-भाई-बहन, माता-पिता आदि तथा मित्रों को लिखे जाते हैं। ऐसे पत्रों का विषय प्रायः व्यक्तिगत होता है। कभी-कभी ऐसे पत्रों में उपदेश या सलाह भी दी जाती है। बधाई पत्र, शोक पत्र तथा सांत्वना पत्र भी इसी कोटि में आते हैं।
2. औपचारिक पत्र-निजी या पारिवारिक पत्रों को छोड़कर हम जितने भी पत्र लिखते हैं, वे सब औपचारिक पत्र होते हैं। ऐसे पत्र प्रायः उन लोगों को लिखे जाते हैं जिन से हमारा व्यक्तिगत सम्बन्ध नहीं होता।
पारिवारिक पत्र लिखते समय ध्यान में रखने योग्य बातें
पारिवारिक या व्यक्तिगत पत्र लिखते समय निम्नलिखित बातों का ध्यान रखना ज़रूरी है-
- लिखने की शैली उत्तम हो अर्थात् पत्र में उचित स्थान पर ठीक शब्दों का प्रयोग किया जाए जिससे पढ़ने वाले को पत्र में लिखी बातें आसानी से समझ में आ जाएं।
- पत्र की भाषा सरल होनी चाहिए। मुश्किल शब्दों का प्रयोग कभी नहीं करना चाहिए।
- पत्र संक्षिप्त होना चाहिए।
- पत्र में छोटे-छोटे वाक्यों का प्रयोग करना चाहिए।
- पत्र में केवल प्रसंग की ही बात लिखनी चाहिए। इस में व्यर्थ कहानियां लिखने नहीं लग जाना चाहिए।
पारिवारिक पत्र के अंग
पारिवारिक पत्र लिखते समय पत्र के निम्नलिखित अंगों पर विशेष ध्यान देना चाहिए-
(1) पत्र का आरंभ-पत्र के आरंभ में सबसे ऊपर दाहिनी ओर पत्र लिखने वाले का अपना पता लिखना चाहिए। पते के नीचे तिथि भी लिखनी चाहिए। जिस पंक्ति में तिथि लिखी जाए उस से अगली पंक्ति में पत्र के बायीं ओर हाशिया छोड़कर जिसे पत्र लिखा जा रहा है उसे यथा विधि सम्बोधन करना चाहिए। आगे सम्बोधन शब्द अलग से दिये गये हैं।
सम्बोधन से अगली पंक्ति में ऊपर की पंक्ति से कुछ अधिक स्थान छोड़कर अभिवादन सूचक शब्द लिखना चाहिए। जहां अभिवादन शब्द समाप्त हो उसके बिल्कुल नीचे अगली पंक्ति से पत्र लिखना शुरू करना चाहिए।
(2) पत्र का कलेवर-पत्र का कलेवर बहुत बड़ा नहीं होना चाहिए। पत्र में हर नया विचार अलग पैरा में लिखना चाहिए।
(3) पत्र का अंत-पत्र समाप्त होने पर लिखने वाले को पत्र के अंत में दायीं ओर अपना नाम, पारिवारिक सम्बन्ध का स्वनिर्देश भी लिखना चाहिए।
पत्र के आरंभ तथा अंत में लिखने वाली
कुछ याद रखने वाली बातें
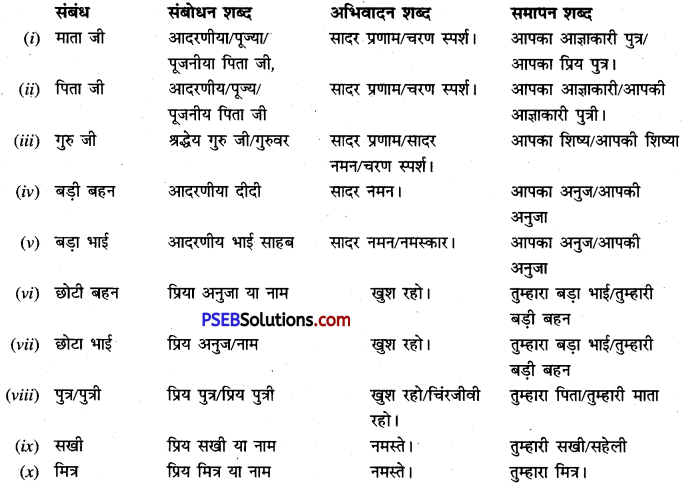
पत्र लिखने वाला जिसे पत्र लिखता है उसके पारिवारिक संबंध के अनुसार पत्र में सम्बोधन, अभिवादन और स्वनिर्देश में परिवर्तन हो जाता है। जैसे नीचे दिए गए ब्योरे में दिया जाता है।
1. अपने से बड़ों को-जैसे माता, पिता, बड़ा भाई, बड़ी बहन, बहन, चाचा, अध्यापक, गुरु आदि।
सम्बोधन : पूज्य, पूजनीय, परमपूज्य, आदरणीय।
अभिवादन : प्रणाम, नमस्कार, नमस्ते, सादर प्रणाम।
स्वनिर्देश : आप का आज्ञाकारी, आप का स्नेह पात्र, आप का प्रिय भाई, आप का प्रिय भतीजा, आप का प्रिय शिष्य।
याद रखिए
स्त्री सम्बन्धी या परिचितों के लिए भी ‘पूज्य’ और ‘आदरणीय’ सम्बोधन का प्रयोग होगा। जैसे पूज्य माता जी, आदरणीय मुख्याध्यापिका जी आदि। ‘पूज्या’ या ‘आदरणीया’ का प्रयोग नहीं करना चाहिए।
2. अपने से छोटों को-जैसे छोटा भाई, मित्र आदि
सम्बोधन : प्रिय, प्रियवर, चिरंजीव, प्यारे।
अभिवादन : खुश रहो, शुभाशीष, शुभाशीर्वाद, स्नेह भरा प्यार, प्यार।
स्वनिर्देश : तुम्हारा शुभचिन्तक, शुभाभिलाषी, हितचिंतकों
3. मित्रों को या हम उमर को:
सम्बोधन : प्रिय भाई, प्रिय दोस्त (मित्र का नाम), प्रियवर, बन्धुवर, प्रिय बहन, प्रिय सखी, प्रिय-(सखी का नाम)
अभिवादन : नमस्ते, जयहिंद, सप्रेम नमस्ते, मधुर स्मरण, स्नेह भरा नमस्ते, प्यार।
स्वनिर्देश : तुम्हारा मित्र, तुम्हारा स्नेही मित्र, तुम्हारा प्यारा दोस्त, तुम्हारी सखी, तुम्हारी स्नेह पात्र, तुम्हारी अपनी, तुम्हारी अभिन्न सखी।
पत्र शुरू किन वाक्यों से करना चाहिए
- आप का कृपा पत्र प्राप्त हुआ। धन्यवाद।
- तुम्हारा हिन्दी में लिखा पत्र मिला। पढ़कर बड़ी खुशी हुई।
- आपका कुशल समाचार बड़ी देर से नहीं मिला। क्या बात है?
- आप का पत्र पाकर कृतज्ञ हूँ।
- आपको यह जानकर प्रसन्नता होगी कि ……………
- यह जानकर हार्दिक हर्ष हुआ कि …………..
- शोक के साथ लिखना पड़ता है कि ………….
- यह जानकर अत्यन्त दुःख हुआ कि ………….
- आप को एक कष्ट देना चाहता हूँ, आशा है कि आप क्षमा करेंगे।
- एक प्रार्थना है, आशा है आप उस पर सहानुभूतिपूर्वक विचार करेंगे।
ध्यान रखें : आजकल पत्र का आरम्भ ऐसे वाक्यों में नहीं किया जाता-
‘हम यहां पर कुशलपूर्वक हैं आप की कुशलता श्री भगवान् से शुभ चाहते हैं।’ यह फैशन पुराना हो गया है। अतः सीधे वर्ण्य विषय का आरम्भ कर देना चाहिए।
पत्र समाप्त करने के लिए कुछ वाक्य:
- कृपया पत्र का उत्तर शीघ्र देने का कष्ट करें।
- पत्र का उत्तर शीघ्र दें/लौटती डाक से दें।
- भेंट होने पर और बातचीत होगी।
- कभी-कभी पत्र लिखते रहा करें।
- तुम्हारे पत्र का इंतज़ार रहेगा।
- यहां सब कुशल है। माँ/पिता की ओर से ढेर सारा प्यार।
- अपने पूज्य पिता जी तथा माता जी को मेरा प्रणाम/नमस्ते कहिए।
- आपके उत्तर की प्रतीक्षा में हूँ।
- सब मित्रों को मेरी ओर से नमस्ते कहना।
- इसके लिए मैं सदा आप का आभारी रहूंगा।

पत्र के प्रकार:
सामान्य रूप से पत्र दो प्रकार के होते हैं-
- औपचारिक पत्र-जो पत्र सरकारी कार्यालयों, संपादकों आदि को लिखे जाते हैं उन्हें औपचारिक पत्र कहते
- अनौपचारिक पत्र-जो पत्र माता-पिता, भाई-बहन, मित्रों, सगे-संबंधियों आदि को लिखे जाते हैं, उन्हें अनौचपारिक पत्र कहते हैं।
अनौपचारिक पत्रों के लिए आवश्यक बातें:
अनौपचारिक पत्र लेखन के लिए निम्नलिखित बातों का ध्यान रखना चाहिए-
- पत्रों में अनावश्यक विस्तार नहीं होना चहिए।
- पत्र में अपशब्दों का प्रयोग नहीं करना चाहिए।
- पत्र में शिष्टाचार का पालन करना चाहिए।
- पत्र में कही भी बनावटीपन नहीं झलकना चाहिए।
- पत्र की भाषा सरल, सहज, स्वाभाविक होनी चाहिए।
अनौपचारिक पत्र के अंग
अनौपचारिक पत्र के मुख्य रूप से पांच अंग होते हैं जो इस प्रकार हैं-
1. भेजने वाले अथवा प्रेषक का पता और दिनांक-पत्र लिखते समय पोस्टकार्ड, लिफाफ़ा अथवा सादे कागज़ को दाईं तरफ शीर्ष पर पत्र लिखने वाले का पता और उसके नीचे भेजने की तिथि लिखनी चाहिए।
नोट (i) यदि पत्र अंतर्देशी लिफाफ़े या पोस्टकार्ड पर लिखना हो तो उस पर प्राप्त करने वाले का पता लिखकर डाकघर में पोस्ट किया जाता है। यदि सादे कागज़ पर लिखना हो तो उसे सामान्य छोटे लिफाफे में डालकर तथा उस पर नियम के अनुसार डाक टिकट लगाकर पोस्ट किया जाता है।
(ii) पोस्टकार्ड पर पत्र लिखने से यह नुकसान हो सकता है कि अपनी गैर-मौजूदगी में डाकिया पत्र को आपके घर से बाहर फेंका जाता है।
(iii) परीक्षा भवन में पत्र लिखते समय प्रश्न-पत्र में दिया गया पता ही लिखना चाहिए। यदि प्रश्न-पत्र में कोई पता न दिया गया हो तो पता इस प्रकार लिखना चाहिए।
परीक्षा भवन,
क, ख, ग केंद्र,
………… दिनांक।
(परीक्षा दिनांक को लिखें)
(iv) पत्र में दिनांक इस प्रकार लिखी जानी चाहिए
12 मार्च 2014 अथवा मार्च 12, 2014 अथवा 12. 02. 2014
2. संबोधन अथवा अभिवादन- पत्र के बाईं तरफ संबोधन लिखा जाता है। उसके बाद अल्प विराम (,) लगाया जाता है। इससे अगली पंक्ति में अभिवादनसूचक शब्द लिखा जाता है। इसके बाद पूर्ण विराम (1) लगाया जाता है। जैसे:
पूज्य पिता जी,
सादर प्रणाम।
3. पत्र का क्लेवर ( मुख्य विषय)-पत्र में अभिवादन सूचक शब्द के नीचे की पंक्ति में पत्र का मुख्य विषय शुरू हो जाता है। इसे आवश्यकता के अनुसार या एक से अधिक अनुच्छेदों में लिखा जा सकता है।
4. समापन-मुख्य विषय के बाद पत्र का समापन किया जाता है। समापन करते हुए आपकी प्रतीक्षा में आदि समापन सूचक शब्दों का प्रयोग किया जाता है। इसके बाद दाईं तरफ आपका प्रिय, आपकी प्रिया, आपका पुत्र या पुत्री आपका बेटा या बेटी आदि समापन सूचक शब्दों का प्रयोग किया जाता है। इसके नीचे पत्र लिखने वाले का नाम लिखा जाता है। जैसे:
आपका प्रिय पुत्र,
लवलीन।
5. प्रेषित अथवा पत्र प्राप्त करने वाले का नाम-पत्र लिखने के बाद पोस्टकार्ड, अथवा अंतर्देशीय लिफ़ाफे पर यथासम्भव प्रेषित का पता (पिन कोड सहित) लिखा जाता है जैसे:
अमनजीत कौर
चंडीगढ़-160032
1. अपनी माता जी को वार्षिक परिणाम का विवरण देते हुए पत्र लिखें।
विक्रम नगर,
मोहाली रोड,
चंडीगढ़।
3 मार्च, 20…….
आदरणीय माता जी,
सादर प्रणाम।
मैं यहाँ कुशलतापूर्वक हूँ और आशा करती हूँ कि आप भी वहाँ बिल्कुल कुशल होंगे। गत सप्ताह हमारी वार्षिक परीक्षाएँ समाप्त हो गई हैं। इसके पश्चात् हमारे स्कूल में एक सप्ताह का एन० एस० एम० का शिविर लगा। आज सुबह ही हमारा वार्षिक परीक्षा परिणाम आया है। आपको जानकर बहुत खुशी होगी कि मैंने इस बार भी पूरे स्कूल में आठवीं का फल है।
मैं आपको विश्वास दिलाती हूँ कि मैं आगे भी इसी तरह से मेहनत करूँगी और सदा आगे बढूँगी। अब मैं नौवीं कक्षा में हो गई हूँ इसलिए मुझे इस कक्षा के लिए नई किताबें, कापियाँ आदि खरीदनी हैं। इसलिए आप मुझे कुछ पैसे भेजने का कष्ट करें।
पिता जी को सादर प्रणाम एवं शुभम को बहुत प्यार।
आपकी प्रिय बेटी,
गार्गी।

2. अपने पुराने स्कूल के अध्यापक को पत्र लिखिए जिसमें उन्होंने अच्छा पढ़ाने के लिए साधुवाद प्रकट किया गया हो तथा भविष्य में मार्गदर्शन की अपेक्षा की गयी हो।
101, सुभाष नगर,
मोहाली।
4 मई, 20……
आदरणीय गुरु जी,
सादर प्रणाम।
मैं शारदा पब्लिक स्कूल अमृतसर का पुराना छात्र हूँ। मैं आपसे पाँच वर्ष पहले आठवीं कक्षा में हिंदी पढ़ता था। मैं कक्षा में सदा पहले स्थान पर आता था। मैंने निबंध और कविता प्रतियोगिताओं में भी पहला स्थान प्राप्त किया था। आप हमें बहुत लगन और प्यार से पढ़ाते थे। कविताएँ तो सदा आप गाकर पढ़ाते थे। मुझे आज भी याद हैं।
अब मैं डी० पी० एस० अमृतसर में बारहवीं कक्षा में पढ़ रहा हूँ। मैं पहले की तरह अब भी पूरी मेहनत से पढ़ता हूँ। मेरे सभी अध्यापक मुझसे बहुत खुश हैं। मैंने आज तक प्रत्येक कक्षा में प्रथम स्थान प्राप्त किया है और आगे भी करता रहूँगा। यह सब आपके आशीर्वाद का फल है। इसके लिए मैं आपका आजीवन आभारी रहूँगा। अब मैं भविष्य में भी आपका मार्गदर्शन चाहता हूँ। आशा करता हूँ कि आप मेरा सदा ही मार्गदर्शन करते रहेंगे।
धन्यवाद,
आपका शिष्य,
अमित भारती।
3. आपको आपके पुराने मित्र का चार वर्ष बाद पत्र मिला। उसके पत्र का जवाब देते हुए पत्र लिखें।
15, अशोक विहार,
चंडीगढ़।
1 जून, 20……
प्रिय मित्र,
नमस्ते।
मुझे आज सुबह ही तुम्हारा पत्र मिला। पढ़कर बहुत प्रसन्नता हुई कि इतने वर्षों के बाद तुम्हे मेरी याद आ गई। तुम्हारे पिता जी की बदली के कारण तुम्हें भी उनके साथ दिल्ली जाना पड़ा था। तुम वहीं पढ़ने लगे थे। तुमने मुझे जो पता दिया था उस पर मैंने कई पत्र डाले किंतु एक का भी जवाब नहीं मिला।
यह बहुत अच्छा है कि पिता जी के रिटायर होने के बाद. तुम अपने ही शहर में वापस आ रहे हो। तुम फिर से मेरे ही स्कूल में दाखिला ले लेना। हम फिर से इकट्ठे पढ़ेंगे। हमें बहुत आनंद आएगा। मेरी ओर से तुम्हारे माता-पिता जी को सादर प्रणाम तथा छोटे भाई को बहुत स्नेह।
तुम्हारी प्रतीक्षा में
तुम्हारा प्रिय मित्र,
वैभव।
4. अपने फुफेरे भाई को राखी भेजते हुए पत्र लिखें।
45, नेता जी मार्ग,
पटियाला।
5 मई, 20……
प्रिय हरप्रीत,
सदा खुश रहो।
मैं यहाँ अत्यन्त कुशलतापूर्वक हूँ और आशा करती हूँ कि आप सब भी वहाँ सकुशल होंगे। आज से दस दिन बाद भाई-बहन के प्रेम का प्रतीक रक्षा-बंधन का पवित्र त्योहार है। मेरी परीक्षाएँ होने वाली हैं इसलिए मैं तुम्हें राखी बांधने नहीं आ सकती। मैं तुम्हें राखी भेज रही हूँ। इसे सहर्ष स्वीकार करना और त्योहार के दिन छोटी बहन से बंधवा लेना। मैं वादा करती हूँ कि अगली बार मैं स्वयं राखी लेकर आऊँगी और तुम्हें कोई उपहार भी दूंगी। मेरी तरफ से बुआ और फूफा जी को सादर प्रणाम तथा स्मृति को बहुत प्यार।
तुम्हारी बहन,
आकृति।
5. अपनी सखी को जन्मदिन पर नियंत्रण देते हुए पत्र लिखें।
भारती सदन,
सेक्टर-24,
चंडीगढ़।
3 जून, 20……
प्रिय सखी लवलीन,
सप्रेम नमस्ते।
मुझे यह बताते हुए बहुत खुशी हो रही है कि अगले सोमवार को मेरा जन्मदिन है। इस उपलक्ष्य में माता-पिता जी ने मेरे घर एक दावत का आयोजन किया है। यह दावत हमारे घर के पास अशोका पार्क में होगी। दावत शाम आठ बजे शुरू होगी। इस अवसर पर मैंने अपनी अन्य सखियों रानी, रीना, अंबिका, डोली, अनामिका आदि सभी को बुलाया है। इसके साथ-साथ हमारे अनेक रिश्तेदार और पड़ोसी भी शामिल होंगे। हम सब मिलकर खूब मस्ती करेंगे।
पापा ने पार्टी के लिए गीत-संगीत की भी व्यवस्था की है। मम्मी ने मुझे बहुत सुंदर पोशाक खरीदकर दी है। इसके साथ-साथ हम बच्चों के लिए अनेक खेल भी होंगे। पापा ने सभी दोस्तों के लिए अच्छे उपहार एवं टॉफियाँ मंगवाई हैं। ठीक नौ बजे केक काटा जाएगा। इसलिए तुम ठीक समय पर पहुँच जाना। मैं तुम्हारा इंतजार करूंगी।
मेरी तरफ से आंटी और अंकल को सादर प्रणाम तथा छोटी बहन को प्यार।।
तुम्हारी प्रिय सखी,
अंशिका।
6. अपनी सहेली को प्रतियोगी-परीक्षा में प्रथम स्थान प्राप्त करने पर बधाई पत्र लिखें।
4-502, अमृत नगर,
अमृतसर।
5 मई, 20……
प्रिय दीप्ति,
सप्रेम नमस्ते।
आज सुबह ही दैनिक जागरण में तुम्हारी फोटो देखी। देखकर बहुत प्रसन्नता हुई कि तुमने राष्ट्रीय स्तर की प्रतियोगी परीक्षा में प्रथम स्थान प्राप्त किया है। यह एक बड़ी उपलब्धि है जो तुमने कठिन परिश्रम से प्राप्त की है। यह तुम्हारे लिए ही नहीं बल्कि तुम्हारे माता-पिता, स्कूल और शहर के लिए बड़े गर्व की बात है।
प्रिय सखी, तुमने इस परीक्षा के लिए बड़े लगन एवं परिश्रम से दिन-रात तैयारी की थी। उससे पूर्ण विश्वास हो गया था कि तुम अवश्य ही एक दिन उन्नति के शिखर पर पहुँच जाओगी। मैं इस उपलब्धि के लिए तुम्हें और तुम्हारे मातापिता को बहुत बधाई देती हूँ। आशा करती हूँ कि तुम इसी तरह सदा आगे बढ़ती रहोगी।
तुम्हारी सखी,
दिव्या।
7. अपने जन्म दिवस पर भेजे गये उपहार के लिए ताया जी को धन्यवाद देते हुए पत्र लिखें।.
ए, शारदा कॉलोनी,
लुधियाना।
15 मई, 20……
आदरणीय ताया जी,
सादर प्रणाम।
मुझे कल ही आपके द्वारा भेजा गया उपहार एवं बधाई कार्ड प्राप्त हुआ। तुम्हारा उपहार मुझे बहुत पसंद आया। मैं इसे सदा संभाल कर रखूगी। यह उपहार मेरे जीवन में सदा काम आने वाला है। विद्यार्थी जीवन में इन अमूल्य पुस्तकों का बड़ा योगदान होता है।
मेरे जन्मदिन पर माता-पिता तथा अनेक दोस्तों ने मुझे अच्छे-अच्छे उपहार दिए हैं किंतु आपकी पुस्तक मुझे सबसे अच्छी लगी। मैं इस बहुमूल्य उपहार के लिए आपको बहुत धन्यवाद देती हूँ। मैं आपको विश्वास दिलाता हूँ कि मैं इस अमूल्य उपहार को सदा संभाल कर रखूगी। तायी जी को मेरा प्रणाम तथा अंकिता-अनिल को बहुत प्यार।
आपकी भतीजी,
वंशिका।
8. आपके चाचा जी के शहर में क्रिकेट मैच हो रहा है। आप उसे स्टेडियम में देखना चाहते हैं। आप अपने चाचा जी से अनुग्रह कीजिए कि वे आपको ये मैच दिखाएँ।
1525, कर्ण विहार,
मोहाली।
1 मार्च, 20……
आदरणीय चाचा जी,
चरण स्पर्श।
मुझे यह जानकर अति प्रसन्नता हुई कि आपके शहर मोहाली के गुरुनानक स्टेडियम में भारत और इंग्लैंड के बीच टी-20 मैच हो रहा है। आप जानते हैं कि मुझे क्रिकेट मैच देखने का बहुत शौक है। इस मैच के लिए मैं बहुत उत्सुक हूँ। मैं इस मैच को अवश्य देखना चाहता हूँ। इसलिए आप मेरे लिए एक टिकट अवश्य खरीद लेना ताकि मैं इस मैच का आनंद उठा सकूँ। मेरे मम्मी-पापा ने मुझे इसके लिए मंजूरी दे दी है।
मैं मैच से एक दिन पूर्व ही आपके पास पहुँच जाऊँगा। आप भी मेरे साथ मैच देखने चलना। चाची जी को प्रणाम तथा रवीना को प्यार।
आपका प्रिय,
रवि।

9. परीक्षा न दे सकने के कारण आपका मित्र परेशान है। उसे हौसला देते हुए जीवन में सकारात्मक रवैया अपनाने के लिए कहते हुए पत्र लिखें।
हरि सदन,
शिवाजी नगर।
5 मार्च, 20……
प्रिय मित्र चरनजीत,
नमस्ते।
आज सुबह ही तुम्हारे पिता जी का पत्र प्राप्त हुआ। पढ़कर पता चला कि वार्षिक परीक्षा न देने के कारण तुम्हारा एक वर्ष बर्बाद हो गया है जिसके कारण आजकल तुम बहुत परेशान हो। इससे आपका स्वास्थ्य दिन-प्रतिदिन खराब होता जा रहा है। यह सब जानते हैं कि इसमें तुम्हारा कोई दोष नहीं है। तुम परीक्षा से एक सप्ताह पहले बहुत बीमार हो गए थे। उसके बाद तुम्हें बीस दिन तक अस्पताल में रहना पड़ा पर आज तुम बिल्कुल स्वस्थ हो। जीवन में सुखदुःख आते-जाते रहते हैं। तुम किसी बात की चिंता मत करना। सब कुछ भूलकर दोबारा अपनी पढ़ाई शुरू करो। मुझे विश्वास है कि अगले वर्ष तुम अवश्य ही प्रथम स्थान प्राप्त करोगो। सदा सकारात्मक सोच रखना क्योंकि नकारात्मक सोच वाला आदमी जीवन में आगे नहीं बढ़ सकता।
मेरी तरफ से अपने मम्मी-पापा को सादर प्रणाम कहना। छोटी बहन को प्यार देना।
तुम्हारा प्रिय मित्र,
रवींद्र।
10. आप अपनी बॉलीबाल टीम और कोच के साथ ट्रेनिंग कैंप गये हैं। अपनी कुशलता का समाचार अपनी माता जी को देते हुए पत्र लिखें।
भगत सिंह माडल स्कूल,
सुभाष पार्क, मोहाली।
15 जून, 20……
आदरणीय माता जी,
चरण स्पर्श।
मैं अपनी बालीबाल टीम और कोच के साथ ट्रेनिंग कैंप में बिल्कुल कुशल हूं। मैं यहाँ कल शाम पहुंच गयी थी। यहाँ सरकार की तरफ रहन-सहन की पूरी व्यवस्था की गई है। हमारी टीम को एक बड़ा कमरा दिया गया है। हम सभी बच्चे इकट्ठे ही रहते हैं। हमारे कोच भी भूपेंद्र सिंह जी भी हमारे साथ ही रहते हैं।
हम सुबह शाम अपने कोच के साथ अभ्यास करते हैं। दोपहर में भोजन करने के बाद घूमने जाते हैं। हमारे कोच हमारा बहुत ध्यान रखते हैं। वे हमें प्रत्येक बात बड़ी गंभीरता से बताते हैं। हम भी उनकी बात पूरे ध्यान से सुनते हैं। हमें लगता है कि हमारी टीम राष्ट्रीय स्तर पर अवश्य ही मैच जीतेगी। आप मेरी तनिक भी चिंता मत करना।
पूज्य पिता जी को मेरा सादर प्रणाम और अंकित को प्यार।
आपका प्रिय पुत्र,
आशु।
11. अपनी सहेली को सर्दियों की छुट्टियों में अपने घर बुलाने का निमंत्रण पत्र लिखें।
786, सेक्टर-22
चंडीगढ़।
20 मई, 20……
प्रिय सखी अमनप्रीत कौर,
सप्रेम नमस्ते।
मैं यहां कुशलतापूर्वक हूँ। आशा करती हूं कि तुम भी सपरिवार कुशल होगी। हमारे स्कूल की सर्दियों की छुट्टियां अगले सप्ताह से शुरू हो जाएंगी। मैं चाहती हूं कि इन छुट्टियों में तुम मेरे पास आ जाओ। इन छुट्टियों में हम प्रतिदिन बाहर घूमने चलेंगे। मेरे पापा की भी इन दिनों छुट्टियां है इसलिए हम पापा के साथ रोज़गार्डन, रॉकगार्डन, सुखना झील आदि दर्शनीय स्थलों की सैर करेंगे। इसी बीच हमारे घर के पास जो राष्ट्रीय स्टेडियम है। वहां भारत-पाकिस्तान के कबड्डी मैच भी हो रहे हैं। हम इन मैंचों का भी खूब आनंद लेंगे। तुम आते समय अपनी किताबें भी लेते आना। एक साथ बैठकर गृह कार्य कर लेंगे।
सखी इस बार तुम्हारा कोई बहाना नहीं चलेगा। तुम जरूर आ जाना। मैं तुम्हारी प्रतीक्षा करूंगी। मम्मी-पापा को मेरी तरफ से सादर प्रणाम कहना और छोटे भाई को प्यार।
तुम्हारी प्रिय सखी,
अमृत कौर।
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()